The global laser welding machine market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for high-precision joining solutions in automotive, aerospace, and electronics manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 1.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.6% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is fueled by advancements in fiber laser technology, rising automation in production lines, and the push toward lightweight materials in key industries. As competition intensifies, manufacturers are differentiating themselves not only through innovation but also through strategic pricing models. Based on current market dynamics and pricing data from leading industrial equipment suppliers, this analysis highlights the top 9 laser welding machine manufacturers and provides insight into their pricing structures, helping buyers make informed decisions in an evolving landscape.
Top 9 Price Of Laser Welding Machine Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Welding Machine
Website: bcamcnc.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsIndustrial 1200W Air-cooled Handheld Laser Welding Machine … $4,150.00 Original price was: $4,150.00. $2,310.00 Current price is: $2,310.00….
#2 LaserStar Technologies
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
#3 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: We Specialize in Laser Welding & Cleaning DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA….
#4 All Types of Laser Welding Machines Prices for Reference
Website: megmeet-welding.com
Key Highlights: Prices generally range from $5,000 to $15,000. They are commonly used in electronics, medical, and small-scale manufacturing sectors. Mid-Range ……
#5 How Much Does a Laser Welding machine Cost? (2024)
Website: longxinlaser.com
Key Highlights: Range: $4,700 – $26,300 · Popular models: Entry-level (1000W): $5,000 – $8,000; Mid-range (1500W): $10,000 – $15,000; High-end (2000W+): $18,000 ……
#6 Laser Welders
Website: everlastgenerators.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returns$7,999.00 Buy Now. As low as $180 ……
#7 Laser Welding Machine
Website: yihailasers.com
Key Highlights: Four-in-One Customized 3000W Laser Welding Machine · 6,800.00 Original price was: $6,800.00. ; Handheld Air-cooled Laser Welding Machine · 3,600.00 Original price ……
#8 How much does it cost for a handheld laser welder machine?
Website: kirinlaser.com
Key Highlights: Discover the real cost of handheld laser welding machines. Compare power levels, features, and ROI to find the right model from $1860 to ……
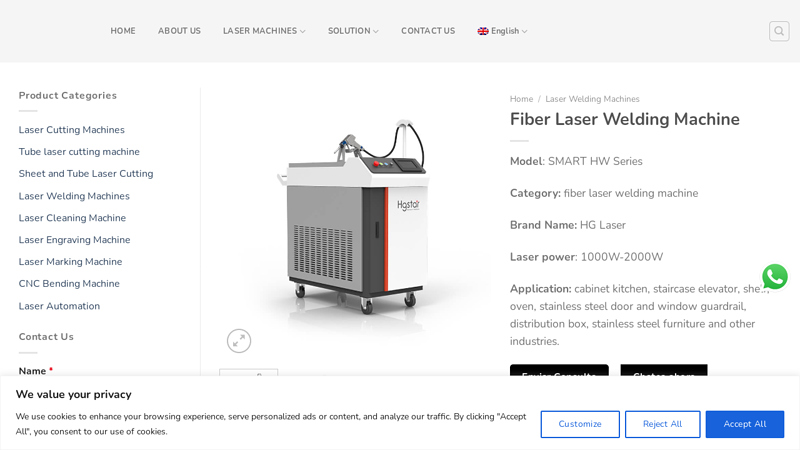
#9 HW series best handheld fiber laser welding machine
Website: hg-star.com
Key Highlights: Handheld fiber laser welding machine has the best fiber laser beam for fast welding speed, high quality weld seam and no consumables….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Price Of Laser Welding Machine

Price of Laser Welding Machine: 2026 Market Trends Analysis
The global market for laser welding machines is undergoing significant transformation, driven by technological innovation, expanding industrial automation, and increasing demand across key sectors such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical devices. As we approach 2026, several factors are shaping the pricing trends of laser welding machines, influencing both cost structures and market accessibility.
Technological Advancements Driving Price Fluctuations
One of the most influential factors affecting the price of laser welding machines by 2026 is rapid technological development. Fiber laser technology continues to dominate the market due to its superior efficiency, lower maintenance, and higher precision compared to traditional CO2 lasers. The widespread adoption of high-power fiber lasers (ranging from 3 kW to 20 kW) has led to economies of scale, gradually reducing unit costs.
Additionally, integration with artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and real-time monitoring systems has enhanced machine performance but also added to the initial price point. However, as these smart features become standardized, their incremental cost is expected to decline, making advanced laser welding systems more affordable.
Increased Competition and Regional Manufacturing Influence
The competitive landscape of the laser welding market is intensifying, particularly with the rise of Chinese manufacturers such as Han’s Laser, Max Photonics, and JPT Opto-electronics. These companies are offering cost-competitive machines with comparable performance to Western brands like Trumpf, IPG Photonics, and Bystronic. By 2026, this competition is expected to put downward pressure on prices, especially in the mid-range and entry-level segments.
Moreover, regional manufacturing hubs in Southeast Asia and India are investing in domestic laser production, reducing import dependencies and logistics costs. This regional localization is anticipated to further moderate machine prices, especially in emerging markets.
Rising Demand in Electric Vehicles and Battery Manufacturing
The electric vehicle (EV) revolution is a major demand driver for laser welding systems. Precision welding is critical in battery pack assembly, motor components, and lightweight vehicle structures. By 2026, the global EV market is projected to grow significantly, increasing demand for high-speed, high-accuracy laser welding solutions.
This surge in demand could initially put upward pressure on prices, especially for specialized machines used in battery welding (e.g., blue light and green lasers for copper welding). However, as production scales and new entrants emerge, prices are expected to stabilize or even decrease due to mass production efficiencies.
Material and Supply Chain Factors
Raw material costs—particularly for rare earth elements used in laser diodes and optics—can impact pricing. Geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions may cause short-term price volatility. However, advancements in diode efficiency and alternative materials are helping mitigate these risks. By 2026, improved supply chain resilience and recycling initiatives are expected to contribute to more stable pricing.
Automation and Integration Premiums
As industries adopt turnkey automation solutions, laser welding machines are increasingly sold as part of larger robotic cells or production lines. While standalone laser units may see price reductions, fully integrated systems with robotics, vision systems, and software packages command premium pricing. The value-added services such as remote diagnostics, predictive maintenance, and cloud-based data analytics also contribute to higher overall system costs.
Forecast for 2026: Price Outlook
By 2026, the average price of a standard fiber laser welding machine (1–3 kW) is projected to decrease by 10–15% compared to 2023 levels, due to increased competition and manufacturing efficiencies. High-power and specialty systems (e.g., hybrid welding or ultrafast lasers) may maintain stable or slightly higher prices due to niche applications and advanced capabilities.
In summary, the price of laser welding machines in 2026 will reflect a balance between cost-reducing innovations and premium features driven by automation and industry-specific demands. Buyers can expect greater affordability in standard models, while cutting-edge systems will remain at a premium, catering to advanced manufacturing needs.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Welding Machines (Quality, IP Protection)
Sourcing a laser welding machine involves significant investment and technical complexity. Overlooking key factors—especially related to quality and intellectual property (IP) protection—can lead to poor performance, safety risks, and legal exposure. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Prioritizing Low Cost Over Long-Term Quality
A major trap is choosing the cheapest machine without evaluating build quality, component reliability, or manufacturer reputation. Low-cost machines often use inferior optics, unstable power sources, and substandard cooling systems, leading to inconsistent welds, frequent breakdowns, and higher total cost of ownership.
Solution: Evaluate total cost of ownership (TCO), including maintenance, downtime, and consumables. Request third-party certifications (e.g., CE, ISO 9001) and perform site visits or product demonstrations.
2. Inadequate Verification of Machine Specifications
Suppliers may exaggerate key parameters such as laser power output, beam quality (M² factor), or duty cycle. A machine advertised as “1kW” may deliver significantly less under real operating conditions, compromising weld penetration and speed.
Solution: Demand detailed technical documentation and third-party test reports. Conduct on-site performance testing under actual production conditions before finalizing the purchase.
3. Ignoring IP Protection in Custom or Integrated Systems
When integrating a laser welding machine into an automated production line or developing proprietary processes, IP risks arise—especially if the supplier uses closed-source software or patented beam delivery systems. Unauthorized modifications or reverse engineering could infringe on patents or void warranties.
Solution: Review supplier contracts for IP clauses. Ensure access to necessary APIs, SDKs, or documentation for integration. Confirm that your process innovations remain your intellectual property.
4. Overlooking Compliance with Safety and IP Standards
Laser welding machines must comply with international safety standards (e.g., IEC 60825 for laser safety, FDA requirements in the U.S.). Non-compliant machines can pose serious safety hazards and lead to regulatory penalties. Additionally, some machines may incorporate IP-protected technology without proper licensing.
Solution: Verify that the machine complies with relevant safety and regional regulations. Ask for proof of licensing for critical technologies (e.g., fiber laser sources, scanning systems).
5. Relying on Unverified Supplier Credentials
Many suppliers—especially in competitive markets—may lack proven track records or transparent manufacturing practices. Sourcing from such vendors increases the risk of receiving counterfeit components or machines assembled with stolen designs.
Solution: Conduct due diligence: check references, visit manufacturing facilities, and verify patents or proprietary technologies claimed by the supplier. Use escrow services for large transactions.
6. Underestimating After-Sales Support and Service Quality
Even high-quality machines require maintenance, calibration, and technical support. Choosing a supplier with poor service infrastructure—especially internationally—can result in long downtimes and loss of productivity.
Solution: Assess the supplier’s global service network, spare parts availability, and response time. Include service-level agreements (SLAs) in procurement contracts.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls, businesses can ensure they acquire a reliable, safe, and legally compliant laser welding solution that supports long-term manufacturing goals.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Price of Laser Welding Machine
When evaluating the price of a laser welding machine, it’s essential to consider not only the upfront cost but also the logistics and compliance aspects that can significantly impact total expenses and operational efficiency. This guide outlines key considerations to ensure smooth procurement, transportation, installation, and regulatory adherence.
Understanding Total Cost of Ownership
The listed price of a laser welding machine is often just the starting point. Additional logistics and compliance-related costs can add 10–30% or more to the total investment. These include shipping, import duties, insurance, installation, training, and regulatory certification fees.
International Shipping and Import Logistics
Shipping a laser welding machine internationally requires careful planning due to the equipment’s size, weight, and sensitivity. Crating must meet international standards (e.g., ISPM 15 for wooden packaging), and freight options (air, sea, or land) affect both cost and delivery time. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for heavy machinery but slower.
Import duties, value-added taxes (VAT), and customs clearance fees vary by country and can significantly influence the final price. For example, tariffs on industrial machinery range from 0% to 10% in many regions, but additional anti-dumping or safeguard duties may apply. Accurate Harmonized System (HS) code classification—typically under 8456.20 (laser beam machines for working metal)—is critical for correct duty assessment.
Export Controls and Licensing Requirements
Laser welding machines, especially high-power models (typically >500W), may be subject to export control regulations due to their dual-use potential (civilian and military applications). In the United States, such equipment may fall under the Export Administration Regulations (EAR) and require a license from the Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS), particularly for destinations on restricted lists (e.g., China, Russia, Iran).
Similarly, the Wassenaar Arrangement regulates the export of high-tech industrial equipment, including certain laser systems. Compliance involves verifying end-user information, obtaining export licenses, and maintaining detailed documentation to avoid penalties.
Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Laser welding machines must comply with safety standards in the destination country. Key certifications include:
- CE Marking (European Union): Requires compliance with the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC), Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive, and Laser Product Safety (EN 60825).
- FDA/CDRH Registration (United States): All laser products must be registered with the Center for Devices and Radiological Health, including reporting and compliance with performance standards (21 CFR 1040.10).
- CSA Certification (Canada): Ensures conformity with Canadian Electrical Code and laser safety standards.
- China CCC Mark: Mandatory for certain industrial equipment sold in China.
Non-compliant machines may be rejected at customs or subjected to costly modifications.
Installation, Training, and Technical Support
The purchase price often excludes on-site installation, calibration, and operator training—critical for safe and efficient operation. Budget for technician travel, especially for international installations. Additionally, verify warranty terms and availability of spare parts and technical support in your region, as delays can impact productivity and increase lifecycle costs.
Environmental and Disposal Regulations
Laser welding machines contain components (e.g., batteries, electronic boards, optical fibers) subject to environmental regulations such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment). End-of-life disposal must follow local hazardous waste protocols, potentially incurring costs not reflected in the initial price.
Conclusion
When comparing prices for laser welding machines, always assess the full logistics and compliance landscape. Engage suppliers early to clarify shipping terms (e.g., Incoterms like FOB, CIF, or DDP), confirm certification status, and verify export eligibility. A comprehensive approach ensures cost predictability, regulatory compliance, and operational readiness upon delivery.
Conclusion on Sourcing Price of Laser Welding Machines
In conclusion, the sourcing price of a laser welding machine is influenced by a range of factors including machine type (fiber, CO2, or disk laser), power output, automation features, brand reputation, and required precision. Prices can vary significantly—from a few thousand dollars for basic models to over $100,000 for high-end, automated industrial systems. Sourcing from different regions, such as China, Europe, or North America, also impacts cost due to variations in manufacturing expenses, quality standards, and after-sales support.
To achieve optimal value, buyers should balance initial cost with long-term considerations such as durability, maintenance, energy efficiency, and technical support. Engaging directly with manufacturers, comparing quotes, and evaluating total cost of ownership can lead to more informed procurement decisions. Ultimately, while competitive pricing is important, the focus should remain on obtaining a reliable, high-performance laser welding solution that meets specific production requirements and delivers a strong return on investment.