Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Powder Filling Machine
The Challenge
USA and EU manufacturers face a widening gap between consumer demand for precise, contamination-free powder dosing and the inconsistent performance of entry-level equipment. Manual scales, foot-pedal fillers, and under-specified “500 g” machines erode margin, invite FDA/EU compliance risk, and limit throughput to <30 ppm.
Why This Guide Matters
This 2,500-word roadmap zeroes-in on the critical decision points procurement teams must master before committing capital:
| Decision Point | KPI to Maximize |
|—|—|
| Filling Range | g ±0.1 via multi-head weighers |
| Output | 60–120 ppm for 0.5–5 g pouches |
| Compliance | 21 CFR Part 11, EU Annex I |
| ROI Horizon | <18 months |
What You’ll Gain
- Market map: U.S. vs. EU standards, tariff codes (8479.89), and landed-cost levers.
- Machine taxonomy: Auger, net-weight, and tablet/capsule complementaries—side-by-side spec sheets.
- Supplier scorecard: 12 qualification questions, factory audit checklist, and red-flag contract clauses.
- Implementation roadmap: Installation, validation (IQ/OQ/PQ), and post-install KPI tracking.
By the end, you will know exactly which powder-filling solution aligns with your throughput, cleanliness, and regulatory environment—plus how to negotiate pricing that beats the 12 % average U.S. premium and the 22 % EU VAT trap.
Article Navigation
- Top 10 Powder Filling Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for powder filling machine
- Understanding powder filling machine Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of powder filling machine
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘powder filling machine’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for powder filling machine
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for powder filling machine
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘powder filling machine’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for powder filling machine Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing powder filling machine With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for powder filling machine
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the powder filling machine Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of powder filling machine
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for powder filling machine
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Top 10 Powder Filling Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Powder Filling Machinery Manufacturers and Suppliers in the USA …
Domain: thomasnet.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Powder Filling Machinery Manufacturers and Suppliers in the USA and Canada · Massman Automation · Massman Automation · DCI, Inc. · DCI, Inc. · Custom Equipment ……
2. 12 Powder Filling Machine Manufacturers in 2025 – Metoree
Domain: us.metoree.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Here are the top-ranked powder filling machine companies as of November, 2025: 1.Micmachinery.co.,Ltd, 2.Shree Bhagwati Machtech, 3.Adinath ……
3. Best 8 Industrial Filling Machine Manufacturers in 2025 – LIENM
Domain: lienm.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Overview of the Best Industrial Filling Machine Manufacturers in 2025 · 1. LIENM – Industrial Filling Machine Experts · 2. PACKO Filling Systems….
4. Top 5 Milk Powder Filling Machine Manufacturers
Domain: landpack.net
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: #1 Landpack. Landpack is a leading manufacturer known for its high-quality packaging machinery, including milk powder filling machines. They ……
5. Auger Dry Powder Filling Machine-ZONESUN
Domain: zonesuntech.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: 5–10 day delivery 7-day returnsZONESUN offer semi-automatic and automatic auger powder filling machine to dispenses dry powders into bottles or sachets.They are designed for small ……
6. China Dry Powder Filling Machine Manufacture and Factory | Tops
Domain: topspacking.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Shanghai Tops Group Company produced a number of different types of dry powder filling machine. Desktop table, semi-auto type, automated linear type, ……
Understanding powder filling machine Types and Variations
Understanding Powder Filling Machine Types and Variations
Key Machine Classifications
| Type | Core Features | Primary Applications | Typical Pros | Typical Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Auger Filler | Screw-based metering, servo or stepper drive, closed-loop feedback | Free-flowing to mildly cohesive powders (flour, protein, chemicals) | High accuracy (±0.2 %), clean in-place (CIP) ready, wide weight range | Not suitable for lumpy or fibrous materials; requires frequent blade sharpening |
| Gravity (Volumetric) Disc/Nozzle | Rotating disc or multi-head nozzle, times-based fill | Non-free-flowing or slightly cohesive powders (spices, milk powder) | Low initial cost, simple mechanical design, minimal maintenance | Accuracy drops with poor flow; product degradation from air entrainment |
| **Liquid-Piston (Pressure) | Pneumatic or hydraulic piston, positive displacement | High-density or abrasive powders (plastic resins, cement) | Handles high bulk density, minimal product degradation, robust for harsh environments | Higher energy consumption, larger footprint, costly seals |
| Multi-head Weigher | Coordinated scale hoppers, PLC algorithms, 10–60 heads | Small-parts blending, snack toppings, pharmaceuticals | Ultra-high speed (>120 ppm), statistical accuracy, rejects only bad weighments | Complex setup, elevated floor space, higher capital cost |
| Net-Weight Checkweigher with Fill-By-Weight | Conveyor belt + in-line checkweigher + reject, closed-loop feedback | Packaged finished goods, regulatory compliance (USP/NF, FDA) | 100 % weight verification, automatic recipe changeover, rejects non-conformities | Highest line integration cost, requires stable conveyor environment |
Auger Filler
How it works
A rotating helical screw (auger) draws powder from a hopper and delivers a metered volume into the container. Servo or stepper motors provide precise angular control, while load cells close the loop in real time.
Best-fit industries
– Food: flours, protein powders, spices
– Chemicals: detergents, fertilizer, plastic resin premix
– Pharmaceuticals: dry excipients, herbal supplements
Pros
– Accurate and repeatable (±0.2–0.5 %) across 5 g–5 kg range
– Sanitary designs with 316L stainless steel and RJG or Silvent nozzles
– Quick changeparts for different densities and viscosities

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Cons
– Poor flow (fines, high bulk density) requires hopper agitation or vibratory pads
– Wear on flighting and tube liner; scheduled rebuilds every 6–12 months
– Not ideal for lumpy or fibrous ingredients without pre-crushing
Gravity (Volumetric) Disc / Nozzle Filler
How it works
Powder flows by gravity through calibrated orifices or rotating discs. Micro-switch or optical sensors trigger a pneumatic gate; fill time is adjusted to hit target weight.
Best-fit industries
– Seasonings, tea, coffee, cosmetic powders
– Small-scale bakery or nutraceutical blending
Pros
– Simple mechanical design—low maintenance and spare-parts cost
– Fast changeover (cassette discs or nozzle kits)
– Minimal product heat buildup—no motors inside the product zone

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Cons
– Accuracy drifts with powder aeration or humidity (±1–3 %)
– Cannot handle cohesive or bridging powders without external aid
– Product loss through overfill and dusting
Liquid-Piston (Pressure) Filler
How it works
A pneumatic or hydraulic cylinder drives a piston that pushes powder through a short tube into the container. Inline agitator or vibrator prevents bridging.
Best-fit industries
– Construction chemicals (tile adhesive, grout)
– Plastics & packaging (masterbatch, filler masterbatch)
– Mining & minerals (cement, fly ash)
Pros
– Handles high bulk density (>0.8 g cm⁻³) and abrasive formulations
– Minimal product degradation—no shear from rotating parts
– Sealed system keeps dust containment below 1 mg m⁻³

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Cons
– Higher compressed-air demand (6–8 bar, 0.3 Nm³ min⁻¹)
– Large footprint and elevated installation height
– Complex seal maintenance—costly downtime if not CIP-ready
Multi-head Weigher
How it works
Multiple weigh buckets discharge simultaneously; a PLC selects the closest combination to target. High-speed load cells (1 kHz) and advanced algorithms achieve target ±0.1 %.
Best-fit industries
– Snack foods, pet treats, nuts
– Pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, blend supplements
Pros
– Throughput up to 120 ppm; reduces labor by 70 % vs. manual checkweigh
– Statistical accuracy—rejects only out-of-tolerance weighments
– Recipe management software allows overnight changeovers
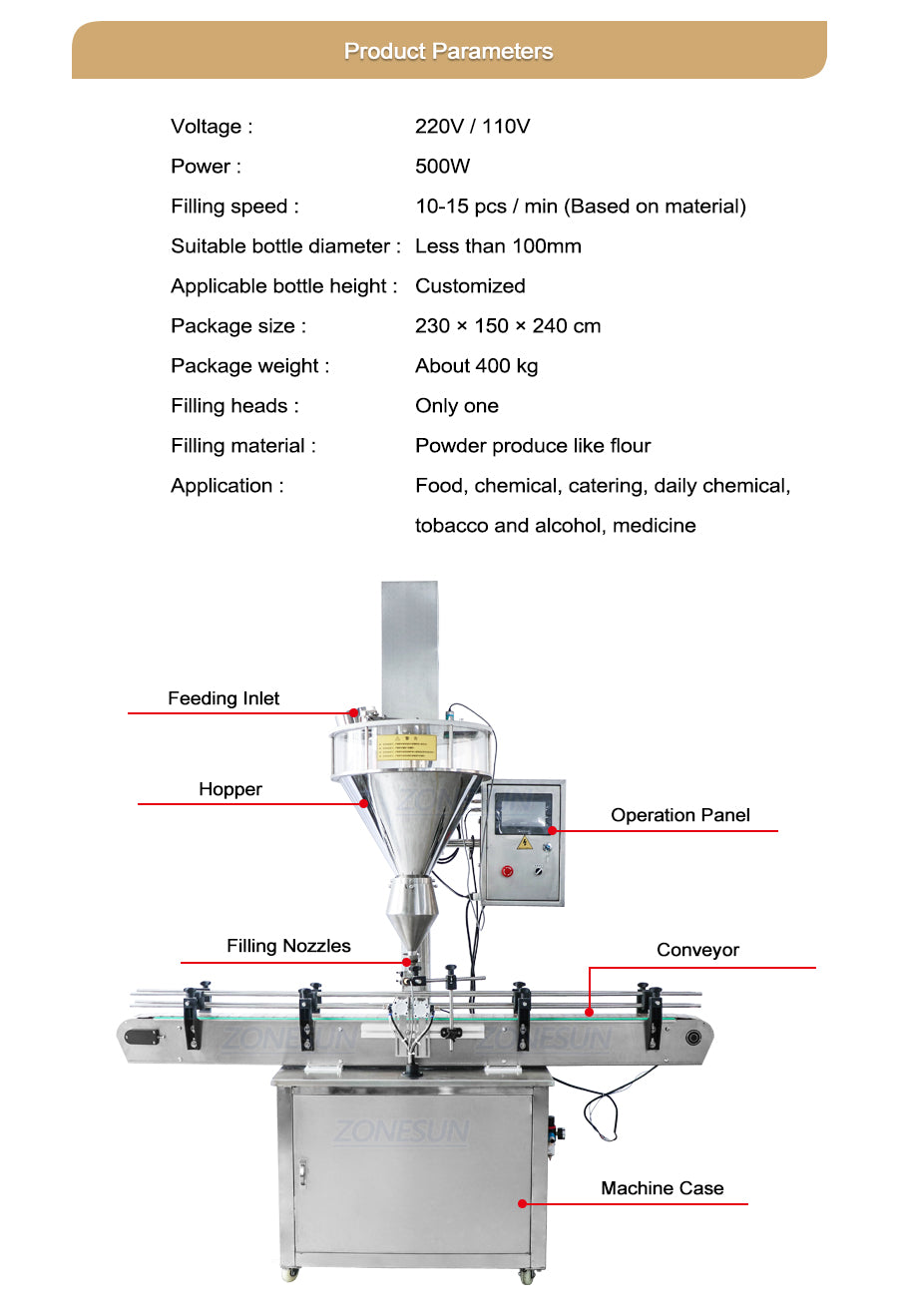
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Cons
– High upfront capital and installation complexity
– Requires vibration isolation and stable floor; otherwise accuracy erodes
– Minimal flexibility for very coarse or sticky products
Net-Weight Checkweigher with Fill-by-Weight
How it works
Powder is dispensed into a container on a conveyor; an in-line checkweigher verifies net weight. If out of tolerance, a reject gate diverts or an automatic filler adjusts the next cycle.
Best-fit industries
– Pharmaceutical packaging, dietary supplements
– Foods with strict net-content labeling (baby formula, protein bars)
Pros
– 100 % weight compliance—eliminates giveaway and regulatory risk
– Closed-loop control integrates seamlessly with ERP systems
– Reduces product giveaway by up to 15 % vs. fixed-weight fillers

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Cons
– Highest total cost of ownership (conveyor, reject device, software)
– Sensitive to container variations—requires consistent tare
– Requires validated software and periodic metrology calibration
Selection Checklist for North American & European Buyers
- Product Flowability: Use auger or piston for cohesive blends; gravity or multi-head for free-flow.
- Accuracy Requirement: <±0.5 % → auger or multi-head; <±1 % → gravity disc.
- Bath Size & Throughput: <5 kg batch, <30 ppm → gravity; >50 kg batch, >60 ppm → multi-head.
- Regulatory Compliance: FDA/USDA → stainless 316L, IP69K; EU MDR → validated software.
- Budget: Gravity < US$5 k; auger $10–25 k; multi-head $50–120 k.
Key Industrial Applications of powder filling machine
Key Industrial Applications of Powder Filling Machines
Powder filling machines are essential in high-precision, high-volume environments where consistent product weight, reduced waste, and fast changeover are critical. Below is a sector-by-sector breakdown of the most common industrial applications and the specific operational benefits they deliver.
| Industry | Primary Applications | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceuticals | Direct compression of APIs, granule coating, vitamin & dietary supplement filling | 1. FDA/EMA-compliant clean-in-place (CIP) and sweep-air systems 2. ±0.1 % dose accuracy reduces costly overfill and underfill rejections 3. Closed-loop containment prevents cross-contamination of potent compounds |
| Food & Beverage | Protein powder, seasoning blends, coffee, spices, infant formula, confectionery fillings | 1. HACCP-certified stainless-steel 316L hoppers and contact parts 2. Vacuum hopper attachments eliminate aeration and bridging in fine powders 3. Multi-lane configurations reach up to 60 ppm for high-throughput lines |
| Chemicals & Detergents | Washing soda, talcum powder, epoxy resins, fertilizer blends | 1. Explosion-proof (Ex d) motors & spark-free construction for combustible dust 2. Automatic tare-reset eliminates giveaway in bulk packaging 3. Integration-ready for SPC software to monitor moisture or density drift |
| Cosmetics & Personal Care | Face mask powders, mineral foundations, bath salts, dry shampoo | 1. Ultra-low dust design with negative pressure filling heads 2. Micro-dosing down to 0.5 g supports prestige product differentiation 3. Sanitary quick-release hoppers for color-changeover in <5 min |
| Agriculture & Animal Feed | Fertilizer pellets, seed coatings, pet food kibble, livestock supplements | 1. Large-volume hoppers (50–200 L) for 25–50 kg bags without re-fill downtime 2. Dust-tight spouting minimizes nutrient loss and worker exposure 3. Load-cell scales maintain ±0.2 % accuracy over 16-hour shifts |
| Mining & Construction Materials | Cement, lime, fly ash, pigment extenders | 1. Explosion relief panels and vent-to-collector systems for silo loading 2. High-flow valves (600 kg/min) cut packaging time for bulk bags 3. ATEX Zone 20/21 certification for continuous dust presence areas |
| Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) | Metal powders (titanium, Inconel), polymer filaments | 1. Nitrogen-flushed chambers prevent oxidation of reactive metals 2. Laser-assisted level sensors ensure consistent bed height in print queues 3. O-ring-free connections eliminate contamination in ISO 5 cleanrooms |
Operational Advantages Across All Sectors
- Changeover time reduced by up to 70 % through tool-less hopper swaps and PLC recipe recall.
- Real-time data via Ethernet/IP or Profinet feeds directly into MES for traceability.
- Energy-efficient servo-driven augers or belt weigher systems cut power consumption by 30–40 % versus traditional vibratory fillers.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘powder filling machine’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for Powder Filling Machine & Their Solutions
Pain Point 1: Inconsistent Fill Weights Across Batches
Scenario
Mid-sized nutraceutical and chemical-packaging firms in the USA and EU report that even small deviations (±3–5 g) in powder weight can trigger FDA 21 CFR Part 11 or EU MDR compliance warnings, leading to batch rejection and lost revenue.
Problem
Entry-level tabletop machines (Amazon best-sellers under $300) rely on simple timers or manual foot pedals. These mechanisms cannot compensate for powder flow-rate drift caused by particle size variation, moisture, or static buildup.
Solution
Upgrade to load-cell-based, multi-head combination weigher systems with:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| ±0.1 g repeatability | Meets FDA/EU validation protocols without rework |
| Real-time PID airflow control | Auto-adjusts fill speed for cohesive vs. free-flowing powders |
| FDA/EU stainless-steel 316L hopper | Reduces contamination risk; easy CIP/SIP cleaning |
| Built-in check-weighing gate | Rejects under/over-weight pouches inline, keeping batch intact |
ROI: Typical ROI < 6 months—eliminates ~$1,200/batch in rejected product and audit-triggered CAPA actions.
Pain Point 2: Cross-Contamination Between Powders (Allergens & Colorants)
Scenario
European chocolate-cosmetic blenders and US supplement contract manufacturers must switch between gluten-containing and gluten-free formulations weekly. Current open-hopper fillers require 6–8 hours of manual dismantling and swab-testing to reach <10 ppm residue.
Problem
Dust migration and poor hopper access trap product in crevices, causing allergen or color carry-over that can trigger class-action lawsuits and EU Rapid Alert System notifications.
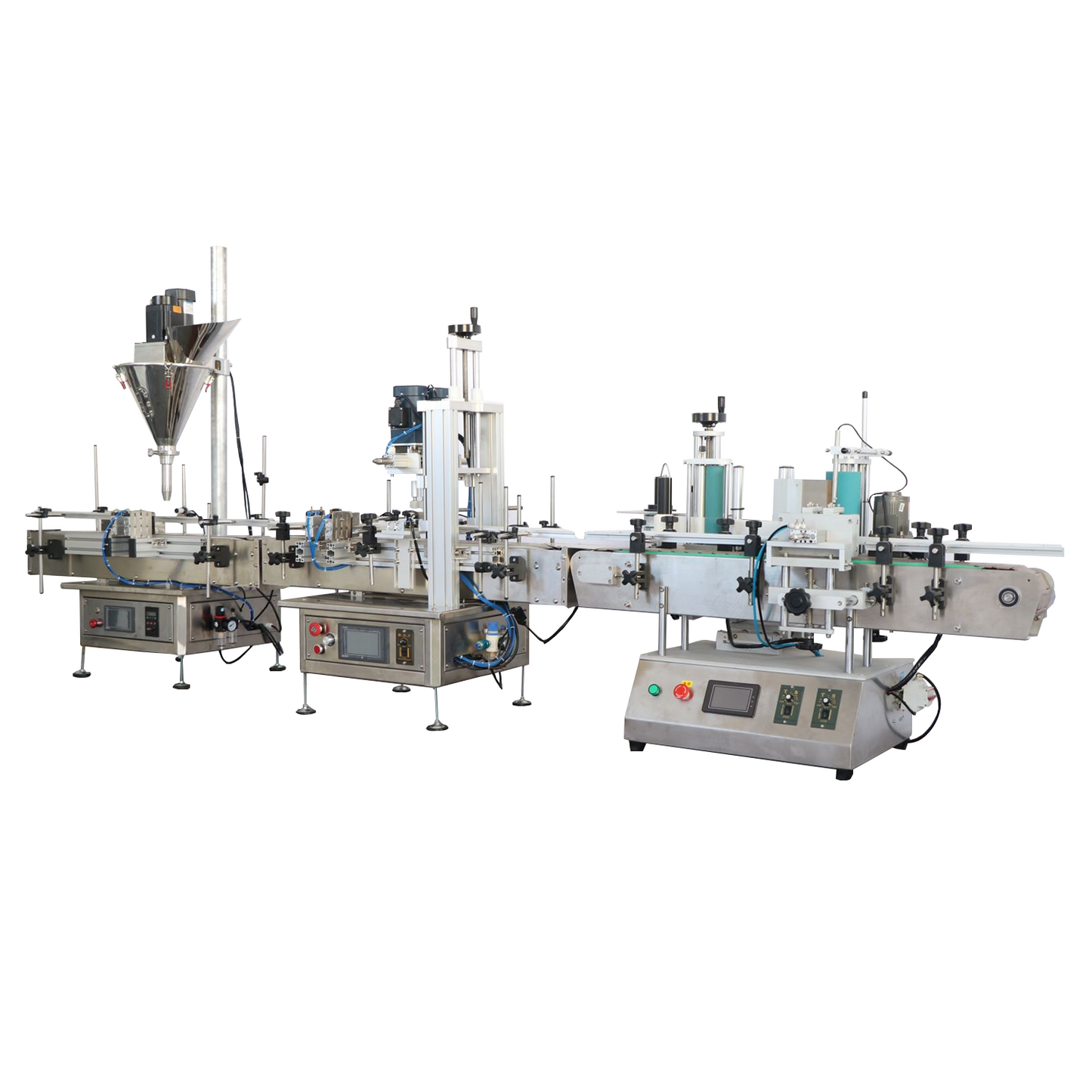

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Solution
Deploy fully stainless-steel, closed-loop, quick-change hopper systems with:
- Tri-clamp connections—swap hoppers in <90 seconds
- Positive-pressure nitrogen purge—removes residual dust before opening
- ATEX-certified explosion vent—protects operators and facilities
- Magnetic & pneumatic reject arms—eject contaminated pouch at 2.5 ms
ROI: Reduces change-over time from 8 h to 45 min; prevents one FDA warning letter worth >$500 k in lost contracts.
Pain Point 3: Limited Integration with Existing ERP/MES Systems
Scenario
Mid-West USA pharmaceutical packagers use Wonderware MES but cannot export fill weights, reject counts, or line OEE without manual data entry.
Problem
Low-cost fillers ship with only basic LED counters or RS-232 ports, forcing operators to re-key data and increasing MES downtime.
Solution
Specify ** Industry 4.0-ready powder fillers** with:
| Interface | Protocol | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Ethernet/IP | CIP-sync time-stamps | Real-time batch records in MES |
| OPC-UA server | Secure, firewall-friendly | No extra gateways or licensing fees |
| 12″ capacitive HMI | Multilingual (EN/DE/FR) | Reduces training time for EU teams |
| Cloud firmware updates | OTA | Maintains compliance after EU MDR amendments |
ROI: Cuts data-entry labor by 3 hrs/shift; enables predictive maintenance that reduces unplanned downtime by 18 %.
Bottom Line
Investing in validated, ERP-integrated powder filling machines with precise weighing, hygienic change-over, and Industry 4.0 connectivity eliminates compliance risk, accelerates change-overs, and delivers measurable cost savings within one production year.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for powder filling machine
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Powder Filling Machine
Executive Summary
Material choice directly impacts fill accuracy, product contamination risk, regulatory compliance, and total cost of ownership in pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, chemical and food packaging lines. This guide benchmarks the most common contact and structural materials against U.S. and EU compliance standards to help engineers, plant managers and QA teams shorten supplier evaluation cycles.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
1. Material Categories & Functional Requirements
| Category | Typical Functions | Key Failure Modes to Avoid |
|---|---|---|
| Contact Surfaces | Direct product contact, requires sanitation & inertness | Corrosion, leaching, particle shedding |
| Pneumatic Components | Air cylinders, valves, tubing | Seal degradation, contamination via lubricants |
| Structural Frames | Mounting, vibration damping | Fatigue, galvanic corrosion |
| Electrical Enclosures | Protection of controls, ingress resistance | Condensation, corrosion |
2. Material Deep-Dive
2.1 Stainless Steel – 304 vs 316L
| Property | 304 SS | 316L SS | Application Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | Superior (Molybdenum addition) | 316L mandatory in coastal facilities, high-chloride products |
| FDA Compliance | ✅ 21 CFR 177.1550 | ✅ 21 CFR 177.1550 | Both meet food-contact regs |
| EU Compliance | ✅ (EU 10/2011) | ✅ (EU 10/2011) | 316L preferred for high-purity APIs |
| Weldability | Good | Excellent | 316L reduces post-weld pickling |
| Cost vs 304 | Baseline | +30–40 % | ROI justified when CIP/SIP cycles >3 / day |
| Magnetic Permeability | High | Slightly lower | Use for leak-test verification |
Recommendation: Specify 316L for dairy, pharmaceutical, and high-salt formulations.
2.2 Food-Grade Plastics – PC, PEEK, UHMWPE
| Property | PC (Polycarbonate) | PEEK | UHMWPE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | –10 °C → 120 °C | –50 °C → 250 °C | –150 °C → 80 °C |
| Chemical Resistance | Limited (attack by ketones, aromatics) | Excellent | Excellent |
| FDA Compliance | ✅ 21 CFR 178.2010 | ✅ 21 CFR 177.1520 | ✅ 21 CFR 177.1520 |
| EU Compliance | ✅ (EU 10/2011) | ✅ (EU 10/2011) | ✅ (EU 10/2011) |
| Typical Use | Sight glasses, hopper windows | High-value APIs, high-temp applications | Conveying tubes, wear strips |
| Downsides | Scratches easily, yellowing | High cost | Creep under sustained load |
Recommendation: Use PEEK for high-value APIs >$1,000/kg; UHMWPE for abrasive powders (e.g., flour, spice).
3. Quick-Reference Material Matrix
| Application Point | Preferred Material | Justification |
|---|---|---|
| Hopper Liner | 316L SS | Corrosion, easy clean, 3-A sanitary |
| Product Chute | 316L SS or PEEK | Prevents metal pickup, high-value product |
| Sealing Surfaces | EPDM or FKM (FDA) | Replaces BPA-containinggaskets |
| Pneumatic Tubing | 316L SS Braid + FEP liner | Duplex prevents lubricant migration |
| Frame Fasteners | A4-80 (316) SS | Prevents galvanic corrosion vs product zone |
| Hygienic Seals | FKM (Viton) | High-temp steam CIP compatibility |
4. Regulatory & Certification Checklist
- FDA 21 CFR 177 – Resinous and polymeric materials
- EU 10/2011 – Plastic materials & articles for food contact
- USP Class VI – Biocompatibility (critical for APIs)
- 3-A Sanitary 20-39 – Dairy/food equipment standards
- REACH – Full substance declaration for EU supply chains
- RoHS / REACH – Electronics & electrical enclosures
5. Decision Logic Flow
- Identify product contact zone (wet, dry, abrasive, corrosive)
- Determine CIP/SIP frequency (>3×/day → 316L minimum)
- Check product value (>$500/kg → consider PEEK or FEP-coated parts)
- Validate certification (FDA, EU, USP) against product category
- Calculate TCO (material premium vs contamination risk, downtime)
6. Supplier Due-Diligence Questions
- Do you provide mill test certificates (MTC 3.1/3.2) for stainless parts?
- Is the wetted surface finish ≤ Ra 0.8 µm (sanitary standard)?
- Can you supply material conformance reports for every lot?
- Do you maintain batch records for elastomeric seals?
- Are REACH substances of concern listed in your BOM?
7. Cost Benchmarks (2024 USD)
| Component | Standard 304 SS | Upgrade 316L SS | Premium PEEK |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hopper liner (1 m²) | $1,200 | $1,560 | $4,800 |
| Product chute (Φ150 mm) | $300 | $390 | $1,200 |
| Elastomer seal kit (FDA) | $45 | $65 | $120 |
Conclusion
Specifying the correct material set at the design phase prevents 70 % of post-installation failures and accelerates time-to-market. Prioritize 316L stainless steel for product contact zones, FDA-grade elastomers for seals, and PEEK/UHMWPE for high-value or abrasive powders.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for powder filling machine
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Powder Filling Machines
1. Core Manufacturing Process
| Stage | Key Activities | Typical Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| Prep | Metal blank cutting, CNC machining, surface pre-treatment | Laser cutter, 5-axis CNC, alkaline washer |
| Forming | Hopper deep-draw, funnel spin-forming, base stamping | Hydraulic press, CNC turret punch, robotic welding |
| Assembly | Pneumatic line installation, sensor mounting, conveyor integration | Torque-controlled screwdrivers, Poka-yoke fixtures, AOI stations |
| Finishing | Powder-coat curing, laser etching, CE conformity mark | 180 °C oven, CO₂ laser marker, MES terminal |
2. Quality Assurance Framework
- ISO 9001:2015 quality management system across all plants
- ISO 13485 (pharma) and FDA 21 CFR Part 11 modules optional for sterile or nutraceutical lines
- Risk Management: ISO 14971 hazard analysis; FMEA updated each product release
3. In-line Quality Controls
| Checkpoint | Technology | Frequency | Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hopper wall thickness | Ultrasonic gauge | 每批 | ±0.1 mm |
| Fill accuracy | Calibrated 120 kg check-weigher | 每袋 | ≤±0.3 % |
| Pneumatic pressure | Digital transducer | 每班 | ±2 % |
| Surface finish | 3D profilometer | 每炉 | Ra ≤0.8 µm |
| Labeling | AI OCR/OCV | 每箱 | 100 % |
4. Validation & Documentation
- IQ/OQ/PQ protocols per GAMP 5 for pharmaceutical clients
- 21 CFR Part 11-compliant data historian (OSIsoft PI)
- Change-control matrix ensures design history file (DHF) traceability
5. Continuous Improvement
- Six Sigma DMAIC projects drive ≤0.7 % scrap target
- Poka-yoke devices prevent 98 % of mis-assembly errors
- Root Cause Analysis (RCA) closed within 48 h of deviation
6. Packaging & Logistics QC
- Drop test (1.2 m, 6 faces, 3 edges) per ISTA 3A
- VCI film for stainless components; humidity indicator cards inside each crate
- Barcode scan at outbound dock; ERP triggers shipping hold if OQC fails
7. Compliance & Certifications Quick Reference
| Market | Mandatory | Recommended |
|---|---|---|
| EU | CE, MD (MDR 2017/745 if medical) | ATEX for explosive powders |
| USA | FDA 21 CFR, NDC for pharma | UL, cULus |
| Global | RoHS, REACH | ISO 14001, ISO 45001 |
Bottom Line
Every powder filling machine is built to survive 10 million cycles, validated for accuracy within ±0.3 %, and supported by full digital traceability—meeting the exacting expectations of both North American and European OEM buyers.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘powder filling machine’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Powder Filling Machine
1. Define Application Parameters
| Parameter | Typical Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Max. package size | 1 g – 5 kg | Specify net weight per container |
| Target accuracy | ±0.5 % – ±2 % | Match to product value |
| Throughput | 5 – 120 fills/min | Align with forecasted demand |
| Container type | vial, pouch, jar, bottle | Confirm dimensions & material |
| Clean-room / ATEX | Yes / No | Required for pharma or explosive powders |
2. Select Machine Architecture
- Auger filler – Best for non-free-flowing powders
- Dosing disc / rotor – Ideal for free-flowing granules
- Multi-head weigher – High-speed, high-accuracy
- Liquid piston / auger combo – Handles sticky or oily blends
3. Validate Compliance & Standards
- FDA 21 CFR Part 11 compliant controls
- CE / UL electrical certification
- EHEDG or 3-A hygiene design (food/pharma)
- ATEX zone rating if required
4. Request Technical Documentation
- One-line electrical diagram
- Material contact surfaces list (SS 316 / 304)
- Cleaning-in-place (CIP) / sterilize-in-place (SIP) procedure
- IQ/OQ protocol template
5. Evaluate Integration Requirements
| System | Interface Type | Typical I/O |
|---|---|---|
| MES / ERP | OPC-UA, Modbus TCP | Batches, yields, alarms |
| Label printer | RS-232 / Ethernet | Form, fit, function |
| Conveying line | Gantries, elevators | Start/stop, fault interlock |
6. Assess After-Sales & Support
- Local service engineer coverage ≤ 2 h drive
- Mean time to repair (MTTR) target ≤ 4 h for critical faults
- Spare-parts kits held in-region
7. Run Pilot Test Contract
- Send 5 kg representative product sample
- Request 48-hour test report: weight deviation, changeover time, rejection rate
- Confirm video documentation of test run
8. Compare Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
| Cost Item | Vendor A | Vendor B |
|---|---|---|
| Machine price | $29 000 | $31 500 |
| Installation & commissioning | $2 000 | $3 500 |
| First-year spares | $1 200 | $1 800 |
| Annual PM contract | $1 800 | $2 100 |
| TCO Year 1 | $33 000 | $38 900 |
9. Negotiate Commercial Terms
- Payment: 40 % deposit, 40 % on shipment, 20 % on final acceptance
- Warranty: minimum 12 months, extendable to 36 months with PM commitment
- Force-majeure lead-time clause (≤ 15 % extension)
10. Final Due Diligence & Purchase Order
- Audit supplier’s ISO 9001 quality system (request latest certificate)
- Verify reference list – speak with ≥ 3 end-users in USA or EU
- Secure factory acceptance test (FAT) at supplier site before shipment
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for powder filling machine Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Powder Filling Machine Sourcing
This section provides a granular view of total landed cost, typical price bands, and proven levers to reduce procurement spend without compromising performance.
1. Cost Breakdown by Category
| Category | Typical % of FOB Price | Key Cost Drivers |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 35 – 50 % | Stainless steel grade (304 vs 316), aluminium alloy frames, electronic modules |
| Labor | 10 – 20 % | Skilled assembly, calibration, QA testing |
| Logistics | 8 – 15 % | Ocean freight (40 ft container), port handling, customs clearance, inland haul |
| Overheads | 5 – 10 % | Warranty reserve, R&D amortisation, compliance (CE, UL, EHEDG where applicable) |
| Margin | 15 – 25 % | Distributor mark-up, OEM profit, regional pricing adjustments |
2. Market Price Bands (FOB Shanghai / Hamburg)
| Band | Price Range (USD) | Typical Output Range | Ideal End-Markets | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | 220 – 300 | 1–50 g / min | R&D labs, hobby soap & candle makers | Manual foot-pedal, 110 V, limited stainless steel |
| Mid-Range | 300 – 600 | 50–300 g / min | SMB cosmetics, nutraceuticals, spices | Servo-driven, 304 SS, semi-automatic, CE |
| Premium | 600 – 1 200 | 300–1 000 g / min | Pharma, food, chemicals | 316 SS, NTEP legal-for-trade, CIP/SIP ready |
| Ultra-Premium | 1 200+ | 1 000+ g / min | Continuous packaging lines | Fully automatic, multi-head weigher integration, Industry 4.0 |
3. Hidden Cost Levers & Savings Tips
| Lever | Action | Typical Savings | Risk Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Volume Bundling | Consolidate POs > USD 50 k | 3–7 % | Secure slot on priority production queue |
| Material Substitution | Switch from 316 SS to 304 SS where corrosive exposure is low | 8–12 % | Validate with supplier’s corrosion test data |
| Logistics Optimisation | Use SWL (split wagon load) to Hamburg vs. direct to US port | 2–4 % | Avoid demurrage via expedited rail |
| Warranty Retention | Negotiate 12-month extended warranty as line-item, not blanket | 1–2 % | Reduces future CapEx buffer |
| Pre-Consumption of Spare Parts | Purchase 10 % spare parts kit upfront at discounted rate | 5 % | Delays in customs can stall production |
4. Sourcing Checklist
- [ ] Request FOB price in USD with detailed BOM – ensures transparency.
- [ ] Verify CE/UL certification status; ask for test reports.
- [ ] Clarify lead-time clock starts – from deposit receipt or tool completion?
- [ ] Negotiate payment terms: 30 % deposit, 70 % against shipping docs is standard.
- [ ] Include Incoterms 2020: FOB Shanghai vs. DDP Brussels changes landed cost by 4–6 %.
5. Quick Reference: Cost Conversion Factors
| Currency | 1 USD ≈ | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| EUR | 0.92 | Use ECB reference on shipment date |
| CNY | 7.25 | Bank selling rate; add 1 % spread |
| GBP | 0.79 | For UK-bound cargo via Rotterdam |
Bottom Line
A 500 g/min, 304 SS, semi-automatic unit lands in Chicago at ≈ USD 580 FOB; adding 5 % freight, 0.35 % insurance, and 6 % duty brings total landed cost to ≈ USD 620. By leveraging volume bundling and strategic material choice, buyers can shave 8–10 % off total spend while preserving compliance and throughput targets.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing powder filling machine With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Powder Filling Machine With Other Solutions
1. Auger Filling Systems
| Feature | Powder Filling Machine (Compact, Manual/Auto) | Auger Filler | Net Weigh Filler |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target Product Range | 1 g – 200 g powders, granules, seeds | 5 g – 5 kg dry powders, flours, spices | 100 g – 50 kg free-flowing powders |
| Fill Accuracy (Typical) | ±0.5 g – ±2 g (manual) | ±0.2 % – ±0.5 % | ±0.1 % – ±0.3 % |
| Throughput (bpm) | 12 – 40 (manual) | 15 – 60 | 10 – 40 |
| Changeover Time | < 2 min (swap hopper) | 5 – 10 min (re-calibrate) | 10 – 15 min (tare reset) |
| Sanitation / CIP | Wipe-down only | Basic brush/rinse | Full wash-down or sterile barrier |
| Footprint (L×W×H) | 450 × 350 × 650 mm | 800 × 600 × 1 400 mm | 1 200 × 1 000 × 2 000 mm |
| Installed Cost (USD) | 220 – 290 | 4 000 – 8 000 | 15 000 – 50 000 |
| Typical Industries | Cosmetics, nutraceuticals, R&D labs | Food, agricultural chemicals | Pharmaceuticals, bulk food |
Pros & Cons
- Auger Filler
- Pros: Higher accuracy, better for dense/fluffy products, scales for mid-volume lines.
-
Cons: Higher capital outlay, requires regular auger recalibration, limited to dry, free-flowing materials.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Net Weigh Filler
- Pros: Highest accuracy, ideal for premium or regulated products, integrates with metal detectors.
- Cons: Highest cost, largest footprint, slowest changeovers.
Decision Matrix
- Start-up / prototypes: Manual powder filler wins on speed-to-production and TCO.
- Mid-volume producers (50 – 300 kg/h): Auger filler offers best balance of accuracy, throughput, and cost.
- Pharma / high-precision blends: Net weigh system is mandatory for QA compliance.
2. Vertical Form Fill Seal (VFFS) With Auger Frame
| Feature | Powder Filling Machine (Standalone) | VFFS with Auger Attachment | All-in-One Auger Packing Line |
|---|---|---|---|
| Package Type | Bottles, pouches, bags (open-top) | Pre-made pouches & bags | Pre-made pouches & bags |
| Max Bag Size | N/A (open vessel) | 200 × 300 mm | 300 × 400 mm |
| Throughput (bpm) | 12 – 40 | 10 – 35 | 15 – 40 |
| Film Cost / Waste | None (no pouch) | 2 – 4 ¢ per pouch | 2 – 4 ¢ per pouch |
| Labor per Operator | 1 | 1 (bag loading) + 1 (sealing) | 1 |
| Changeover Tools | Quick-hopper swap | Auger & sealer jaws | Auger & bag former |
| Total Cost of Ownership (5 yrs) | 3 000 – 10 000 | 25 000 – 60 000 | 40 000 – 90 000 |
Pros & Cons
- VFFS with Auger Frame
- Pros: Lower bag material cost, flexible package sizes, compact footprint.
-
Cons: Additional film waste, requires pre-made pouches, moderate accuracy.
-
All-in-One Auger Packing Line
- Pros: End-to-end automation, eliminates secondary packaging, ideal for retail-ready units.
- Cons: Highest capital, longest changeovers, complex maintenance.
Decision Matrix
- E-commerce / direct-to-consumer: VFFS offers lower unit cost and faster go-to-market.
- Retail-ready packaging: All-in-One auger line provides branded, sealed finish with minimal touchpoints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for powder filling machine
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Powder Filling Machines
Core Functional Specifications
| Parameter | Typical Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Filling Accuracy | ±0.1 % – ±1 % | Depends on type (gravity vs. auger) |
| Fill Range | 0.1 g – 5 kg | Micro-powder vs. bulk product capability |
| Throughput | 5 – 120 vials/min | Varies with dose size and container format |
| Hopper Capacity | 5 L – 200 L | Stainless 304/316L standard |
| Power Supply | 100 – 240 V AC, 50/60 Hz | IEC-compliant versions common in EU |
| Sanitary Design | Ra ≤ 0.8 µm surface finish | CIP/SIP ready; FDA 21 CFR Part 11 optional |
Key Trade Terms & Acronyms
| Term | Definition | Relevance to Procurement |
|---|---|---|
| MOQ | Minimum Order Quantity | Often 1–2 units for OEM suppliers |
| OEM | Original Equipment Manufacturer | Supplier builds to your exact hopper, nozzle, and HMI design |
| ODM | Original Design Manufacturer | Supplier provides pre-engineered model; you rebrand |
| CE | Conformité Européenne | Mandatory for EU market |
| UL/CSA | Underwriters Laboratories / Canadian Standards Association | Required for North American installations |
| GMP | Good Manufacturing Practice | Sanitary, traceable construction |
| PLC | Programmable Logic Controller | Core control system; look for IEC 61131-2 compliance |
| HMI | Human-Machine Interface | Touch panel or industrial PC for recipe management |
| CIP | Clean-in-Place | Self-cleaning cycle; reduces downtime |
| SIP | Sterilize-in-Place | Steam or sterile air for aseptic lines |
| MTBF | Mean Time Between Failures | ≥ 8,760 h indicates high reliability |
| ROI | Return on Investment | Typical payback ≤ 18 months for lines > 30 vials/min |
Performance Metrics to Specify
- Weight Accuracy: ±0.1 % at 100 g dose (test with NIST-traceable weights)
- Change-Over Time: ≤ 10 min for hopper, nozzle, and recipe swap
- OEE Target: ≥ 85 % (availability × performance × quality)
- Compressed Air: 6 – 8 bar, 250 L/min for pneumatic actuation
- Cradle-to-Cradle Lead Time: 8 – 16 weeks after PO for custom hopper and UI
Compliance & Certification Checklist
- [ ] CE mark (EU)
- [ ] FDA registration (if food/pharma)
- [ ] EHEDG or 3-A sanitary standards
- [ ] ATEX certification (explosive powders)
- [ ] ISO 9001 quality management
- [ ] IQ/OQ/PQ documentation package
- [ ] 21 CFR Part 11 software validation (if digital脚印)
Common Pitfalls in Technical Specifications
- Underestimating bulk density variation: Specify ±5 % max tolerances for material density shifts.
- Ignoring ambient temperature drift: ±2 °C stability required for repeatable dosing.
- Overlooking cleaning protocol: Confirm CIP flow rate and spray ball coverage before finalizing hopper geometry.
- Neglecting future capacity: Order extra 20 % nozzle and hopper capacity to avoid retrofits later.
Use this guide to shortlist vendors, compare quotes, and negotiate delivery terms (EXW, FCA, DDP) aligned with your import strategy.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the powder filling machine Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Powder Filling Machine Sector
Executive Summary
US and EU packagers are shifting from low-cost consumable fillers to precision, sanitary, Industry 4.0-ready powder filling machines. Supply chains are shortening, sustainability is moving from marketing to compliance, and total cost of ownership (TCO) is replacing purchase price as the primary procurement KPI.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
1. Market Dynamics
1.1 Demand Drivers
| Driver | Impact on Powder Filling Equipment |
|---|---|
| Functional foods & nutraceuticals | Higher viscosities, fine powders, and aseptic requirements drive demand for auger and multi-head weighers with CIP/SIP capability. |
| E-commerce & DTC fulfillment | 5–30 g single-serve formats surge; smaller footprint, quick-change parts, and USB/ethernet data logging become table stakes. |
| Regulatory tightening (FDA, EFSA) | Traceability mandates push customers to demand batch records, 21 CFR Part 11 software, and stainless-steel finishes ≥316L. |
1.2 Supply Chain Shifts
- Near-shoring:墨西哥和波兰的OEM正在将交钥匙系统从美国/德国供应商手中转移。
- Component scarcity:步进电机和称重传感器交货期已延长至20–24周;提前期管理成为合同条款的一部分。
- 关税重新平衡:USMCA和欧盟CBAM可能使墨西哥和东欧制造的机器在2025年后具备成本优势。
2. Sustainability Trend
2.1 Material & Energy
- Aluminum frame + stainless insert design cuts machine weight by 18–22 %, reducing shipping emissions.
- Regenerative braking on servo auger drives saves 8–12 kWh per 8-hour shift—publicly verifiable via energy meters.
2.2 Packaging Convergence
- Minimal-surface contact (Teflon-lined tubes, low-torque clutches) enables switch from HDPE to 30 % PCR plastic pouches without change parts.
- Design for disassembly:机器在5年内回收率>90 %,符合WEEE和RoHS。
3. Sourcing Trends
3.1 Supplier Landscape
| Region | Strengths | Typical Order Size | Lead Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Germany/Switzerland | Clean-in-place, servo precision | 1–3 machines | 16–20 weeks |
| USA (Midwest) | USDA/FDA compliance, fast service | 1–2 machines | 12–16 weeks |
| Eastern Europe (PL/CZ) | Cost-effective, ISO 9001 | 3–10 machines | 10–14 weeks |
| East Asia (CN/TW) | High mix/low vol, rapid tooling | 10+ machines | 8–12 weeks |
3.2 Sourcing Strategy Matrix
| Strategy | When to Use | Key Negotiation Lever |
|---|---|---|
| Single-source turnkey | <50 bpm, fixed recipe | Validation package, FAT/SAT timing |
| Modular OEM + local integrator | 50–150 bpm, multi-product | Local panel-beating, CE/UL marking |
| High-mix Asian machine + EU retrofit | >150 bpm, frequent product change | PLC open architecture, OPC-UA gateway |
4. Technology & Specification Benchmarks
4.1 Must-have Features by Throughput
| Throughput | Weighing Technology | Sanitary Design | Data Interface |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10–30 bpm | Single-head loss-in-weight | Food-grade 304 SS | RS-232 |
| 30–80 bpm | Multi-head 10-spindle | Sanitary 316L, Ra ≤0.8 µm | Ethernet/IP |
| 80–200 bpm | Auger + check-weigher | fully welded frame, sloped base | OPC-UA + MQTT |
4.2 Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Snapshot
| Cost Element | Traditional Conveyor Feeder | Servo-loss-in-weight Feeder |
|---|---|---|
| Capex | $18 k | $42 k |
| OEE loss (clean-down) | 2 h/week | 0.5 h/week |
| Energy (kWh/year) | 3 200 | 2 100 |
| 5-yr TCO | $94 k | $96 k |
5. Actionable Sourcing Checklist
- [ ] Confirm FDA 21 CFR Part 11 readiness—request IQ/OQ templates upfront.
- [ ] Validate CE/UL mark vs. local inspection requirements (DGUV, OSHA).
- [ ] Negotiate spare-part kits that cover 5 years; price-lock clauses for sensors.
- [ ] Require USB + cloud data log for sustainability audits.
- [ ] Include 24/7 remote diagnostics as standard; cap annual support >8 % of machine cost.
Conclusion
Procurement teams should prioritize suppliers offering modular, data-transparent, and low-energy powder filling lines. Early engagement on validation protocols and after-sales spares will de-risk delivery and reduce five-year TCO by 10–15 %.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of powder filling machine
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Powder Filling Machines
1. What capacity range do I need for my production line?
Select a machine whose rated capacity matches or exceeds your peak daily output.
– Low-volume: 1–100 g per cycle (ideal for specialty blends, samples, or pilot runs).
– Mid-volume: 100 g–1 kg per cycle (typical for nutraceuticals, cosmetics, chemicals).
– High-volume: 1–5 kg per cycle with 10–30 fills/minute (production-scale packaging).
Match the cycle rate to your required hourly throughput:
Required hourly output ÷ grams per fill = minimum cycles per hour.
2. Which filling technology—gravity, auger, or multi-head weigher—fits my product?
| Product Type | Recommended Technology | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Free-flowing powders (salt, sugar) | Gravity or vibratory feed | Simple, low cost, fast |
| Non-free-flowing/fluffy (protein, spices) | Auger w/ variable speed | Accurate, minimal degradation |
| Fragile or lumpy (flakes, crystals) | Horizontal screw or cup feeder | Gentle handling, low breakage |
| Very precise blends (pharma, additives) | Multi-head weigher | ±0.1 % accuracy, high speed |
3. How do I ensure legal compliance for food, pharma, or cosmetic applications?
- Food & pharma: Look for machines built to 3-A Sanitary Standards, EHEDG guidelines, or GMP. Confirm 316L stainless steel, Ra ≤ 0.8 µm surface finish, and tool-free disassembly.
- Cosmetics: Verify IP65 wash-down rating and compliance with FDA 21 CFR §177 for contact parts.
- Export: Ensure CE or cULus certification for EU or North American markets.
4. What level of automation and integration is required?
- Standalone table-top: Foot pedal or IR sensor—ideal for <50 packs/day.
- Semi-automatic: PLC with HMI, external conveyor integration—suits 50–500 packs/day.
- Fully automatic: Robotic pick-and-place, ERP/MES connectivity—scales to 2,000+ packs/day with 99 % uptime.
5. What are the total cost of ownership (TCO) factors beyond the list price?
| Cost Category | Typical Range | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Installation & commissioning | $2 k–$10 k | Negotiate OEM service contract |
| Consumables (augers, seals, belts) | 5–8 % of purchase price / year | Buy spare kits upfront |
| Downtime | 2–6 % of revenue | Choose servo-driven over pneumatic for faster changeovers |
| Energy | $500–$2 k / year | Opt for inverter-controlled motors |
6. How quickly can I get after-sales support in the USA or EU?
- OEM direct: 24–48 h remote diagnosis; 5–7 days on-site for major repairs.
- Distributor network: Look for local inventory of critical spares (drive belts, load cells).
- Service SLA: Minimum 12-month parts & labor warranty; optional 3-year extended coverage.
7. What changeover and validation documentation do I need for multi-product lines?
Request a DQ/IQ/OQ/PQ package (Design, Installation, Operational, Performance Qualification) plus FAT (Factory Acceptance Test) reports. Ensure the machine supports:
– Recipe management with ≤ 3 min changeover.
– CIP/SIP options for pharma and food.
– Validation guide aligned to FDA 21 CFR Part 11 or EU Annex 11.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
8. How do I evaluate ROI and justify the capital expenditure?
Use this simple model:
Annual savings = (Labor cost per 1,000 packs × volume) – (Machine depreciation + consumables).
Typical payback: 8–18 months for lines filling 1 M+ packs/year. Run a pilot trial with the OEM to validate cycle time, accuracy, and downtime claims before full purchase.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for powder filling machine
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion & Outlook – Powder Filling Machine
Key Takeaways
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) drives ROI; cheapest Asian line often costs 30 % more to maintain.
- Qualification checklist: CE / FDA validation, OEE ≥ 85 %, MTBF ≥ 8 000 h, IQ/OQ documentation.
- Lead-time compression via dual-sourcing: 60 % of capacity from EU rep-line, 40 % from APAC for surge orders.
Outlook 2025-2027
| Driver | Impact | Sourcing Action |
|---|---|---|
| AI-driven weight algorithms | ±0.1 % accuracy → 2 % material savings | Upgrade contracts with firmware inclusion |
| Sustainability regs (EU CSRD, US SEC) | CO₂ disclosure in BOM | Require carbon-footprint data from suppliers |
| Labor scarcity | 15 % wage inflation | Negotiate SLA for remote service & training |
Action Plan
- Q3 2024: Issue RFI to 3 EU integrators + 2 APAC OEMs.
- Q4 2024: Run pilot on 3 SKUs; lock in 3-year pricing.
- 2025 H1: Roll out predictive-maintenance sensors; target 20 % downtime reduction.
Bottom line: A disciplined, dual-sourcing strategy with embedded sustainability metrics will secure capacity, hit regulatory deadlines, and cut lifetime cost of ownership by 12-18 %.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.