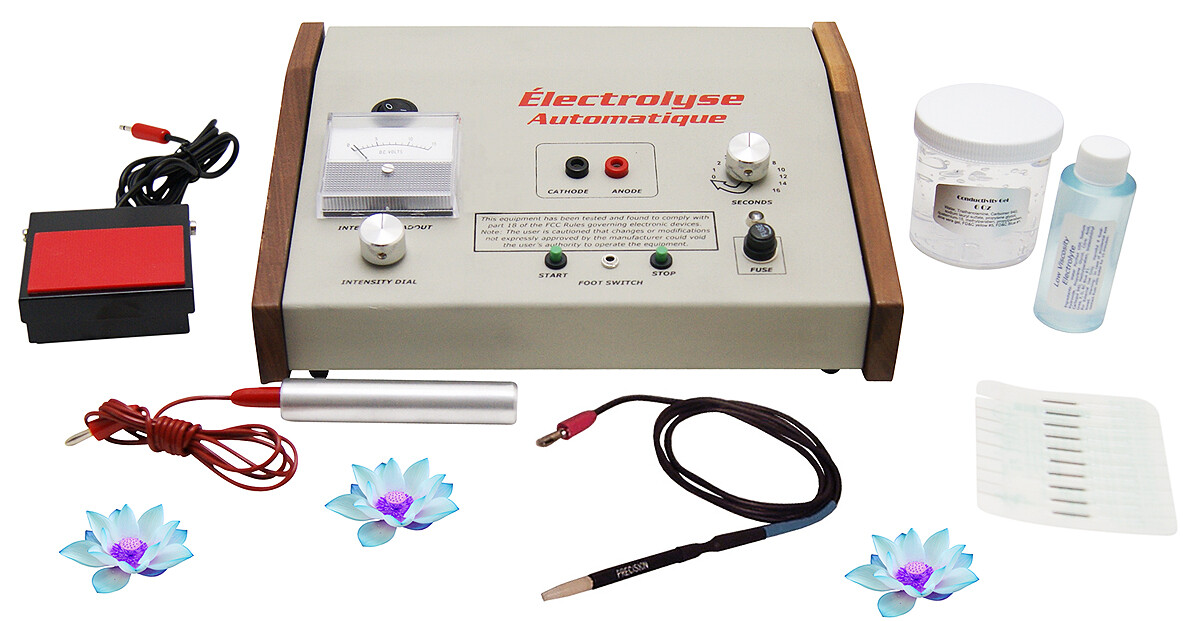
The global electrolysis machine market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for permanent hair removal solutions and increasing consumer awareness of advanced cosmetic procedures. According to Grand View Research, the global hair removal devices market was valued at USD 26.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.4% from 2023 to 2030, with professional-grade electrolysis equipment representing a significant segment. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence reports that growing adoption of electrology in dermatology clinics and aesthetic centers, along with technological advancements in thermolysis and blend methods, is fueling market expansion. As demand for precision, safety, and efficiency in permanent hair removal continues to rise, manufacturers are innovating with FDA-cleared devices featuring enhanced comfort, customizable settings, and improved durability. This growing landscape underscores the importance of identifying the top professional electrolysis machine manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 10 Professional Electrolysis Machine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Electrolysis Equipment Suppliers
Domain Est. 1997
Website: professionals.electrology.com
Key Highlights: Suppliers of electrolysis equipment and permanent hair removal supplies….
#2 AR Hinkel Co.
Domain Est. 1997
Website: arhinkel.com
Key Highlights: Elevate your electrolysis practice with AR Hinkel Co.’s premium supplies. For 70+ years, we’ve empowered professionals worldwide with innovative, high-quality ……
#3 Electrolysis machines
Domain Est. 1998
Website: dectro.com
Key Highlights: The number one brand of electrolysis equipment that guarantees gentle 100% permanent hair removal. Since 1875, electrolysis has been and remains the only 100% ……
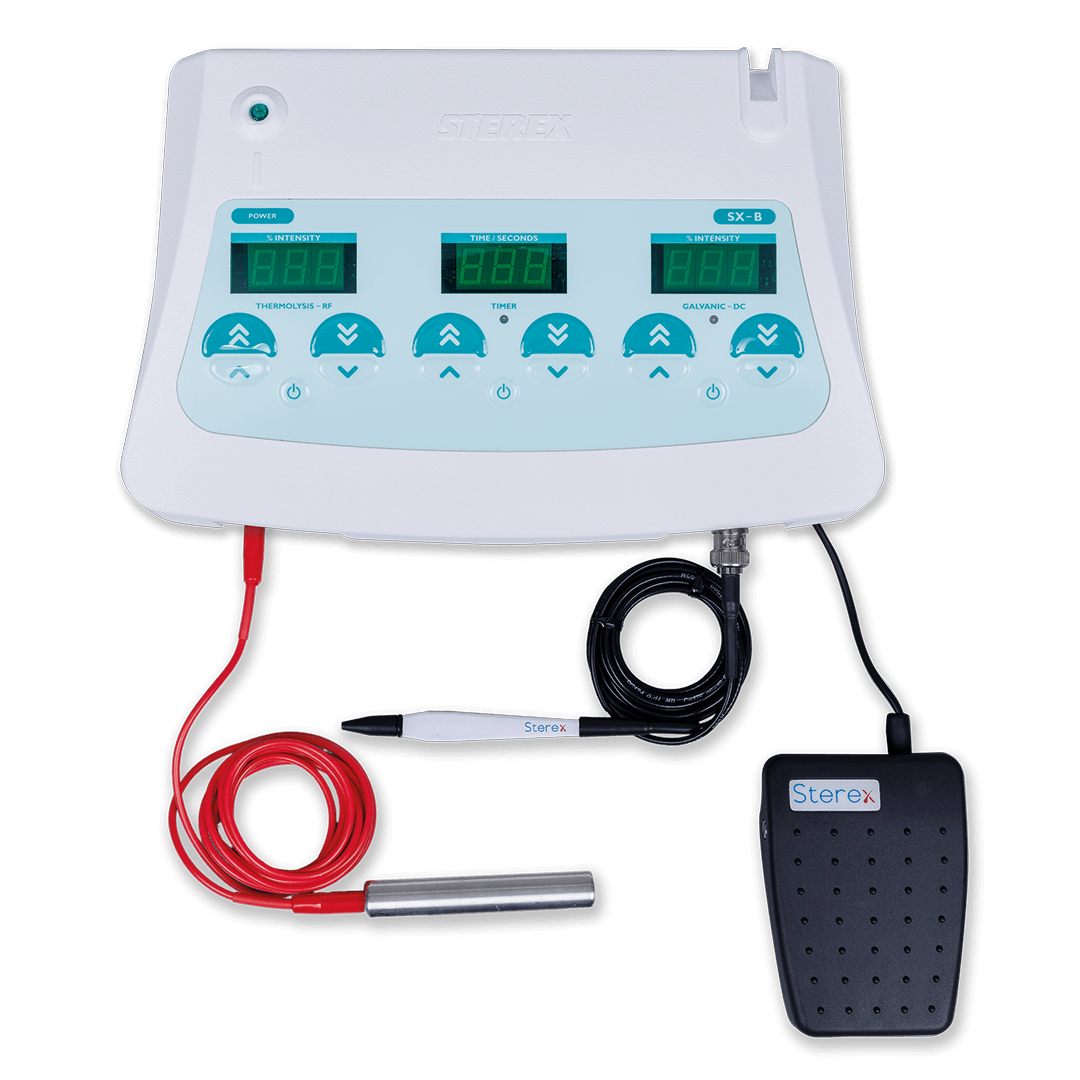
#4 Sterex
Domain Est. 2003
Website: sterex.com
Key Highlights: Your partner in electrolysis & diathermy. Sterex is world renowned as the brand that electrologists know, use and trust for electrolysis and diathermy….
#5 Electrolysis Equipment
Domain Est. 2004 | Founded: 1987
Website: electrolysissupplies.com
Key Highlights: Choose us as your electrolysis equipment supplier. We’ve been offering FDA-approved tools and support for beauty and health professionals since 1987….
#6 Electrolysis
Domain Est. 2007
Website: aestheticssystems.com
Key Highlights: Explore our range of cutting-edge electrolysis machines designed to tackle unwanted hair with unparalleled precision and minimal discomfort….
#7 Electrolysis
Domain Est. 2009
Website: silhouettone.us
Key Highlights: Silhouet-Tone USA offers top-quality electrolysis equipment. Find professional machines and accessories for effective hair removal. Shop now….
#8 Effective electrolysis hair removal machines buy
Domain Est. 2015
#9 Simplify your purchasing
Domain Est. 2017
Website: prestige-supply.com
Key Highlights: Leading provider of wholesale electrolysis, laser, and spa supplies. We strive to simplify your purchasing and be your first choice business partner!…
#10 SKRILIX Electrolysis Pro 003
Domain Est. 2021
Website: skrilixglobal.com
Key Highlights: Free deliveryThe SKRILIX Electrolysis Pro 003 is a state-of-the-art professional hair removal device designed for dermatologists, cosmetologists, and skincare professionals….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Professional Electrolysis Machine

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Professional Electrolysis Machines
The global market for professional electrolysis machines is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, rising demand for permanent hair removal, and evolving consumer preferences in aesthetic and dermatological treatments. Key trends shaping the industry include:
-
Advanced Technology Integration
By 2026, professional electrolysis machines are expected to feature enhanced precision through AI-assisted targeting and real-time skin analysis. Devices will increasingly incorporate smart sensors and IoT connectivity, enabling practitioners to monitor treatment efficacy and customize settings based on skin type, hair density, and patient history. This integration improves treatment outcomes and reduces risks of adverse effects. -
Miniaturization and Ergonomic Design
Manufacturers are focusing on creating compact, lightweight, and ergonomically designed machines to improve practitioner comfort during long procedures. Portable yet high-performance units are gaining traction, especially in mobile clinics and boutique aesthetic studios, offering flexibility without compromising power or precision. -
Rise in Demand for Permanent Hair Removal
Growing consumer awareness about long-term benefits of electrolysis over temporary methods (like shaving or waxing) is fueling demand. With increasing acceptance of body grooming across genders, the client base for professional electrolysis services is expanding, especially in emerging markets across Asia-Pacific and Latin America. -
Regulatory and Safety Standards
As the market grows, regulatory bodies are expected to enforce stricter safety and performance standards for electrolysis devices. By 2026, compliance with international medical device regulations (e.g., FDA, CE marking) will become a competitive advantage, ensuring consumer trust and facilitating global market access. -
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental considerations are influencing product development. Manufacturers are adopting eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient power systems in electrolysis machines. Refurbished and rental equipment models are also emerging, supporting a circular economy and reducing carbon footprint. -
Expansion of Training and Certification Programs
The demand for skilled electrologists is rising in tandem with market growth. In 2026, we anticipate an increase in accredited training programs and digital learning platforms, enabling practitioners to stay updated on the latest techniques and equipment usage, thereby improving service quality and patient satisfaction. -
Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The professional electrolysis machine market is witnessing increased competition, with established players expanding their portfolios and startups introducing innovative solutions. Strategic partnerships, mergers, and acquisitions are expected to rise, particularly between technology firms and aesthetic device manufacturers.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for professional electrolysis machines will be characterized by smart, safe, and sustainable innovations, catering to a broader and more diverse consumer base. As the industry evolves, success will depend on technological leadership, regulatory compliance, and a strong focus on user experience for both practitioners and clients.

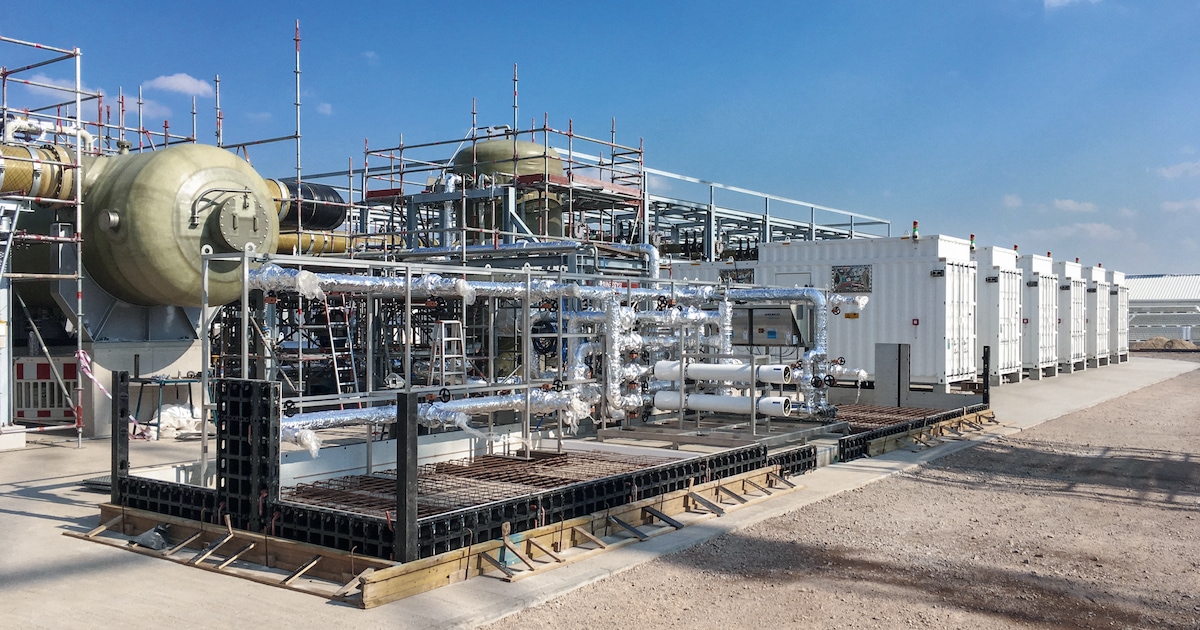
H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Professional Electrolysis Machines (Focusing on Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing professional electrolysis machines—especially those designed for industrial, medical, or high-efficiency hydrogen (H₂) production—requires careful evaluation to avoid critical pitfalls related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Below are key challenges buyers often face:
- Substandard Materials and Construction
- Pitfall: Many suppliers, particularly low-cost manufacturers, use inferior materials (e.g., non-grade stainless steel, low-purity catalysts) that degrade quickly under electrolytic conditions, reducing efficiency and lifespan.
- Impact: Poor durability, increased maintenance, and compromised H₂ purity.
-
Mitigation: Verify material specifications (e.g., 316L stainless steel, platinum or iridium oxide coatings) and request third-party test reports for corrosion resistance and gas purity.
-
Lack of Certification and Compliance
- Pitfall: Machines may lack essential certifications (e.g., CE, UL, ATEX, ISO 22734) required for safe operation in professional environments.
- Impact: Safety hazards, legal non-compliance, and insurance issues.
-
Mitigation: Confirm compliance with international safety and performance standards before procurement.
-
Inaccurate or Exaggerated Performance Claims
- Pitfall: Overstated H₂ output, energy efficiency (kWh/Nm³), or uptime guarantees. Some vendors provide lab-condition results that are unachievable in real-world settings.
- Impact: Operational inefficiencies and financial losses due to underperformance.
-
Mitigation: Require real-world performance data, conduct pilot testing, and review independent validation reports.
-
Inadequate Cooling and Thermal Management
- Pitfall: Poorly designed thermal systems lead to overheating, reducing efficiency and damaging cell stacks.
- Impact: Shortened equipment life and inconsistent H₂ production.
-
Mitigation: Evaluate cooling mechanisms (e.g., liquid vs. air cooling) and check for built-in temperature monitoring and control.
-
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
- Pitfall: Some machines, particularly from lesser-known manufacturers, may incorporate patented technologies (e.g., membrane designs, catalyst formulations, control algorithms) without licensing.
- Impact: Buyers could face legal liability, import bans, or forced decommissioning if IP disputes arise.
-
Mitigation: Perform due diligence on the manufacturer’s IP portfolio, request proof of patent licenses, and avoid suppliers reluctant to disclose technical origins.
-
Opaqueness in Technology Origins and Design
- Pitfall: Vendors may obscure the actual design source—some rebrand machines from original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) without adding value or ensuring quality control.
- Impact: Lack of technical support, spare parts, or software updates.
-
Mitigation: Demand transparency about design and manufacturing processes; prefer suppliers with in-house R&D and clear technical documentation.
-
Poor After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
- Pitfall: Limited access to technical support, service engineers, or replacement parts—especially critical for electrolyzer stacks and control units.
- Impact: Extended downtime and high operational costs.
-
Mitigation: Assess service network coverage, warranty terms, and spare parts inventory before purchase.
-
Software and Control System Vulnerabilities
- Pitfall: Proprietary control systems may lack cybersecurity protections or compatibility with existing infrastructure.
- Impact: Risk of system failure, data breaches, or integration challenges.
- Mitigation: Evaluate software architecture, update policies, and ensure API access or SCADA compatibility.
Conclusion:
To avoid these pitfalls, prioritize suppliers with proven track records, transparent technology sourcing, full compliance certifications, and robust IP integrity. Conduct technical audits, request customer references, and consider third-party engineering assessments before finalizing procurement—especially when H₂ output, safety, and long-term reliability are mission-critical.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Professional Electrolysis Machine
Introduction
This guide outlines the logistics and regulatory compliance requirements for the import, export, distribution, and use of a Professional Electrolysis Machine. These devices are used in medical, aesthetic, or industrial settings for hair removal or hydrogen production and are subject to international, national, and regional regulations. Proper handling, documentation, and certification are essential to ensure legal compliance, safety, and product integrity.
-
Regulatory Classification
Professional Electrolysis Machines are typically classified as medical or aesthetic devices, depending on their intended use and regional regulations. -
United States (FDA)
- Regulated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) under 21 CFR Part 880.
- Classification: Class II medical device (K106564 standard may apply).
- Requires 510(k) premarket notification unless exempt.
-
Must comply with Quality System Regulation (QSR), including design controls and labeling.
-
European Union (EU)
- Falls under the Medical Devices Regulation (MDR) (EU) 2017/745.
- Classification: Typically Class IIa or IIb, depending on intended use and risk.
- Requires CE marking with involvement of a Notified Body.
-
Technical documentation, risk assessment, and post-market surveillance (PMS) are mandatory.
-
Canada (Health Canada)
- Regulated under the Medical Devices Regulations (SOR/98-282).
- Classification: Class II device.
-
Requires a Medical Device License (MDL) prior to sale.
-
Other Regions
- Australia (TGA): Requires inclusion in the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG).
- UK (MHRA): Follow UKCA marking requirements post-Brexit; transitional arrangements may apply.
- Japan (PMDA): Requires approval under the Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Act (PMD Act).
-
China (NMPA): Requires registration via the National Medical Products Administration.
-
Product Certification & Technical Documentation
Ensure the following certifications and documentation are in place: -
CE Certificate (EU)
- FDA 510(k) Clearance or Exemption Letter (US)
- ISO 13485:2016 Certification (Quality Management System)
- IEC 60601-1:2020 (Safety of Medical Electrical Equipment)
- IEC 60601-1-2 (EMC Requirements)
- Technical File or Design Dossier (per MDR/FDA requirements)
- Risk Management File (ISO 14971)
-
Clinical Evaluation Report (CER) – if required by regulation
-
Packaging & Labeling Requirements
Proper packaging and labeling are critical for compliance and safe handling. -
Labeling (per FDA, MDR, etc.):
- Device name and model number
- Manufacturer name and address
- Intended use and indications
- CE mark, UKCA, or other applicable conformity marks
- UDI (Unique Device Identification) – required in US, EU, and other markets
- Lot number and serial number
- Expiry date (if applicable)
-
Symbols per ISO 15223-1
-
Language Requirements:
-
Labels and instructions for use (IFU) must be in the official language(s) of the destination country (e.g., French in Quebec, German in Austria).
-
Packaging:
- Must protect against shock, moisture, and temperature extremes.
- Use anti-static materials if sensitive electronics are included.
-
Include tamper-evident seals.
-
Shipping & Logistics
-
Transportation Modes:
- Air, sea, or ground freight depending on urgency and volume.
-
Use IATA-compliant packaging if shipping by air (even if device does not contain batteries, electrical components must be protected).
-
Temperature & Environmental Controls:
- Store and transport within manufacturer-specified temperature and humidity ranges (typically 10°C–40°C).
-
Avoid freezing and direct sunlight.
-
Hazardous Materials:
- Most electrolysis machines are not hazardous, but verify if accessories (e.g., gels, solutions) contain restricted substances.
-
If batteries are included (e.g., for portable units), classify under UN 3480 (lithium-ion) or UN 3090 (lithium metal) and comply with IATA/IMDG regulations.
-
Customs Documentation:
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
- Certificate of Origin
- FDA Establishment Registration Number (for US imports)
- CE Certificate or other conformity declarations
-
Import licenses (if required by destination country)
-
Import & Export Compliance
-
Export Controls:
- Verify if the device is listed under dual-use or strategic trade controls (e.g., Wassenaar Arrangement).
-
Most electrolysis machines are not export-controlled, but software or precision components may require review.
-
Import Regulations:
- Register with local regulatory authorities (e.g., Health Canada, TGA, ANVISA in Brazil).
-
Appoint an Authorized Representative (EU) or Local Agent (China, Saudi Arabia, etc.).
-
Duties & Tariffs:
- Use HS Code: Typically 9018.90 (other medical, surgical, or veterinary instruments).
-
Confirm country-specific tariff rates and free trade agreement eligibility.
-
Post-Market Compliance
-
Vigilance & Reporting:
- Report adverse events and field safety corrective actions (FSCAs) to relevant authorities (e.g., FDA MAUDE, EUDAMED).
-
Maintain a Post-Market Surveillance (PMS) system and Periodic Safety Update Reports (PSURs) under MDR.
-
UDI Implementation:
-
Ensure UDI is applied to labels and entered into GUDID (US) and EUDAMED (EU).
-
Software Updates & Cybersecurity:
-
If the device includes software, comply with cybersecurity standards (e.g., IEC 81001-5-1) and patch management protocols.
-
Training & Installation
-
Provide certified training for users and technicians.
- Include installation protocols and calibration requirements.
-
Maintain service logs and ensure only qualified personnel perform maintenance.
-
Environmental & End-of-Life Compliance
-
Comply with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) Directive in the EU.
- Provide take-back programs or recycling instructions.
- Label products with the crossed-out wheeled bin symbol.
Conclusion
Compliance with logistics and regulatory standards ensures the safe and legal distribution of Professional Electrolysis Machines worldwide. Manufacturers and distributors must stay current with evolving regulations, maintain thorough documentation, and prioritize patient and user safety throughout the product lifecycle.
For continued compliance, conduct regular audits, update technical files, and monitor regulatory changes in all target markets.
— End of Guide —
In conclusion, sourcing a professional electrolysis machine requires careful consideration of several key factors, including machine type (galvanic, blend, or thermolysis), regulatory compliance (such as FDA or CE certification), durability, precision, manufacturer reputation, and after-sales support. It is essential to select a device that meets clinical standards, ensures client safety, and aligns with the specific needs of your practice. Investing in a high-quality, medically approved electrolysis machine not only enhances treatment efficacy and client satisfaction but also reinforces the professionalism and credibility of your service. Conducting thorough research, reading expert reviews, and consulting with industry professionals can guide you toward a reliable and long-term solution for permanent hair removal.