The global power receptacle market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising infrastructure development, increasing demand for electrical safety, and growing adoption of industrial and commercial power distribution systems. According to Grand View Research, the global electrical connectors market—of which power receptacles are a key component—was valued at USD 77.1 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.3% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is further fueled by advancements in industrial automation, expanding renewable energy installations, and stricter regulatory standards governing electrical safety across regions. As demand for reliable, high-capacity, and secure power connections rises across sectors such as manufacturing, healthcare, data centers, and construction, the role of leading power receptacle manufacturers becomes increasingly critical. In this evolving landscape, innovation in materials, design, and compliance with international standards like IEC and NEMA differentiates top-tier players. Based on market presence, product diversity, global reach, and technological advancement, the following are the top 10 power receptacle manufacturers shaping the industry today.
Top 10 Power Receptacle Types Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Meltric
Domain Est. 1997
Website: meltric.com
Key Highlights: MELTRIC offers a full line of industrial plugs and receptacles, including our signature brand of UL-listed Switch-Rated devices with DECONTACTOR™ ……
#2 Leviton
Domain Est. 1995
Website: leviton.com
Key Highlights: Leviton offers a wide range of lighting controls, wiring devices and networking to meet the needs of today’s residential, commercial and industrial ……
#3 Power Dynamics, Inc.
Domain Est. 1997
Website: powerdynamics.com
Key Highlights: Power Dynamics ganged 15/20A NEMA receptacles are designed to use minimal panel space. They are available in 3 and 4 gang versions….
#4 Power Cord Manufacturer • Custom & Standard
Domain Est. 1997
Website: conwire.com
Key Highlights: Consolidated Offers Standard & Custom Power Cords for North American & International Applications. Serving Multiple Industries. Get a Free Quote Today!…
#5 Wall Industries
Domain Est. 1998
Website: wallindustries.com
Key Highlights: Wall Industries manufactures and markets a full line of DC DC converters and AC DC power supplies. Browse our standard and customized power solutions ……
#6 Types of Electrical Connectors and Wire Connectors
Domain Est. 1992
Website: te.com
Key Highlights: From USB connectors and RJ45 connectors to TE’s DEUTSCH connectors and AMP connectors, we design and manufacture the electrical connectors and wire connectors ……
#7 Amphenol Connectors
Domain Est. 2021
Website: amphenol-cs.com
Key Highlights: Amphenol Communications Solutions (ACS), a division of Amphenol Corporation, is a world leader in interconnect solutions for Communications, Mobile, RF, ……
#8 World plugs
Website: iec.ch
Key Highlights: The Type C electrical plug (or Europlug) is a two-wire plug that has two round pins. It fits into any socket that accepts 4.0 – 4.8 mm round contacts on 19 mm ……
#9 Power plug & outlet Types A & B
Website: worldstandards.eu
Key Highlights: There are two types of domestic wall outlets in use in the US, Canada, Japan and Central America: the ungrounded type A (NEMA 1-15) and the grounded type B ( ……
#10 Types of Electrical Plugs
Domain Est. 2004
Website: iqsdirectory.com
Key Highlights: Explore the many uses and types of electrical plugs. Learn about plug adapters, replacement plugs, two-pronged and three-pronged plugs….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Power Receptacle Types
2026 Market Trends for Power Receptacle Types
The global power receptacle market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, evolving energy demands, and heightened safety and sustainability standards. Key receptacle types are adapting to meet the needs of smart infrastructure, electric mobility, renewable integration, and energy efficiency. Below is an analysis of the dominant trends shaping specific power receptacle categories.
Smart and Networked Receptacles
Smart receptacles are projected to experience the highest growth rate by 2026. Integrated with IoT connectivity (Wi-Fi, Zigbee, Z-Wave), these devices enable remote monitoring, energy usage tracking, and automation via smartphone apps or voice assistants. Driven by the expansion of smart homes and commercial building automation, smart outlets will increasingly feature built-in surge protection, load balancing, and compatibility with renewable energy systems. The demand is further fueled by energy-conscious consumers and commercial facilities aiming to reduce operational costs through real-time power analytics.
Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Receptacles
EVSE (Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment) receptacles, particularly Level 2 charging connectors like NEMA 14-50 and Tesla’s proprietary connectors, will see substantial adoption as global EV penetration increases. By 2026, there will be a marked shift toward standardized, high-efficiency charging solutions, with growing deployment of J1772 (SAE) and emerging adoption of the North American Charging Standard (NACS). Additionally, receptacles integrated with smart grid capabilities will allow for load management, time-of-use optimization, and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) functionality, positioning them as critical components in distributed energy networks.
Industrial and Heavy-Duty Receptacles
In industrial and commercial sectors, ruggedized receptacle types such as NEMA L-series (locking connectors) and IEC 60309 (CEEform) will maintain strong demand due to their reliability in harsh environments. The trend toward electrification of industrial processes and increased automation will drive demand for higher amperage and three-phase power receptacles. Enhanced safety features—including tamper resistance, environmental sealing (IP66/IP67), and arc-fault protection—will become standard, complying with updated electrical codes and OSHA/NEC regulations.
USB-C and Hybrid Power Receptacles
By 2026, USB-C integrated receptacles will become commonplace in both residential and commercial installations. These hybrid outlets combine traditional AC sockets with high-wattage USB-C PD (Power Delivery) ports capable of charging laptops, tablets, and other high-power devices efficiently. Driven by consumer preference for convenience and reduced e-waste from AC adapters, building codes in several regions are beginning to encourage or mandate USB-equipped outlets in new constructions and renovations, particularly in kitchens, bedrooms, and office spaces.
Sustainable and Energy-Efficient Receptacles
Sustainability will be a major design driver. Receptacles made from recycled or bio-based materials, with low standby power consumption and high energy efficiency, will gain market share. Energy Star and similar certifications will increasingly apply to smart and hybrid receptacles. Furthermore, receptacles designed for easy disassembly and recycling will align with circular economy principles, responding to tightening environmental regulations in the EU, North America, and parts of Asia.
Regional and Regulatory Influences
Regional standards will continue to shape receptacle design and adoption. In North America, NEMA configurations will dominate, while the EU will rely on Type F (Schuko) and Type E receptacles, with growing integration of smart features. Regulatory updates, such as the 2023 National Electrical Code (NEC) amendments mandating AFCI/GFCI protection in more locations, will drive replacement cycles and influence receptacle functionality. International harmonization efforts may emerge, particularly for EV and smart grid applications.
In conclusion, by 2026, power receptacles will evolve from passive components to intelligent, connected nodes within broader energy ecosystems. Innovation will focus on safety, efficiency, integration, and sustainability, with smart, EV, and hybrid USB-C receptacles leading market transformation.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Power Receptacle Types
Poor Quality Components
Sourcing low-quality power receptacles often leads to premature failure, overheating, or inconsistent electrical connections. Cheaply manufactured receptacles may use substandard metals for contacts, resulting in increased resistance, arcing, and potential fire hazards. Always verify material specifications (e.g., brass or phosphor bronze contacts) and prioritize reputable manufacturers with proven track records in power connectivity.
Incorrect Ingress Protection (IP) Rating
Selecting a receptacle with an inadequate IP rating for the operating environment is a frequent oversight. For outdoor, industrial, or washdown applications, a low IP rating (e.g., IP44) may allow dust or moisture ingress, leading to short circuits or corrosion. Conversely, over-specifying (e.g., using IP68 where IP54 suffices) can unnecessarily increase costs. Match the IP rating precisely to environmental demands—such as humidity, dust, or direct water exposure—to ensure reliability and safety.
Lack of Compliance with Regional Standards
Power receptacles must comply with regional electrical standards (e.g., UL in North America, CE in Europe, CCC in China). Sourcing non-certified components can result in failed inspections, safety risks, or legal liabilities. Always confirm that the receptacle meets the required certifications for the target market and application.
Mismatched Current and Voltage Ratings
Using a receptacle with insufficient current or voltage ratings for the application can lead to overheating and system failure. For example, selecting a 10A receptacle for a 15A load creates a dangerous overload condition. Ensure that the receptacle’s electrical ratings exceed the maximum expected load, including surge and startup currents.
Inadequate Mechanical Durability
In high-vibration or frequent connect/disconnect environments (e.g., industrial machinery or electric vehicles), standard receptacles may suffer from loosening or contact wear. Overlooking mechanical robustness—such as locking mechanisms, strain relief, and mating cycle ratings—can reduce operational lifespan. Choose receptacles designed for durability in demanding conditions.
Poor Environmental Resistance
Beyond IP ratings, factors like operating temperature range, UV exposure, and chemical resistance are often overlooked. Receptacles used in extreme temperatures or corrosive environments must be made from suitable materials (e.g., UV-stabilized plastics or stainless steel housings). Failure to consider these factors can lead to housing brittleness, seal degradation, or contact corrosion.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Power Receptacle Types
Understanding power receptacle types is essential for global logistics, equipment deployment, and regulatory compliance. Mismatched receptacles can lead to shipment delays, safety hazards, and non-compliance with local electrical codes. This guide provides an overview of key considerations for managing power receptacle types across international operations.
Understanding Regional Receptacle Standards
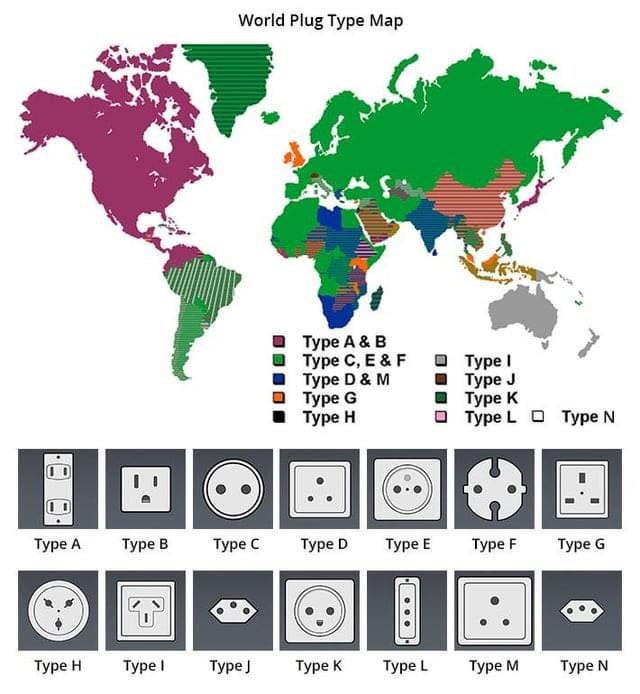
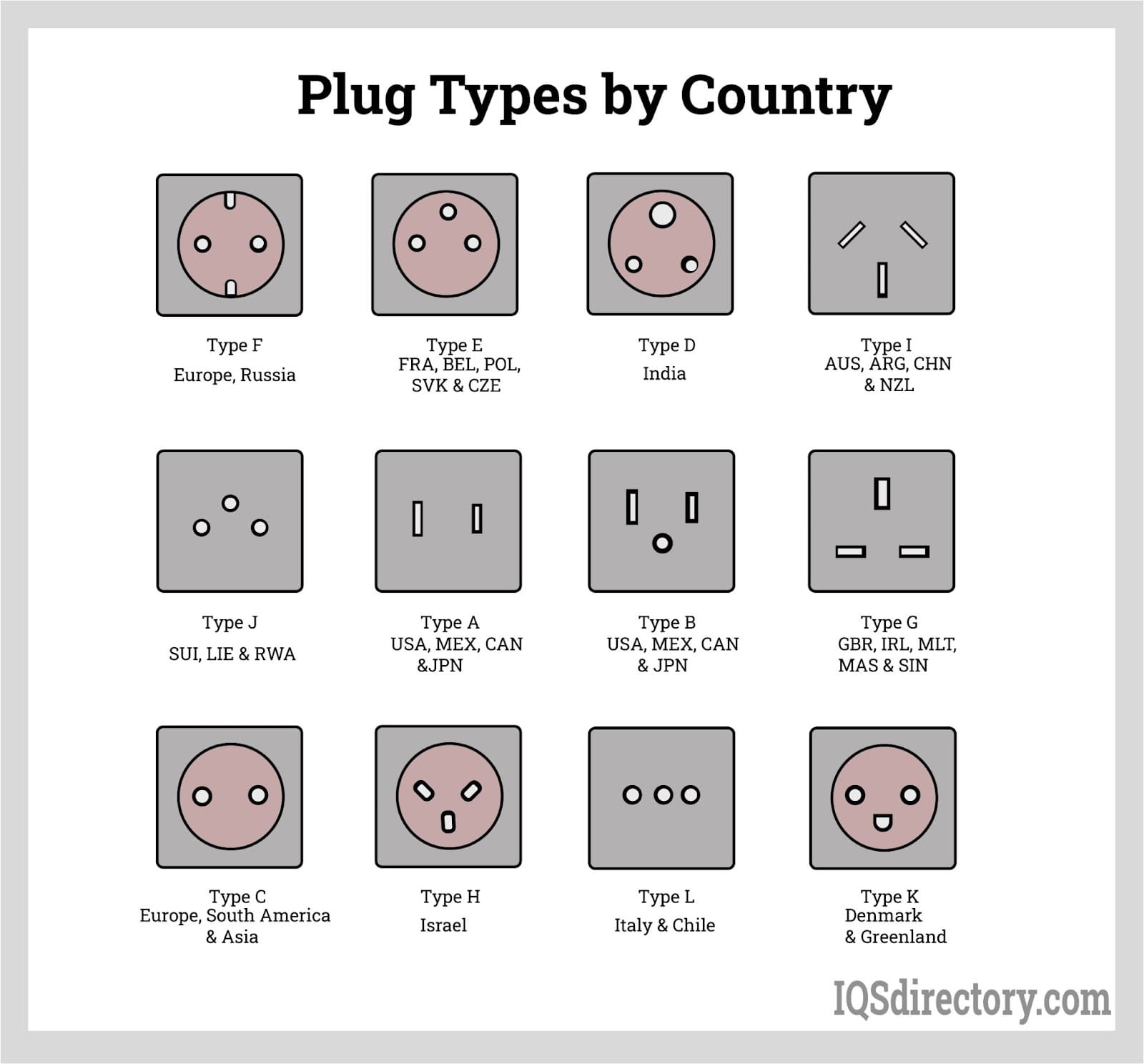
Power receptacle designs vary significantly by country and region, primarily due to historical development and national safety regulations. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) categorizes plugs and sockets into types (e.g., Type A, B, C, etc.), each with distinct physical configurations and voltage/frequency standards.
- Type A & B (North America, Japan, parts of South America): Flat parallel pins (Type A) or with a grounding pin (Type B). Operate at 100–127V, 60Hz.
- Type C (Europe, Africa, parts of Asia): Two round pins; commonly used with 230V, 50Hz systems.
- Type D (India, Nepal, South Africa): Three large round pins in a triangular pattern; 230V, 50Hz.
- Type G (UK, Ireland, UAE, Malaysia): Three rectangular pins in a triangular configuration; 230V, 50Hz, with built-in fuse.
- Type I (Australia, New Zealand, China): Two flat pins in a V-shape with a grounding pin; 230V, 50Hz.
Ensure equipment is compatible with the destination country’s receptacle type to avoid operational disruptions.
Voltage and Frequency Compatibility
Beyond physical plug shape, voltage and frequency differences are critical for equipment functionality and safety.
- Verify that electrical devices support the local voltage range (e.g., 100–127V vs. 220–240V).
- Check frequency compatibility (50Hz vs. 60Hz), especially for motors and timing devices.
- Use transformers or voltage converters when necessary, but ensure they meet local safety certifications.
Failure to address voltage mismatches can result in equipment damage, fire hazards, or voided warranties.
Regulatory and Safety Compliance
Each country enforces electrical safety standards that must be met for receptacle and plug use.
- North America: UL (Underwriters Laboratories) and CSA (Canadian Standards Association) certifications are mandatory.
- European Union: CE marking and compliance with the Low Voltage Directive (LVD) and EN 60320 standards are required.
- Australia/New Zealand: AS/NZS 3112 standard governs plug and socket outlets; compliance with RCM (Regulatory Compliance Mark) is mandatory.
- China: CCC (China Compulsory Certification) applies to electrical equipment and plugs.
Always confirm that power cords, adapters, and equipment meet the required certifications for the destination market.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
When shipping equipment with integrated power cords:
- Label voltage and plug type clearly on packaging and user manuals.
- Include region-specific power cords or specify the need for adapters.
- Avoid shipping non-compliant plug types; consider modular power cord designs (IEC 60320) that allow local cord sets to be used.
This reduces returns and supports compliance with import regulations.
Logistics Best Practices
- Pre-shipment Audits: Verify receptacle type, voltage, and certification markings before dispatch.
- Use of Universal or Interchangeable Cords: Where feasible, use detachable IEC cables with locally compliant plugs.
- Supplier Coordination: Work with manufacturers to produce or configure equipment with destination-specific power configurations.
- Training: Educate logistics and field service teams on receptacle types and compliance requirements.
Adhering to these practices minimizes customs delays, ensures user safety, and supports smooth global operations.
Summary
Managing power receptacle types requires attention to physical compatibility, electrical standards, and regulatory compliance. By integrating receptacle considerations into procurement, logistics, and compliance planning, organizations can avoid costly errors and ensure safe, efficient deployment of electrical equipment worldwide.
In conclusion, sourcing the appropriate power receptacle types requires careful consideration of regional electrical standards, voltage and current requirements, plug configurations, safety certifications, and environmental conditions. Compatibility with local regulations—such as NEMA standards in North America, IEC standards internationally, or BS standards in the UK—is essential to ensure safety, reliability, and legal compliance. Additionally, factors like intended application (residential, commercial, industrial, or medical), frequency of use, and need for grounding or locking mechanisms further influence the selection process. By thoroughly evaluating these criteria and partnering with reputable suppliers who adhere to recognized quality standards, organizations can ensure the efficient, safe, and compliant integration of power receptacles across diverse electrical systems and global markets.