The global printed circuit board (PCB) market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand across consumer electronics, automotive, telecommunications, and industrial sectors. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 72.7 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.3% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence forecasts a CAGR of approximately 4.9% over the 2024–2029 period, citing increasing adoption of advanced electronics and miniaturized components as key growth catalysts. As technological innovation accelerates and industries transition toward smarter, connected devices, the role of reliable PCB manufacturing becomes increasingly critical. This list highlights the top 10 PCB manufacturers leading the industry in capacity, technological expertise, and global reach, based on revenue, market presence, and innovation in high-density interconnect (HDI), flexible, and rigid-flex board solutions.
Top 10 Printing Circuit Boards Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 TTM Technologies
Domain Est. 1995
Website: ttm.com
Key Highlights: TTM Technologies is an advanced Printed Circuit Board (PCB) manufacturer and a leading supplier in technology solutions….
#2 Summit Interconnect leads Complex Circuits and Rigid Flex PCB
Domain Est. 2016
Website: summitinterconnect.com
Key Highlights: Summit Interconnect is a manufacturer of advanced technology printed circuit boards focused on complex rigid, flex and rigid-flex PCBs….
#3 Printed Circuit Board Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1998
Website: pcbnet.com
Key Highlights: Imagineering is a trusted printed circuit board manufacturer, offering precision PCB assembly, fabrication, & protoype services with quick turnaround….
#4 China PCB Prototype & Fabrication Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2012
#5 AdvancedPCB
Domain Est. 2018
Website: advancedpcb.com
Key Highlights: Prototype to Production PCBs from AdvancedPCB. Choose us as your trusted PCB board manufacturer and circuit board manufacturer….
#6 PCBAA
Domain Est. 2021
Website: pcbaa.org
Key Highlights: PCBAA is the leading voice for U.S. printed circuit board manufacturers and suppliers. Discover how we’re strengthening the future of the ……
#7 Sunstone Circuits Printed Circuit Boards
Domain Est. 1995
Website: sunstone.com
Key Highlights: Sunstone Offers Expert Service In High Quality Printed Circuit Board Manufacturing & PCB Assembly, Including Prototype & Production PCBs….
#8 Manufacturing Advanced Printed Circuit Boards
Domain Est. 1995
Website: sanmina.com
Key Highlights: Sanmina manufactures printed circuit boards for defense, aerospace, medical and other mission critical environments. Explore PCB solutions from Sanmina….
#9 Sierra Circuits
Domain Est. 1997
Website: protoexpress.com
Key Highlights: Sierra Circuits can manufacture your PCB and have it expedited to you within 24 hours. Full turnkey boards, with assembly and components in as fast as 5 days….
#10 ALLPCB
Domain Est. 2011
Website: allpcb.com
Key Highlights: Explore the ALLPCB approach to PCB manufacturing and assembly: From prototype to production, we’ve got you covered….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Printing Circuit Boards
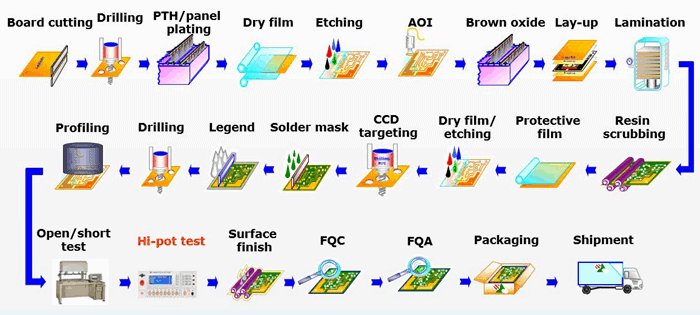
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs)
The global Printed Circuit Board (PCB) market in 2026 is expected to be shaped by powerful technological shifts, evolving demand patterns, and strategic regional dynamics. Driven by the proliferation of advanced electronics and the need for higher performance, key trends are converging to redefine the industry landscape.
H2: Technological Advancements and Miniaturization
As electronic devices become smaller, faster, and more complex, PCBs must evolve accordingly. In 2026, high-density interconnect (HDI) PCBs will dominate high-end applications such as smartphones, wearables, and medical devices. The adoption of advanced packaging technologies, including System-in-Package (SiP) and Package-on-Package (PoP), will accelerate the demand for ultra-thin, flexible, and rigid-flex PCBs capable of supporting tighter integration. Additionally, improvements in materials—such as low-loss laminates and enhanced thermal management substrates—will be critical for 5G infrastructure, AI accelerators, and high-performance computing, where signal integrity and heat dissipation are paramount.
H2: Rising Demand from Automotive and Electric Vehicles (EVs)
The automotive sector will be one of the fastest-growing drivers of PCB demand in 2026. With the rapid adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), autonomous driving systems, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), vehicles now require significantly more PCBs than traditional internal combustion engine models. High-power PCBs for battery management systems (BMS), motor control units, and in-vehicle infotainment (IVI) will see strong growth. Additionally, the need for reliable, high-temperature resistant PCBs (e.g., metal-core PCBs) will increase to meet the harsh operational environments under the hood.
H2: Expansion of 5G and Telecommunications Infrastructure
The global rollout of 5G networks will continue to fuel demand for specialized PCBs in 2026. 5G base stations, small cells, and core network equipment require PCBs with high-frequency capabilities, low signal loss, and excellent impedance control. Materials such as Rogers and other engineered laminates will gain market share over standard FR-4 in these applications. Moreover, the densification of network infrastructure will drive demand for compact, high-efficiency PCBs in edge computing and data center hardware, further expanding opportunities in the telecom segment.
H2: Growth in AI and Data Center Applications
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are creating unprecedented demand for high-speed, high-power computing infrastructure. In 2026, data centers deploying AI workloads will rely heavily on advanced multilayer PCBs capable of handling high data throughput and managing thermal loads. Graphics processing units (GPUs), tensor processing units (TPUs), and high-speed interconnects will require PCBs with finer lines and spaces, blind/buried vias, and enhanced power delivery networks. This trend will push manufacturers to invest in next-generation fabrication capabilities to meet the stringent performance requirements.
H2: Sustainability and Supply Chain Resilience
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals will increasingly influence PCB manufacturing practices in 2026. There will be a stronger emphasis on lead-free processes, recyclable materials, and reduced chemical usage. Simultaneously, geopolitical tensions and past supply chain disruptions have prompted companies to diversify manufacturing bases. While Asia—particularly China, Taiwan, and South Korea—will remain dominant, North America and Europe are expected to see modest growth in domestic PCB production, driven by nearshoring initiatives and government incentives (e.g., U.S. CHIPS Act).
H2: Regional Market Dynamics and Competitive Landscape
Asia-Pacific will continue to lead the global PCB market in 2026, accounting for over 50% of production and consumption. China remains the largest producer, although rising labor costs and U.S.-China trade tensions are encouraging some capacity shifts to Vietnam, Malaysia, and India. Meanwhile, Japan and South Korea maintain strong positions in high-tech and IC substrate manufacturing. In contrast, North America and Europe will focus on high-mix, low-volume, and specialized PCBs for aerospace, defense, and medical applications, where quality and reliability are critical.
Conclusion
By 2026, the PCB market will be characterized by innovation, diversification, and resilience. Success will depend on the ability of manufacturers to adapt to rapidly changing technological requirements, invest in advanced production processes, and navigate complex global supply chains. As PCBs remain the backbone of virtually all modern electronics, their evolution will directly enable the next wave of digital transformation across industries.
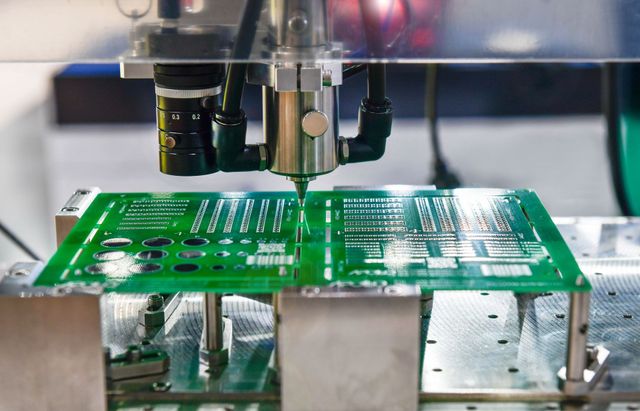
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Printed Circuit Boards: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Poor Quality Control and Inconsistent Manufacturing Standards
One of the most frequent challenges when sourcing PCBs—especially from overseas manufacturers—is inconsistent quality. Suppliers may lack rigorous quality assurance processes, leading to defects such as delamination, poor solder mask application, incorrect trace widths, or insufficient plating in vias. These issues can cause field failures, increased return rates, and damage to brand reputation. Relying solely on price as a selection criterion often leads to cutting corners in materials and processes, such as using substandard substrates or omitting critical testing steps like electrical testing (flying probe or fixture testing).
Inadequate Material Specifications and Substitutions
Some PCB fabricators may substitute materials without explicit approval, using lower-grade laminates (e.g., non-TG170 FR-4 instead of high-TG materials) to reduce costs. This can impact thermal performance, signal integrity, and long-term reliability, especially in high-temperature or high-frequency applications. Without clear documentation and verification, such substitutions go unnoticed until product failure occurs.
Lack of Traceability and Process Documentation
Many suppliers, particularly smaller or less established ones, fail to maintain detailed process records or offer full traceability for materials and production batches. This absence of documentation complicates root cause analysis during failures and can hinder compliance with industry standards (e.g., IPC, ISO, or aerospace/medical certifications). Without batch-level tracking, identifying and isolating defective units becomes nearly impossible.
Intellectual Property (IP) Theft and Unauthorized Production
Sourcing PCBs from certain regions poses significant IP risks. Design files (Gerbers, drill files, BOMs) shared with manufacturers can be copied and used to produce counterfeit or competing products without authorization. Some suppliers may overproduce beyond the agreed quantity and sell excess boards on the gray market. This is especially prevalent in regions with weak enforcement of IP laws.
Insecure Data Handling and Design Leakage
Manufacturers may lack secure data transfer protocols or internal access controls, increasing the risk of design files being exposed to unauthorized third parties. Uploading sensitive designs to vendor portals without non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) or data protection clauses exacerbates this risk. Once IP is leaked, it is often impossible to contain or litigate effectively.
Insufficient Verification of Supplier Credentials
Many companies fail to conduct thorough due diligence on PCB suppliers, relying on online marketplaces or referrals without auditing the manufacturer’s certifications, production capabilities, or reputation. This can result in working with subcontractors or brokers who lack direct control over fabrication, further distancing you from quality oversight and increasing vulnerability to fraud.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, implement strict supplier qualification processes, require NDAs and IP protection agreements, conduct on-site audits when possible, use trusted partners with verifiable certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, IPC standards), and employ design watermarking or encryption. Additionally, perform incoming quality inspections and retain design rights explicitly in contracts.
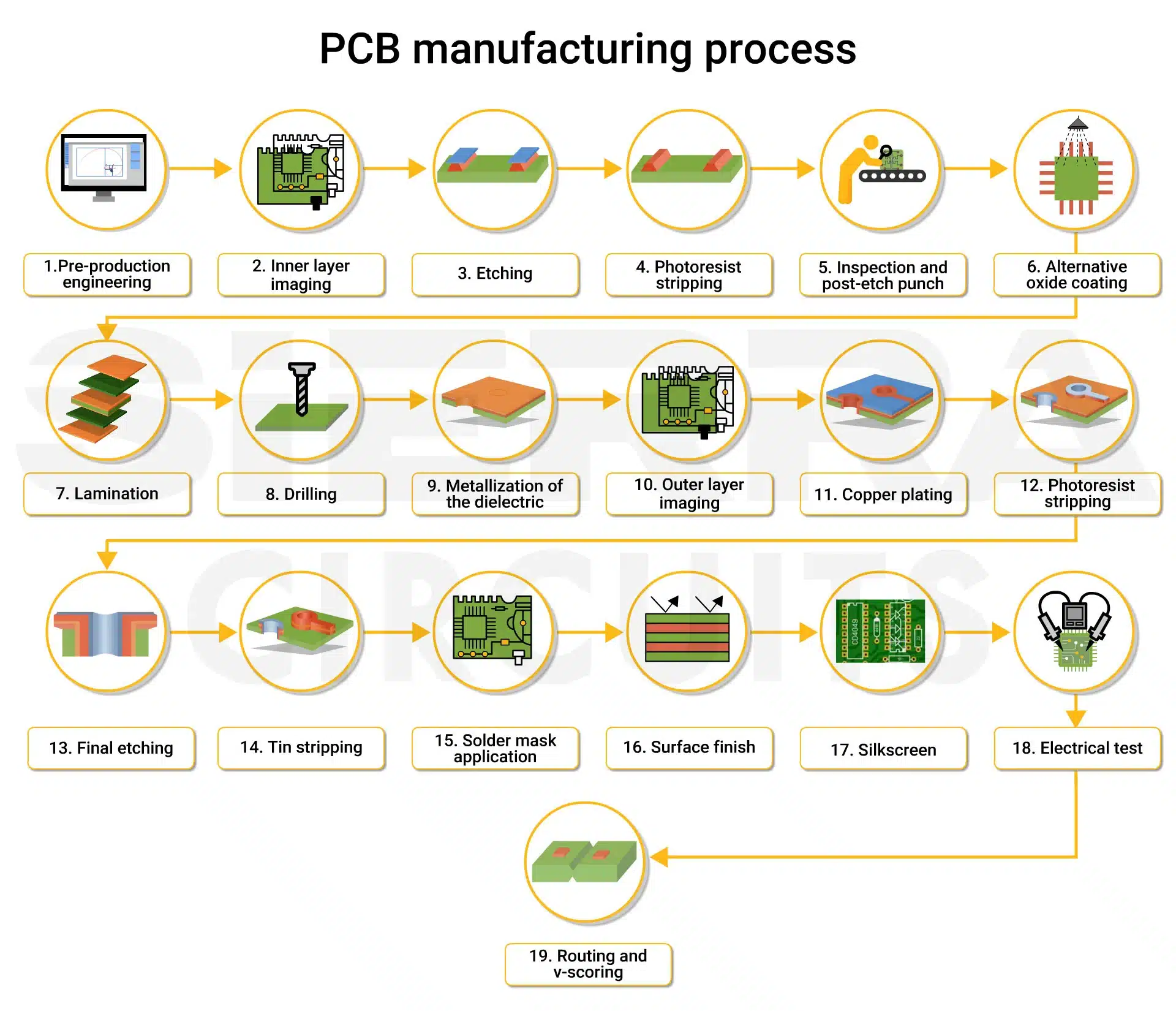
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs)
Overview
This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for the manufacturing, transportation, storage, and disposal of Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs). Adhering to these guidelines ensures regulatory compliance, supply chain efficiency, and product integrity.
Regulatory Compliance
RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances)
PCBs must comply with RoHS directives (e.g., EU Directive 2011/65/EU), which restrict the use of hazardous materials such as lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, polybrominated biphenyls (PBB), and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE). Ensure all components and materials are RoHS-compliant and properly documented with a Declaration of Conformity (DoC).
REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals)
Manufacturers and importers must comply with REACH regulations for chemical substances used in PCB production. This includes registering substances of very high concern (SVHCs) and providing safety data sheets (SDS) when required.
IPC Standards
Adhere to IPC (Association Connecting Electronics Industries) standards such as IPC-6012 (qualification and performance of rigid PCBs) and IPC-A-600 (acceptability of printed boards). These standards ensure quality, reliability, and consistency in PCB manufacturing.
Conflict Minerals Compliance
Under regulations like the U.S. Dodd-Frank Act Section 1502, companies must report the use of conflict minerals (tantalum, tin, tungsten, gold) sourced from the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) or adjoining countries. Maintain due diligence and conduct supply chain audits.
Packaging & Handling
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Protection
PCBs are sensitive to electrostatic discharge. Use ESD-safe packaging such as static-shielding bags, conductive foam, and ESD-safe trays. Label all packaging with ESD warning symbols.
Moisture Sensitivity
Moisture-sensitive PCBs (especially those with surface-mounted components) must be stored in dry environments. Use moisture barrier bags (MBBs) with desiccant packs and humidity indicator cards. Follow IPC/JEDEC J-STD-033 guidelines for handling and baking if necessary.
Mechanical Protection
Use rigid containers, edge protectors, and cushioning materials to prevent physical damage during transit. Avoid stacking PCBs without proper support.
Transportation & Shipping
International Shipping Regulations
Comply with international shipping standards such as IATA (air), IMDG (sea), and ADR (road) when transporting PCBs, especially if they contain hazardous substances or batteries. Declare contents accurately on shipping documents.
Labeling Requirements
Clearly label packages with:
– Electrostatic discharge (ESD) warnings
– Moisture sensitivity level (MSL)
– Handling orientation (e.g., “This Side Up”)
– RoHS compliance marking (“Pb-free” or lead symbol if applicable)
Temperature & Humidity Control
During transit, protect PCBs from extreme temperatures and high humidity. Use climate-controlled transport when necessary, especially for long-distance or international shipments.
Warehousing & Storage
Environmental Conditions
Store PCBs in a clean, dry environment with:
– Temperature: 15°C to 25°C (59°F to 77°F)
– Relative Humidity: 30% to 60%
– Minimal exposure to dust, chemicals, and direct sunlight
Shelf Life Management
Monitor shelf life, especially for PCBs with conformal coatings or moisture-sensitive components. Follow FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory practices.
Storage Positioning
Store PCBs vertically in racks or flat in static-safe containers. Avoid bending or placing heavy objects on top.
End-of-Life & Disposal
WEEE Compliance (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment)
Under EU WEEE Directive 2012/19/EU, producers are responsible for the collection, recycling, and environmentally sound disposal of electronic waste, including PCBs. Register with national WEEE compliance schemes and affix the “crossed-out wheeled bin” symbol on products.
Recycling & Material Recovery
Partner with certified e-waste recyclers to recover valuable materials (e.g., copper, gold) and ensure safe disposal of hazardous substances. Maintain records of recycling and disposal activities.
Export Restrictions
Be aware of the Basel Convention, which controls the transboundary movement of hazardous waste, including PCBs. Obtain proper permits before exporting waste PCBs.
Documentation & Traceability
Bill of Materials (BOM)
Maintain a detailed BOM including part numbers, material specifications, and supplier information. Ensure traceability for all components.
Certifications & Declarations
Keep up-to-date copies of:
– RoHS compliance certificates
– REACH SVHC declarations
– Conflict minerals reporting (e.g., CMRT – Conflict Minerals Reporting Template)
– ISO 9001 or IATF 16949 quality management certifications (if applicable)
Batch & Serial Tracking
Implement a system to track PCB batches and serial numbers through manufacturing, shipping, and customer delivery to support recalls or quality investigations.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management is essential for PCB manufacturers and distributors. By adhering to environmental regulations, protecting product integrity during handling and shipping, and maintaining accurate documentation, companies can ensure reliability, avoid penalties, and support sustainable practices.
Conclusion on Sourcing Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs):
Sourcing printed circuit boards is a critical step in the development and manufacturing of electronic products, directly impacting product quality, reliability, time-to-market, and overall cost. A successful PCB sourcing strategy requires careful evaluation of several key factors including design complexity, required materials, production volume, lead times, quality standards, and cost considerations.
When selecting a PCB supplier, it is essential to balance cost-efficiency with consistent quality and technical capability. Domestic suppliers may offer faster turnaround and easier communication, while overseas manufacturers—particularly in regions like Asia—often provide competitive pricing for high-volume production. However, potential challenges such as longer lead times, logistical complexities, and intellectual property concerns must be addressed.
Partnering with reputable manufacturers that adhere to international quality standards (e.g., ISO 9001, IPC-A-600), conduct rigorous testing (e.g., AOI, flying probe, X-ray), and offer transparent communication enhances reliability and reduces risk. Additionally, early collaboration with suppliers during the design phase (DFM checks) can prevent costly revisions and streamline production.
In conclusion, effective PCB sourcing is a strategic decision that should align with both technical requirements and business objectives. By conducting thorough due diligence, maintaining clear communication, and building strong supplier relationships, companies can ensure a reliable supply of high-quality PCBs that support the long-term success of their electronic products.