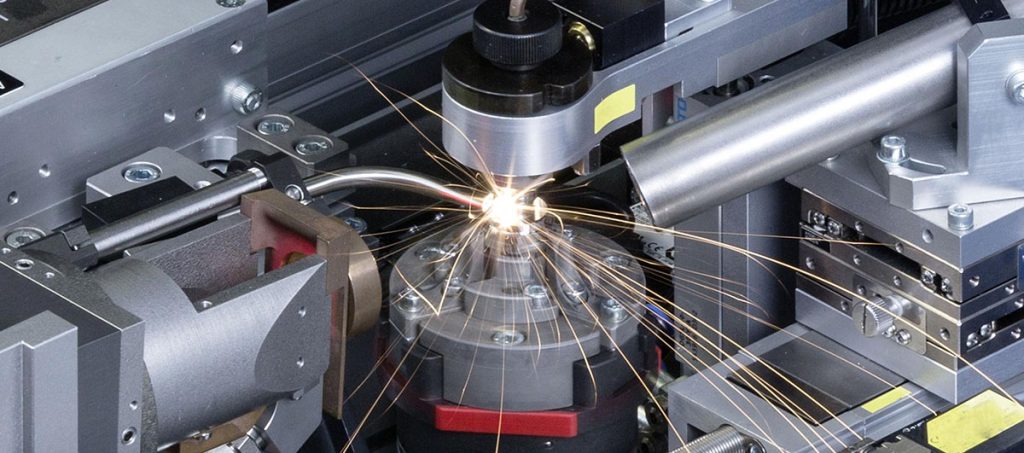
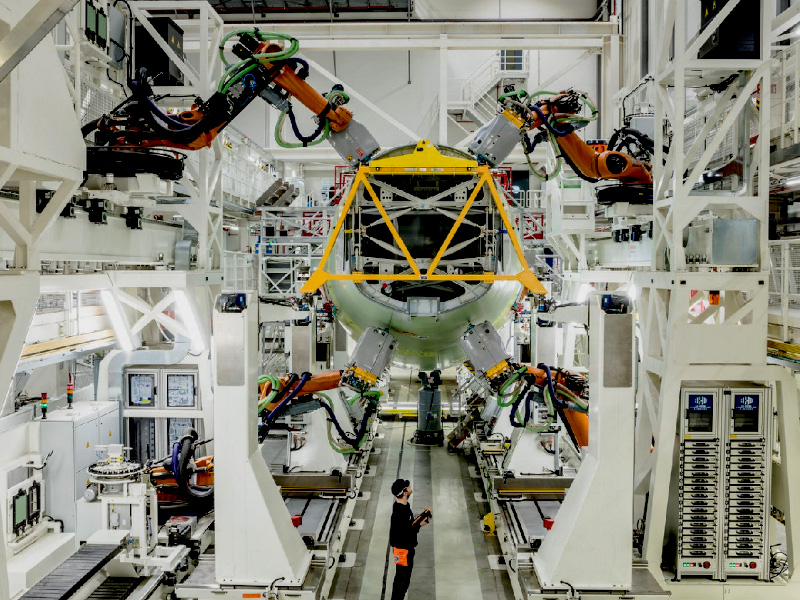
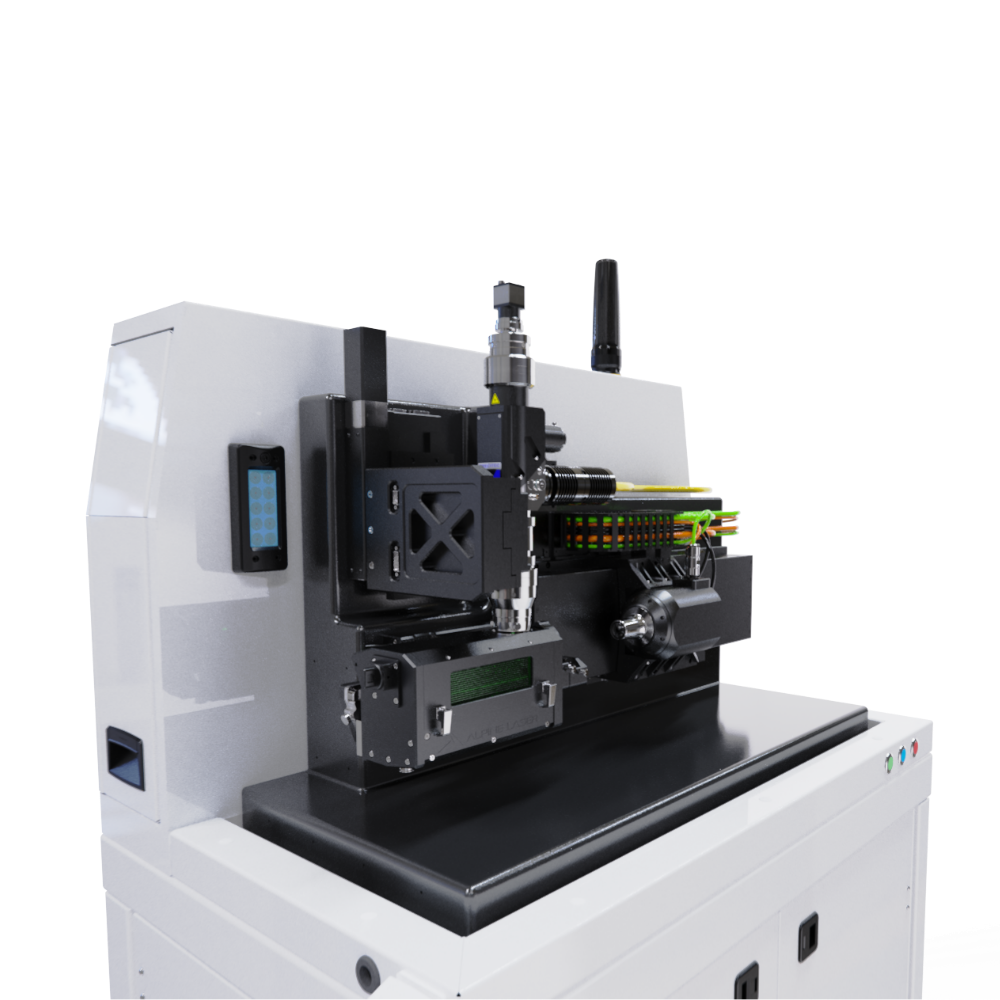
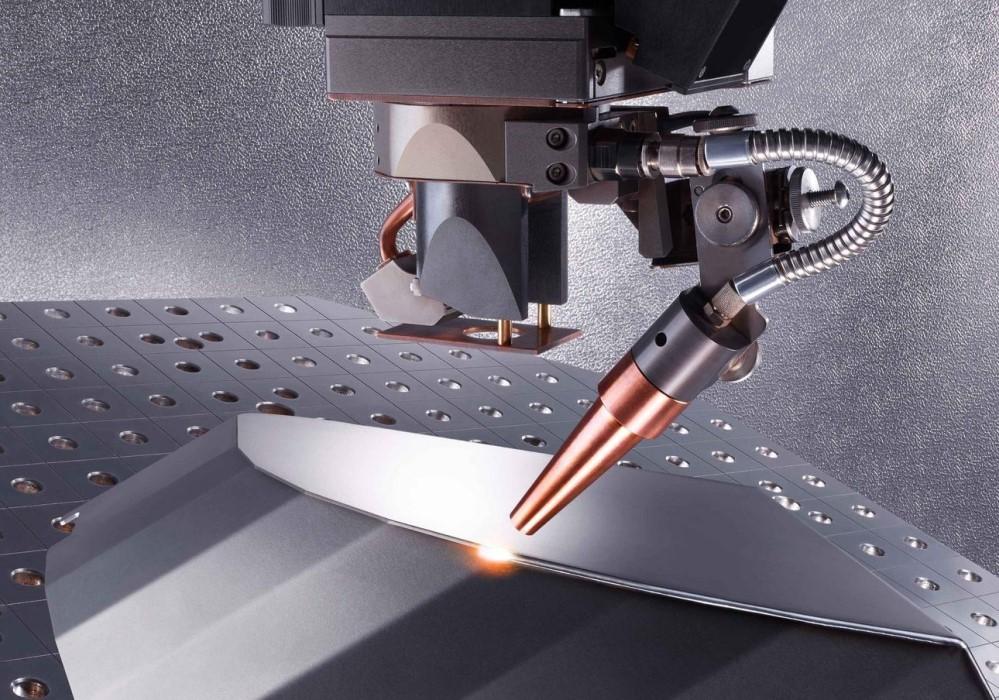
The global laser welding market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for high-precision joining technologies in industries such as automotive, medical devices, and electronics. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 2.87 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 4.74 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 8.7% during the forecast period. Similarly, Grand View Research highlights the increasing adoption of automation and advanced manufacturing techniques as key growth accelerators, with fiber laser welding emerging as the preferred solution due to its accuracy, speed, and minimal heat distortion. As manufacturers prioritize quality and efficiency, precision laser welding systems have become essential across high-tolerance applications. This growing demand has fueled innovation among leading suppliers, setting the stage for intense competition and rapid technological advancement. In this landscape, nine manufacturers stand out for their technical excellence, global reach, and proven track records in delivering cutting-edge laser welding solutions.
Top 9 Precision Laser Welding Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Precision Laser Technology
Website: precisionlasertech.com
Key Highlights: Precision Laser Technology (PLT) is a leader in laser engraving services providing OEM’s and contract manufacturers with the right expertise to enhance the ……
#2 Laser Welding Technology for Aerospace Applications
Website: precisionxmfg.com
Key Highlights: At PrecisionX, we provide advanced laser welding services for mission-critical metal components used in industries such as aerospace, defense, ……
#3 LaserStar Technologies
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
#4 Alpine Laser
Website: alpinelaser.com
Key Highlights: Alpine Laser, a Machine Solutions company, is the leader in innovative precision laser technology for medical device manufacturing. Explore advanced laser ……
#5 Equipment & Systems
Website: amadaweldtech.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer of equipment and systems for welding, cutting, marking, micromachining, sealing, and bonding. Resistance welding. Laser….
#6 Welding
Website: laserprecision.com
Key Highlights: Laser Precision’s welding techniques allow for maximum strength and a clean finish through the precise localized fusion of metals….
#7 Laser Welding
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Whether for precision or structural welding, laser welding is an easily automated solution for creating excellent quality welds rapidly and reliably. Laser ……
#8 Precision in laser processing & metrology
Website: precitec.com
Key Highlights: Precitec offers solutions for laser cutting, welding, metrology and additive manufacturing – leading in precision, quality and process reliability….
#9 Orotig: Laser Machinery
Website: orotig.com
Key Highlights: We specialise in engineering and manufacturing laser solutions for welding, engraving, casting and cutting precious and non-precious metals….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Precision Laser Welding
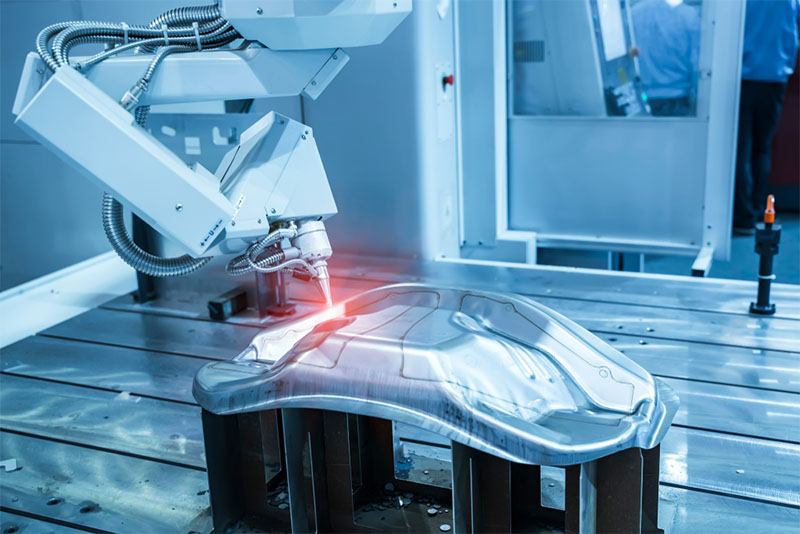

2026 Market Trends for Precision Laser Welding
The precision laser welding market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, evolving industry demands, and global manufacturing shifts. This analysis outlines the key trends shaping the landscape.
Advancements in Laser Technology Driving Performance and Accessibility
By 2026, the adoption of ultrafast (picosecond and femtosecond) and high-brightness fiber lasers will accelerate, enabling cleaner, higher-precision welds with minimal heat-affected zones. These advancements will expand applications in sensitive industries like medical devices and microelectronics. Simultaneously, cost reductions in laser diodes and improved beam delivery systems will make precision laser welding more accessible to small and medium-sized enterprises, broadening market penetration beyond traditional heavy industries.
Rising Demand from Electric Vehicles and Renewable Energy
The rapid growth of the electric vehicle (EV) sector will be a primary growth driver. Precision laser welding is critical for manufacturing battery packs, power electronics, and lightweight structural components, where reliability and thermal management are paramount. Similarly, demand will surge in renewable energy applications, particularly for welding components in solar inverters, fuel cells, and wind turbine electronics, as global decarbonization efforts intensify.
Integration with Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0
Precision laser welding systems will increasingly integrate with digital twin technology, IoT-enabled sensors, and AI-driven process monitoring. By 2026, real-time weld quality assurance, predictive maintenance, and adaptive control systems will become standard, enhancing yield rates and enabling fully traceable, closed-loop manufacturing processes. This integration will be essential for meeting stringent quality standards in aerospace, automotive, and medical sectors.
Focus on Sustainability and Material Efficiency
Growing environmental regulations and ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) priorities will push manufacturers toward energy-efficient laser systems and processes that minimize material waste. Precision laser welding, with its high energy density and localized heating, supports lightweighting strategies and reduces scrap rates—key factors in sustainable production. Recycling-friendly designs enabled by precise joining techniques will further enhance its appeal.
Regional Shifts and Supply Chain Localization
Asia-Pacific, led by China, Japan, and South Korea, will remain the dominant market due to robust electronics and automotive production. However, North America and Europe are expected to see accelerated growth due to onshoring initiatives and investments in advanced manufacturing. Geopolitical factors and supply chain resilience concerns will drive localized production, increasing demand for automated, precision welding solutions in nearshore facilities.
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Precision Laser Welding (Quality & IP)
Sourcing precision laser welding services or equipment involves critical considerations beyond simple cost and lead time. Overlooking key quality and intellectual property (IP) risks can lead to defective products, project delays, legal disputes, and compromised competitive advantage. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Verification of Process Capability and Consistency
Many suppliers claim precision welding capabilities, but lack the process controls to ensure repeatability. Relying solely on marketing materials or a single demonstration part can be misleading. Without documented process validation (e.g., Statistical Process Control data, weld consistency reports across multiple production runs), there’s a high risk of inconsistent weld quality, especially at scale. Always request and review historical quality data, conduct on-site audits, and require a formal Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (PFMEA).
Overlooking Cleanliness and Environmental Controls
Precision laser welding, especially in medical, aerospace, or semiconductor applications, demands stringent environmental conditions. A supplier operating in a non-cleanroom or with poor particulate control can introduce contamination that compromises weld integrity or leads to product failure. Ensure the supplier maintains appropriate cleanliness standards (e.g., ISO Class 7 or better) and has protocols for handling and storing components pre- and post-weld.
Insufficient Traceability and Documentation
Lack of comprehensive weld traceability—such as laser parameters, machine calibration records, operator logs, and material certifications—makes it difficult to diagnose quality issues or comply with regulatory requirements (e.g., FDA, AS9100). Without proper documentation, reproducing a successful weld or proving conformance during audits becomes nearly impossible. Insist on a documented quality management system with full data traceability for each weld or batch.
Failure to Define and Protect Intellectual Property (IP) Rights
Sharing detailed designs, proprietary materials, or unique welding procedures exposes your IP. A common pitfall is using generic contracts that don’t explicitly assign ownership of process innovations or improvements developed during the project. Ensure a robust Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) is in place before disclosure, and include clear IP clauses in the main contract stating that all pre-existing IP remains yours and defining ownership of any jointly developed IP.
Unsecured Access to Sensitive Process Parameters
Precision welding often relies on proprietary laser settings, pulse profiles, or fixturing designs. If these parameters are stored or managed on shared or supplier-owned equipment without access controls, they may be exposed or inadvertently reused for other clients. Require data encryption, restricted access to welding programs, and contractual prohibitions on using your process data for other purposes.
Absence of Change Control Procedures
Suppliers may make undocumented changes to equipment, software, or personnel without notifying the customer. Even minor adjustments can significantly affect weld quality. A lack of formal change control processes increases variability risk. Require the supplier to implement and adhere to a documented change management system that mandates notification and approval for any process or equipment modifications.
Underestimating Post-Weld Inspection and Testing Requirements
Some suppliers offer basic visual inspection but lack advanced non-destructive testing (NDT) capabilities such as X-ray, ultrasonic testing, or metallography. Relying on insufficient inspection can allow substandard welds to pass. Clearly define acceptance criteria and required inspection methods in the contract, and verify the supplier’s certification and proficiency in performing these tests.
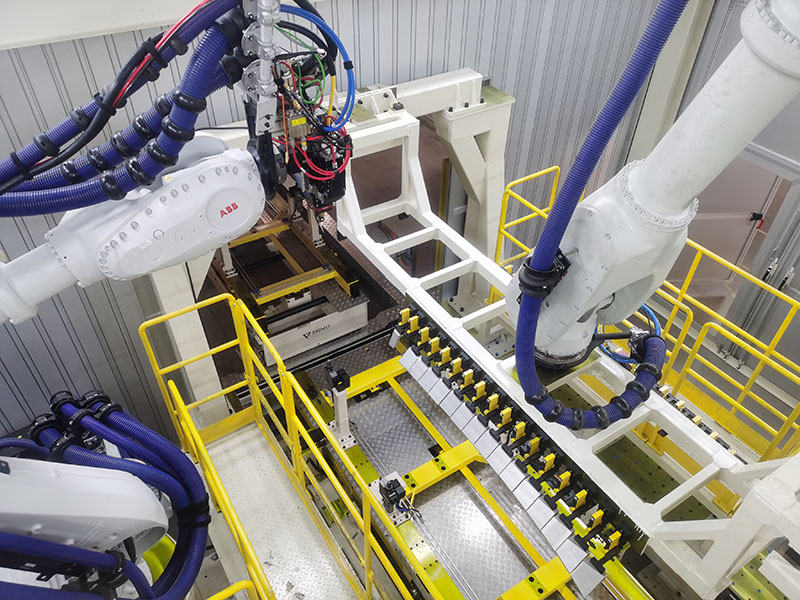

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Precision Laser Welding
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe, efficient, and legally sound operation of precision laser welding systems. Adherence ensures personnel safety, product quality, regulatory compliance, and smooth operations.
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with national and international standards is mandatory for all precision laser welding operations.
Laser Safety Standards
- Adhere to IEC 60825-1: This international standard classifies lasers and specifies safety requirements for laser products. Precision laser welding systems typically fall under Class 4, requiring strict engineering and administrative controls.
- Follow ANSI Z136.1 (US): The American National Standard for Safe Use of Lasers provides detailed guidelines on hazard evaluation, control measures, and training for laser operations.
- Implement Laser Safety Officer (LSO) Program: Appoint a qualified LSO responsible for overseeing laser safety, conducting risk assessments, and ensuring compliance with all safety protocols.
Workplace Health and Safety
- Comply with OSHA (US) or Local Equivalent Regulations: Ensure general workplace safety standards are met, including machine guarding, lockout/tagout (LOTO), and hazard communication.
- Control of Hazardous Substances (COSHH/OSHA Hazard Communication): Assess and manage fumes and particulates generated during laser welding. Implement local exhaust ventilation (LEV) and provide appropriate respiratory protection when necessary.
- Electrical Safety: Follow NFPA 70 (NEC) or equivalent standards for installation and maintenance of high-power laser equipment.
Environmental Regulations
- Waste Management: Properly dispose of consumables (e.g., lenses, nozzles), contaminated filters, and metal waste in accordance with EPA or local environmental regulations.
- Emissions Control: Ensure fume extraction systems meet air quality standards and are regularly maintained and tested.
Equipment Handling and Installation
Proper logistics during equipment setup are vital for performance and safety.
Shipping and Receiving
- Verify all components (laser source, welding head, motion system, chiller, safety enclosures) are received undamaged.
- Use certified rigging equipment and trained personnel for unloading; precision laser systems are sensitive to shock and misalignment.
Site Preparation
- Ensure adequate floor space with proper load-bearing capacity.
- Provide stable power supply with correct voltage, phase, and grounding. Install power conditioners if necessary.
- Guarantee sufficient cooling capacity (chiller requirements) and compressed air supply (clean, dry air).
- Prepare exhaust ducting for fume extraction systems.
Installation and Commissioning
- Installation must be performed by manufacturer-certified technicians.
- Conduct beam alignment, calibration, and safety interlock verification during commissioning.
- Document all installation and calibration procedures for compliance audits.
Operational Logistics
Efficient daily operations depend on structured processes and resource management.
Material Flow and Workcell Design
- Design workflow to minimize part handling and optimize throughput.
- Use automated loading/unloading systems (e.g., robots, conveyors) where justified by production volume.
- Implement 5S principles for tool and material organization to reduce errors and downtime.
Consumables and Spare Parts Management
- Maintain inventory of critical consumables: protective windows, focusing lenses, nozzles, and shielding gas.
- Track usage and establish reorder points to prevent production delays.
- Store sensitive optical components in clean, dry, temperature-controlled environments.
Maintenance and Calibration Scheduling
- Follow manufacturer-recommended preventive maintenance (PM) schedules.
- Log all maintenance activities, including lens cleaning, alignment checks, and calibration.
- Recalibrate measurement systems (e.g., seam tracking, vision systems) regularly to ensure weld precision.
Quality Assurance and Documentation
Traceability and documentation are essential for compliance with industry quality standards.
Process Validation
- Perform qualification testing (e.g., tensile, metallurgical analysis) for new weld procedures.
- Establish and document Welding Procedure Specifications (WPS) and Procedure Qualification Records (PQR).
Inspection and Traceability
- Implement in-process monitoring (e.g., photodiode sensors, plasma monitoring) to detect anomalies.
- Conduct post-weld inspection using non-destructive testing (NDT) methods such as X-ray, ultrasound, or dye penetrant as required.
- Maintain traceability of parts, materials, and weld parameters (e.g., laser power, pulse duration, travel speed).
Record Keeping
- Archive all compliance-related documents: safety certifications, maintenance logs, calibration records, and operator training records.
- Retain quality records (inspection reports, NDT results) for the required duration per internal or customer specifications (e.g., ISO 9001, AS9100).
Personnel Training and Certification
Qualified personnel are critical for safe and compliant operations.
Operator Training
- Provide comprehensive training on machine operation, emergency procedures, and safety protocols.
- Include hands-on practice and written/oral assessments before granting operational authorization.
Safety and Emergency Procedures
- Train all personnel on laser hazard recognition, emergency shutdown, and evacuation procedures.
- Conduct regular drills for fire, fume exposure, and laser incidents.
Certification and Competency
- Require operators and technicians to be certified per internal standards or industry requirements.
- Re-certify personnel periodically or after significant equipment changes.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and strict compliance are foundational to successful precision laser welding. By following this guide—covering regulatory standards, equipment handling, operational procedures, quality assurance, and personnel training—organizations can ensure safe, repeatable, and high-quality welding processes that meet all legal and customer requirements. Regular audits and continuous improvement are recommended to maintain compliance and operational excellence.
Conclusion: Sourcing Precision Laser Welding
Sourcing precision laser welding services or equipment requires careful consideration of technical expertise, quality standards, and long-term reliability. As industries such as medical devices, aerospace, automotive, and electronics continue to demand tighter tolerances, minimal heat-affected zones, and repeatable high-quality welds, the importance of selecting the right laser welding partner becomes critical. Key factors in successful sourcing include evaluating the provider’s technological capabilities—such as fiber or pulsed laser systems—certifications (e.g., ISO standards), experience in relevant applications, and their ability to support automation and process validation.
Additionally, total cost of ownership, service and support, and scalability should be weighed alongside upfront pricing. A strategic sourcing approach not only ensures superior weld quality and process efficiency but also contributes to improved product performance and reduced manufacturing defects. Ultimately, partnering with a qualified and technologically advanced laser welding provider enables organizations to maintain a competitive edge through innovation, precision, and reliability in their production processes.