The global printed circuit board (PCB) market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand across electronics, automotive, telecommunications, and industrial applications. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 76.4 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.3% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence estimates a CAGR of over 5.5% during the forecast period of 2024–2029, citing advancements in high-density interconnect (HDI) PCBs and the rising adoption of smart devices as key growth catalysts. As technological innovation accelerates and supply chains evolve, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders in capacity, quality, and innovation. Below are the top 10 printed circuit board manufacturers shaping the future of electronics manufacturing worldwide.
Top 10 Printed Circuit Boards Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 TTM Technologies
Domain Est. 1995
Website: ttm.com
Key Highlights: TTM Technologies is an advanced Printed Circuit Board (PCB) manufacturer and a leading supplier in technology solutions….
#2 Summit Interconnect leads Complex Circuits and Rigid Flex PCB
Domain Est. 2016
Website: summitinterconnect.com
Key Highlights: Summit Interconnect is a manufacturer of advanced technology printed circuit boards focused on complex rigid, flex and rigid-flex PCBs….
#3 to American Standard Circuits
Domain Est. 1996
Website: asc-i.com
Key Highlights: Explore top-tier printed circuit board manufacturing with American Standard Circuits. Your USA-based solution for quality PCBs and circuit boards….
#4 Printed Circuit Board Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1998
Website: pcbnet.com
Key Highlights: Imagineering is a trusted printed circuit board manufacturer, offering precision PCB assembly, fabrication, & protoype services with quick turnaround….
#5 NCAB Group: Printed circuit boards
Domain Est. 2009
Website: ncabgroup.com
Key Highlights: We work with a global network of carefully selected partner factories and help our customers produce reliable printed circuit boards….
#6 AdvancedPCB
Domain Est. 2018
Website: advancedpcb.com
Key Highlights: Prototype to Production PCBs from AdvancedPCB. Choose us as your trusted PCB board manufacturer and circuit board manufacturer….
#7 Sunstone Circuits Printed Circuit Boards
Domain Est. 1995
Website: sunstone.com
Key Highlights: Sunstone Offers Expert Service In High Quality Printed Circuit Board Manufacturing & PCB Assembly, Including Prototype & Production PCBs….
#8 Sierra Circuits
Domain Est. 1997
Website: protoexpress.com
Key Highlights: Sierra Circuits can manufacture your PCB and have it expedited to you within 24 hours. Full turnkey boards, with assembly and components in as fast as 5 days….
#9 SOMACIS
Domain Est. 1998
Website: somacis.com
Key Highlights: SOMACIS is a worldwide partner supplying HDI, rigid, rigid-flex and flex PCBs for time critical and mass production requirements….
#10 OSH Park ~
Domain Est. 2011
Website: oshpark.com
Key Highlights: We produce high quality bare printed circuit boards, focused on the needs of prototyping, hobby design, and light production….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Printed Circuit Boards

2026 Market Trends for Printed Circuit Boards
The global Printed Circuit Board (PCB) market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving technological demands, supply chain recalibration, and the proliferation of next-generation electronics. Key trends shaping the industry include:
Advancement in High-Density Interconnect (HDI) and Miniaturization
As consumer electronics, wearables, and medical devices continue to shrink in size while increasing in functionality, HDI PCBs will dominate growth segments. The demand for finer lines and spaces, microvias, and stacked vias will accelerate, particularly in smartphones, AR/VR headsets, and implantable medical devices. By 2026, HDI technology is expected to represent over 30% of the total PCB market value, driven by 5G-enabled devices and advanced computing applications.
Surge in Automotive Electronics and EV Adoption
The automotive sector will be a primary growth engine, with electric vehicles (EVs) and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) requiring sophisticated multilayer and flexible PCBs. High-reliability, thermally efficient PCBs capable of withstanding harsh environments will be critical. The shift toward autonomous driving will further boost demand for rigid-flex and high-frequency laminates. By 2026, automotive PCBs are projected to account for nearly 20% of global demand, outpacing traditional consumer electronics in growth rate.
Expansion of 5G and Telecommunications Infrastructure
The global rollout of 5G networks will continue to fuel demand for high-frequency, low-loss PCB materials such as PTFE and modified epoxy resins. Base stations, small cells, and data center equipment will require advanced RF and microwave PCBs with tight impedance control and enhanced signal integrity. With 6G research gaining momentum, PCB manufacturers will need to innovate in materials and design to support multi-gigahertz frequencies.
Growth in Flexible and Rigid-Flex PCBs
Flexible PCBs will see increasing adoption across industries due to their space-saving benefits and durability. Applications in foldable smartphones, robotics, aerospace, and IoT sensors will drive innovation in ultra-thin and stretchable substrates. Rigid-flex PCBs, combining mechanical stability with dynamic flexibility, will become standard in high-performance computing and military/aerospace systems.
Sustainability and Supply Chain Resilience
Environmental regulations and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) mandates will push manufacturers toward lead-free processes, recyclable materials, and reduced chemical usage. Simultaneously, geopolitical factors and post-pandemic disruptions will accelerate supply chain diversification. By 2026, North America and Europe are expected to increase domestic PCB production, reducing reliance on East Asian manufacturing hubs while boosting nearshoring and automation investments.
Integration of AI and Smart Manufacturing
AI-driven design optimization, predictive maintenance, and automated optical inspection (AOI) will become standard in PCB fabrication. Digital twins and Industry 4.0 technologies will enhance yield rates, reduce time-to-market, and enable mass customization. This digital transformation will be essential for maintaining competitiveness in a high-complexity, low-margin environment.
In summary, the 2026 PCB market will be defined by technological sophistication, sector-specific customization, and strategic resilience. Companies that invest in R&D, sustainable practices, and agile manufacturing will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities across automotive, telecommunications, and advanced electronics sectors.
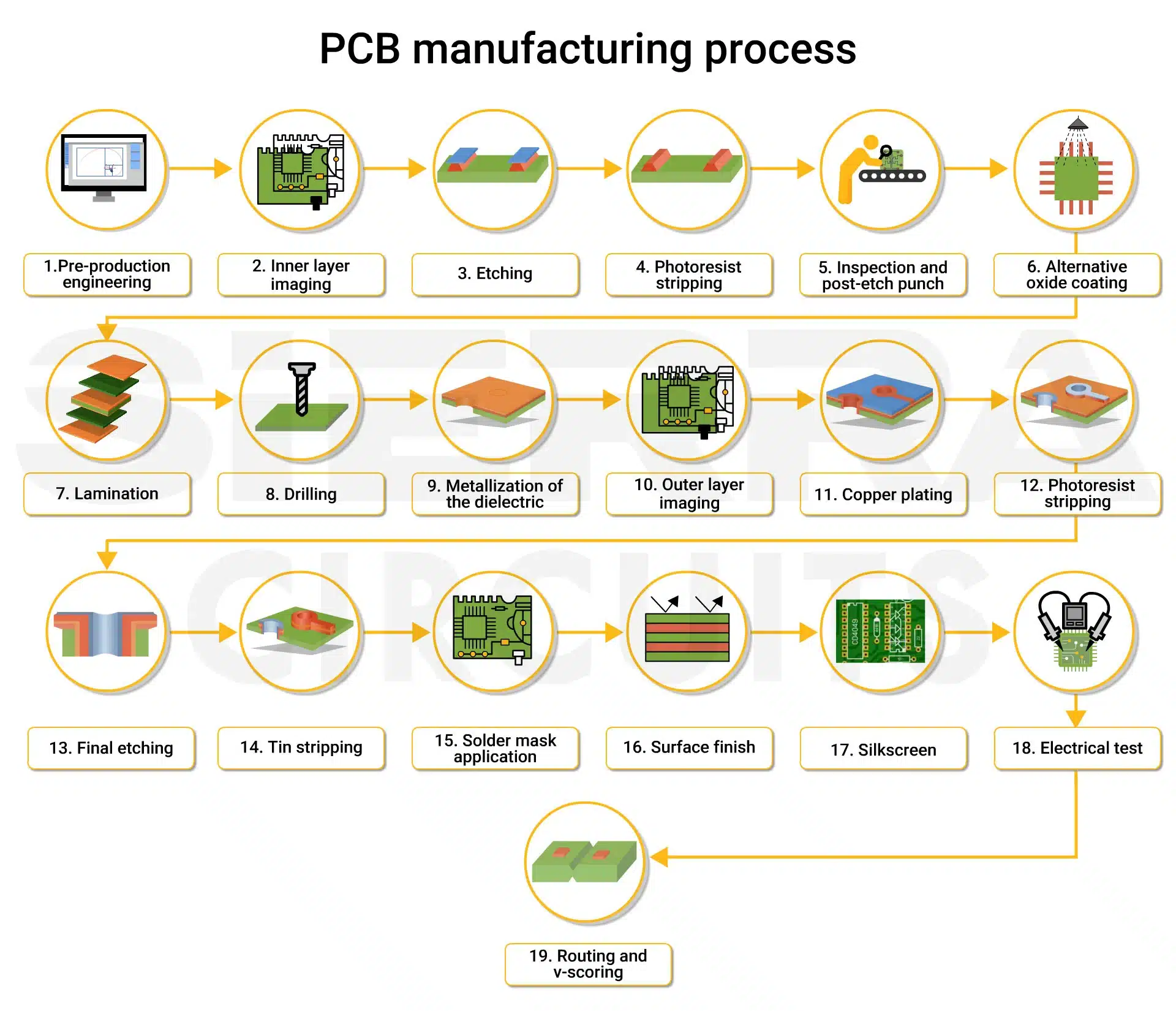
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Printed Circuit Boards: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Poor Quality Control and Inconsistent Manufacturing Standards
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing PCBs—especially from low-cost or overseas manufacturers—is inconsistent quality. Variations in materials, lamination, trace etching, solder mask application, and plating can lead to premature failures, signal integrity problems, or outright non-functionality. Buyers may receive boards that pass basic visual inspection but fail under thermal stress or prolonged operation due to substandard substrates or inadequate IPC compliance. Without clear specifications and third-party testing, defects may go unnoticed until late in the production cycle.
Lack of Transparency in Materials and Processes
Many PCB suppliers, particularly in competitive markets, may use cheaper or unverified materials to cut costs. For example, using FR-1 instead of specified FR-4, or non-TG170 laminates in high-temperature applications, can compromise reliability. Similarly, unclear documentation around surface finishes (e.g., HASL vs. ENIG) or copper thickness can lead to assembly issues or reduced product lifespan. Ensuring material traceability and process validation is critical but often overlooked during sourcing.
Intellectual Property (IP) Theft and Data Security Risks
Sharing detailed Gerber files, BOMs, and schematics with PCB manufacturers exposes sensitive design IP. In regions with weak IP enforcement, there’s a real risk of unauthorized replication, reverse engineering, or sale of design data to competitors. Even trusted suppliers may subcontract manufacturing to third parties without consent, further increasing exposure. Without robust NDAs, data encryption, and strict access controls, companies risk losing competitive advantage or facing counterfeit products in the market.
Inadequate Supplier Vetting and Communication Barriers
Choosing a supplier based solely on price or lead time without verifying certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, IPC standards), production capacity, or engineering support can lead to costly delays and rework. Language barriers, time zone differences, and cultural nuances may exacerbate misunderstandings in design intent, tolerances, or inspection criteria, resulting in non-conforming deliveries.
Insufficient Testing and Documentation
Many PCB suppliers offer limited or no electrical testing (e.g., Flying Probe or AOI), especially for low-volume orders. Relying on visual inspection alone can miss latent defects such as micro-cracks, via stubs, or impedance mismatches. Additionally, incomplete or missing documentation—like impedance reports, drill files, or material certifications—can hinder compliance, traceability, and root cause analysis during failure investigations.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Require compliance with IPC-6012 or equivalent standards
– Use trusted manufacturing partners with strong IP protection policies
– Employ secure data-sharing methods (e.g., encrypted portals, watermarked files)
– Conduct pre-production sample testing and audits
– Include clear quality clauses and IP ownership terms in contracts
Proactive management of both quality and IP risks is essential for reliable, secure, and scalable PCB sourcing.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Printed Circuit Boards
Overview
This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for shipping, handling, and regulating Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) across global supply chains. Adhering to these guidelines ensures product integrity, regulatory compliance, traceability, and operational efficiency.
Packaging and Handling
- ESD Protection: Use electrostatic discharge (ESD)-safe packaging such as shielding bags, conductive foam, or static-dissipative containers to prevent damage to sensitive components.
- Moisture Sensitivity: For PCBs with surface-mount components, follow IPC/JEDEC J-STD-033 standards. Use moisture barrier bags (MBBs) with desiccant and humidity indicator cards (HICs) when necessary.
- Mechanical Protection: Secure PCBs in rigid containers or trays to avoid bending, scratching, or physical impact during transit.
- Labeling: Clearly mark packages with ESD warnings, orientation indicators, handling instructions, and moisture sensitivity levels (MSL).
Transportation & Storage
- Temperature and Humidity Control: Store and ship PCBs in environments with controlled temperature (typically 15°C to 30°C) and relative humidity (30% to 60%). Avoid condensation.
- Shelf Life Management: Observe manufacturer-defined shelf life, especially for moisture-sensitive devices (MSDs). Track time outside dry packaging using floor life timers.
- Shipping Methods: Use reliable carriers with tracking and insurance. For high-value or time-sensitive PCBs, consider air freight with climate control.
- Stacking and Weight Limits: Follow packaging guidelines to avoid crushing lower layers in storage or transport.
Regulatory Compliance
- RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): Ensure PCBs comply with EU Directive 2011/65/EU, restricting lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, PBB, and PBDE. Provide RoHS compliance documentation.
- REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals): Comply with EU regulation EC 1907/2006. Declare substances of very high concern (SVHCs) above threshold levels.
- IPC Standards: Follow relevant IPC standards such as IPC-A-600 (acceptability of printed boards) and IPC-6012 (qualification and performance specification).
- WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment): Include WEEE marking (wheelie bin symbol) on applicable products and support recycling programs.
- Conflict Minerals (U.S. Dodd-Frank Act): Report use of tin, tantalum, tungsten, and gold (3TG) sourced from conflict-affected regions, if applicable.
Export Controls and Trade Compliance
- ECCN Classification: Determine Export Control Classification Number (ECCN) under the U.S. Commerce Control List (CCL). Many PCBs fall under ECCN 3A999 or 3A001, depending on performance characteristics.
- ITAR vs. EAR: Confirm whether PCBs are subject to International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) or Export Administration Regulations (EAR). Most commercial PCBs are EAR-controlled.
- Destination Restrictions: Screen end-users and destinations against denied party lists (e.g., U.S. BIS, EU, UN sanctions). Avoid shipments to embargoed countries without proper licensing.
- Documentation: Prepare commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and export declarations as required. Include technical specifications for customs clearance.
Traceability and Documentation
- Lot and Batch Tracking: Maintain traceability of PCBs through serial or batch numbers, including manufacturing date, revision, and material composition.
- Compliance Certificates: Provide Certificates of Compliance (CoC), RoHS/REACH declarations, and IPC inspection reports as needed.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Require suppliers to provide material declarations (e.g., IPC-1752) and ensure sub-tier compliance.
Sustainability and End-of-Life
- Recyclability: Design PCBs with recyclability in mind—minimize hazardous materials and use standardized components.
- Take-Back Programs: Participate in or establish PCB recycling programs in accordance with local regulations.
- Environmental Reporting: Track and report environmental impact metrics, including carbon footprint and waste generation.
Best Practices Summary
- Conduct regular compliance audits.
- Train logistics and procurement teams on ESD, packaging, and export procedures.
- Partner with certified manufacturers and freight forwarders experienced in electronics logistics.
- Automate compliance data management using ERP or compliance software platforms.
Adhering to this guide ensures safe, legal, and efficient handling of PCBs throughout their lifecycle—from manufacturing to end-of-use.
Conclusion for Sourcing Printed Circuit Boards:
Sourcing printed circuit boards (PCBs) is a critical aspect of developing reliable and cost-effective electronic products. The decision-making process should balance factors such as quality, cost, lead time, technical capabilities, and supplier reliability. Whether sourcing locally or internationally, it is essential to partner with reputable manufacturers who adhere to industry standards (e.g., IPC, ISO, RoHS compliance) and offer strong quality control processes.
For prototyping and low-volume production, domestic or quick-turn PCB suppliers may offer better communication, faster turnaround, and easier troubleshooting. For high-volume manufacturing, offshore suppliers—particularly in regions like East Asia—can provide significant cost savings but require careful vetting and robust supply chain management to mitigate risks related to quality, logistics, and intellectual property protection.
Ultimately, a strategic sourcing approach that aligns with your product requirements, production scale, time-to-market goals, and risk tolerance will ensure a reliable supply of high-performance PCBs and contribute to the overall success of your electronic product development. Regular evaluation of suppliers and maintaining contingency plans further strengthen supply chain resilience.