The global power generation systems market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising energy demand, the transition toward cleaner energy sources, and increasing investments in grid modernization. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 1.37 trillion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.9% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence forecasts continued momentum, attributing growth to the rapid adoption of renewable technologies, government decarbonization initiatives, and escalating electrification across industrial and residential sectors. In this evolving landscape, leading manufacturers are differentiating through innovation in combined-cycle gas turbines, wind and solar integration, and digital plant optimization. Here’s a data-driven look at the top 10 power generation systems manufacturers shaping the future of global energy infrastructure.
Top 10 Power Generation Systems Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Power Management Solutions
Domain Est. 2005
Website: globalpwr.com
Key Highlights: We are an authorized distributor and reseller for several high quality manufacturers of diesel generators, natural gas generators, and UPS systems….
#2 Integrated and reliable power generation systems
Domain Est. 1990
Website: cummins.com
Key Highlights: Cummins delivers residential and industrial power generation solutions to customers across the world. Browse our power generation products and systems and ……
#3 Energy Management Solutions for Business & Service
Domain Est. 1995
Website: generac.com
Key Highlights: Generac Industrial Energy isn’t just a power provider; we’re a total energy solutions partner guiding businesses through every step of their energy journey….
#4 Net Power
Domain Est. 1998
Website: netpower.com
Key Highlights: Discover how Net Power delivers clean, reliable energy with cutting-edge technology. Join us in redefining the energy landscape for a sustainable future….
#5 Power Systems
Domain Est. 2024
Website: powersystems.rehlko.com
Key Highlights: Rehlko Power Industrial Generators provide backup, prime and continuous power solutions you need, available in diesel, gas and LP configurations….
#6 PSM
Domain Est. 1994
Website: psm.com
Key Highlights: PSM, a global provider of engineered gas turbine upgrades and aftermarket retrofit solutions delivers flexible, reliable, and efficient gas turbine solutions….
#7 Power Generation
Domain Est. 1996
Website: yanmar.com
Key Highlights: YANMAR’s power generation business, which began in 1953, has been solving energy challenges for customers around the world for more than 60 years….
#8 HIPOWER SYSTEMS a Yanmar Company, Generator Sets
Domain Est. 2008
Website: hipowersystems.com
Key Highlights: Equipment for stationary applications. Continuous or backup power with an immediate response time to guarantee continuous supply in the event of a grid failure….
#9 Power Generation Solutions
Domain Est. 2018
Website: mtu-solutions.com
Key Highlights: Our highly efficient continuous power solutions provide primary power for your operation. When used as part of a combined heat and power system (CHP), you ……
#10 Taylor Power Systems
Domain Est. 2019
Website: taylorpowergenerators.com
Key Highlights: Taylor Power Systems combines over 30 years of innovation and reliability to deliver world-class power solutions for industries and homes around the globe….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Power Generation Systems

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Power Generation Systems
The global power generation systems market in 2026 is poised for significant transformation, driven by the urgent need for decarbonization, technological advancements, and evolving energy security concerns. The overarching theme is the acceleration of the energy transition, with H2 (hydrogen, particularly green and low-carbon hydrogen) emerging as a critical enabler and market segment. Here’s a breakdown of key trends shaping the landscape, with a specific focus on H2’s role:
1. Accelerated Deployment of Renewable Energy & Grid Integration Challenges
- Dominant Growth: Solar PV and onshore/offshore wind will continue to be the fastest-growing segments, driven by plummeting costs, supportive policies (e.g., US IRA, EU Green Deal), and corporate PPAs. Capacity additions will set new records.
- Grid Modernization Imperative: The inherent intermittency of renewables will intensify the need for grid modernization (smart grids, advanced inverters) and massive investments in transmission infrastructure to connect remote generation sites to demand centers.
- Storage Synergy: Utility-scale battery storage (BESS) will see exponential growth, moving beyond short-duration peaking to longer-duration applications, becoming an inseparable part of renewable generation projects.
2. The Rise of Hydrogen (H2) as a Strategic Power Generation Fuel
- Green Hydrogen Momentum: 2026 will see a tangible ramp-up in green hydrogen production (via electrolysis using renewable electricity), moving beyond pilot projects to larger commercial-scale facilities. Falling electrolyzer costs and policy support (e.g., EU Hydrogen Bank, US H2Hubs) are key drivers.
- H2-Blending in Gas Turbines: A major trend will be the increased adoption of hydrogen-blended combustion in existing and new gas turbines. OEMs (GE, Siemens Energy, Mitsubishi Power) are actively developing and certifying turbines for higher H2 blends (20-30%, with pathways to 100%). This offers a vital decarbonization pathway for existing gas infrastructure.
- Dedicated Hydrogen Turbines: Commercial deployment of turbines designed for 100% hydrogen or very high blends (e.g., Siemens Energy’s HL class) will begin, particularly in new-build projects or where dedicated H2 infrastructure is being developed (e.g., industrial clusters, power-to-X hubs).
- H2 as Grid Balancing & Long-Duration Storage: While not direct “generation,” the use of H2 in fuel cells or turbines for power generation from stored hydrogen will gain traction. This addresses the critical need for long-duration energy storage (LDES) to back up renewables over days, weeks, or seasons, differentiating it from batteries.
3. Resilience, Flexibility, and Distributed Energy Resources (DERs)
- Energy Security Focus: Geopolitical instability and extreme weather events will prioritize grid resilience. This boosts demand for flexible generation (like modern gas turbines with fast ramping) and localized power solutions.
- Growth of DERs & Microgrids: Rooftop solar, behind-the-meter storage, and combined heat and power (CHP) systems will proliferate. Microgrids, often incorporating renewables, storage, and potentially H2 fuel cells, will become crucial for critical infrastructure (hospitals, data centers, military bases) and remote communities.
- Virtual Power Plants (VPPs): Aggregation of distributed assets (DERs, EVs, demand response) into VPPs will mature, providing grid services and acting as flexible generation resources.
4. Evolution of Gas-Fired Generation & Carbon Management
- Transitional Role for Gas: Natural gas will remain a key source for flexibility and backup, especially in regions with less renewable potential or grid constraints. However, its role is firmly as a bridge.
- Focus on Decarbonization: The future of gas generation hinges on integration with H2-blending and Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS). Projects combining gas turbines with CCUS will move beyond pilots, and H2-blending will be the primary near-term decarbonization lever.
- Methane Emission Reduction: Regulatory and investor pressure will drive significant investments in detecting and reducing methane leaks across the gas value chain, impacting the lifecycle emissions profile of gas-to-power.
5. Technological Innovation & Digitalization
- Advanced Turbines: Continued improvements in gas turbine efficiency (exceeding 64% in combined cycle) and flexibility (faster start-up, deeper turndown) will be crucial.
- AI & Predictive Maintenance: Widespread adoption of AI and machine learning for predictive maintenance, optimizing plant operations, forecasting renewable output, and managing grid stability.
- Digital Twins: Use of digital twins for design, simulation, and operational optimization of power plants, including complex H2-ready systems.
6. Regulatory & Investment Landscape
- Policy as Primary Driver: Climate mandates (net-zero targets), carbon pricing mechanisms, renewable portfolio standards, and specific H2 strategies (production targets, infrastructure funding) will be the dominant forces shaping investment.
- Financing Challenges & Opportunities: While overall investment in clean energy is high, securing financing for first-of-a-kind projects (like large-scale green H2 or CCUS) remains challenging. However, mechanisms like Contracts for Difference (CfDs) and green bonds are evolving to de-risk these projects.
- Supply Chain Focus: Geopolitical concerns and the need for secure critical mineral (lithium, cobalt, rare earths) and component (electrolyzers, turbines) supply chains will drive regionalization and vertical integration efforts.
H2-Specific Outlook for 2026
By 2026, H2’s role in power generation will be transitioning from pilot projects and announcements to tangible, albeit still niche, commercial deployment. Key indicators:
* H2-Blending: Widespread certification and deployment of turbines for 20-30% H2 blends in existing and new plants, particularly in Europe, North America, and Japan/Korea.
* 100% H2 Plants: First commercial-scale power plants using dedicated 100% H2 turbines will likely be operational or under construction, often linked to industrial H2 hubs or large-scale renewable projects with integrated electrolysis.
* Cost Reduction: Significant reductions in green H2 production costs (driven by cheaper renewables and electrolyzers) and H2 turbine costs will be critical enablers, approaching $2-3/kg H2 in ideal locations.
* Infrastructure: Development of H2 pipeline networks and storage (salt caverns, liquid H2) will accelerate, though infrastructure remains a major bottleneck.
Conclusion
The 2026 power generation market will be characterized by the rapid expansion of renewables, the urgent need for grid flexibility and storage, and the increasingly prominent role of hydrogen (H2). H2, particularly through blending in gas turbines and as a long-duration storage vector for power generation, will be a cornerstone technology for decarbonizing the power sector and ensuring grid stability in a high-renewables future. Success will depend on continued technological innovation, significant policy support, cost reductions (especially for green H2), and the parallel build-out of enabling infrastructure. The market is moving decisively towards a cleaner, more flexible, and resilient system, with H2 playing a pivotal transitional and long-term role.
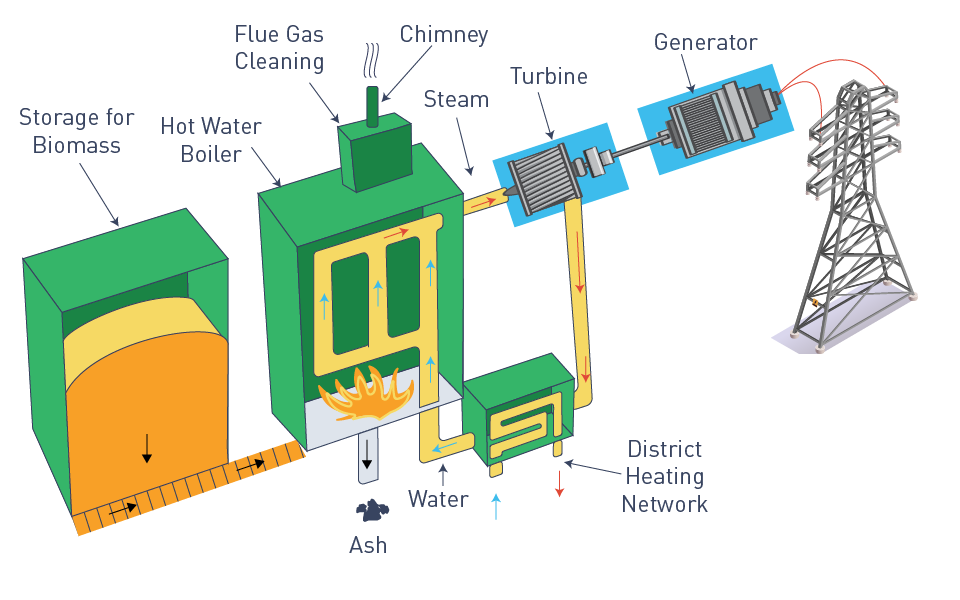
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Power Generation Systems: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Sourcing power generation systems—whether diesel generators, gas turbines, solar inverters, or emerging hydrogen solutions—presents significant challenges beyond cost and delivery. Two critical, often underestimated, pitfalls are ensuring consistent quality and protecting intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these areas can lead to operational failures, safety hazards, financial losses, and legal disputes.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Inadequate Supplier Qualification
Failing to thoroughly vet suppliers based on technical capabilities, manufacturing standards, and track record can result in substandard equipment. Many buyers focus solely on price, selecting vendors without proven experience in the required power output range, environmental conditions (e.g., extreme temperatures, humidity), or regulatory compliance (e.g., ISO, UL, CE). -
Lack of Robust Quality Assurance Protocols
Absence of clear quality control milestones—such as Factory Acceptance Tests (FAT), witness inspections, or third-party certifications—exposes buyers to defective or non-compliant systems. Without defined inspection points in the contract, issues may only surface during commissioning or operation, leading to costly delays and downtime. -
Component and Material Substitution
Some suppliers may substitute critical components (e.g., alternators, control systems, catalysts) with lower-grade or unapproved alternatives to reduce costs. This compromises system efficiency, reliability, and lifespan. Contracts must explicitly prohibit unauthorized substitutions and require pre-approval of all changes. -
Insufficient Testing and Validation
Power systems must be tested under simulated real-world conditions. Relying only on manufacturer-provided test reports without independent verification increases the risk of undetected design flaws or performance shortcomings. For instance, a generator may meet nameplate output in lab conditions but fail under sustained load or high ambient temperatures. -
Poor Documentation and Traceability
Incomplete or inaccurate technical documentation (e.g., schematics, maintenance manuals, calibration records) hampers operation and troubleshooting. Lack of component traceability also complicates warranty claims and safety investigations.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
-
Unauthorized Use or Reverse Engineering
When suppliers provide custom-engineered systems or control software, there is a risk they may reuse design elements, firmware, or proprietary algorithms in competing products. Without strong contractual safeguards, buyers may inadvertently enable competitors to access their technical innovations. -
Ambiguous IP Ownership Clauses
Contracts that fail to clearly define ownership of custom designs, modifications, or software developed during the project can lead to disputes. For example, if the buyer funds a unique control system integration, does the IP belong to the buyer, the supplier, or is it jointly owned? Unclear terms may result in loss of exclusivity or licensing fees. -
Export Control and Compliance Violations
Advanced power generation systems—especially those involving dual-use technologies (e.g., high-efficiency turbines, battery management systems)—may be subject to export control regulations (e.g., ITAR, EAR). Sourcing from non-compliant suppliers can expose the buyer to legal penalties and reputational damage. -
Use of Infringing Third-Party IP
Suppliers may incorporate components or software that violate third-party patents or copyrights. If the delivered system infringes existing IP, the buyer could face legal action, forced system modifications, or costly licensing demands—even if unaware of the infringement. -
Inadequate Protection of Operational Data and Software
Modern power systems often include embedded software and data analytics platforms. Without proper licensing agreements and cybersecurity measures, sensitive operational data or proprietary algorithms may be exposed or exploited by the supplier or third parties.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct comprehensive due diligence on suppliers, including site audits and reference checks.
- Define clear quality requirements, inspection points, and acceptance criteria in procurement contracts.
- Specify approved components and require change notifications for any deviations.
- Include robust IP clauses assigning ownership of custom developments to the buyer and restricting supplier reuse.
- Engage legal and technical experts to review contracts for IP and compliance risks.
- Use non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and secure data-sharing protocols during design and integration phases.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns during sourcing, organizations can ensure reliable, compliant, and secure power generation systems while safeguarding their competitive advantage.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Power Generation Systems
Overview
This guide outlines essential logistics and compliance considerations for the transportation, installation, and operation of power generation systems, including diesel, natural gas, and renewable-based generators. Adhering to these guidelines ensures safety, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency across the project lifecycle.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Environmental Regulations
Power generation systems must comply with environmental standards set by agencies such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), European Environment Agency (EEA), or equivalent national bodies. Key requirements include:
– Emissions controls (NOx, SOx, particulate matter) per EPA Tier 4 or EU Stage V standards.
– Noise level restrictions based on ISO 3744 or local ordinances.
– Proper handling and disposal of hazardous materials (e.g., used oil, batteries, coolant).
Permits and Approvals
Prior to installation and operation, obtain the following:
– Air quality permits for emissions.
– Building and electrical permits.
– Grid interconnection agreements (for systems feeding into the utility network).
– Environmental impact assessments (EIAs) for large-scale installations.
Safety and Operational Standards
Ensure compliance with:
– OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) standards for workplace safety.
– NFPA 70 (National Electrical Code) and NFPA 110 (Standard for Emergency and Standby Power Systems) in the U.S.
– IEC 60034 series (rotating electrical machines) for international projects.
– Local fire codes regarding fuel storage and system placement.
Logistics Planning
Transportation and Handling
- Use certified carriers experienced in heavy equipment transport.
- Secure oversized load permits when required.
- Protect sensitive components from moisture, vibration, and extreme temperatures during transit.
- Provide detailed lifting and rigging instructions based on equipment weight and center of gravity.
Site Preparation and Delivery
- Confirm site accessibility for delivery vehicles (road width, turning radius, ground bearing capacity).
- Prepare foundation or mounting structure per manufacturer specifications prior to delivery.
- Schedule deliveries to minimize on-site storage; ensure secure laydown areas if staging is required.
Inventory and Documentation
- Maintain accurate logs of all equipment, spare parts, and consumables.
- Verify serial numbers and conformance with purchase orders upon delivery.
- Store manuals, certificates of compliance, and as-built drawings in a central, accessible location.
Installation and Commissioning Compliance
Qualified Personnel
- All installation and commissioning activities must be performed by certified and trained technicians.
- Ensure contractors hold valid licenses and insurance coverage.
Quality Assurance
- Follow manufacturer-recommended procedures and checklists.
- Conduct pre-commissioning inspections and system testing (e.g., load bank testing, fuel system integrity checks).
- Document all tests and retain records for audits and warranty validation.
Ongoing Operational Compliance
Maintenance and Monitoring
- Implement a preventive maintenance program aligned with OEM guidelines.
- Monitor emissions and performance metrics regularly using integrated control systems or third-party tools.
- Keep logs of maintenance, repairs, and component replacements.
Reporting and Audits
- Submit required reports to regulatory agencies (e.g., annual emissions reports).
- Prepare for periodic compliance audits with up-to-date documentation.
- Update compliance plans when modifying systems or changing fuel types.
Decommissioning and End-of-Life
Equipment Disposal
- Follow local and international regulations (e.g., WEEE Directive in the EU) for recycling or disposing of components.
- Use certified e-waste or hazardous waste handlers for batteries, oils, and electronic controls.
Site Restoration
- Remove all equipment and restore the site to agreed conditions.
- Conduct environmental assessments if contamination is suspected.
Conclusion
Successful deployment of power generation systems depends on meticulous logistics planning and strict adherence to compliance requirements. By integrating these guidelines into project execution, stakeholders can ensure safety, regulatory approval, and long-term operational reliability.
Conclusion for Sourcing Power Generation Systems
Sourcing power generation systems is a critical decision that significantly impacts operational efficiency, reliability, cost-effectiveness, and environmental sustainability. A strategic and well-informed procurement approach ensures that the selected power solutions align with current energy demands while remaining adaptable to future changes. Key considerations—such as energy requirements, fuel type, system scalability, maintenance support, regulatory compliance, and total cost of ownership—must be thoroughly evaluated. Additionally, advancements in renewable and hybrid technologies offer opportunities to enhance energy resilience and reduce carbon footprints. Ultimately, successful sourcing involves not only selecting the right technology but also partnering with reputable suppliers who provide quality equipment, technical expertise, and responsive service. By adopting a holistic evaluation process, organizations can secure reliable, efficient, and sustainable power generation systems that support long-term operational goals.