The global power supply unit (PSU) market, valued at approximately USD 51.9 billion in 2023, is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% through 2030, driven by rising demand for energy-efficient electronics, expanding data center infrastructure, and advancements in industrial automation, according to Grand View Research. As voltage regulation becomes increasingly critical across consumer electronics, telecommunications, and renewable energy systems, manufacturers specializing in precision power supply solutions are gaining strategic importance. This growth is further amplified by the proliferation of high-performance computing and the adoption of compact, reliable power modules in electric vehicles and IoT devices. With such robust market momentum, identifying the leading PSU voltage manufacturers—companies that combine innovation, efficiency, and scalability—offers valuable insight for OEMs, system integrators, and procurement leaders navigating an evolving power landscape.
Top 10 Power Supply Unit Voltage Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 MEAN WELL Switching Power Supply Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1997
Website: meanwell.com
Key Highlights: MEAN WELL is one of the world’s few standard power supply mainly professional manufacturers, covering 0.5 to 25600W products are widely used in industrial ……
#2 TDK
Domain Est. 1996
Website: us.lambda.tdk.com
Key Highlights: Browse our wide range of AC-DC, DC-DC, Programmable and High Voltage power supplies, DIN rails and EMI filters, as well as Value Add solutions….
#3 Wall Industries
Domain Est. 1998
Website: wallindustries.com
Key Highlights: Wall Industries manufactures and markets a full line of DC DC converters and AC DC power supplies. Browse our standard and customized power solutions ……
#4 XP Power
Domain Est. 2000
Website: xppower.com
Key Highlights: Looking for the leading manufacturer of AC-DC power supplies, DC-DC converters, high voltage, RF & custom power products? Discover our extensive range….
#5 Vicor Corporation
Domain Est. 2001
Website: vicorpower.com
Key Highlights: A better way to deliver power: Vicor is a leading, global power technology company, focused on advancing power delivery with modular power components….
#6 Acopian Power Supplies
Domain Est. 1996
Website: acopian.com
Key Highlights: Millions of Reliable Power Supplies. Acopian can design, build and ship the power supply that meets your needs. The possibilities are endless….
#7 Basler Electric
Domain Est. 1996
Website: basler.com
Key Highlights: Discover Basler Electric’s innovative power solutions, now amplified by Littelfuse. Explore our products and industry-leading energy technologies….
#8 Power supplies
Domain Est. 1996
Website: phoenixcontact.com
Key Highlights: Find the perfect power supply for your application, whether for the DIN rail, suitable for panel mounting, or in 19′′ format for rack mounting….
#9 High Voltage Power Supply (HVPS)
Domain Est. 1999
Website: iseg-hv.com
Key Highlights: The iseg company group specialises in the development and production of High Voltage Power Supplies for Industry and Research. Our business goal is to provide ……
#10 AMETEK Programmable Power
Domain Est. 2007
Website: programmablepower.com
Key Highlights: The AMETEK Programmable Power designs, manufactures, and markets precision, ac & dc programmable power supplies, electronic loads, application-specific ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Power Supply Unit Voltage
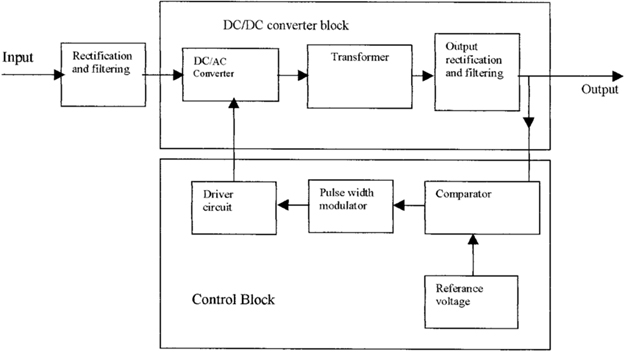
2026 Market Trends for Power Supply Unit Voltage
As technological advancements continue to shape the electronics and computing industries, the Power Supply Unit (PSU) market is undergoing significant transformation, particularly in the realm of voltage standards and efficiency. By 2026, several key trends are expected to define the evolution of PSU voltage design, driven by demands for energy efficiency, sustainability, and compatibility with next-generation hardware.
Rising Demand for Higher Efficiency and Lower Voltages
One of the most prominent trends shaping the 2026 PSU voltage landscape is the increasing demand for lower output voltages combined with higher efficiency. Modern processors, GPUs, and AI accelerators are operating at lower core voltages—often below 1.0V—to manage heat and power consumption. This shift necessitates PSUs capable of delivering ultra-stable, low-voltage power with minimal ripple and noise.
To meet these needs, PSU manufacturers are integrating advanced voltage regulation modules (VRMs) and multi-phase DC-DC conversion directly into or near the load (point-of-load regulation). This allows for tighter voltage control and reduced energy loss in power delivery, particularly in high-performance computing (HPC) and data center environments.
12V-Powered Ecosystem Dominance
The 12V rail will remain the cornerstone of PSU design in 2026, especially as consumer and enterprise systems grow more power-hungry. Graphics cards and CPUs continue to draw the majority of their power from the 12V line, and new standards like PCIe 5.0 and the ATX12VO (12V-only) specification are accelerating this trend.
The ATX12VO standard, which eliminates the traditional 3.3V and 5V rails from the PSU and instead generates them on the motherboard, is expected to gain broader adoption by 2026. This shift improves overall efficiency by reducing conversion losses and allows for better thermal management in compact systems. OEMs, particularly in the small form factor (SFF) and ultra-thin desktop markets, are likely to adopt ATX12VO PSUs to meet energy regulations and consumer demand for quieter, cooler-running systems.
Adoption of GaN and SiC Semiconductors for Voltage Conversion
Gallium Nitride (GaN) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) technologies are enabling next-generation PSUs with higher switching frequencies, reduced size, and improved voltage conversion efficiency. By 2026, these wide-bandgap semiconductors are expected to be more widely used in mid-to-high-end PSUs, particularly in applications requiring precise voltage regulation and compact designs—such as gaming consoles, workstations, and edge computing devices.
These materials allow PSUs to operate efficiently across a broader range of input voltages and deliver cleaner output, supporting dynamic voltage scaling for adaptive power management in CPUs and GPUs.
Smart PSUs with Adaptive Voltage Management
Intelligent power supply units featuring digital monitoring and adaptive voltage control are anticipated to become mainstream by 2026. Leveraging PMBus (Power Management Bus) and digital signal controllers (DSCs), these “smart PSUs” can dynamically adjust output voltages based on system load, improving energy efficiency and extending hardware lifespan.
This trend aligns with the broader push toward predictive maintenance and energy-aware computing in enterprise and data center environments. Real-time voltage telemetry enables system administrators to detect anomalies, optimize power usage effectiveness (PUE), and prevent overvoltage or undervoltage conditions that could damage sensitive components.
Sustainability and Regulatory Drivers
Global energy regulations, such as the EU’s Ecodesign Directive and the U.S. ENERGY STAR program, are pushing PSU manufacturers to achieve higher efficiency at various load levels—especially at light and partial loads where voltage stability is critical. By 2026, compliance with Tier 3 or potential future iterations of the 80 PLUS certification will likely require PSUs to maintain tight voltage regulation (±1–2%) across a wider operating range.
These regulations indirectly influence voltage design by encouraging innovations in soft-switching topologies, resonant converters, and active power factor correction (PFC), all of which contribute to more stable and efficient voltage delivery.
Conclusion
The 2026 market for Power Supply Unit voltage technologies will be defined by a convergence of efficiency, miniaturization, and intelligence. The dominance of the 12V rail, adoption of ATX12VO, integration of GaN/SiC components, and rise of smart voltage management systems will collectively redefine how power is delivered and regulated in electronic devices. As computing demands grow and sustainability becomes paramount, PSU voltage design will play a crucial role in enabling the next wave of high-performance, energy-conscious technology.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Power Supply Unit Voltage (Quality and IP Protection)
Sourcing the right power supply unit (PSU) involves more than just matching voltage and wattage. Overlooking quality and Ingress Protection (IP) ratings can lead to system failures, safety hazards, and reduced lifespan. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Prioritizing Cost Over Quality
One of the most frequent mistakes is selecting the cheapest PSU available. Low-cost units often use inferior components—such as poor-quality capacitors, undersized transformers, and inadequate filtering—which can result in unstable voltage output, increased electrical noise, and premature failure. These issues not only degrade performance but may also damage connected equipment.
2. Ignoring Voltage Regulation and Ripple
A high-quality PSU maintains stable output voltage under varying loads. Poor regulation can lead to voltage spikes or drops, harming sensitive electronics. Additionally, excessive ripple (AC noise on the DC output) can interfere with device operation. Always verify that the PSU meets industry standards (e.g., ±3% voltage regulation, low ripple <1%) and includes specifications in the datasheet.
3. Overlooking Efficiency Ratings
Efficiency impacts heat generation, energy consumption, and reliability. Units with no or low efficiency ratings (e.g., below 80 Plus Bronze) waste more energy as heat, increasing cooling requirements and reducing component lifespan. High-efficiency PSUs also typically incorporate better design and materials, contributing to overall quality.
4. Misunderstanding or Ignoring IP Ratings
The IP (Ingress Protection) rating defines a PSU’s resistance to dust and moisture. Selecting a unit with an insufficient IP rating for the operating environment—such as using an IP20 unit in a dusty or humid industrial setting—can lead to internal contamination, short circuits, or corrosion. Always match the IP rating to the environment (e.g., IP65 for outdoor or washdown areas).
5. Assuming All PSUs Are Interchangeable
Even with the same nominal voltage, output tolerances, transient response, and protection features (over-voltage, over-current, short-circuit) can vary significantly between manufacturers. Substituting a PSU without verifying compatibility may compromise system stability or void equipment warranties.
6. Neglecting Certifications and Safety Standards
Reputable PSUs carry certifications like UL, CE, TÜV, or CCC, indicating compliance with safety and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards. Sourcing uncertified units increases the risk of fire, electric shock, and interference with other devices. Always verify relevant certifications for your region and application.
7. Failing to Consider Thermal Management
Poor thermal design in low-quality PSUs can lead to overheating, especially in enclosed or high-ambient-temperature environments. Check for adequate heat dissipation methods (e.g., heatsinks, cooling fans) and ensure the PSU’s operating temperature range matches the deployment environment.
8. Overlooking Long-Term Availability and Support
Some low-cost or generic PSUs are discontinued quickly, making replacements difficult. This is critical in industrial or medical applications where long-term maintenance is essential. Choose suppliers with proven track records and product longevity.
By carefully evaluating both electrical performance (voltage quality) and environmental resilience (IP rating), you can avoid these common sourcing pitfalls and ensure reliable, safe, and durable power delivery.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Power Supply Unit Voltage
Overview
Power Supply Units (PSUs) are critical components in electronic devices, converting incoming electrical power into usable voltage and current for internal components. Ensuring proper logistics handling and regulatory compliance for PSUs—particularly regarding voltage specifications—is essential for safety, performance, and legal adherence across global markets.
Voltage Specifications and Regional Compliance
Different regions operate on varying mains voltage standards (e.g., 100–127V in North America and Japan, 220–240V in Europe, Asia, and Africa). PSUs must be compatible with these standards to prevent equipment damage, ensure user safety, and meet regulatory requirements.
Key Regional Voltage Standards
- North America: 120V AC, 60 Hz
- Europe (EU/UK): 230V AC, 50 Hz
- Australia/New Zealand: 230V AC, 50 Hz
- Japan: 100V AC, 50/60 Hz (depending on region)
- China: 220V AC, 50 Hz
PSUs sold internationally should either be auto-switching (able to handle 100–240V) or clearly labeled for region-specific use.
International Regulatory Compliance
PSUs must comply with regional safety and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) regulations. Voltage compatibility is a central component of these requirements.
Key Certifications
-
UL (Underwriters Laboratories) – USA/Canada
Ensures safety for 120V systems; UL 60950-1 or UL 62368-1 for IT equipment. -
CE Marking – European Union
Requires compliance with Low Voltage Directive (LVD) and EMC Directive. PSUs must support 230V ±10% and operate safely within EU grid standards. -
UKCA Marking – United Kingdom
Post-Brexit equivalent to CE; applies to 230V systems. -
PSE Mark – Japan
Mandatory for electrical products; includes voltage tolerance testing for 100V systems. -
CCC (China Compulsory Certification) – China
Applies to PSUs operating at 220V; includes safety and EMC testing. -
KC Mark – South Korea
Required for 220V systems; covers electrical safety and EMC.
Logistics Considerations
Proper logistics planning ensures PSUs reach their destination without damage and remain compliant with local regulations.
Packaging and Labeling
- Clearly label PSUs with input voltage range (e.g., “Input: 100–240V AC, 50/60 Hz”)
- Include region-specific warnings (e.g., “For use in 120V regions only” if not auto-ranging)
- Use multilingual labels where applicable
- Include certification marks (UL, CE, PSE, etc.) on packaging and product
Storage and Handling
- Store in dry, temperature-controlled environments to prevent component degradation
- Avoid exposure to voltage spikes during transit (e.g., use shielded containers if necessary)
- Segregate region-specific PSUs to prevent misshipping
Shipping and Distribution
- Verify destination country’s voltage standards before shipment
- Partner with customs brokers familiar with electrical product regulations
- Prepare technical documentation (test reports, certificates of conformity) for customs clearance
- Use carriers experienced in handling sensitive electronic components
Testing and Quality Assurance
Ensure all PSUs undergo rigorous testing for voltage tolerance and safety:
- Input Voltage Range Testing: Verify operation across full range (e.g., 90–264V) for universal models
- Surge and Overvoltage Testing: Simulate grid fluctuations to ensure resilience
- Efficiency Testing: Confirm compliance with standards like 80 PLUS (energy efficiency)
- Safety Testing: Dielectric strength, insulation resistance, and ground continuity checks
Best Practices
- Use Auto-Ranging PSUs whenever possible to simplify logistics and global distribution.
- Maintain Compliance Documentation for each market, including test reports and certificates.
- Train Logistics Teams on electrical product handling and regional requirements.
- Conduct Regular Audits of supplier compliance and certification validity.
- Monitor Regulatory Updates (e.g., new EU directives, changes to safety standards).
Conclusion
Managing logistics and compliance for PSU voltage requires a thorough understanding of regional electrical standards, certification requirements, and supply chain best practices. By ensuring voltage compatibility and maintaining up-to-date certifications, businesses can mitigate risk, avoid customs delays, and deliver safe, reliable products worldwide.
In conclusion, sourcing a power supply unit (PSU) with the correct voltage output is critical to ensuring the safe, efficient, and reliable operation of electronic devices and systems. Matching the PSU’s voltage to the requirements of the load prevents damage, performance issues, and potential safety hazards such as overheating or component failure. It is essential to consider not only the nominal voltage but also voltage tolerance, stability under load, and compatibility with input power sources. Additionally, selecting a PSU from a reputable manufacturer, verifying certifications, and accounting for future scalability and environmental conditions further contribute to a successful integration. Ultimately, careful evaluation and proper selection of the voltage specifications in a power supply unit are fundamental steps in building robust and dependable electronic systems.