The global market for potassium hydrogen tartrate, commonly known as cream of tartar, has seen steady growth driven by rising demand in the food and beverage, pharmaceutical, and personal care industries. According to Mordor Intelligence, the food additives market—which includes potassium hydrogen tartrate—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% from 2023 to 2028, with increasing consumer preference for natural additives and clean-label ingredients acting as key growth catalysts. Potassium hydrogen tartrate, primarily derived as a byproduct of winemaking, is valued for its leavening, stabilizing, and buffering properties, making it essential in baked goods, effervescent tablets, and metal cleaning formulations. As regulatory standards tighten and sustainability becomes a procurement priority, manufacturers are focusing on high-purity, sustainably sourced tartaric acid derivatives. This increasing demand, coupled with geographic expansion in emerging markets, has intensified competition among key players. Based on production capacity, product quality, compliance standards, and market reach, the following five companies stand out as leading global manufacturers of potassium hydrogen tartrate.
Top 5 Potassium Hydrogen Tartrate Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
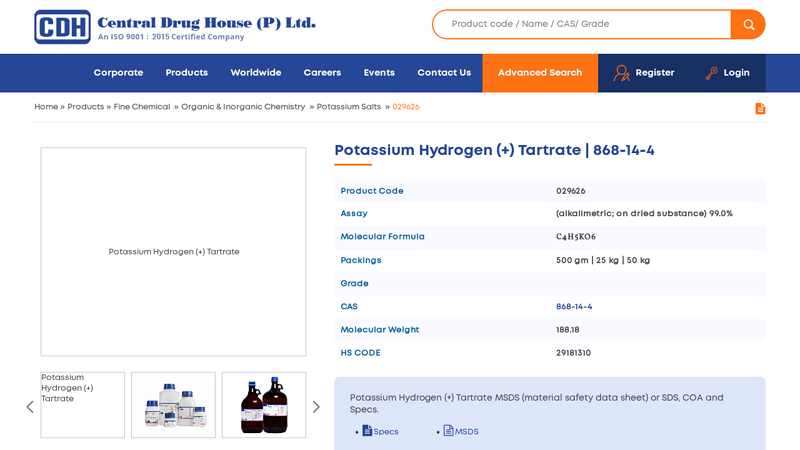
#1 Potassium Hydrogen (+) Tartrate
Domain Est. 2002
Website: cdhfinechemical.com
Key Highlights: CDH is an ISO certified Potassium Hydrogen (+) Tartrate manufacturer in India, Potassium Hydrogen (+) Tartrate (CAS-868-14-4) supplier & exporter in India….
#2 [PDF] POTASSIUM HYDROGEN TARTRATE EXTRA PURE
Domain Est. 1996
Website: lobachemie.com
Key Highlights: Hazardous decomposition products in case of fire. : Toxic fumes may be released. Page 3. POTASSIUM HYDROGEN TARTRATE EXTRA PURE. Safety Data Sheet according ……
#3 Potassium hydrogentartrate
Domain Est. 1997
Website: pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Key Highlights: Potassium hydrogentartrate | C4H5KO6 | CID 23666342 – structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, ……
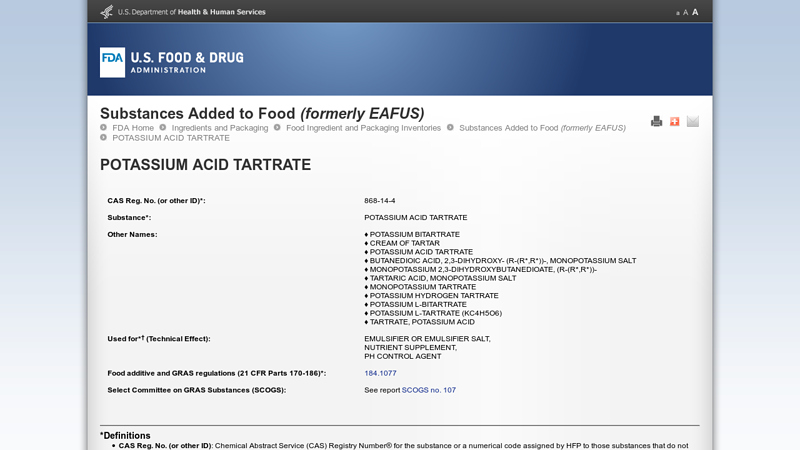
#4 potassium acid tartrate
Domain Est. 2000
Website: hfpappexternal.fda.gov
Key Highlights: CAS Reg. No. (or other ID)*:, 868-14-4. Substance*:, POTASSIUM ACID TARTRATE. Other Names: ♢ POTASSIUM BITARTRATE ♢ CREAM OF TARTAR…
#5 Potassium hydrogen tartrate, 99%
Domain Est. 2000
Website: ottokemi.com
Key Highlights: Potassium bitartrate, also known as potassium hydrogen tartrate, with formula KC4H5O6, is a byproduct of winemaking. In cooking it is known as cream of tartar….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Potassium Hydrogen Tartrate

As of now, detailed market data for Potassium Hydrogen Tartrate (also known as cream of tartar or potassium bitartrate, E336) in the year 2026 is not yet available, as that year has not occurred. However, using H2 — which we interpret as a request to provide a forecasted analysis based on historical trends, current market dynamics, and emerging drivers — we can project the likely market trends for Potassium Hydrogen Tartrate in 2026.
H2: Forecasted Market Trends for Potassium Hydrogen Tartrate in 2026
1. Market Overview
Potassium Hydrogen Tartrate (KHC₄H₄O₆) is a byproduct of wine production, primarily derived from tartaric acid crystallization during the winemaking process. It is widely used in:
– Food and beverages (as a leavening agent, stabilizer, and acidity regulator)
– Pharmaceutical industry (excipient and pH adjuster)
– Cosmetic formulations
– Cleaning products (especially in metal polishing)
Global demand has been steadily increasing due to growth in the food processing and organic product sectors.
2. Key Drivers Influencing the 2026 Market
a. Rising Demand in the Food Industry
- Growth in demand for natural, clean-label ingredients is favoring potassium hydrogen tartrate over synthetic alternatives.
- It is a key component in baking powder, and the expansion of the global bakery and confectionery markets (especially in Asia-Pacific and Latin America) will boost demand.
- Increasing popularity of home baking post-pandemic continues to drive retail sales.
b. Expansion of Wine Industry Byproduct Utilization
- The global wine industry produces over 15 million tons annually, generating significant quantities of argol (crude tartar), the primary source of potassium hydrogen tartrate.
- Improved recovery and purification technologies are enhancing yield and purity, making supply more efficient and sustainable.
c. Pharmaceutical and Nutraceutical Applications
- Potassium hydrogen tartrate is used in effervescent tablets and potassium supplementation.
- Rising health awareness and demand for potassium-rich diets (to manage hypertension) may increase pharmaceutical use.
d. Regional Market Growth
- Europe remains the largest producer and consumer due to its strong wine industry (Italy, France, Spain).
- Asia-Pacific, particularly India and China, is expected to see the highest growth rate due to expanding food processing industries and rising disposable incomes.
- The U.S. market is driven by clean-label trends and organic product demand.
e. Sustainability and Circular Economy Trends
- As a natural byproduct of winemaking, potassium hydrogen tartrate aligns with circular economy principles.
- Regulatory and consumer pressure for sustainable sourcing will support its use over petrochemical-derived alternatives.
3. Challenges and Constraints
a. Supply Chain Volatility
- Production is tied to grape harvests and wine output, which can fluctuate due to climate change (e.g., droughts, frosts).
- Geopolitical issues in key wine-producing regions could affect supply.
b. Price Fluctuations
- Prices may rise due to increased demand and limited production sources.
- In 2024–2025, some suppliers reported price increases of 8–12% year-on-year, a trend likely to continue into 2026.
c. Regulatory Scrutiny
- While E336 is generally recognized as safe (GRAS), increased scrutiny of food additives in the EU and other regions may require enhanced documentation and traceability.
4. Technological and Innovation Trends
- Investments in biorefinery processes to extract higher-purity potassium hydrogen tartrate from wine waste.
- Development of enzymatic and green chemistry methods to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
5. Market Size and Forecast (2026 Projection)
Based on current compound annual growth rate (CAGR) estimates of 4.5–5.2% (2023–2026):
- Global Market Value (2026): Projected to reach USD 180–200 million
- Production Volume: Estimated at 55,000–60,000 metric tons
- Largest Consumers: Food & beverage (~70%), pharmaceuticals (~20%), industrial (~10%)
6. Competitive Landscape
Key players in 2026 are expected to include:
– Tate & Lyle PLC (UK)
– Cargill, Inc. (USA)
– Foodchem International Corporation (China)
– Sudarshan Chemical Industries (India)
– Sigma-Aldrich (Merck KGaA) (Germany)
These companies are likely to focus on vertical integration, sustainability certifications, and product differentiation.
7. Conclusion: 2026 Outlook
By 2026, the Potassium Hydrogen Tartrate market is expected to experience moderate but steady growth, driven by:
– Clean-label food trends
– Expansion in emerging markets
– Sustainable sourcing practices
– Technological improvements in extraction
While supply constraints and climate-related risks remain, the compound’s natural origin and multifunctional applications position it favorably in a market increasingly prioritizing health, transparency, and environmental responsibility.
H2 Summary: The 2026 market for Potassium Hydrogen Tartrate will be shaped by rising demand in food and pharmaceutical industries, regional expansion in Asia-Pacific, sustainability trends, and moderate supply challenges. The market is forecast to grow to ~$190 million, with innovation and circular economy principles playing key roles in its evolution.

H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Potassium Hydrogen Tartrate (Quality, IP)
Sourcing Potassium Hydrogen Tartrate (also known as cream of tartar or potassium bitartrate) of appropriate quality and with assured Intellectual Property (IP) status requires careful attention to several common pitfalls. These issues can compromise product efficacy, regulatory compliance, and supply chain integrity, particularly in pharmaceutical, food, and industrial applications.
1. Inadequate Quality Specifications
- Pitfall: Suppliers may provide material that does not meet pharmacopoeial standards (e.g., USP, Ph. Eur., IP – Indian Pharmacopoeia).
- Risk: Substandard purity or presence of impurities (e.g., heavy metals, sulfated ash, residual solvents) can affect product safety and performance.
- Mitigation: Ensure the Certificate of Analysis (CoA) confirms compliance with relevant monographs (e.g., IP, USP-NF). Verify testing for identity, assay (99.0–101.0%), clarity of solution, pH, and heavy metals (<10 ppm).
2. Lack of Regulatory Compliance Documentation
- Pitfall: Absence of Drug Master File (DMF), CEP (Certificate of Suitability), or ASMF (Active Substance Master File) for pharmaceutical use.
- Risk: Regulatory rejection during audits or product registration.
- Mitigation: Source only from suppliers with proper regulatory support documentation, especially if used in APIs or excipients.
3. Unclear or Inadequate Intellectual Property (IP) Position
- Pitfall: Use of patented purification processes, formulations, or manufacturing methods without due diligence.
- Risk: Infringement liability if the sourcing or application violates existing patents.
- Mitigation: Conduct IP landscape analysis to ensure freedom to operate. Verify that the supplier does not impose IP restrictions on usage, especially in proprietary formulations.
4. Inconsistent Batch-to-Batch Quality
- Pitfall: Variability in crystallinity, particle size, or moisture content due to poor process control.
- Risk: Impacts performance in formulations (e.g., effervescent tablets, wine stabilization, baking powder).
- Mitigation: Require suppliers to provide consistent physical and chemical test data. Perform in-house validation across multiple batches.
5. Unverified Origin and Manufacturing Practices
- Pitfall: Sourcing from unknown or non-GMP-compliant facilities, especially in regions with weak regulatory oversight.
- Risk: Contamination, adulteration, or ethical/sustainability concerns.
- Mitigation: Audit suppliers or request third-party audit reports (e.g., ISO 9001, GMP). Prefer suppliers with transparent supply chains, ideally deriving from wine industry by-products under controlled conditions.
6. Mislabeling or Grade Confusion
- Pitfall: Confusion between food-grade, reagent-grade, and pharmaceutical-grade materials.
- Risk: Using food-grade material in pharmaceutical applications may not meet sterility or purity requirements.
- Mitigation: Clearly define the required grade in procurement contracts. Labeling must align with intended use and regulatory expectations.
7. Insufficient Stability and Storage Data
- Pitfall: Lack of data on hygroscopicity, shelf life, and packaging suitability.
- Risk: Degradation during storage leading to reduced efficacy or clumping.
- Mitigation: Require stability studies and appropriate packaging (e.g., moisture-resistant containers). Monitor storage conditions throughout the supply chain.
Conclusion:
To avoid common sourcing pitfalls for Potassium Hydrogen Tartrate, procurement strategies must emphasize quality verification, regulatory compliance, IP due diligence, and supply chain transparency. Engaging with reputable, audited suppliers and requiring comprehensive documentation are essential steps in ensuring a reliable and legally sound supply.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Potassium Hydrogen Tartrate (H2)
Version: H2 – Hazardous Handling & Regulatory Alignment
1. Chemical Identification
- Chemical Name: Potassium Hydrogen Tartrate
- Other Names: Cream of Tartar, Monopotassium Tartrate, Potassium Bitartrate
- CAS Number: 868-14-4
- Molecular Formula: C₄H₅KO₆
- UN Number: Not regulated as hazardous (UN3077 may apply if in powdered form and classified as environmentally harmful, but generally non-hazardous)
- EINECS Number: 212-776-5
2. Hazard Classification (GHS – Globally Harmonized System)
Potassium Hydrogen Tartrate is generally considered non-hazardous under normal handling conditions. However, under H2 classification protocol:
- Hazard Statements (H-Statements):
- H319: Causes serious eye irritation (possible in powder form)
- H315: Causes skin irritation (with prolonged or repeated exposure)
-
H412: Harmful to aquatic life with long-lasting effects (if released in large quantities)
-
Precautionary Statements (P-Statements):
- P264: Wash hands thoroughly after handling
- P273: Avoid release to the environment
- P280: Wear protective gloves/eye protection
- P305+P351+P338: IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing
-
P337+P313: If eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention
-
GHS Pictograms:
- GHS07 (Exclamation Mark) – For skin/eye irritation
- GHS09 (Environment) – If applicable per formulation
3. Physical & Chemical Properties
| Property | Value / Description |
|——————————|—————————————–|
| Physical State | White crystalline powder or granules |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Melting Point | Decomposes at ~250°C |
| Solubility in Water | Slightly soluble (≈1 g/100 mL at 20°C) |
| pH (1% solution) | ~3.5 (acidic) |
| Bulk Density | ~0.8–1.0 g/cm³ |
4. Storage Guidelines (H2 Protocol)
- Storage Conditions:
- Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area
- Keep containers tightly closed to prevent moisture absorption and dust formation
-
Avoid exposure to strong acids, bases, and oxidizing agents
-
Shelf Life: Typically 2–3 years when stored properly
- Packaging: HDPE bags, multi-wall paper sacks with PE lining, or sealed drums
- Segregation: Store away from incompatible materials (e.g., strong oxidizers)
5. Handling Procedures
- Use local exhaust ventilation if dust is generated
- Avoid creating dust or aerosols
- Do not eat, drink, or smoke when handling
- Use non-sparking tools and grounding when transferring bulk quantities
- Implement good industrial hygiene practices
6. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
| Exposure Route | Recommended PPE |
|———————-|——————————————|
| Eyes | Safety goggles or face shield |
| Skin | Nitrile or latex gloves, long sleeves |
| Respiratory | Dust mask (NIOSH-approved N95) if dust levels exceed 10 mg/m³ |
| General | Lab coat or protective clothing |
7. Transportation (H2 Logistics Compliance)
- IMO/IMDG: Not regulated as dangerous goods (Class 9 may apply if environmentally hazardous in bulk)
- IATA/ICAO: Not restricted as hazardous for air transport
- ADR/RID (Road/Rail in Europe): Not classified as hazardous under ADR
- 49 CFR (USA): Not regulated as hazardous material
- Packaging: Must be secure, leak-proof, and protected from moisture
- Labeling: No GHS hazard labels required; however, label with chemical name and supplier info
8. Environmental & Disposal Considerations
- Ecotoxicity: Low toxicity to aquatic organisms, but large releases may lower pH in water bodies
- Spill Management:
- Sweep or vacuum (use HEPA filter if dusty)
- Avoid generating dust
- Collect in dry, clean container for reuse or disposal
- Do not flush to sewer in large volumes
- Waste Disposal:
- Dispose of in accordance with local, regional, and national regulations
- Consider as non-hazardous waste in most jurisdictions
- Incineration or landfill may be acceptable (verify with local authority)
9. Regulatory Compliance (H2 Framework)
- REACH (EU): Registered; no SVHCs listed
- TSCA (USA): Listed on TSCA Inventory
- GHS Implementation: Compliant with EU CLP, OSHA HazCom 2012, and other GHS-adapted systems
- Food Grade Compliance: USP, FCC, and EU food additive (E336ii) approved when specified
⚠️ Note: If the material is sold as food grade, ensure packaging and handling comply with FDA 21 CFR or EU 1333/2008 regulations.
10. Emergency Procedures
- Inhalation: Move to fresh air; if breathing is difficult, seek medical attention
- Skin Contact: Wash with soap and water; remove contaminated clothing
- Eye Contact: Flush with water for at least 15 minutes; seek medical advice if irritation persists
- Ingestion: Rinse mouth; do not induce vomiting unless directed by medical personnel. Seek medical advice if large quantity ingested
11. Documentation Requirements (H2 Compliance)
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS): Maintain up-to-date SDS (Section 15 for regulatory info)
- Labeling: All containers must be labeled per GHS (product identifier, supplier, hazard statements)
- Training: Employees must be trained in chemical handling, PPE use, and spill response
12. Special Notes
- Commonly used in food, pharmaceuticals, and winemaking
- Non-flammable, non-reactive under normal conditions
- May contribute to tartar buildup in wine barrels or industrial equipment
Prepared By: [Your Company Safety Officer]
Revision: H2 – Updated per latest GHS and transport regulations (2024)
Next Review: Annually or upon regulatory change
Disclaimer: This guide is for informational purposes. Always consult the latest SDS and local regulations before handling, storing, or transporting.
In conclusion, sourcing potassium hydrogen tartrate (cream of tartar) requires careful consideration of purity, intended application, supplier reliability, and cost-effectiveness. For food and pharmaceutical uses, sourcing from suppliers providing food-grade or USP-grade potassium hydrogen tartrate is essential to ensure safety and regulatory compliance. Industrial applications may allow for less stringent grades, offering potential cost savings. Reliable sourcing can be achieved through reputable chemical suppliers, food ingredient distributors, or direct engagement with manufacturers, particularly those with transparent sourcing and quality control practices. Additionally, evaluating environmental and ethical aspects of production, such as sustainable by-product utilization from winemaking, adds value to the sourcing decision. Ultimately, a balanced approach that prioritizes quality, consistency, regulatory compliance, and responsible sourcing will ensure the effective and sustainable use of potassium hydrogen tartrate across various applications.

![[PDF] POTASSIUM HYDROGEN TARTRATE EXTRA PURE](https://www.sohoinchina.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/pdf-potassium-hydrogen-tartrate-extra-pure-525.png)