The global paper and packaging market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for sustainable and recyclable materials across industries such as food and beverage, healthcare, and e-commerce. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global paper market was valued at USD 375.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 3.2% from 2024 to 2029. Polypropylene (PP) paper, known for its durability, moisture resistance, and print quality, has emerged as a preferred alternative to traditional fiber-based papers in specialty applications. This growth is further supported by innovations in synthetic and laminated PP paper, particularly in labeling, packaging, and outdoor graphics. As demand surges, manufacturers are scaling production and investing in sustainable practices to meet evolving regulatory and consumer expectations. Below are the top nine PP paper manufacturers leading this transformation through technological advancement, global reach, and product innovation.
Top 9 Pp Paper Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Polypropylene Film Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1996
Website: profol.com
Key Highlights: Profol specializes in cast polypropylene film because it is a cost-effective, flexible, durable, and versatile choice for thermoplastic materials….
#2 PP Lite
Domain Est. 1998
Website: paperone.com
Key Highlights: PP Lite is a high-quality and reliable copy paper designed for day-to-day use. The PCC pigment technology improves smoothness, thickness and opacity….
#3 Polyester, Polypropylene Film Manufacturers, Polyplex
Domain Est. 2000
Website: polyplex.com
Key Highlights: ABOUT US. One of the leading PET Film Manufacturers. Polyplex Corporation Ltd. (Polyplex) has the seventh-largest capacity of polyester (PET) film globally….
#4 Lincon Polymers
Domain Est. 2004
Website: linconpolymers.com
Key Highlights: Lincon Polymers is a leading PP woven bags manufacturers and exporters worldwide. The woven polypropylene we offer are suitable for all kinds of packaging ……
#5 PP Woven Fabric Roll Manufacturer and Supplier In the US
Domain Est. 2007
Website: anitaplastics.com
Key Highlights: Anita Plastics sets the standard in PP/HDPE woven fabric manufacturing through a unique blend of quality, customization, and customer focus….
#6 Polypropylene Material Solutions
Domain Est. 1996
Website: oq.com
Key Highlights: Our polyprolypene material is low weight, versatile, cost effective and used widely across different areas and applications. Learn about OQ PP solutions ……
#7 The Application Specific Synthetic Paper
Domain Est. 2007
Website: hopsyn.com
Key Highlights: Hop-Syn® G1 is a white, opaque, tear-resistant synthetic paper made from a unique mixture of calcium carbonate and polypropylene resin….
#8 Paperline Global
Website: app.co.id
Key Highlights: Paperline Global Product by Paperline. MultiPurpose Copy Paper For All Needs. Specifications: 70 GSM Specification, 75 GSM Specification, 80 GSM….
#9 Materials
Website: renner-print.at
Key Highlights: We print on all desired and available materials. From the most modern circular PP to wet-strength paper, the right material is available for all requirements….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Pp Paper
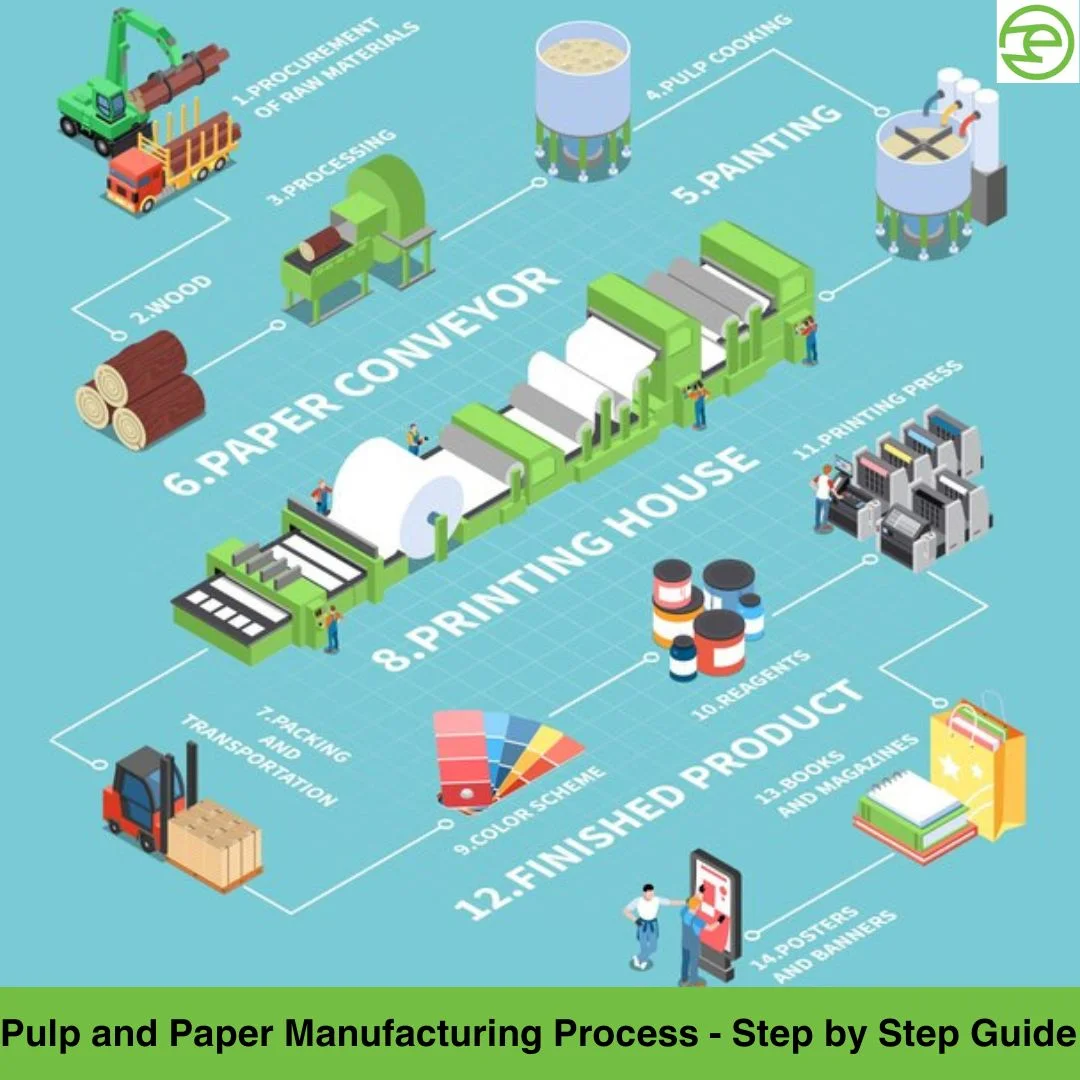
H2: 2026 Market Trends for PP (Polypropylene) Paper
The global market for polypropylene (PP) paper is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by shifting consumer demands, regulatory changes, and technological advancements. As sustainability becomes a central focus across industries, PP paper—known for its durability, water resistance, and recyclability—is emerging as a preferred alternative to traditional paper and plastic materials.
-
Growing Demand for Sustainable Packaging
By 2026, the shift toward eco-friendly packaging solutions will continue to accelerate. PP paper, which is recyclable and often used in place of laminated or plastic-coated papers, aligns with global sustainability goals. Industries such as food & beverage, cosmetics, and e-commerce are increasingly adopting PP synthetic paper for labels, pouches, and flexible packaging due to its lower environmental footprint compared to conventional plastics. -
Regulatory Support and Plastic Substitution Initiatives
Governments worldwide are implementing stricter regulations on single-use plastics. The European Union’s Single-Use Plastics Directive and similar policies in Asia-Pacific and North America are pushing manufacturers to seek compliant materials. PP paper benefits from being a viable substitute in applications where moisture resistance and printability are essential, such as in outdoor signage and hygiene product wrappers. -
Technological Advancements in Production
Innovations in biaxially oriented polypropylene (BOPP) film processing are enhancing the performance and cost-efficiency of PP paper. By 2026, improved manufacturing techniques are expected to reduce energy consumption during production and expand the range of textures and finishes available, making PP paper more competitive with traditional paper and other synthetic substrates. -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Rapid industrialization and urbanization in countries like India, Vietnam, and Brazil are fueling demand for durable and versatile packaging materials. The rise of organized retail and e-commerce in these regions is further boosting the adoption of PP paper for product labeling and protective wrapping, creating new growth avenues for suppliers. -
Increased Investment in Recycling Infrastructure
A key challenge for PP paper has been limited recycling infrastructure in certain regions. However, by 2026, investments in closed-loop recycling systems and partnerships between material producers and waste management firms are expected to improve recovery rates. Enhanced recyclability will strengthen the circular economy appeal of PP paper, encouraging brand owners to specify it in their packaging designs. -
Competition and Price Volatility
While demand grows, the PP paper market may face headwinds from fluctuating raw material prices, particularly propylene, which is derived from oil and natural gas. Companies are likely to adopt hedging strategies and invest in bio-based polypropylene research to mitigate cost volatility and enhance sustainability credentials.
In conclusion, the 2026 outlook for PP paper is optimistic, marked by strong demand across packaging and labeling sectors, supported by environmental regulations and innovation. Stakeholders who prioritize sustainability, invest in R&D, and expand into high-growth regions are likely to gain a competitive edge in this evolving market landscape.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing PP Paper (Quality, IP)
Sourcing polypropylene (PP) paper—often used in packaging, labels, and specialty printing—can present significant challenges, particularly concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these pitfalls helps ensure reliable supply and protects your business from legal and reputational damage.
Quality Inconsistencies
One of the most frequent issues in sourcing PP paper is variability in material quality, which can directly impact product performance and end-user satisfaction.
- Inconsistent Thickness and Tensile Strength: Suppliers, especially those in emerging markets, may lack stringent process controls, resulting in batch-to-batch variations. This inconsistency can lead to printing defects, lamination failures, or packaging malfunctions.
- Poor Surface Coating and Print Adhesion: PP paper often requires specific surface treatments (e.g., corona treatment) for ink adhesion. Inadequate or inconsistent treatment can result in smudging, peeling, or poor print quality.
- Contamination and Impurities: Recycled or low-grade PP resins may introduce contaminants, affecting clarity, strength, and suitability for food-grade or medical applications.
- Thermal and UV Stability Issues: Lower-quality PP paper may degrade under heat or UV exposure, leading to brittleness or discoloration—especially problematic for outdoor or high-temperature applications.
Best Practice: Require third-party certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), conduct regular audits, and perform incoming quality inspections with standardized testing protocols.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Sourcing PP paper, particularly from regions with weak IP enforcement, exposes companies to significant legal and operational risks.
- Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Materials: Some suppliers may replicate proprietary PP paper formulations or branded products without authorization, infringing on patents or trade secrets.
- Unauthorized Use of Patented Technologies: Certain PP paper manufacturing processes (e.g., biaxial orientation, coating technologies) are protected by patents. Sourcing from suppliers using these methods without licensing can implicate your company in IP violations.
- Lack of Transparency in Supply Chain: Opaque sourcing networks may hide IP-infringing practices, making it difficult to ensure downstream compliance, especially under regulations like the U.S. Section 337 or EU IP enforcement directives.
- Risk of Seizures and Legal Action: Importing materials that infringe IP rights can lead to customs seizures, product recalls, or lawsuits, resulting in financial loss and reputational harm.
Best Practice: Conduct due diligence on suppliers’ IP compliance, request documentation on material origin and process legitimacy, and include IP warranties in procurement contracts.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, businesses can mitigate risks, ensure product reliability, and safeguard innovation when sourcing PP paper.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for PP (Polypropylene) Paper
Overview of PP Paper
PP paper, also known as synthetic paper, is a durable, water-resistant material made from polypropylene resin. Unlike traditional wood pulp paper, PP paper is a plastic film engineered to mimic the look and printability of paper while offering enhanced strength, moisture resistance, and longevity. It is widely used in packaging, labeling, outdoor signage, and industrial applications.
Transportation and Handling
- Temperature Sensitivity: PP paper rolls or sheets should be stored and transported within a temperature range of 10°C to 35°C (50°F to 95°F). Exposure to extreme heat may cause warping or deformation; cold temperatures can make the material brittle.
- Moisture Resistance: One of PP paper’s advantages is its resistance to water and humidity. However, condensation during transit should be avoided to prevent surface contamination or ink smudging in printed rolls.
- Protection from Physical Damage: Use edge protectors and pallet wrapping to prevent scratches, dents, and core crushing during shipping. Store rolls vertically to avoid deformation.
- Stacking Guidelines: Do not stack heavy items on top of PP paper sheets or rolls. Limit stack height to manufacturer recommendations to prevent compression damage.
Storage Requirements
- Indoor Storage: Always store PP paper indoors in a clean, dry, and well-ventilated area.
- UV Exposure: Limit exposure to direct sunlight or strong UV sources, which can cause yellowing or degradation over time. Use UV-protective films or opaque covers if long-term outdoor storage is unavoidable.
- Shelf Life: Properly stored PP paper typically has a shelf life of 12–24 months. Check manufacturer specifications for exact duration.
- Compatibility: Keep PP paper separate from solvents, oils, and aggressive chemicals that may cause surface reactions or degradation.
Regulatory Compliance
- REACH (EU): Confirm that the PP paper and any additives (e.g., pigments, stabilizers) comply with REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) regulations. Suppliers must provide a Safety Data Sheet (SDS) upon request.
- RoHS Compliance (EU and Global): Ensure PP paper used in electrical or electronic applications meets RoHS directives, particularly restrictions on lead, cadmium, mercury, and certain flame retardants.
- FDA Compliance (USA): For food packaging applications, verify that the PP paper complies with FDA Title 21 CFR for indirect food contact materials. Only food-grade PP paper should be used in such contexts.
- REACH SVHC: Check for Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC). Suppliers should declare if any SVHCs are present above 0.1% weight by weight.
Environmental and Recycling Considerations
- Recyclability: PP paper is recyclable under resin identification code #5 (PP). However, recycling infrastructure varies by region. Confirm local capabilities before designating as recyclable.
- Labeling: Clearly label PP paper products with the recycling code #5 and appropriate disposal instructions.
- Waste Management: Follow local waste disposal regulations. Incineration should only occur in facilities equipped to handle polyolefins with proper emission controls.
- Sustainability Claims: Avoid unsubstantiated claims like “biodegradable” or “compostable” unless certified by recognized standards (e.g., ASTM D6400). Standard PP paper is not biodegradable.
Import and Export Regulations
- Customs Documentation: Provide accurate Harmonized System (HS) codes. PP paper typically falls under HS code 3921.12 or 3921.90, depending on form and composition.
- Country-Specific Restrictions: Some countries restrict the import of non-biodegradable plastics. Verify regulations in destination markets (e.g., single-use plastic bans in certain regions).
- Phytosanitary and Packaging Requirements: While PP paper is not organic, international shipments may still require ISPM 15-compliant wooden pallets if used in transport.
Safety and Handling Precautions
- Cutting and Processing: Use appropriate machinery guards and personal protective equipment (PPE) when slitting or cutting PP paper, as sharp edges or static buildup may pose risks.
- Static Electricity: PP paper can generate static. Use ionizers or anti-static agents in printing and converting environments to prevent dust attraction or electrical hazards.
- Ventilation: During high-heat processing (e.g., lamination), ensure adequate ventilation to avoid inhalation of fumes.
Supplier and Certification Requirements
- Material Certification: Require suppliers to provide certificates of compliance (CoC) for REACH, RoHS, and FDA (if applicable).
- Quality Assurance: Insist on batch-specific test reports for thickness, tensile strength, and optical properties.
- Traceability: Ensure full supply chain traceability, especially for regulated industries like food and medical packaging.
Summary
Proper logistics and compliance management for PP paper ensures product integrity, regulatory adherence, and environmental responsibility. From transportation and storage to international regulations and end-of-life handling, stakeholders must follow best practices tailored to PP’s synthetic nature. Always consult technical data sheets and regulatory experts when in doubt.
Conclusion for Sourcing PP (Polypropylene) Paper:
Sourcing polypropylene (PP) paper requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, sustainability, and supply chain reliability. As a durable, water-resistant, and recyclable synthetic paper alternative, PP paper is increasingly favored across packaging, labeling, and printing industries. However, selecting the right supplier involves evaluating key factors such as material specifications, certifications (e.g., FDA, REACH, or environmental standards), production capacity, and geographic proximity to minimize lead times and logistics costs.
Moreover, with growing environmental concerns, prioritizing suppliers that use recycled content or offer recyclable end-of-life solutions can enhance brand sustainability and meet regulatory demands. Building long-term relationships with reliable suppliers, conducting rigorous quality audits, and staying informed about innovations in PP paper technology will ensure a resilient and responsible sourcing strategy. Ultimately, effective sourcing of PP paper supports not only operational efficiency but also environmental stewardship and market competitiveness.