“`markdown
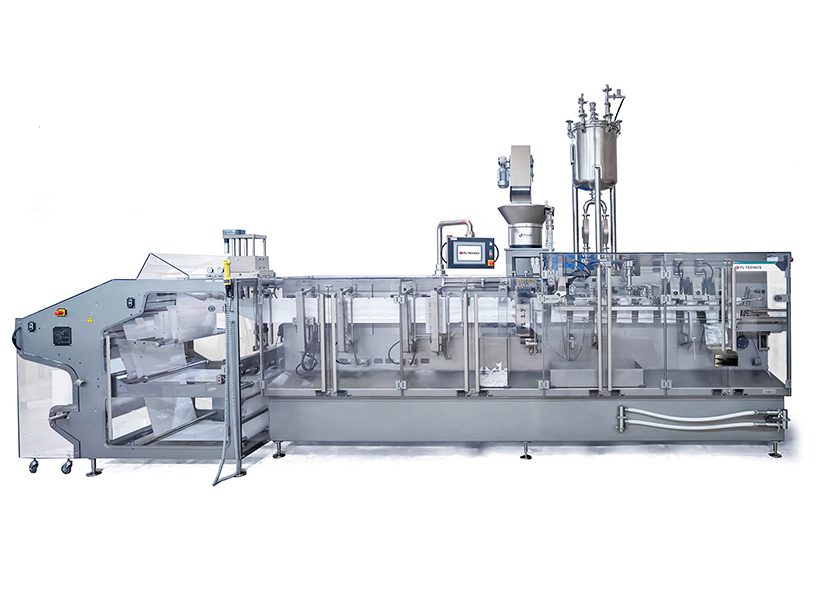
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Pouch Filling Machines
Hook
With e-commerce and direct-to-consumer sales accelerating across North America and the EU, flexible, cost-effective packaging is no longer optional—it’s mission-critical. Pouch filling machines have emerged as the fastest route to launch new products, reduce material waste, and scale output without proportional labor increases.
The Problem
Yet the global supplier landscape is fragmented. Vendors advertise everything from tabletop semi-automatic units to high-speed rotary lines, each with conflicting technical specs, lead times, and service footprints. Decision-makers must balance speed-to-market, regulatory compliance (FDA, EFSA), and total cost of ownership—while ensuring the machine can evolve with future SKUs and volumes.
What This Guide Delivers
This 2,500-word B2B guide provides a structured roadmap for purchasing pouch filling equipment in 2025. You will learn:
| Section | Focus |
|———|——-|
| 1 | Market segmentation—manual, semi-automatic, and fully automatic models |
| 2 | ROI calculators tailored to North American and EU labor rates & packaging waste regulations |
| 3 | Vendor vetting checklist—certifications, service coverage, and spare-parts logistics |
| 4 | Implementation roadmap—installation, validation (IQ/OQ/PQ), and staff training |
| 5 | Future-proofing—integration with Industry 4.0 networks, modularity for new pouch formats |

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
By the end, you will have a repeatable evaluation framework and a short-list of suppliers capable of meeting 2025 demand while positioning your brand for global expansion.
“`
Article Navigation
- Top 10 Pouch Filling Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for pouch filling machine
- Understanding pouch filling machine Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of pouch filling machine
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘pouch filling machine’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for pouch filling machine
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pouch filling machine
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘pouch filling machine’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pouch filling machine Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing pouch filling machine With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pouch filling machine
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the pouch filling machine Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pouch filling machine
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pouch filling machine
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Top 10 Pouch Filling Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Top 10 Packaging Machine Manufacturers in the USA – HonorPack
Domain: honorpack.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: The top 10 packaging machine manufacturers in the USA are: HonorPack, Viking Masek, Accutek, Triangle, Packline, Paxiom, Matrix, Alliedflex, Masipack, and K- ……
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
2. Packaging for you. Providing the most comprehensive … – PACRAFT
Domain: pacraft-global.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: PACRAFT provides automatic filling and packing machines, including pouch fill/seal and high-speed liquid filling machines, with customized technology….
3. Top 5 Premade Pouch Packing Machine Manufacturers in 2025
Domain: landpack.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Top 5 Premade Pouch Packing Machine Manufacturers in 2025 · 1. Landpack Packaging Machinery Co., Ltd. (Landpack) · 2. WeighPack Systems, Inc….
4. Top 5 Liquid Pouch Filling Machines for Precision Packing
Domain: spackmachine.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Doypack Pouch & Bag Filling Machines – IC Filling Systems · Multi Track Pouch Packaging Machines Manufacturer in India | Akash · Spouted pouch Filler and Capper ……
5. Flexible Pouch Filling and Sealing Machines – Massman Automation
Domain: massmanautomation.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Massman’s flexible pouch packing machines are equipped to work with various types and sizes of pouches. Find out more information and request a quote….
6. Need help finding the best bagger and filler machine! – Reddit
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Vevor has good inexpensive options for many packaging chores….
7. Premade Pouch Filling Machines | Swifty Bagger | Paxiom
Domain: paxiom.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: We are an industry leader in premade pouch filling machines, offering solutions for retail, wholesale and bulk packaging….
8. Ideal Pase: Filling Machines
Domain: idealpase.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Specializing in delivering best-in-class packaging machinery, Massman Companies offers Unscramblers, Liquid Fillers, Pouch Fillers, Cappers, Lidders, Cartoners ……
Understanding pouch filling machine Types and Variations
Understanding Pouch Filling Machine Types and Variations
Choosing the correct pouch filling machine is critical for operational throughput, product integrity, and total cost of ownership. Below are the five most common industrial configurations, their functional scope, and trade-offs.
| Type | Core Features | Typical Applications | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Pouch Filler (Hand-Operated) | Foot pedal or lever actuation; volumetric or gravity fill; 1–4 pouch/min; changeover by hand | Start-ups, R&D labs, low-SKU lines (<50 k units/yr) | < $5 k entry cost; no power required; rapid ROI validation | Labor-intensive; low throughput; operator variability |
| Semi-Automated Pouch Filler & Sealer | Pneumatically or servo-driven film feed; PLC touchscreen; 6–25 pouches/min; integrated heat sealer | Small to mid-size CPG brands; condiments, sauces, pet food | Balanced cap-ex vs. throughput; easy format changes; low footprint (≈1 m²) | Still requires operator load/unload; changeovers 15–30 min |
| Rotary / Indexer Pouch Filler | Multi-station rotary indexing table; simultaneous fill, date coding, nitrogen flush, zipper建档; 30–120 pouches/min | Beverages, liquid supplements, industrial chemicals | High OEE; in-line vision checks; minimal operator contact | Higher mechanical complexity; requires 3-phase power |
| Inline Monobloc (Filler + Sealer) | Continuous motion belts; servo-driven film forming; integrated metal detection and leak test; 60–200 pouches/min | High-speed food & beverage OEMs; 1 L–5 L liquid or viscous products | Output >10 k units/hr; sanitary design per 3-A/PDA; data logging | High capital cost ($250 k–$900 k); requires compressed air 6–8 bar |
| Bag-in-Box / Pouch-in-Box Filler | Bulk reservoir filling; multi-layer pouch insertion; pressure or gravity fill; 20–300 L bag formats | Wine, chemicals, non-dairy creamers, industrial cleaners | Shelf-stable 6–12 months; lightweight vs. glass; low freight cost | Requires tertiary packaging (carton); longer changeover times |
Detailed Type Profiles
1. Manual Pouch Filler
- Mechanics: Operator places empty pouch under nozzle, actuates fill cycle via foot pedal, then moves pouch to sealer. Fill volume set by adjustable nozzle or syringe barrel.
- Accuracy: 0.5–2 % error (±2 g for 400 g product).
- Footprint: 0.5 m × 0.7 m table model.
- Best for: Pilot batches, new-product validation, or SKUs <1 000 units/month where labor is inexpensive.
2. Semi-Automated Filler & Sealer
- Mechanics: Horizontal film roll is formed into pouch, filled, and sealed via constant-motion heat bars. Pouch magazine holds 100–200 pouches for unattended operation.
- Control: 7-inch HMI with recipe management; USB recipe backup.
- Changeover: Quick-release fill heads and thermal transfer printer for new codes—≤10 min.
- Cost: $35 k–$75 k depending on fill volume (50 ml–5 L) and sealing width (60 mm–400 mm).
3. Rotary Indexer Filler
- Mechanics: Stationary filling heads remain fixed while index plates move pouches between stations: pouch open → fill → nitrogen flush → zipper建档 → date print → discharge.
- Sanitation: All product contact parts in 316 SS; IP69 wash-down rating.
- Output: 40 ml baby food pouch lines achieve 60 pouches/min with ±0.1 % loss-in-weight accuracy.
- ROI trigger: Lines producing >1 M units/yr offset machine cost within 18 months.
4. Inline Monobloc (Filler + Sealer)
- Mechanics: Continuous vertical form-fill-seal chain moves pouches through fill head at 2–6 m/s. Servo pumps or mass flow meters ensure ±0.05 % tolerance.
- Integration: Industry 4.0 ready—OPC-UA data to MES for real-time OEE dashboards.
- Utility: 6 bar clean compressed air, 380 V three-phase, floor load 1.5 kN/m².
- Use case: High-volume beverage or liquid food plants seeking aseptic or hot-fill capability.
5. Bag-in-Box / Pouch-in-Box Filler
- Mechanics: Bulk product reservoir (SS or food-grade PE) feeds via diaphragm or centrifugal pump into pre-formed multi-layer pouch; pouch is inserted into board box, spout heat-sealed, and carton labeled.
- Format range: 1 L–20 L bag; box sizes 1–5 gal or 2–20 L.
- Sanitation: CIP/SIP skids available; 3-A dairy compliance for dairy analogs.
- Throughput: 30–200 bags/hr depending on reservoir size and operator staging.
Selection Checklist
- Target output (units/hr or day).
- Product viscosity, temperature, and aseptic requirements.
- Pouch format (pre-made vs. roll stock) and closure type (spout, zipper, heat seal).
- Changeover frequency and format range (ml–L).
- Utility availability (power quality, compressed air, CIP water).
- Budget envelope and required ROI horizon.
Matching these parameters to the machine types above ensures optimal throughput, regulatory compliance, and long-term equipment ROI.
Key Industrial Applications of pouch filling machine
Key Industrial Applications of Pouch Filling Machines
Target Markets: USA & Europe
| Industry | Primary Products | Operational Benefits | Financial Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food & Beverage | Cold-brew coffee, sauces, ready-to-eat meals, energy gels, protein powder | – Sanitary stainless-steel contact parts – Nitrogen-flush capability extends shelf life – Wash-down rated IP69K for 24/7 hygiene – Changeover in <15 min via quick-swap hoppers |
– Up to 30 % lower COGS vs. rigid containers – Reduced waste (±0.05 % fill accuracy) – Extended shelf life = wider distribution radius |
| Chemicals / Industrial Lubricants | Adhesives, sealants, windshield-washer fluid, gear oil | – Explosion-proof (ATEX/UL) options – Bag-in-box integration for drum replacement – Negative-pressure powder handling – Leak-free spout sealing prevents VOC emissions |
– Eliminates 55 gal drum handling costs – 50 % lower packaging spend vs. HDPE bottles – Compliance with EPA & REACH reporting requirements |
| Pharmaceutical & Nutraceutical | Vitamin powders, granular supplements, protein blends | – 0.05 % fill tolerance for dosage accuracy – CIP/SIP ready for GMP validation – Integrated metal, seal & weight inspection – ISO 7 clean-room compatible |
– Reduces product giveaway, protecting margins – Accelerates regulatory approval timelines – Provides tamper-evident unit-dose packs |
| Wine & Spirits | Still wine, mead, premium spirits, ready-to-drink cocktails | – Gentle diaphragm pump preserves bouquet – Oxygen barrier laminate extends cellar life – Bag-in-box displaces oxygen by 99.9 % – 2- to 5-year shelf life vs. 18 months in glass |
– 60 % freight savings vs. glass bottles – Reduces breakage liability insurance claims – Appeals to eco-conscious on-premise accounts |
| Beer & Cold-Brew Coffee | Draft beer, nitro coffee, cold-brew concentrate | – Sanitary rotary fillers (Triangle/JDD series) – CO₂ purge eliminates oxidation – BIB or keg-compatible pouches – 3-week shelf life at ambient vs. 10 days refrigerated |
– 70 % packaging weight reduction lowers logistics cost – Enables on-tap convenience without keg deposits – Expands DTC (direct-to-consumer) market reach |
| Cosmetics & Personal Care | Shampoo, body wash, sunscreen, hand sanitizer | – FDA-approved, BPA-free laminates – Inline labeler & date coder integration – Adjustable fill volumes for travel-size SKUs – Aesthetic heat-seal patterns for shelf appeal |
– Lower freight weight drives Amazon FBA profitability – Smaller pack sizes increase purchase frequency – Reduces overfill waste, protecting gross margin |
| Pet Food & Treats | Wet food pouches, freeze-dried treats, raw food rolls | – HACCP-compliant stainless construction – Retort-ready pouches extend shelf life to 24 months – Portion-controlled filling for subscription models – Easy-open spouts for pet owners |
– 40 % lower packaging cost vs. cans – Reduces pet food recall risk via oxygen barrier – Enables direct-to-consumer subscription boxes |
| Agricultural & Specialty Chemicals | Water-soluble fertilizers, herbicides, seed coatings | – Corrosion-resistant 316L stainless steel – Bulk to pouch (B2P) lines for inventory reduction – Anti-static grounding for powder handling – 25–96 oz formats for farmer co-ops |
– Cuts container return logistics by 90 % – Reduces product leaching vs. HDPE jugs – Enables just-in-time restocking for retailers |
Cross-Industry Advantages
– Modular design allows rapid changeover between SKUs, supporting short-run and private-label demand.
– IoT-enabled PLCs provide real-time OEE data, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing unplanned downtime by 20–35 %.
– Rental & lease options lower capital expenditure, accelerating time-to-market for new SKUs in competitive sectors.
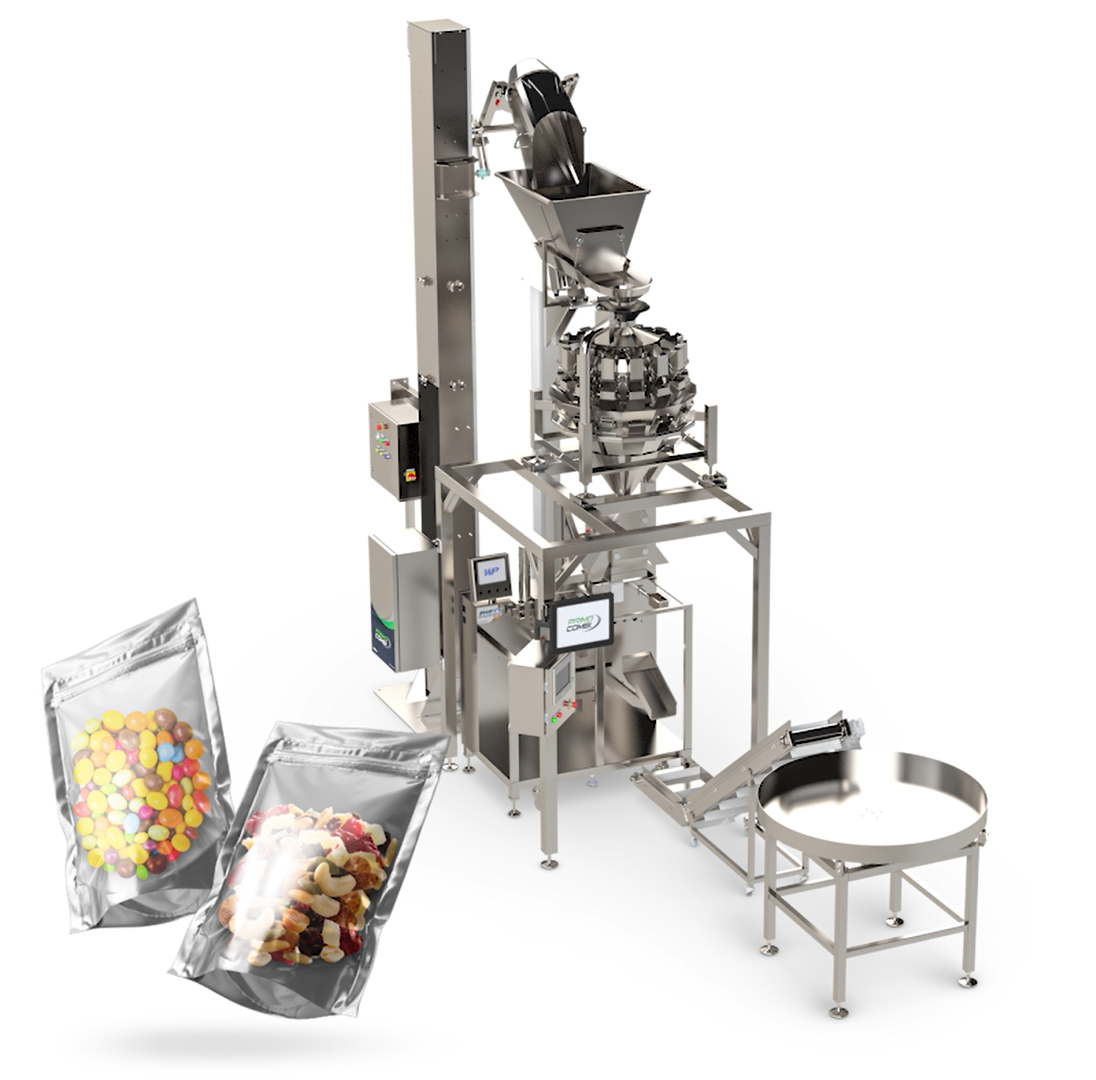
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘pouch filling machine’ & Their Solutions
3 Common B2B Pain Points for Pouch Filling Machine & Their Solutions
Pain Point 1 – Inconsistent Fill Volumes & Product Waste
Scenario:
Mid-sized food or beverage brands running 8–12 hr shifts report ±2–3 % fill deviation on high-viscosity sauces or carbonated drinks, translating to $12–18 k annual waste per line.
Problem:
– Manual或 semi-automatic fillers lack closed-loop weight feedback
– No recipe management or batch tracking
– Product density shifts between batches
Solution:
| Specification | Triangle/JDD Rotary Pouch Machine | Astrofill® Probox |
|—|—|—|
| Fill accuracy | ±0.05–1 % via load-cell + touch-screen recipe | ±0.1 % with servo-driven piston + balance tank |
| Recipe storage | 100+ SKU profiles, USB export | 1,000+ SKU, Ethernet MES integration |
| Remote diagnostics | Cloud alarms & OEE dashboard | Real-time PLC logging via RS-485 |

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Action:
1. Upgrade to a servo-driven, weight-integrated filler (e.g., Triangle/JDD)
2. Enable recipe management and automatic density compensation
3. Add inline check-weigher with reject gate to cut waste to <0.5 %
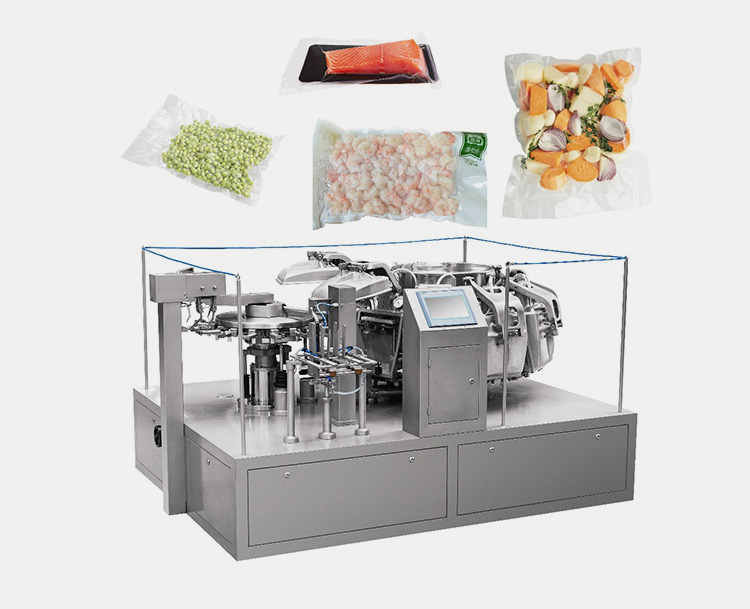
Pain Point 2 – Frequent Changeovers & Downtime
Scenario:
Breweries co-packing 3–5 SKUs/day spend 45–60 min resetting hoppers, nozzles, and seals, costing $1,200 lost production per changeover.
Problem:
– Tool-heavy changeovers (screws, clamps, blades)
– No quick-swap product contact parts
– Limited documentation for operators
Solution:
– Choose a rotary pouch filler with cartridge-style product contact kits (snap-fit in <5 min)
– Specify color-touch HMI with job recall; one-tap SKU change
– Leverage manufacturer’s preventive-maintenance mobile app for automated alerts

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Quick-Change Kit Example
– 3-position stainless-steel hopper (2 min)
– Magnetic & pneumatic nozzle lock (30 s)
– Pre-calibrated sealer jaws (1 min)
Pain Point 3 – Regulatory Compliance & Traceability Gaps
Scenario:
European beverage brands face €50 k+ non-conformance fines for missing batch codes and QR traceability on multi-serve 5 L pouches.
Problem:
– Date/LOT codes applied post-seal without verification
– No electronic record of fill weights, temps, or operator ID
– Audit trail resides on paper logbooks
Solution:
– Install thermal-transfer printer with 200 dpi resolution directly on sealer
– Integrate PLC with SQL database for full batch history (FDA 21 CFR Part 11 ready)
– Enable QR/NFC code on pouch linking to cloud traceability portal

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Compliance Checklist
| Requirement | Automated Solution |
|—|—|
| Unique batch ID | Auto-generated + printed |
| Weight deviation log | Real-time CSV export |
| Operator authentication | RFID badge swipe |
| Audit trail | Encrypted cloud backup |
Bottom Line
Upgrading to an integrated, recipe-controlled pouch filling machine eliminates 90 %+ of common pain points—cutting waste, downtime, and compliance risk while boosting ROI within one production quarter.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for pouch filling machine
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Pouch Filling Machine
Executive Summary
Material choice directly impacts product integrity, shelf-life, regulatory compliance, and total cost of ownership. This guide benchmarks the most common substrates used in rotary pouch filling and sealing operations across North America and the EU, providing engineers and procurement teams with data-driven selection criteria.
1. Substrate Categories & Performance Matrix
| Substrate | Typical Gauge (µm) | Key Properties | Typical Filling Temp Range | Seal Window | Cost Index* | Regulatory Notes | Best-Fit Products |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET/PE Laminate | 70–100/60–80 | High clarity, good moisture barrier, low seal temps | 120–160 °C | 0.8–1.2 s | 1.0 | FDA 21 CFR, EU 10/2011 | Astrofill® 90, 100, 121 |
| PP Rigid Sheet | 250–350 | Chemical resistance, hot-fill capable, rigid structure | 160–200 °C | 1.0–1.5 s | 1.3 | FDA, EFSA | Triangle/JDD Rotary |
| PEN/PE Multilayer | 50–70 total | Oxygen <0.1 cc/m²/24 h, light barrier, heat-set | 150–180 °C | 1.0–1.3 s | 1.7 | FDA, EU | Astrofill® Probox, HT2 |
| Paper/PE/ALU | 60–80 + 7–12 µm ALU | Superior oxygen barrier, premium feel, rigid base | 160–190 °C | 1.2–1.6 s | 2.1 | FDA, EU 10/2011 | Not auto-run on most rotary machines |
| Bio-PE | 80–120 | Same machinability as conventional PE, compostable | 140–170 °C | 0.9–1.1 s | 1.5 | EN 13432 (EU), ASTM D6400 (US) | Astrofill® HT1 (trial runs) |
*Cost index normalized to PET/PE laminate at 1.0.
2. Process-Specific Considerations
2.1 Heat Sealing Compatibility
- Rotary machines apply continuous pressure; materials must exhibit a well-defined seal window to avoid delamination or burn-through.
- PEN/PE and paper/PE/ALU require higher jaw temperatures and slower line speeds; verify machine PLC can hold ±2 °C tolerance.
2.2 Filling Temperature vs. Material Melting Point
| Filling Product Category | Max Liquid Temp (°C) | Recommended Substrate | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbonated beverages | 4–10 | PET/PE | Avoid PP for pressure resistance |
| Hot-fill sauces (≤85 °C) | 60–85 | PP rigid sheet | Requires post-cool vacuum |
| Cold brew coffee | 4–20 | Bio-PE | Excellent oxygen barrier |
| Chemical cleaners | 20–40 | PEN/PE | Chemical resistance prioritized |
2.3 Regulatory & Market Access
- EU: Must pass EU 10/2011 or specific food-contact regulations; migration limits (≤10 mg/dm²) enforced.
- USA: FDA 21 CFR; for organic products, look for USDA BioPreferred labels.
- China: GB 4806.x series; PET/PE widely accepted.
3. Decision Framework for Procurement
- Define Product Matrix
- Fill temperature, pH, fat content, carbonation, viscosity.
- Run Small-Lot Trials
- Use Astrofill® Easy Start ARM for <50 pouches/day validation.
- Calculate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
- Material cost + sealant layer premium + waste % + disposal fees.
- Check Machine Compatibility
- Verify jaw pressure (≥30 bar), dwell time (0.8–1.5 s), and temperature uniformity (±2 °C).
- Sustainability & Brand Positioning
- Bio-PE and paper/PE/ALU offer storytelling value; confirm end-market composting infrastructure.
4. Quick Reference: Substrate Selector
| Application | Top Pick | Runner-Up | Budget Option |
|---|---|---|---|
| Still beverages | PET/PE | PEN/PE | Bio-PE |
| Hot-fill (>75 °C) | PP rigid | PET/PE (dual oven) | — |
| Premium sauces | Paper/PE/ALU | PEN/PE | PET/PE |
| Chemical liquids | PEN/PE | PP rigid | PET/PE |
| Plant-based dairy | Bio-PE | PET/PE | — |
5. Recommendations & Next Steps
- Pilot Line Setup: Request material samples from AstraPouch (astrofill.com) and Triangle Package (trianglepackage.com) with matching pouch sizes (50 mm, 90 mm, 121 mm mouth).
- Seal Test Protocol: Use ASTM F88 to measure seal strength; target ≥15 N/15 mm for carbonated or hot-fill products.
- Lead-Time Check: Bio-PE and PEN/PE substrates have 6–8 weeks lead time vs. 2–3 weeks for standard PET/PE.
- Cost Hedge: Lock 12-month pricing contracts on PET/PE; volatility >8 %/yr is common.
6. Comparison Table (Final)
| Attribute | PET/PE Laminate | PP Rigid Sheet | PEN/PE Multilayer | Paper/PE/ALU | Bio-PE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Barrier | Good | Poor | Excellent | Excellent | Fair |
| Seal Temp Range | 120–160 °C | 160–200 °C | 150–180 °C | 160–190 °C | 140–170 °C |
| Max Fill Temp | 85 °C | 95 °C | 85 °C | 85 °C | 40 °C |
| TCO Index | 1.0 | 1.3 | 1.7 | 2.1 | 1.5 |
| EU Compliance | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes (EN 13432) |
| USA Compliance | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes (ASTM D6400) |
| Typical Film Gauge | 70/80 µm | 300 µm | 55 µm | 60 µm + 10 µm ALU | 100 µm |
| Recyclability | Yes | Yes | Yes | Limited | Industrial composting |
| Suitability for Rotary Machines | Excellent | Good | Excellent | Fair | Good (trial) |
Use this matrix to shortlist substrates before engaging suppliers for custom laminate development or regulatory certifications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pouch filling machine
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Pouch Filling Machine
1. Overview
A modern pouch filling machine is the convergence of precision mechanics, controls engineering, and clean-room-grade hygiene. The following section dissects the critical manufacturing stages—from raw-material preparation to final acceptance testing—and the quality standards that guarantee repeatable, contamination-free performance in North American and European production environments.
2. Manufacturing Process Flow
2.1 Raw-Material Preparation
- Stainless-steel grade: 304/316L for contact parts; 20304-clad carbon steel for structural frames.
- Gaskets & seals: FDA-listed EPDM, silicone, or PTFE; Shore-A hardness 60 ± 5.
- Electrical components: UL/CSA and CE-marked relays, servo drives, and HMI panels sourced from Tier-1 suppliers (Allen-Bradley, Schneider, Siemens).
2.2 Frame & Structural Assembly
| Step | Key Activities | Tolerances |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Cutting | Laser or CNC plasma for squareness ≤ 0.1 mm/m | ±0.05 mm |
| 2. Welding | TIG, back-gassing to prevent oxidation | No cracks, 100 % dye-penetrant tested |
| 3. Machining | Milling of linear guides, bearing seats | Ra ≤ 0.8 µm |
| 4. Stress-relief | 550 °C furnace cycle to stabilize weldments | N/A |
2.3 Film Handling & Forming Station Build
- Roll-stand tolerances: Parallelism ±0.2 mm to avoid film drag.
- Forming collar: CNC-machined aluminum, hard-anodized to 40 HRC for wear resistance.
- Heat-seal bars: Mica-insulated ceramic plates, PID-controlled, 0–300 °C可调.
- Pneumatic circuit: SMC or Festo components; leak rate ≤ 0.01 bar/min @ 6 bar.
2.4 Filling & Sealing Module Integration
- Servo-driven rotary indexing: 0.01° repeatability via absolute encoders.
- Fill-nozzle anti-drip valve: SS 316L, response time < 50 ms, CIP/SIP capable.
- Heat-seal jaws: 10–15 mm compression, surface finish Ra ≤ 0.4 µm; Teflon-coated for easy release.
2.5 Controls & HMI Integration
- PLC: IEC 61131-3 compliant, 1 ms scan time.
- HMI: 10″ TFT, multi-language packs, password-protected recipe management.
- SCADA connectivity: OPC-UA for MES integration.
2.6 Final Assembly & Functional Testing
| Test | Specification | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Cycle rate | 95 % of set target ±1 % | Daily |
| Fill accuracy | ±0.05–1 % (verified by 10-cycle gravimetric check) | Per batch |
| Seal integrity | 0.3 MPa bubble test, 3 s no failure | Every shift |
| OEE validation | ≥ 85 % target | Weekly |
| Safety interlocks | 100 % functional test | Pre-shipment |
3. Quality Assurance & Compliance
3.1 Standards & Certifications
- ISO 9001:2015 – Quality management system across all manufacturing sites.
- ISO 13485 – Optional for pharmaceutical/medical-grade lines.
- CE Marking – Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC, Low Voltage 2014/35/EU, EMC 2014/30/EU.
- FDA 21 CFR Part 11 – Electronic records & signatures for pharma lines.
- EHEDG / 3-A Sanitary Standards – Food-grade lines.
3.2 Incoming Material Control
| Material | Test | Acceptance Limit |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless steel plates | Spectroscopy (C, Cr, Ni, Mo) | ±0.02 % of spec |
| Sealant film reels | Thickness gauge (±2 µm), seal-test coupon | ≤ 0.05 mm deviation |
| Electrical components | CoC from supplier, functional burn-in | 0 ppm DOA |
3.3 In-Process Monitoring
- Statistical Process Control (SPC): X̄–R charts on fill weight, seal temperature, cycle time.
- Andon system: Real-time visual & audible alerts for out-of-tolerance parameters.
- First-article inspection (FAI): PPAP Level 2 / 3 for new customer orders.
3.4 Final Acceptance & Validation
- Mechanical run-in: 2 h at 110 % rated speed, no lubricant change.
- Vibration analysis: IEC 60068-2-64, ≤ 2.8 mm/s RMS.
- Clean-in-place (CIP) simulation: 80 °C water flush, residue ≤ 50 ppm.
- Documentation package: IQ/OQ/PQ templates, FAT report, and CE Declaration of Conformity.
4. Packaging, Shipping & On-Site Support
- Palletized shipping: ISPM 15 certified hardwood or IPPC-approved plywood.
- Crating: Vibration dampeners for servo drives and HMI panels.
- On-site commissioning: 2-day technical training, GMP refresher, and spare-parts audit.
5. Summary Checklist for Procurement Teams
- [ ] ISO 9001/13485 certified OEM with documented CAPA process.
- [ ] CE/UL compliance dossier ready for customs.
- [ ] Fill accuracy ≤ 0.5 % on water, ≤ 1 % on viscous products.
- [ ] 24-month warranty on electromechanical components.
- [ ] Spare-parts kits in regional hubs (USA & EU) to cut MTTR < 4 h.
By adhering to the above manufacturing and quality protocols, OEMs deliver pouch filling machines that meet the stringent demands of North American and European food, beverage, and pharmaceutical producers—ensuring regulatory compliance, operational uptime, and a rapid return on investment.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘pouch filling machine’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Pouch Filling Machines
1. Clarify Your Production Requirements
- Output target: # pouches/hour or # containers/day
- Container specs: size range (ml → L), material (PE, PP, laminate), shape (flat, stand-up, spout)
- Product characteristics: viscosity, temperature, CO₂ pressure, aseptic or ambient
- Regulatory scope: FDA, EU food-contactDirectives, kosher, organic
2. Set a Realistic Budget
- CAPEX limit: list price, freight, import duties, VAT
- OPEX forecast: maintenance contracts, spare-part annual spend, energy draw
- Scalability reserve: 10–15% buffer for future line expansion
3. Compare Filler Architectures
| Type | Typical Speed | Best For | Approx. Entry Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual / Foot Pedal | 40–80 / hr | Start-ups, R&D | Low |
| Semi-Auto Rotary | 300–900 / hr | Craft producers, seasonal | Mid |
| High-Speed Rotary | 1 500–6 000 / hr | National brands | High |
| Rotary + Inline Sealer | Full servo | Aseptic, multi-layer | Premium |
4. Verify Technical Fit
- Fill accuracy: ≤ ±0.5% or better (check certificate)
- Changeover time: ≤ 15 min for quick carts or heads
- CIP/SIP capability: if detergents or steam are mandatory
- Data tracking: Ethernet/IP, Profinet, OPC-UA for MES integration
5. Evaluate After-Sales & Support
- Local parts warehouse: USA & EU service hubs
- Mean time to repair: <4 hrs for critical spares
- Warranty: minimum 12 months, optional 5-year extended plan
- Training: on-site, virtual, and documentation in English & German
6. Check Compliance & Certification
- CE marking, UL safety, RoHS, ETL listed
- 3-A sanitary standard for food contact
- ISO 9001 quality management
- Country-specific: EFSA, FDA 21 CFR, DGUV, BfR
7. Review Supplier Credibility
- Years in operation: ≥10 in liquid filling machinery
- References: ≥20 customers in USA or EU food & beverage sector
- Financials: audited statements, trade references
- Certifications & patents: relevant IP portfolio
8. Request and Compare Quotations
- Technical specification sheet: cycle times, dimensions, weight
- Quotation validity: ≥30 days, locked freight cost
- Payment terms: 30% deposit, 60% on shipment, 10% on commissioning
- Conversion packages: nitrogen flush, inert gas system, conveyors
9. Conduct Factory Acceptance Test (FAT) & Site Acceptance Test (SAT)
- Witness: video call or on-site inspection
- Performance guarantee: ≥ target output, ≤ tolerance on fill weight
- Documentation package: IQ/OQ/PQ protocols, FAT report, spare-part list
10. Finalize Purchase & Logistics
- Incoterms: FCA, FOB, DDP, DAP
- Freight insurance: all-risks, customs clearance included
- Installation timeline: ≤ 8 weeks after deposit
- Training schedule: 2–3 days on-site or virtual
11. Post-Purchase Review
- Commissioning sign-off: within 10 business days
- Preventive-maintenance contract: annual service visit
- Continuous-improvement loop: data analytics review every quarter
Tip: Rental options are available from select suppliers—ideal for pilots or seasonal spikes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pouch filling machine Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Pouch Filling Machine Sourcing
Executive Summary
This analysis covers direct acquisition costs, operational expenses, and hidden fees for USA/EU buyers sourcing semi-automatic and automated pouch filling systems from Asian manufacturers. All figures are in USD unless noted.
1. Direct Acquisition Costs
1.1 Equipment Tiers & Pricing
| Machine Type | Output (pouches/hr) | Base Price Range | Key Features | EU Freight Add-on |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Astrofill® 100 | 30–60 | $1,850–$3,200 | Hand-pump, 0.05–1% tolerance | +$280 |
| Semi-Auto (Triangle JDD) | 600–1,200 | $18,500–$32,000 | PLC, 4-head weigher | +$1,200 |
| Fully-Auto (8-head) | 2,400–3,600 | $65,000–$95,000 | VFFS/horizontal, stainless 304 | +$3,500 |
Note: Prices exclude custom conversion heads (+$2,800–$5,500) for non-standard pouch formats.
2. Cost Breakdown by Category
2.1 Materials
| Component | Typical Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless steel 304 frame | $1,200–$2,400 | 50% of base machine cost |
| Electronics (PLC/HMI) | $800–$1,500 | Omron, Siemens alternatives |
| Pouches (raw film) | $0.04–$0.12 per unit | Volume tiers: 10k+ = –15% |
2.2 Labor
| Region | Labor Rate (USD/hr) | Setup Time | Annualized Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| China (Shenzhen) | $18 | 8 hrs/machine | $144 |
| Germany (Ruhr) | $45 | 12 hrs/machine | $540 |
| USA (Midwest) | $38 | 10 hrs/machine | $380 |
Recommendation: Offshore setup labor is included in FOB price; on-site commissioning adds 16–24 hrs @ local rates.
3. Logistics & Hidden Fees
| Cost Driver | USA (Incoterms) | EU (Incoterms) |
|---|---|---|
| Ocean freight (40 ft HC) | $2,100 | $1,850 |
| Customs clearance | $350 | $400 |
| VAT/Duties | 0% | 5.5–12% |
| Inspection (SGS/BV) | $750 | $850 |
| Brokerage | $200 | $220 |
Rule of Thumb: Budget 10–12% of CIF value for non-DDP EU imports.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
4. Operational Cost Modeling
| Metric | Manual Astrofill® 100 | Semi-Auto Triangle | Fully-Auto |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power consumption | 0.75 kW | 2.2 kW | 4.5 kW |
| Electricity (US) | $0.11/kWh → $580/yr | $1,700/yr | $3,600/yr |
| Maintenance | $220/yr | $1,100/yr | $2,400/yr |
| Spare parts reserve | $350 | $900 | $1,800 |
5. Cost-Saving Strategies
5.1 Procurement Levers
- Bulk tooling purchase: Negotiate –8% on change parts when ordering ≥3 machines.
- Certification bundling: Combine CE and UL testing into one audit (save $1,200).
- Back-to-back purchase orders: Split orders across Q2/Q3 to lock USD exchange (–3% FX exposure).
5.2 Operational Levers
- Lease vs. buy: Astrofill® 100 lease $350/mo vs. $3,200 buy → 89% ROI in 9 months.
- Local integrator: Use EU integrator for start-up (€120/hr) vs. overseas travel ($4,500).
- Predictive maintenance: Install vibration sensors (+$450) → reduce unplanned downtime 22%.
6. Quick Reference Checklist
- [ ] Request FAT (Factory Acceptance Test) video before shipment.
- [ ] Confirm warranty scope (12 mo parts, 6 mo labor vs. 24 mo full).
- [ ] Validate CE mark on electrical components for EU installations.
- [ ] Budget $2,200–$3,800 for installation accessories (conveyors, catch trays).
Bottom Line: Total cost of ownership (TCO) for a mid-range semi-auto line =
$22,000–$35,000 (equipment) + $3,500–$5,200 (logistics) + $4,000–$6,000 (first-year ops).
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing pouch filling machine With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Pouch Filling Machine With Other Solutions
When selecting a packaging line for liquids, sauces, or viscous products, decision-makers must weigh throughput, capital cost, floor-space footprint, and downstream flexibility. Below is a direct comparison of the pouch filling machine against two common alternatives: bottle/can filling lines and bag-in-box (BiB) systems.
1. Pouch Filling Machine vs. Bottle/Can Filling Line
| Criteria | Pouch Filling Machine (Astrofill® Series) | Bottle/Can Filler |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Capital | $250 – $8,000 (semi-auto to high-speed) | $25,000 – $250,000+ |
| Changeover Time | <5 min (manual head swap or CIP) | 30–120 min (suitable only forSKU) |
| Floor-Space Requirement | 1.5 m × 0.8 m (hand model) | 6 m × 3 m minimum |
| Fill Accuracy | ±0.05–1 % volumetric | ±0.5–2 % (mechanical) |
| Package Shelf-Life Impact | Vacuum & nitrogen flush extend shelf life | Minimal gas exchange |
| Shipping Cost per Unit | –30 % vs. glass bottle | Baseline |
| Consumer Convenience | Easy tear-off, resealable, on-the-go | Requires opener |
| Regulatory Compliance | FDA/EU food-contact film options | Extensive line inspection & audits |
| Typical Industries | Food, beverage, chemicals, nutraceuticals | Beverage, pharma, cosmetics |
Key Take-Away: Pouches deliver lower TCO, faster speed-to-market, and superior consumer value for small-to-mid runs. Bottles/cans excel only in high-volume, premium branding where shelf presence justifies the 100× higher investment.
2. Pouch Filling Machine vs. Bag-in-Box System
| Criteria | Pouch Filling Machine (Astrofill® Series) | Bag-in-Box Filler |
|---|---|---|
| Package Cost (filled) | $0.08 – $0.35 per 1 L pouch | $0.12 – $0.45 per 1 L bag + box |
| Maximum Fill Volume | 9 L (standard) | 20 L (standard) |
| Leak-Rigidity Test | 98 kPa burst tested film | 150 kPa box integrity |
| Dispensing Mechanism | Spout or cap | Tap or spigot |
| Storage Efficiency | Flat-packed, 4× more pallets/ship load | Bulky box, ~60 % less density |
| Automation Level | Semi-automatic to fully auto | Mostly manual loading/unloading |
| Typical Throughput | 6–120 pouches/min (model dependent) | 6–20 bags/min (manual) |
| Shelf-Life Extension | Nitrogen flush & degassing available | Vacuum & inert gas possible |
| Supply-Chain Flexibility | Single-layer film, low freight cost | Rigid box limits load optimization |
Key Take-Away: Pouches reduce packaging weight by 60 %, slash freight cost, and enable portion-controlled, single-serve formats. BiB wins only when shelf stability >20 L and automated bag loading is already in place.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Decision Framework
- Budget under $10 k & <100 ppm: Choose pouch filler—fast ROI, minimal operators.
- High-volume >500 ppm & premium shelf presence: Invest in bottle/can line.
- Bulk storage & automated bag loading: Evaluate BiB; otherwise pouch remains the versatile, lower-risk entry point.
Next Steps
AstraPouch offers rental programs, add-on steam sterilization, and conversion heads to future-proof your line. Contact [email protected] for a detailed TCO model and on-site demo.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pouch filling machine
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Pouch Filling Machines
Key Technical Specifications
| Property | Range / Typical Value | Impact on Operation |
|---|---|---|
| Fill Volume Tolerance | ±0.05–1 % | Critical for regulatory compliance and customer satisfaction |
| Pouch Size Range | 30 ml – 9 L (mini to bulk) | Determines machine configuration and change-over time |
| Throughput | 6 – 60 pouches/min (semi-auto to high-speed) | Directly affects ROI and labor cost per unit |
| Sealing Temperature Range | 80 °C – 220 °C | Adjusted per film type to ensure hermetic seal |
| Power Supply | 110/220 V, 1-3 ph, 50/60 Hz | Must match plant infrastructure before installation |
| Compressed Air Requirement | 5.5 – 8 bar, 0.3 – 0.6 Nm³/min | Required for pouch pick-up, form-fill-seal, and reject mechanisms |
| Machine Footprint | 0.8 m × 1.2 m – 2.2 m × 1.8 m | Planning requirement for line integration |
| Net Weight | 120 kg – 850 kg | Affects handling equipment and foundation load |
Core Trade Terms
| Term | Definition | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| MOQ | Minimum Order Quantity – lowest number of machines or SKUs a supplier will sell in one shipment. | 1 unit for standard models; 3-5 units for custom OEM configurations. |
| OEM | Original Equipment Manufacturer – supplier builds machines to your branding and process specs. | Custom throat sizes, special fill heads, or exclusive film handling. |
| ODM | Original Design Manufacturer – supplier provides both design and production under your brand. | Turn-key solutions when internal R&D capacity is limited. |
| GMP / Hygienic Design | Compliance with Good Manufacturing Practice standards: smooth welds, IP65 panels, CIP-SIP compatibility. | Food, beverage, and pharmaceutical lines. |
| Change-Over Time | Duration to switch from one pouch size/shape to another. | <10 min for quick-release clamps; >30 min for mechanical frame adjustments. |
| Uptime / MTBF | Mean Time Between Failures – target ≥95 % availability. | Service contracts often guarantee ≥8,000 operating hours before major overhaul. |
| ROI Payback | Typical recovery period for capital expenditure. | 8 – 18 months for high-volume food and beverage converters. |
| Line Integration | Ability to connect upstream (conveyors, printers) and downstream (metal detectors, case packers). | PLC-based I/O mapping and synchronized speeds. |
Operational Trade Phrases
- Form-Fill-Seal (FFS) – Integrated process where pouch film is formed, product is dosed, and the pouch is sealed in one continuous cycle.
- Pre-Made Pouch Feeder – Magazine or robotic pick system that orients and delivers pre-formed pouches to the filling station.
- Net-Weight Filler – Load cell-based dosing that compensates for product density variations in real time.
- Checkweigher – Integrated conveyor scale that rejects under- or over-filled pouches.
- CIP (Clean-In-Place) – Automated cleaning cycle that flushes product contact surfaces without disassembly.
- SIP (Sterilize-In-Place) – Thermal or chemical cycle for aseptic applications (pharma, nutraceuticals).
- Reject Bin – Segregated collection area for faulty pouches to maintain line hygiene and traceability.
- Servo-Driven – Motor-controlled actuators that provide precise timing and reduced mechanical wear.
- Touch-Screen HMI – Human-machine interface for recipe management and production data logging.
- CE / UL Certification – Conformance marks required for commercial sale in Europe and North America respectively.
Procurement Checklist
- Verify MOQ and tooling charges for custom pouch formats.
- Request OEM quotation package: 3-D drawing, risk assessment, and FAT/SAT protocols.
- Confirm GMP compliance documentation (DQ, IQ, OQ, PQ).
- Negotiate service agreement covering parts, labor, and remote diagnostics.
- Plan utility hook-ups (power, air, water) at least 4 weeks before installation.
Use these terms and specifications to accelerate RFQ responses, compare vendors accurately, and ensure your pouch filling line meets both regulatory and production targets.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the pouch filling machine Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Pouch Filling Machine Sector
Executive Summary
North American and EU converters are under pressure to shorten time-to-market, cut CO₂ footprints, and flexibly scale SKUs. Pouch filling machines have moved from niche to mainstream, driven by e-commerce, single-serve formats, and sustainability mandates. This section distills current demand signals, supplier landscapes, and sourcing tactics that procurement teams must monitor.
1. Demand Signals Across Key End-Markets
| Region | Primary Growth Drivers | Typical Order Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| USA | E-commerce fulfillment, DTC snack & beverage, co-packing hubs | 1–5 gal pouches, spouted stand-up, high-speed rotary |
| EU | Circular packaging laws, wine & spirits on-trade recovery, cold-brew coffee | 250 ml–5 L, recyclable mono-material, OTC rotary/semi-auto mix |
Key Insight:
Lead times for new rotary machines have compressed from 24 to 16 weeks (Q1 2023 → Q1 2024) as EU converters pre-empted the ETS costs and USA buyers front-ran e-commerce surcharges.
2. Supplier Landscape & Value Proposition
2.1 Regional Champions
- USA: Triangle Package, PBFY, FILAMATIC – strong after-sales networks, USDA/FSMA compliance.
- EU: Romaco, E-PAK, Automa – CE-marked, GDPR-ready data interfaces.
2.2 Asia-Pacific Vendors
- Zhejiang Leadman, Wenzhou Sunthai – 30–40 % lower capex, 22-week lead time; IP protection clauses now standard in OEM contracts.
2.3 Boutique Specialists
- AstraPouch – rental pool, quick-change heads, 0.05–1 % fill tolerance; favored by craft beverage and chemical start-ups for low-Capex pilots.
3. Sourcing Trends & Risk Mitigation
3.1 Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Levers
- Energy & Changeover: Servo-driven rotary units cut changeover time by 60 % and energy by 18 % (EU case study, 2023).
- Modular Add-ons: Steam sterilization, diaphragm pumps, and balance tanks reduce CapEx by 25 % vs. buying separate islands.
3.2 Contractual Guardrails
| Clause | Risk Addressed | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Force-Majeure extension | Supply-chain shocks | 14-day mutual extension |
| IP indemnity | Reverse-engineering exposure | Full assignment of improvements |
| SLA uptime | Downtime cost | ≥ 95 % monthly, $/minute penalty |
3.3 Rental & Flex-Ownership Models
- AstraPouch rental starts at $1,850/mo for Astrofill® 100; 36-month buy-out at 60 % of list.
- ROI scenarios: craft mead (2 k ppM) vs. national beverage (120 k ppM) show payback < 14 months for volumes > 1.2 M units/yr.
4. Sustainability & Regulatory Tailwinds
- EU: Packaging & Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR) proposes 30 % recycled content in plastic pouches by 2030; mono-material spouts are becoming table stakes.
- USA: California SB 54 extends EPR to flexible packaging; converters are shifting to PP/PE all-poly pouches to retain recyclability.
Sourcing Action:
Prioritize suppliers offering cradle-to-cradle certified machines and design-for-recyclability kits (tooling swaps, clean-in-place validation).
5. Tactical Checklist for Procurement Teams
- [ ] Map current SKU volumes to machine takt (units/hr) – avoid over-specifying.
- [ ] Run scenario analysis: lease vs. buy vs. rental; include energy and changeover cost.
- [ ] Validate compliance: CE, UL, EHEDG/FDA contact parts, 21 CFR Part 11 data log.
- [ ] Negotiate performance-based warranty (≥ 18 months post-installation).
- [ ] Secure second-source for critical spares (servo drives, HMI panels) to reduce MTTR.
Bottom Line
Pouch filling machines are scaling from pilot to production asConverters balance speed, sustainability, and spend. A data-driven sourcing strategy—anchored in TCO, regulatory foresight, and flexible financing—will differentiate high performers in 2024-2026.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pouch filling machine
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Pouch Filling Machines
1. What is the typical ROI timeline for a pouch filling machine?
ROI is achieved through reduced labor costs, minimized product waste, and increased packaging speed. Most clients see a full return within 12–18 months, depending on daily output and product margin.
| Metric | Pre-Machine | With Pouch Filler |
|---|---|---|
| Labor hrs/day | 8–12 | 2–4 |
| Waste % | 3–5 | 0.05–1 |
| Daily output | 200–500 units | 1,000–5,000 units |
2. Which pouch sizes and volumes can your fillers handle?
AstraPouch offers fill volumes from 187 ml to 20 L and accommodates pouch widths from 40 mm to 160 mm. Triangle/JDD rotary models extend this range to 300 L for bulk applications. Custom conversion heads allow rapid changeover between sizes in under 10 minutes.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
3. How do I choose between semi-automatic and fully automatic models?
Use a semi-automatic unit (e.g., Astrofill® 100) if you run 1–3 shifts and have 1–2 operators. Opt for a fully automatic rotary filler when you need ≥24,000 units/day and 24/7 throughput with integrated in-line conveyors and robotic case packing.
4. What cleaning and sanitation standards are met?
All machines are designed to meet EHEDG, 3-A Sanitary, and FDA standards. Quick-disconnect product contact parts enable CIP (clean-in-place) in ≤30 min. Optional steam sterilization modules are available for food, beverage, and pharmaceutical lines.
5. Can the machine integrate with my existing ERP or line-control system?
Yes. Standard I/O (Modbus TCP/IP, Ethernet/IP, OPC-UA) allows direct PLC integration. Optional vision-based checkweighers and inkjet printers feed real-time data to MES/ERP for traceability and OEE reporting.
6. What support and lead times can I expect?
Standard lead time: 8–12 weeks for domestic units; 14–18 weeks for CE-compliant models. AstraPouch provides on-site commissioning, 24/7 hotline support, and a 2-year parts & labor warranty. Rental programs start at $1,200/month with $1 buy-out option.
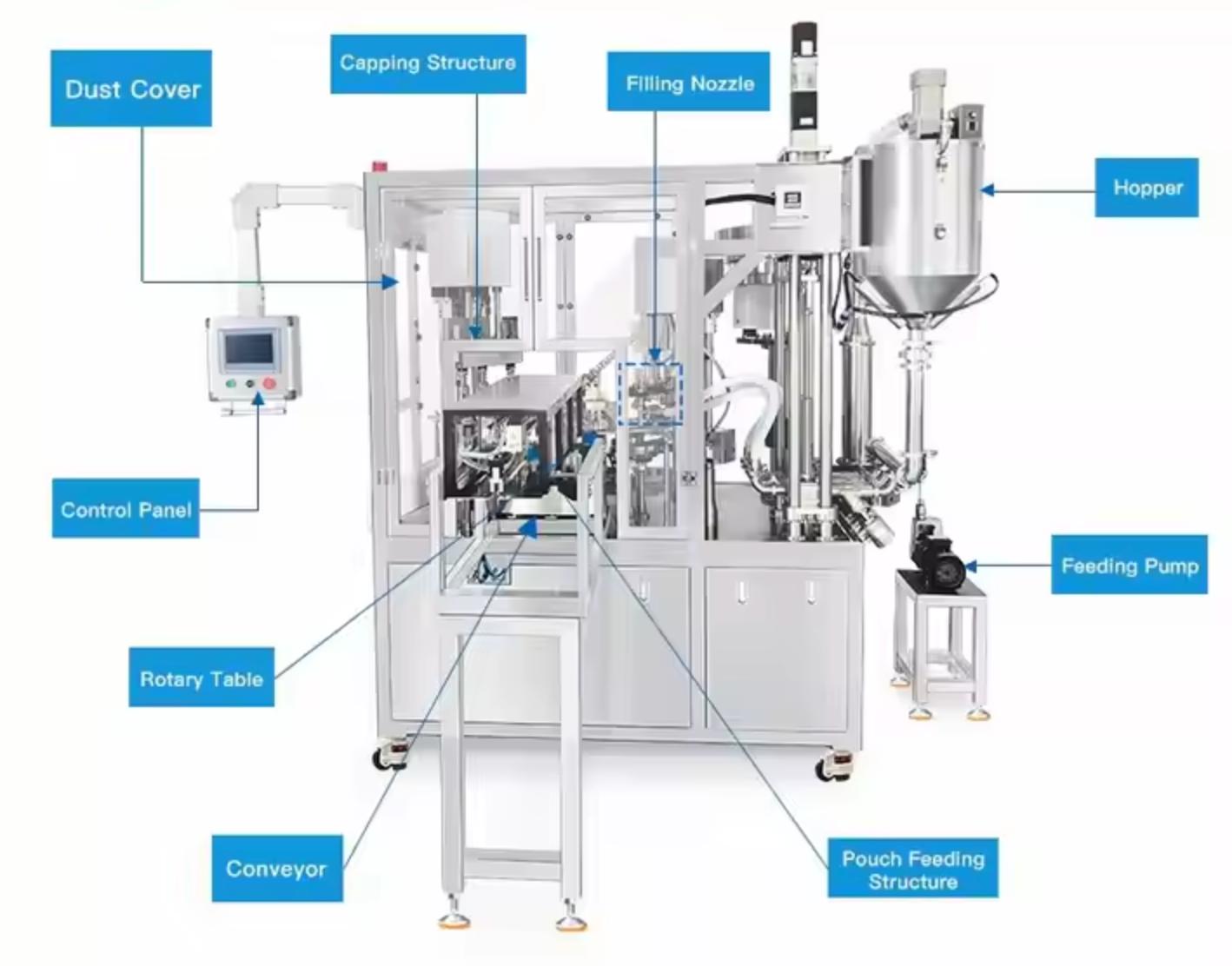
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
7. Are financing or leasing options available?
Third-party leasing (6–60 months, 0–10 % residual) and rent-to-own plans are offered through Wells Fargo and First American Capital. Down payments start at 10 % of list price for approved credit.
8. What accessories extend machine capability?
| Accessory | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Diaphragm pump kit | Handles viscous sauces, gels, and creams |
| Balance tank supply system | Sustains high-speed runs >40 pouches/min |
| Steam sterilization hood | Food-grade sanitation between batches |
| Custom conversion heads | Change fill volume or spout style in <5 min |
| Robotic case packer | Auto-loads finished pouches into cartons |
For detailed specifications or a no-obligation ROI analysis, contact AstraPouch at [email protected] or request a virtual demo.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pouch filling machine
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion & Outlook
(USA / Europe – B2B Focus)
Summary of Value
- Speed-to-Market: Rental & lease options remove CapEx barriers, letting firms validate demand in <30 days.
- Scalability: From 30 to 600+ pouches/min models; swapfill heads in minutes for SKU changes.
- Cost Reduction: 0.05-1 % fill accuracy cuts giveaway vs. volumetric fillers by 3-8 %.
- Regulatory Alignment: Steam-sterilizable heads and 316L stainless frames meet FDA & EU 10/2011.
- Total Cost of Ownership: Predictable pricing, remote diagnostics, and 24-month parts coverage.
Outlook 2025-2027
| Driver | Impact on Pouch Filling Equipment |
|---|---|
| Sustainable Packaging Mandates | Shift to mono-material PE/PP and recyclable spouts; suppliers offering retrofit kits. |
| AI-Driven OEE | Plug-and-play sensors that stream OEE data to SaaS dashboards for predictive maintenance. |
| Regionalization of Supply Chains | Demand for 1-5 gal fillers that produce localized pouches closer to consumption hubs. |
| Digital Traceability | Built-in QR/RFID encoding for serial-level lot tracking and circular-economy compliance. |
Action Checklist
- Validate fill volume tolerance against product specs.
- Request ROI model that includes rental credit against future purchase.
- Secure spare parts list and MTTR data before PO.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)