The global prefabricated bathrooms market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for faster construction timelines, labor cost savings, and increasing adoption in modular housing, hospitality, and healthcare infrastructure. According to Mordor Intelligence, the prefabricated homes market—which includes modular bathroom solutions—is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.5% from 2024 to 2029, with off-site construction methods gaining traction due to improved quality control and sustainability benefits. Additionally, Grand View Research estimates that the global modular construction market size was valued at USD 145.8 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 7.1% through 2030, fueled by advancements in design flexibility and regulatory support for rapid urban development. As a critical component of modular buildings, prefabricated bathrooms are at the forefront of this shift, prompting increased innovation among manufacturers globally. The following list highlights the top 10 prefabricated bathroom manufacturers leveraging scalable solutions, advanced materials, and digital integration to lead this evolving market.
Top 10 Prefabricated Bathrooms Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
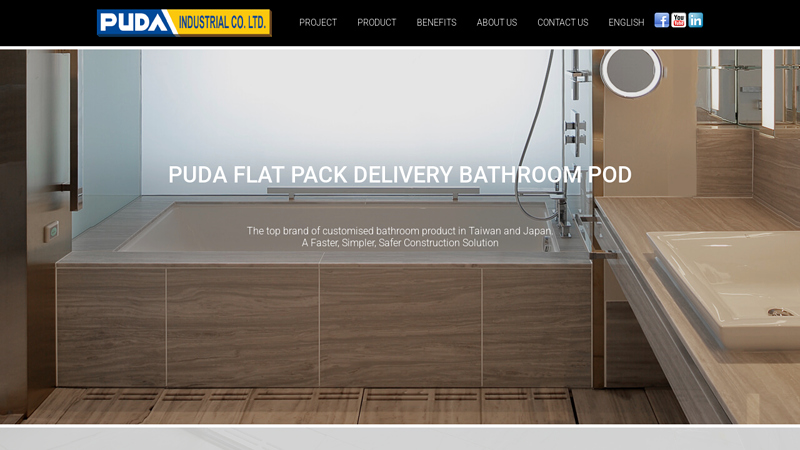
#1 PUDA High Quality Prefabricated Bathroom
Domain Est. 2000
Website: puda.com.tw
Key Highlights: WHY A PUDA BATHROOM. PUDA is the leading bathroom pod designer & manufacturer in Asia. Panelised bathroom structures, custom design, flat-pack delivery. 100 ……
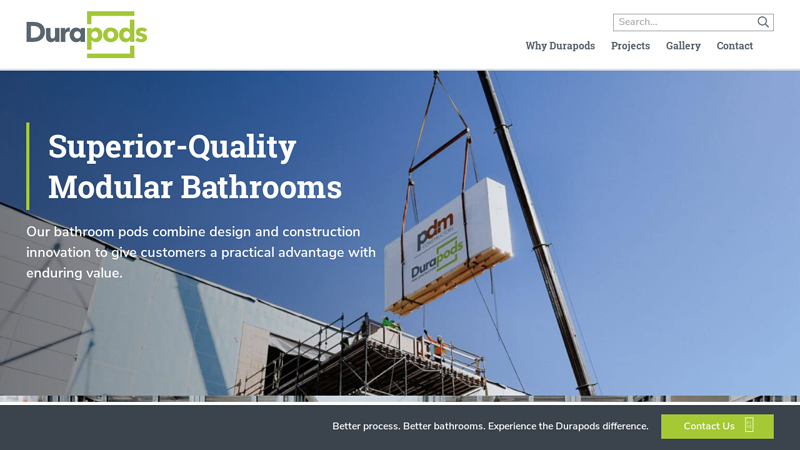
#2 Modular Bathrooms by Durapods
Domain Est. 2020
Website: durapods.com
Key Highlights: Modular bathrooms for large-scale construction projects. Achieve cost and schedule certainty. Factory-built for turnkey installation….
#3 KraftMaid Cabinetry
Domain Est. 1995
Website: kraftmaid.com
Key Highlights: Discover custom kitchen and bath cabinets from KraftMaid—built for style and storage. Start designing your dream space today with our easy planning tools….
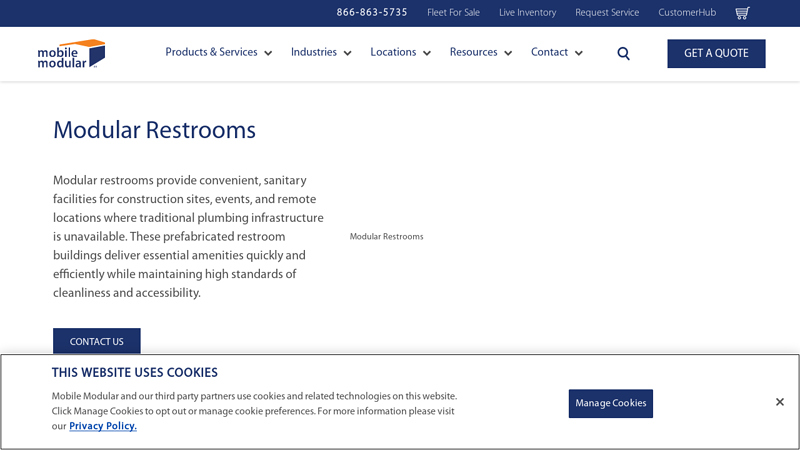
#4 Premium Commercial Modular Restroom Solutions for Businesses
Domain Est. 1997
Website: mobilemodular.com
Key Highlights: Rating 4.8 (315) Modular Restrooms designed for commercial use with multiple configurations, premium fixtures & rapid installation. Ideal for construction, events ……
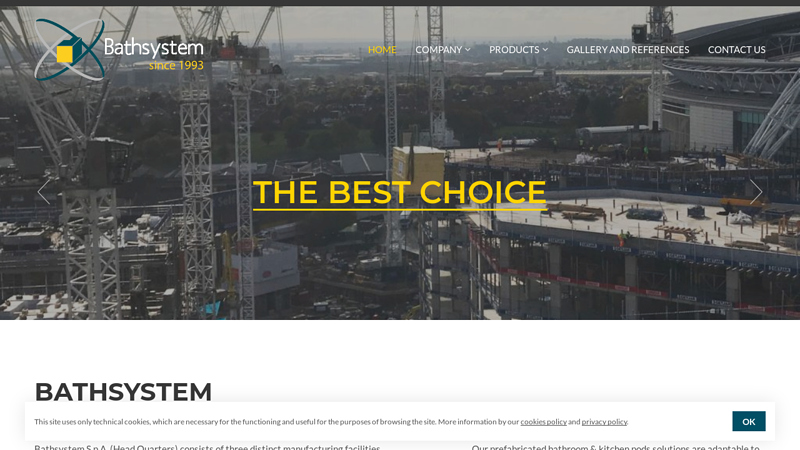
#5 Bathsystem
Domain Est. 1998 | Founded: 1993
Website: bathsystem.com
Key Highlights: Since 1993, the international leader in production of premium prefabricated bathrooms pods and kitchens units….
#6 wedi System World
Domain Est. 2004
Website: wedi.net
Key Highlights: Discover building boards, flush-to-floor showers, steam baths, bathroom furniture, wellness features, and expert installation tips….
#7 BAUDET
Domain Est. 2007
Website: baudet-sa.com
Key Highlights: Prefab Bathrooms in Polyester or Metal for Hotels, Healthcare Facilities, Residential Housing, Student & Social Housing – BAUDET – Call 02 51 66 27 85….
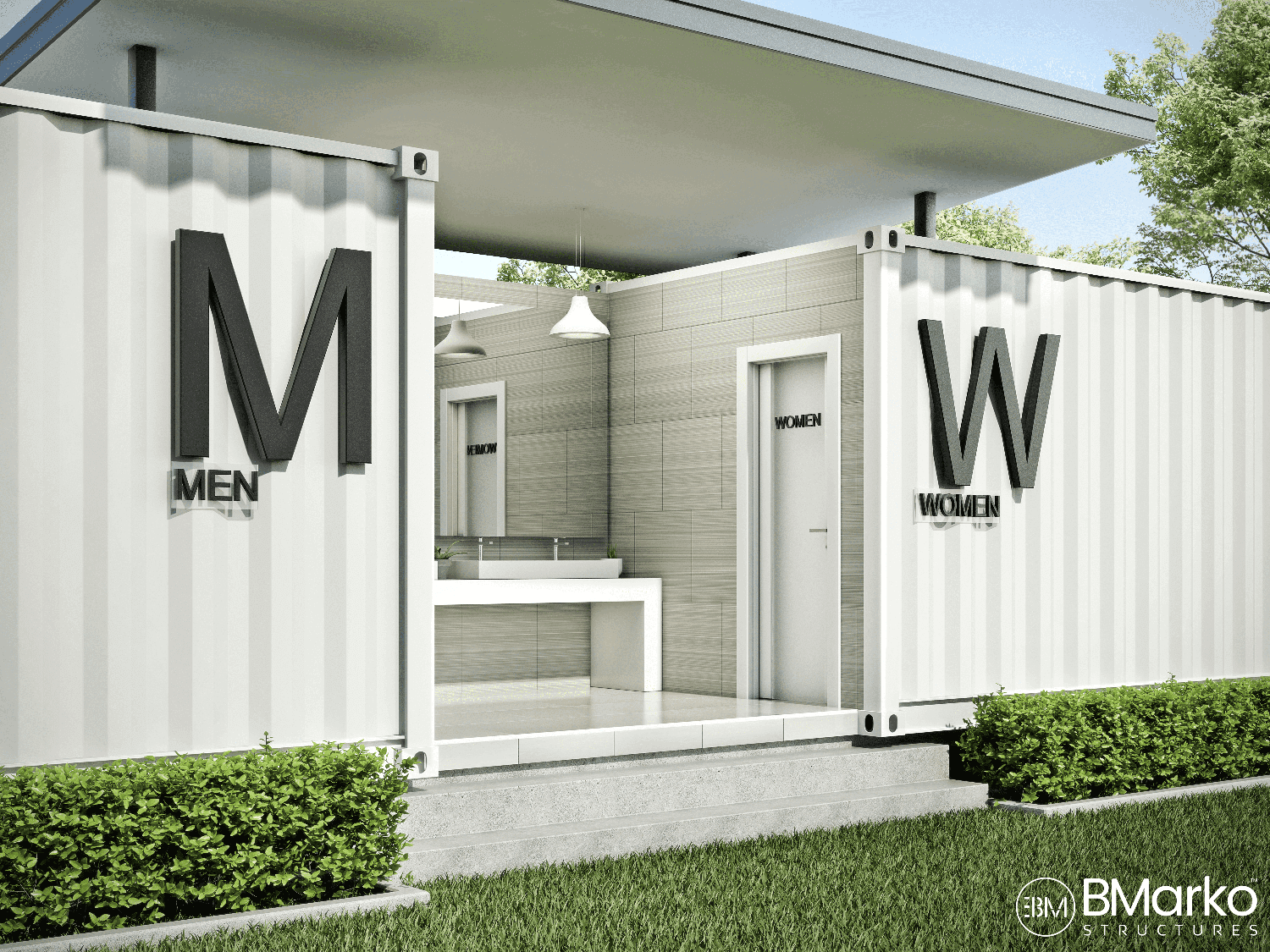
#8 Modular Bathrooms
Domain Est. 2014
Website: bmarkostructures.com
Key Highlights: BMarko Structures is a leader in modular bathroom manufacturing. We want to ensure your users stay comfortable when using the bathroom….
#9 Modular Bathroom Pods
Domain Est. 2015
Website: bandtmfg.com
Key Highlights: Discover modular bathroom pods by B&T Manufacturing—prefab, fast to install, and built for commercial efficiency. Designed for quality and ease….
#10 Hydrodiseño
Domain Est. 2017 | Founded: 2005
Website: hydrodiseno.com
Key Highlights: Hydrodiseño is a company dedicated to the manufacture of modular pods, especially prefabricated bathroom pods and kitchens. Based in Spain since 2005….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Prefabricated Bathrooms

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Prefabricated Bathrooms
The global prefabricated bathroom market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, sustainability demands, and shifting construction practices. As urbanization accelerates and labor shortages intensify, the adoption of modular and prefabricated bathroom solutions is expected to expand across residential, commercial, and hospitality sectors. Below are key trends shaping the market in 2026:
-
Increased Demand in Multifamily and Affordable Housing
Urban population growth and housing shortages are fueling demand for rapid construction methods. Prefabricated bathrooms offer reduced build times and cost efficiencies, making them ideal for high-density housing projects. Governments and developers are increasingly investing in modular solutions to meet affordable housing targets, particularly in Asia-Pacific and North America. -
Sustainability and Green Building Standards
Environmental regulations and green certifications (e.g., LEED, BREEAM) are pushing developers to adopt eco-friendly construction. Prefabricated bathrooms contribute to sustainability through reduced material waste, optimized manufacturing processes, and integration of water-saving fixtures and energy-efficient systems. Recyclable and low-carbon materials are becoming standard features. -
Advancements in Smart Bathroom Technology
By 2026, smart features—such as touchless faucets, integrated lighting controls, voice-activated mirrors, and IoT-connected health monitoring—are being embedded into prefabricated bathroom units. These innovations enhance user experience and are increasingly expected in premium residential and hospitality developments. -
Customization and Design Flexibility
Manufacturers are leveraging digital design tools and flexible production lines to offer personalized finishes, layouts, and premium fixtures without sacrificing the speed of modular construction. This shift is broadening appeal beyond budget-conscious projects to luxury markets. -
Growth in Hospitality and Healthcare Sectors
Hotels, student accommodations, and healthcare facilities are adopting prefabricated bathrooms to minimize downtime during renovations and ensure consistent quality. The pandemic highlighted the need for hygienic, easily cleanable surfaces, which prefabricated units can deliver through seamless, non-porous materials. -
Regional Expansion and Supply Chain Localization
While North America and Europe lead in adoption, Asia-Pacific—especially China, India, and Southeast Asia—is emerging as the fastest-growing market. Localized manufacturing hubs are reducing shipping costs and lead times, supporting regional scalability. -
Integration with Off-Site Construction Ecosystems
Prefabricated bathrooms are increasingly part of broader modular construction strategies. Integration with structural wall panels, MEP (mechanical, electrical, plumbing) systems, and digital BIM (Building Information Modeling) enables faster on-site assembly and fewer errors. -
Labor Shortages and Cost Pressures
Persistent labor shortages in the construction industry are accelerating the shift toward off-site fabrication. Prefabricated bathrooms reduce on-site labor needs and mitigate delays, offering a compelling ROI for developers facing rising wages and project timelines.
In conclusion, the 2026 prefabricated bathroom market is defined by a convergence of efficiency, sustainability, and technological integration. As the construction industry embraces industrialized methods, prefabricated bathrooms are transitioning from a niche solution to a mainstream component of modern building practices.
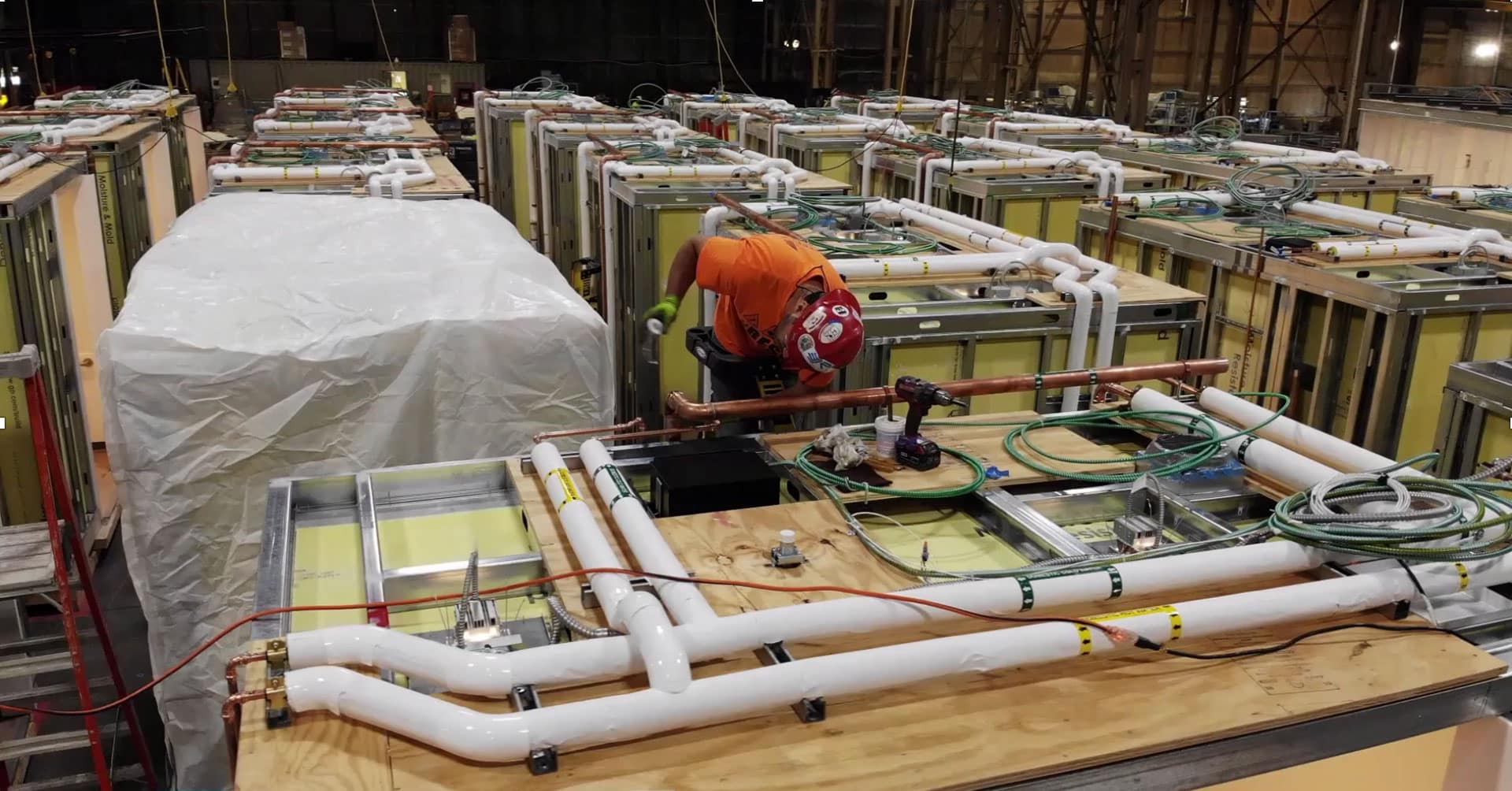

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Prefabricated Bathrooms (Quality, IP)
Sourcing prefabricated bathrooms offers speed and efficiency, but overlooking key quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations can lead to significant issues. Here are common pitfalls to avoid:
Quality Control Variability
Prefabricated bathroom units (PBUs) manufactured off-site are only as reliable as the supplier’s quality assurance processes. Inconsistent welding, poor sealant application, or improper installation of fixtures can result in leaks, mold, and costly rework once installed on-site. Without rigorous third-party inspections or adherence to international standards (e.g., ISO 9001), buyers risk receiving substandard units.
Lack of Standardized Testing and Certification
Many suppliers fail to provide comprehensive performance testing data—such as water tightness, structural load capacity, or fire resistance—validated by accredited laboratories. Without certified test reports, there’s no objective proof that the units meet safety and durability requirements, increasing liability and compliance risks.
Material Substitution Without Approval
Suppliers may substitute materials (e.g., cheaper tiles, lower-grade plumbing fixtures, or non-compliant waterproofing membranes) to cut costs, especially under tight budgets or compressed timelines. These substitutions, if not contractually prohibited and monitored, degrade long-term performance and user satisfaction.
Inadequate Waterproofing and Moisture Management
Poorly executed factory-installed waterproofing is a leading cause of failure in prefabricated bathrooms. Seams, joints, and pipe penetrations are common weak points. If the supplier lacks expertise in integrated moisture barriers and fails to conduct flood testing, on-site leaks and structural damage are likely.
Poor Integration with Building Systems
Prefabricated bathrooms must seamlessly connect to on-site MEP (mechanical, electrical, plumbing) systems. Units designed without proper coordination can result in misaligned service connections, incorrect pipe routing, or incompatible interfaces—leading to delays, rework, and compromised functionality.
Intellectual Property Infringement
Some suppliers use design elements, patented technologies, or proprietary systems (e.g., modular connection methods, ventilation solutions) without proper licensing. Sourcing from such vendors exposes the buyer to legal risks, including infringement claims, project stoppages, and reputational damage.
Lack of Design Ownership and Customization Rights
Contracts that do not clearly assign IP rights to custom-designed PBUs may leave buyers unable to replicate or modify the units for future projects. Suppliers might retain design ownership, limiting scalability and innovation reuse, especially in multi-phase developments.
Insufficient Documentation and As-Built Records
Missing or inaccurate “as-built” drawings, material specifications, and maintenance manuals complicate long-term facility management. Without comprehensive documentation, troubleshooting issues or conducting repairs becomes difficult, increasing lifecycle costs.
Overlooking Lifecycle and Maintenance Requirements
Prefabricated bathrooms are often evaluated on upfront cost rather than total cost of ownership. Units with non-serviceable components or proprietary parts can lead to expensive maintenance and shortened lifespans. Buyers must assess ease of repair and availability of spare parts.
Inadequate Supplier Vetting and Track Record
Choosing a supplier based solely on price or speed, without reviewing past projects, client references, or manufacturing facility audits, increases the risk of poor quality and IP issues. A supplier’s experience with similar projects and compliance history is critical to success.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough due diligence, clear contractual terms covering quality standards and IP rights, and ongoing collaboration between designers, contractors, and suppliers throughout the procurement process.
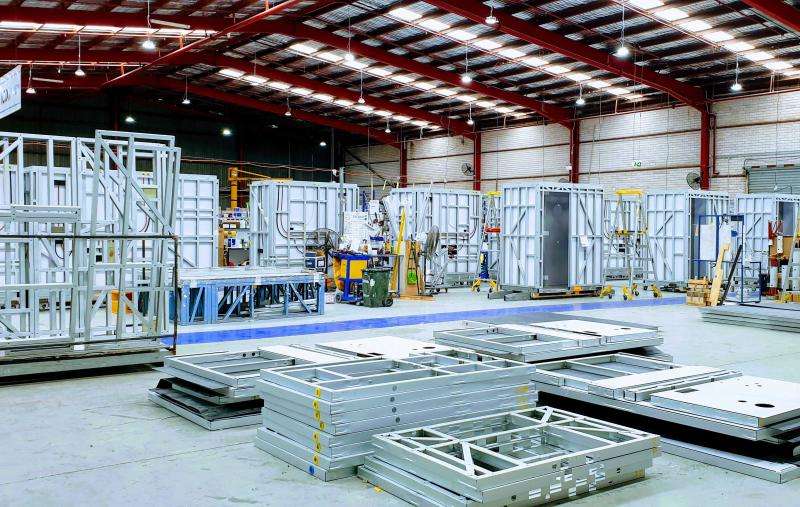

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Prefabricated Bathrooms
Overview
Prefabricated bathrooms, also known as modular or prefabs, are factory-built bathroom units that are transported to construction sites for installation. Efficient logistics and strict compliance with regulations are critical to ensure timely delivery, structural integrity, and adherence to building codes and safety standards.
Transportation Planning
- Route Assessment: Evaluate transport routes for clearances (height, width, weight), bridge restrictions, road conditions, and turn radii. Use GPS and route simulation tools.
- Load Securing: Use cradles, braces, and straps to prevent shifting or damage during transit. Ensure units are protected from weather (tarpaulins or enclosed trailers).
- Permits and Escorts: Obtain oversized load permits where required. Arrange pilot cars or police escorts for wide or heavy units.
- Delivery Timing: Coordinate with site supervisors to align delivery with crane availability and construction schedules, minimizing on-site storage.
Packaging and Handling
- Protective Packaging: Seal plumbing fixtures, drains, and openings to prevent debris entry. Apply corner guards and foam padding to vulnerable edges.
- Lifting Points: Use designated lifting points (e.g., embedded steel frames or lifting lugs) during hoisting. Never lift from plumbing or finishes.
- Stacking and Storage: Store units vertically on level ground with proper supports. Avoid stacking unless designed for it. Use breathable covers to prevent condensation.
Regulatory Compliance
- Building Codes: Ensure units comply with local and national codes (e.g., International Building Code (IBC), International Plumbing Code (IPC), ADA for accessibility).
- Fire Safety: Verify fire resistance ratings of materials and assemblies (e.g., walls, doors). Comply with fire compartmentation requirements.
- Energy Efficiency: Meet insulation and air-tightness standards (e.g., IECC). Include proper vapor barriers and thermal breaks.
- Environmental Regulations: Adhere to VOC limits for paints and adhesives (e.g., EPA, GREENGUARD). Manage waste per local environmental laws.
Certification and Documentation
- Third-Party Certification: Obtain certifications such as ICC-ES, UL, or CE (for EU) to validate compliance with safety and performance standards.
- Quality Assurance: Maintain records of factory inspections, pressure tests for plumbing, and material certifications.
- As-Built Drawings: Provide detailed installation manuals, plumbing schematics, and electrical diagrams with each unit.
On-Site Installation Compliance
- Foundation and Interface: Verify structural support and alignment at the installation point. Ensure waterproofing membranes and sealants are properly applied at joints.
- Plumbing and Electrical Connections: Use licensed professionals to connect water supply, drainage, vents, and electrical systems per code. Test for leaks and grounding.
- Inspection Readiness: Schedule municipal or third-party inspections post-installation. Provide all compliance documentation for review.
Risk Management
- Insurance: Carry cargo insurance during transit and liability insurance for on-site handling.
- Contingency Plans: Prepare for weather delays, transport damage, or non-compliance issues with backup units or repair protocols.
- Training: Ensure installers are trained in modular unit handling and safety procedures (e.g., OSHA standards).
Sustainability and Waste Management
- Recyclable Materials: Use recyclable packaging and minimize single-use plastics.
- End-of-Life Planning: Design for disassembly and material recovery where possible. Follow local regulations for disposal of damaged units.
Conclusion
Successful deployment of prefabricated bathrooms hinges on meticulous logistics planning and rigorous compliance with regulatory standards. By integrating certified manufacturing practices, secure transportation, and code-compliant installation, stakeholders can ensure safety, efficiency, and long-term performance of modular bathroom solutions.
In conclusion, sourcing prefabricated bathrooms presents a strategic advantage for construction projects seeking efficiency, cost savings, and quality control. These factory-built units offer faster installation times, reduced on-site labor, and minimized waste, contributing to sustainable building practices. With advancements in design flexibility and material quality, prefabricated bathrooms can meet diverse aesthetic and functional requirements across residential, hospitality, and healthcare sectors. However, successful sourcing requires careful consideration of suppliers, transportation logistics, integration with on-site work, and compliance with building standards. When executed with thorough planning and collaboration, sourcing prefabricated bathrooms can significantly enhance project timelines, reduce costs, and deliver consistent, high-quality results—making them a compelling solution for modern construction demands.