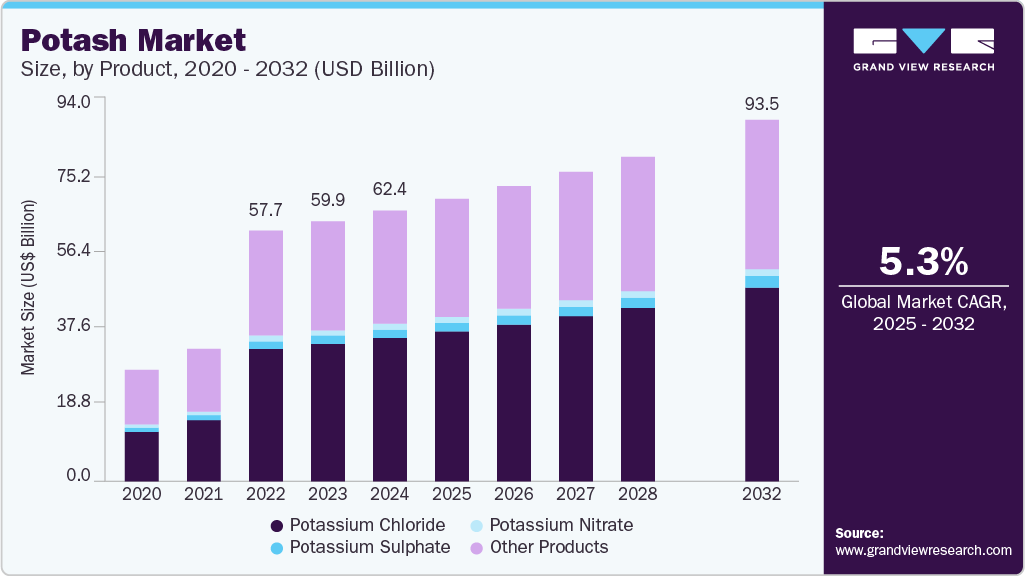
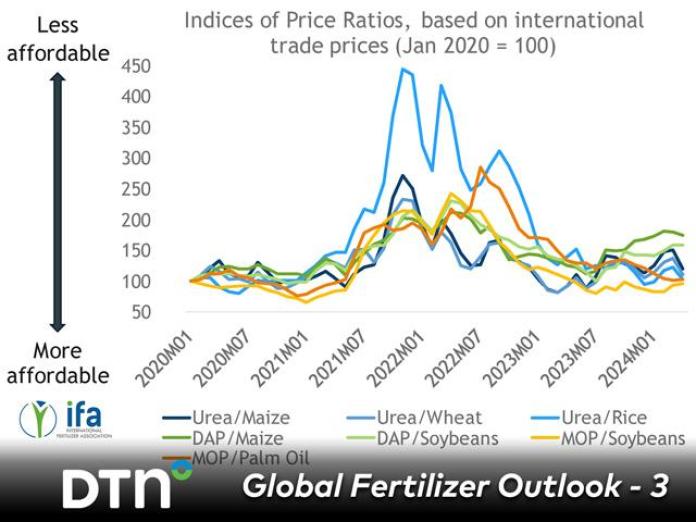
The global potash fertilizer market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising agricultural demand and increasing emphasis on crop yield optimization. According to Mordor Intelligence, the potash fertilizer market was valued at USD 18.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by surging food demand from a growing population, limited arable land, and government initiatives promoting efficient fertilizer use. As one of the three primary macronutrients essential for plant health, potassium plays a critical role in enhancing drought resistance, improving crop quality, and boosting overall productivity. With supply concentrations in countries like Canada, Russia, and Belarus, pricing dynamics are heavily influenced by geopolitical factors, logistics, and production capacity. In this evolving landscape, a select group of manufacturers dominate both supply and price-setting mechanisms. Based on production scale, global reach, and market influence, the following eight companies represent key players shaping potash fertilizer prices worldwide.
Top 8 Potash Fertiliser Prices Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Intrepid Potash
Domain Est. 2004
Website: intrepidpotash.com
Key Highlights: Intrepid is the only producer in the United States dedicated solely to potash and sulfate of potash magnesia fertilizers….
#2 Fertilizers Solutions
Domain Est. 1998
Website: spglobal.com
Key Highlights: With our extensive coverage of key fertilizer and mineral commodities such as ammonia and low-carbon ammonia, nitrates, phosphates, potash, cement, clinker and ……
#3 Canpotex
Domain Est. 1998
Website: canpotex.com
Key Highlights: Exporting Canadian potash to help feed the world for over 50 years. We market and deliver high-quality, Canadian potash to more than 40 overseas countries….
#4 Potash Prices, Analytics & Forecasts
Domain Est. 1999
Website: icis.com
Key Highlights: Gain a reliable view of potash markets and emerging trade routes, with ICIS market reports covering global pricing and trade flow data….
#5 Potash Market Prices & Analysis
Domain Est. 2007
Website: argusmedia.com
Key Highlights: Potash market insights, price trends, and fertilizer cost analysis. Get the latest potash price updates, including potash fertilizer price and market outlook ……
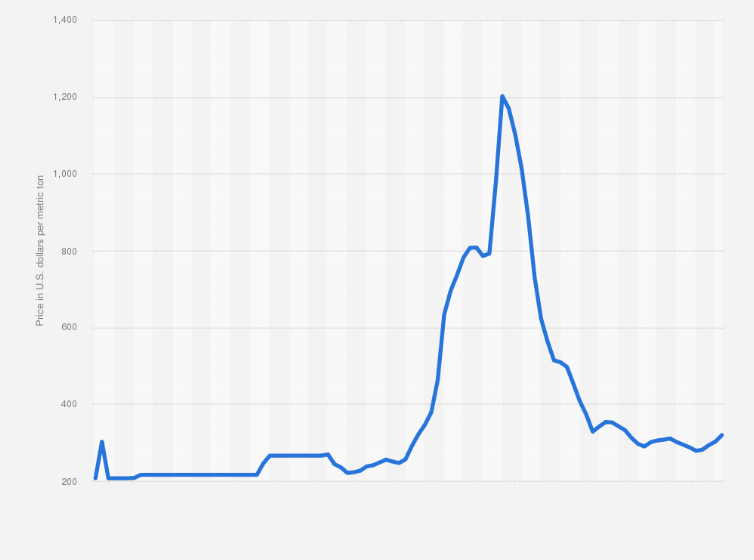
#6 Potassium Chloride (Muriate of Potash) Spot Price (Monthly)…
Domain Est. 2008
Website: ycharts.com
Key Highlights: Potassium Chloride (Muriate of Potash) Spot Price is at a current level of 358.33, up from 353.75 last month and up from 292.50 one year ago….
#7 Green Markets
Domain Est. 2010
Website: fertilizerpricing.com
Key Highlights: Green Markets ongoing coverage delivers: Fertilizer Market Prices Gain insight with over 300 price reports on 30 fertilizer commodities….
#8 Potash Price Trend and Forecast
Domain Est. 2017
Website: procurementresource.com
Key Highlights: Procurement Resource provides latest Potash prices and a graphing tool to track prices over time, compare prices across countries, and customize price data….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Potash Fertiliser Prices
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Potash Fertilizer Prices
The global potash fertilizer market in 2026 is expected to reflect a complex interplay of supply dynamics, agricultural demand, geopolitical factors, and macroeconomic conditions. After significant volatility in previous years due to supply disruptions and shifting trade policies, the market is projected to stabilize moderately in 2026, though prices are likely to remain elevated compared to historical averages.
1. Supply and Production Outlook
Global potash supply is anticipated to see incremental growth in 2026, driven primarily by expanded production capacity in key regions:
– Canada, the world’s largest potash exporter, continues to increase output through projects by Nutrien, Mosaic, and K+S. Expansion at mines such as Nutrien’s Estevan and Mosaic’s Esterhazy K3 are expected to add millions of tonnes of annual capacity by 2026.
– Russia and Belarus remain major suppliers, albeit under constrained export channels due to ongoing sanctions related to the Ukraine conflict. Despite logistical challenges, these countries are finding alternative export routes through Asia and the Middle East, sustaining global supply but at higher freight and insurance costs.
– China is increasing domestic production and investing in overseas potash assets (e.g., in Canada and Southeast Asia) to secure long-term supply, reducing reliance on imports.
These developments suggest a gradual easing of supply tightness, which could cap sharp price increases.
2. Demand Drivers
Global demand for potash in 2026 is expected to grow modestly, supported by:
– Strong agricultural fundamentals, including high grain and oilseed prices, which incentivize farmers to maintain or increase fertilizer application.
– Food security initiatives in emerging markets, particularly India and Brazil. India, one of the largest importers, has maintained robust government subsidies (e.g., through the Nutrient-Based Subsidy scheme), supporting potash uptake.
– Precision farming adoption and sustainable agriculture initiatives are optimizing potash use efficiency, potentially moderating per-hectare demand growth but sustaining overall market volume.
Brazil’s expanding farmland and increasing crop intensity will continue to drive Latin American demand, reinforcing potash’s role in soil nutrient replenishment, especially in potassium-deficient tropical soils.
3. Trade and Geopolitical Factors
Geopolitical tensions will remain a critical price influencer:
– Sanctions on Belarusian and Russian potash (e.g., via the Baltic ports) continue to reroute supply chains, increasing landed costs in Europe and parts of Africa.
– Trade diversification efforts—such as India sourcing more from Canada and the Middle East, and China building strategic stockpiles—are reducing dependency on traditional Eastern European suppliers.
– The stability of the Black Sea logistics corridor and any potential normalization of trade relations could ease supply pressures by 2026, though this remains uncertain.
4. Price Projections
Potash prices in 2026 are forecasted to stabilize in the range of $400–$480 per tonne (FOB, Vancouver or equivalent), depending on grade and destination. This represents a moderation from the peak levels seen in 2022–2023 ($700–$900/tonne) but remains above the 10-year average (~$350–$400/tonne), reflecting:
– Persistently higher production and logistics costs.
– Ongoing cost pass-through from energy and natural gas inputs.
– Firm demand in key agricultural regions.
Regional price differentials will persist due to freight costs and local subsidy regimes. For example, prices in India may remain lower due to government support, while spot prices in Southeast Asia or Latin America could be higher due to transportation premiums.
5. Long-Term Structural Shifts
- Sustainability and ESG pressures are prompting fertilizer producers to invest in lower-carbon mining and processing technologies, potentially increasing compliance costs.
- Digital agriculture and blended fertilizers are creating differentiated demand, favoring premium potash products with added micronutrients.
- Vertical integration by agribusinesses and food producers into fertilizer supply chains could alter traditional pricing models.
Conclusion:
In 2026, potash fertilizer prices are expected to consolidate at a moderate-to-high plateau, supported by resilient agricultural demand and constrained supply flexibility. While new production capacity will alleviate some supply concerns, geopolitical risks and rising input costs will prevent a return to pre-2022 price levels. Market participants should anticipate regional volatility and closely monitor policy changes in key importing nations and shifts in global trade flows.
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Potash Fertiliser: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
Sourcing potash fertiliser involves navigating complex supply chains and technical specifications. Overlooking quality inconsistencies and intellectual property (IP) issues can lead to significant operational, financial, and legal risks. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality Variability and Specification Misalignment
One of the most frequent challenges in potash sourcing is inconsistent product quality. Potash (primarily potassium chloride, KCl) varies in purity, moisture content, particle size, and the presence of impurities such as sodium chloride, magnesium, and sulfates. Buyers may assume all potash meets standard agricultural grades, but suppliers—especially in less regulated markets—may offer material that falls below international standards (e.g., less than 60% K₂O content). This can reduce crop yield and damage equipment due to caking or corrosion.
Additionally, mismatched specifications between buyer requirements and delivered product often arise when contracts lack precise technical parameters. For example, granular versus standard-grade potash has different application needs and pricing. Failure to clearly define and verify quality benchmarks in purchase agreements increases the risk of receiving substandard fertiliser.
Counterfeit or Mislabelled Products
In global markets, especially those with weak regulatory oversight, counterfeit or misrepresented potash fertiliser is a growing concern. Some suppliers may label lower-grade or blended products as premium-grade potash to command higher prices. These products may not only underperform but also introduce harmful elements into the soil. Buyers relying on documentation alone—without third-party laboratory testing—risk accepting adulterated or falsely certified shipments.
Intellectual Property and Brand Infringement
While potash itself is a commodity chemical, certain proprietary formulations, granulation technologies, and brand names (e.g., specialty potash blends or coated products) are protected by IP rights. Sourcing from unauthorised manufacturers or distributors may lead to unintentional IP infringement, particularly when purchasing “generic” versions of branded specialty fertilisers. This exposes buyers to legal liability and reputational harm, especially in markets with strong IP enforcement.
Moreover, using patented application technologies or formulations without licensing can result in disputes, even if the potash source is legitimate. Buyers must ensure that their sourcing agreements include warranties regarding IP compliance and that suppliers have the right to distribute the products they offer.
Lack of Traceability and Certification
Transparent sourcing requires verifiable documentation, including certificates of analysis (CoA), origin tracing, and compliance with environmental and ethical standards. Without proper traceability, it becomes difficult to verify quality claims or ensure that the product was produced sustainably and legally. This is particularly important for companies adhering to ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) criteria, where sourcing from mines linked to human rights or environmental violations can damage brand integrity.
In summary, mitigating risks in potash fertiliser sourcing demands rigorous due diligence, clear contractual specifications, independent quality verification, and awareness of IP considerations. Engaging reputable suppliers, demanding full documentation, and conducting regular audits are essential steps to avoid these common pitfalls.
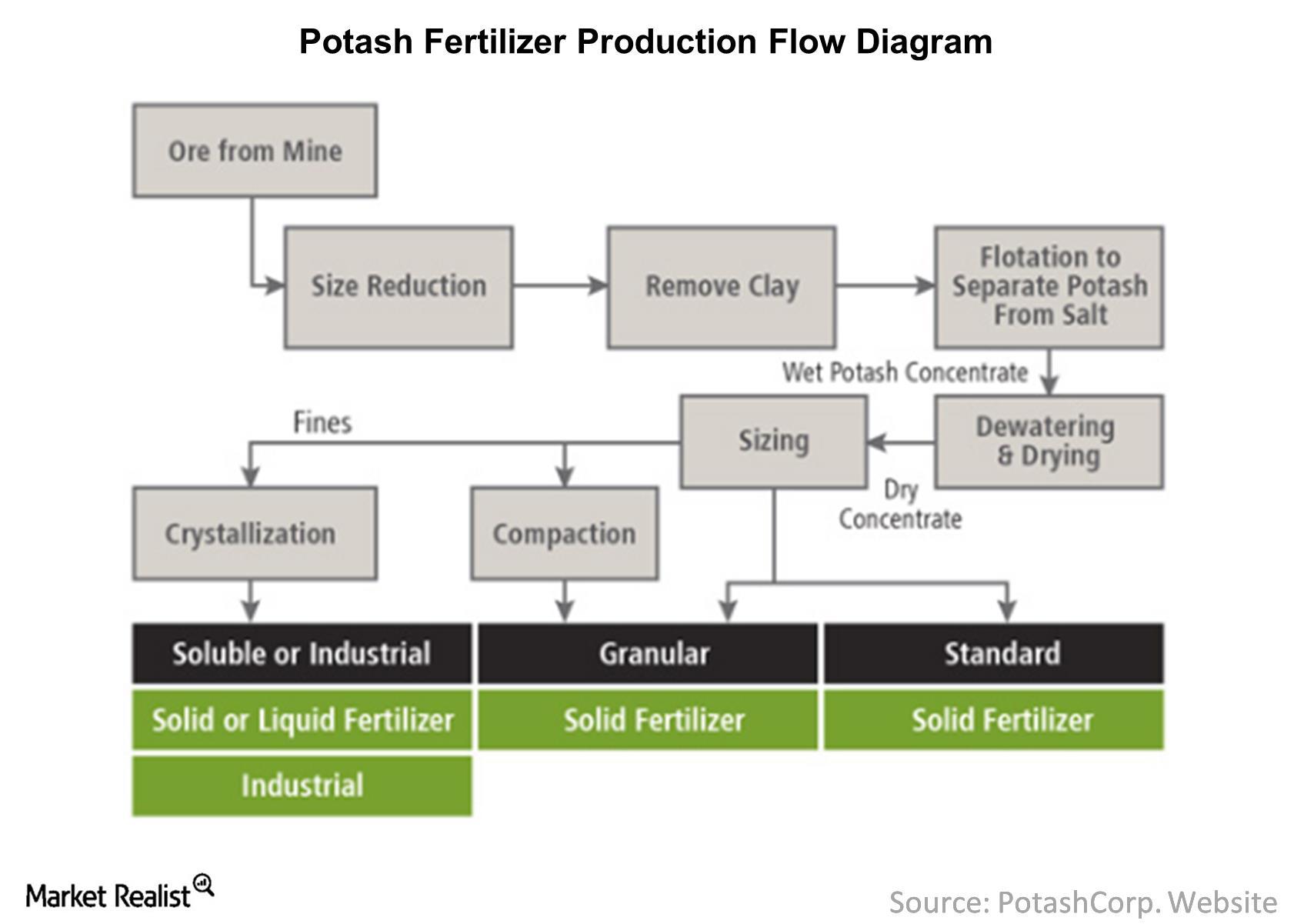
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Potash Fertiliser Prices
Understanding the logistics and compliance factors influencing potash fertiliser prices is essential for importers, distributors, and agricultural businesses. These elements significantly impact supply chain efficiency, cost structures, and regulatory adherence, ultimately affecting market pricing.
Transportation and Freight Costs
Global potash supply relies heavily on long-distance shipping from major producers in Canada, Russia, Belarus, and Germany. Ocean freight rates, fuel surcharges, port handling fees, and vessel availability directly influence landed costs. Disruptions such as port congestion, geopolitical tensions, or sanctions (e.g., on Belarusian or Russian exports) can lead to increased shipping premiums and supply volatility, pushing prices upward.
Import Regulations and Trade Compliance
Importing potash fertiliser requires compliance with destination country regulations, including customs documentation, product classification (e.g., HS Code 3104.20), and adherence to agricultural input standards. Importers must also monitor trade policies such as tariffs, anti-dumping duties, or embargoes—particularly relevant given sanctions on certain exporters. Non-compliance risks shipment delays, penalties, or seizure, increasing operational costs and affecting price stability.
Quality Standards and Certification
Potash (primarily Muriate of Potash – MOP or Sulphate of Potash – SOP) must meet specified quality benchmarks (e.g., K₂O content, moisture levels, particle size). Certifications such as ISO or country-specific agricultural ministry approvals are often mandatory. Failure to meet these standards can result in rejected shipments or price discounts, influencing procurement strategies and final pricing.
Storage and Handling Requirements
Potash is hygroscopic and can cake if exposed to moisture, necessitating dry, covered storage facilities and careful handling procedures. Compliance with occupational health and safety (OHS) regulations during loading, transport, and storage is critical. Investment in proper infrastructure adds to logistics costs, which are reflected in final product pricing.
Environmental and Safety Regulations
Transport and storage of potash must comply with environmental protection and hazardous materials regulations where applicable (e.g., IMDG Code for maritime transport). While potash is generally non-toxic, dust control and spill management protocols are required. Regulatory changes or stricter enforcement can increase compliance costs, indirectly affecting market prices.
Regional Supply Chain Infrastructure
The efficiency of local logistics networks—including rail, trucking, and inland waterways—impacts final delivery costs. Regions with underdeveloped infrastructure face higher distribution expenses, leading to price disparities between urban and remote agricultural areas. Investment in logistics hubs and cold chain alternatives (for SOP) can mitigate these differentials.
Sanctions and Geopolitical Risk Management
Due to the concentration of production in geopolitically sensitive regions, compliance with international sanctions (e.g., EU or U.S. restrictions on Belarusian potash) is crucial. Buyers must perform due diligence on supply chain origins to avoid legal exposure. Alternative sourcing routes may involve higher costs, contributing to price fluctuations.
By proactively managing logistics and ensuring full regulatory compliance, stakeholders can mitigate risks, optimize costs, and maintain competitive pricing in the global potash fertiliser market.
Conclusion on Sourcing Potash Fertiliser Prices:
Sourcing potash fertiliser prices requires a comprehensive understanding of global supply chain dynamics, market volatility, and regional demand patterns. Prices are influenced by key factors such as production concentration in major exporting countries (notably Canada, Russia, and Belarus), transportation costs, geopolitical risks, currency fluctuations, and agricultural demand cycles.
To secure competitive pricing, buyers should consider long-term contracts to hedge against volatility, explore multiple suppliers to diversify risk, and monitor market trends closely. Engaging with reliable suppliers, leveraging industry reports, and utilizing procurement platforms can enhance price transparency and negotiation power. Additionally, regional availability and logistical efficiency play a crucial role in final landed costs.
Ultimately, a strategic and informed sourcing approach—balancing cost, quality, reliability, and sustainability—is essential for optimising potash fertiliser procurement and supporting efficient agricultural production.