The global magnet market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for high-performance magnetic solutions across industries such as automotive, electronics, renewable energy, and industrial automation. According to Grand View Research, the global permanent magnet market size was valued at USD 17.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.4% from 2023 to 2030. Mordor Intelligence further supports this trajectory, projecting the permanent magnets market to grow at a CAGR of over 6.5% during the forecast period of 2023–2028. Within this expanding ecosystem, pot magnets—valued for their enhanced magnetic force, durability, and safety due to their encased design—have become critical components in holding, lifting, and fixing applications. As industrial automation and smart manufacturing continue to accelerate, the need for reliable, high-efficiency pot magnets has intensified. This growing demand has propelled a number of manufacturers to the forefront through innovation, scalability, and consistent product quality. The following list highlights the top 10 pot magnets manufacturers shaping the market today, based on production capacity, technological advancement, global reach, and customer reviews.
Top 10 Pot Magnets Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
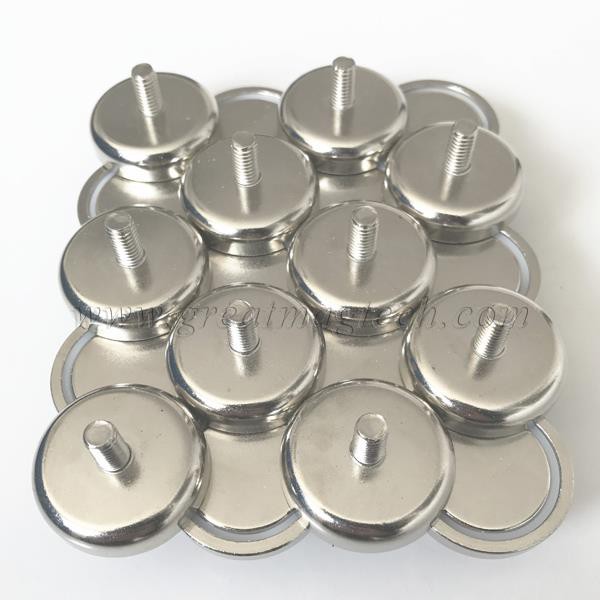
#1 Pot Magnets Factory, Manufacturers and Suppliers
Domain Est. 2015
Website: greatmagtech.com
Key Highlights: Excellent quality pot magnets from ISO9001 and TS16949 certificated supplier, manufacturer and factory….
#2 Stanford Magnets
Domain Est. 1998
Website: stanfordmagnets.com
Key Highlights: Stanford Magnets is a rare earth magnet manufacturer including various custom magnets, specializes in the design, engineering, and manufacture of custom ……
#3 Magnets
Domain Est. 2012
Website: kippusa.com
Key Highlights: KIPP offers a wide range of different industrial magnets. A distinction is made between several types eg pot magnets, round magnets, retention magnets or raw ……
#4 Neodymium Pot Magnets Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2016
Website: hspotmagnets.com
Key Highlights: Our range of Neodymium Pot Magnet is a rare earth ndfeb permanent magnet enclosed in a metal “pot”, while the active neo magnet face is not enclosed….
#5 Pot magnets
Domain Est. 1998
Website: bakkermagnetics.com
Key Highlights: Permanent pot magnets. Powerful magnets with a focused magnetic field, often used as tools for various activities in workshops and in industry….
#6 Magnets
Domain Est. 1998
Website: magnetshop.com
Key Highlights: Magnet shop is an industry leading magnets supplier for high-quality, rare-earth and permanent magnets in assorted shapes, sizes and premium grades….
#7 Coloured Neodymium NdFeB Pot Magnets
Domain Est. 2002
Website: eclipsemagnetics.com
Key Highlights: Coloured Neodymium NdFeB Pot Magnets. Ideal for clamping or holding applications. Supplied with countersunk hole for screw attachment; Available in black, ……
#8 Pot Magnets 101
Domain Est. 2015
Website: winnieindustries.com
Key Highlights: Pot magnets are used to mount signs, tools, fixtures, sensors, and cable runs to metal surfaces in shops, warehouses, vehicles, and job sites. They’re also used ……
#9 Pot Magnet
Domain Est. 2018
Website: weizhongmagnetics.com
Key Highlights: Weizhong Magnetics supplies a wide selection of neodymium and ferrite pot magnets with different accessories and shape components: pot magnet with a hole, ……
#10 Pot Magnets
Domain Est. 2022
Website: sdmmagnets.com
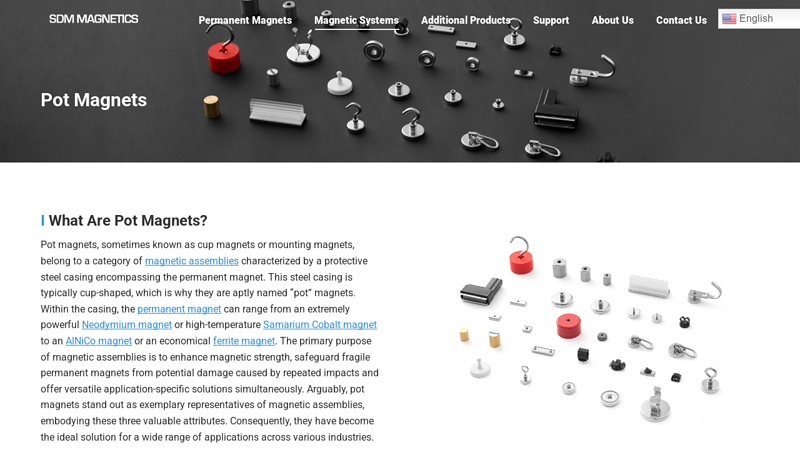
Key Highlights: Pot magnets, also known as cup magnet or mounting magnets, are a type of magnetic assemblies that have a steel shell surrounding the magnet….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Pot Magnets
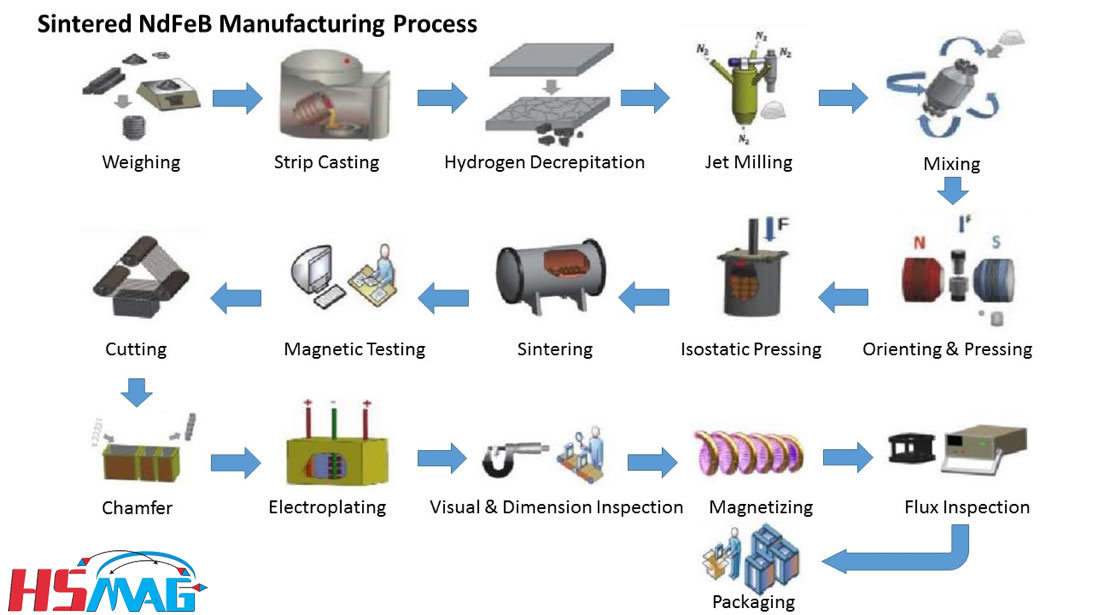
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Pot Magnets
The global pot magnets market is poised for steady growth through 2026, driven by rising demand across industrial, automotive, electronics, and renewable energy sectors. These robust magnetic assemblies—comprising a permanent magnet encased in a steel shell or “pot”—are valued for their enhanced magnetic force, durability, and resistance to demagnetization. Key market trends shaping the industry in 2026 include:
-
Increased Industrial Automation
As smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 initiatives accelerate, pot magnets are increasingly used in automated assembly lines, robotic grippers, and sensor systems. Their reliable holding power makes them essential for precision positioning and material handling applications, fueling demand in industrial automation. -
Growth in Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Automotive Applications
The automotive sector, particularly electric vehicle production, is a major growth driver. Pot magnets are utilized in EV motors, sensors, and battery systems. With global EV adoption surging due to environmental regulations and infrastructure investment, the need for high-performance magnetic components like pot magnets is expected to rise significantly by 2026. -
Expansion in Renewable Energy Infrastructure
Wind turbines and solar tracking systems increasingly incorporate pot magnets in generator assemblies and actuation mechanisms. As countries ramp up investments in clean energy, the demand for durable and efficient magnetic solutions is set to increase, benefiting the pot magnets market. -
Technological Advancements in Magnet Materials
Innovations in rare-earth magnets—particularly neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB)—are enhancing the performance of pot magnets, allowing for smaller, stronger, and more temperature-resistant designs. Manufacturers are focusing on optimizing magnetic efficiency and corrosion resistance, especially for use in harsh environments. -
Asia-Pacific as a Key Manufacturing and Consumption Hub
China, Japan, and South Korea remain dominant in both production and consumption of pot magnets, supported by strong electronics and automotive industries. India and Southeast Asia are emerging as high-growth markets due to industrial expansion and government incentives for manufacturing. -
Sustainability and Supply Chain Resilience
With growing scrutiny on rare-earth mining practices, companies are investing in recycling technologies and alternative materials to reduce environmental impact. In 2026, supply chain diversification—especially to reduce dependence on single-source rare earths—will be a strategic priority for manufacturers. -
Customization and Application-Specific Designs
End-users are demanding tailored pot magnets for niche applications in medical devices, aerospace, and defense. This trend is pushing manufacturers to adopt modular designs and agile production processes to meet specific performance and form-factor requirements.
In conclusion, the 2026 pot magnets market will be defined by technological innovation, sectoral expansion, and geographic shifts. Companies that invest in R&D, sustainability, and application-focused solutions will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
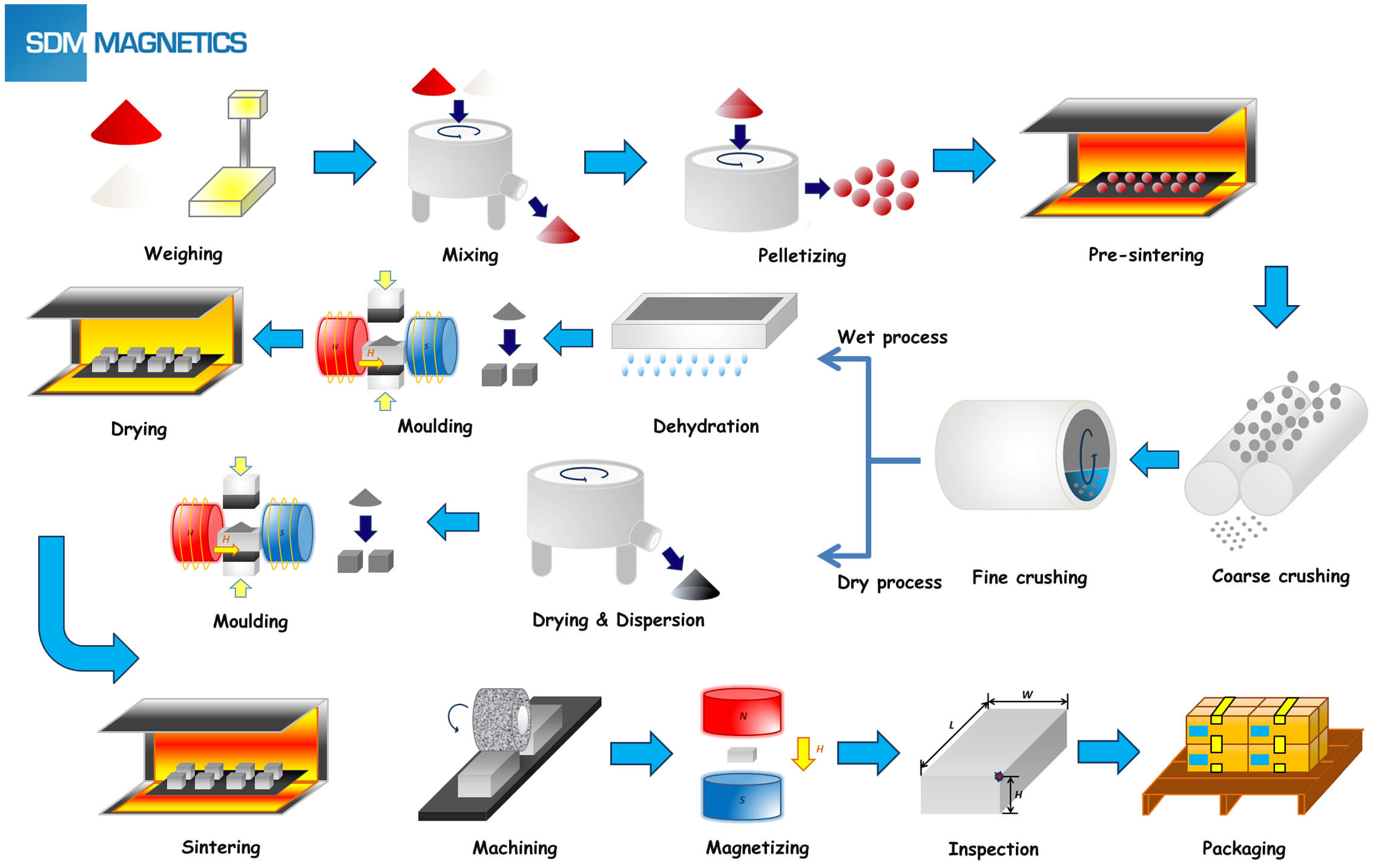
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Pot Magnets: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing pot magnets—especially from international suppliers—can present significant challenges related to quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these pitfalls helps mitigate risks and ensures reliable, legally compliant procurement.
Quality Inconsistencies and Substandard Materials
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing pot magnets is variability in quality. Suppliers may use inferior materials such as low-grade neodymium, poor-quality steel housings, or subpar adhesives to reduce costs. This leads to magnets with reduced pull force, premature corrosion, or structural failure. Additionally, inconsistent plating (e.g., inadequate nickel-copper-nickel coating) increases susceptibility to environmental degradation, especially in humid or corrosive environments.
Lack of standardized testing and certification further compounds the problem. Reputable manufacturers provide pull force data, temperature resistance ratings, and compliance with international standards (e.g., RoHS, REACH). Without rigorous quality control and third-party verification, buyers risk receiving products that fail to meet specifications, resulting in field failures and increased warranty claims.
Inadequate or Misrepresented Performance Specifications
Suppliers may exaggerate performance metrics such as magnetic strength (measured in kilograms or pounds of pull force), temperature tolerance, or durability. These inflated claims are often based on ideal laboratory conditions rather than real-world performance. Buyers who rely solely on supplier datasheets without independent validation may end up with magnets that underperform in actual applications.
Moreover, differences in test methodologies (e.g., pull force measured on thick steel vs. thin sheet metal) can lead to misleading comparisons. Failing to verify specifications through sample testing or third-party labs increases the risk of design and functional failures.
Intellectual Property Infringement and Design Copying
Pot magnet designs—particularly proprietary configurations involving specific geometries, multi-pole arrangements, or integrated features—can be protected under design patents or utility patents. Sourcing from manufacturers in regions with weak IP enforcement increases the risk of inadvertently procuring counterfeit or cloned products.
Some suppliers may reverse-engineer branded pot magnets and replicate them without authorization, potentially exposing the buyer to legal liability, especially in regulated industries or export markets. Additionally, custom-designed magnets developed in collaboration with a supplier may lack clear IP ownership agreements, leading to disputes or unauthorized reuse of the design by the manufacturer.
Lack of Traceability and Supply Chain Transparency
Without full traceability, it’s difficult to verify the origin of raw materials (e.g., ethically sourced rare earth elements) or ensure compliance with environmental and labor standards. Some suppliers may subcontract production without disclosure, introducing uncontrolled variables in quality and ethics. This lack of transparency can result in reputational damage or non-compliance with regulatory requirements.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls:
– Conduct thorough supplier audits and request quality certifications (ISO 9001, etc.).
– Require sample testing under real-world conditions before bulk orders.
– Use legally binding agreements that define IP ownership and prohibit unauthorized replication.
– Work with trusted partners or sourcing agents familiar with magnet manufacturing standards.
– Include clear performance warranties and acceptance criteria in procurement contracts.
By addressing these quality and IP risks proactively, businesses can ensure reliable performance and legal compliance when sourcing pot magnets.
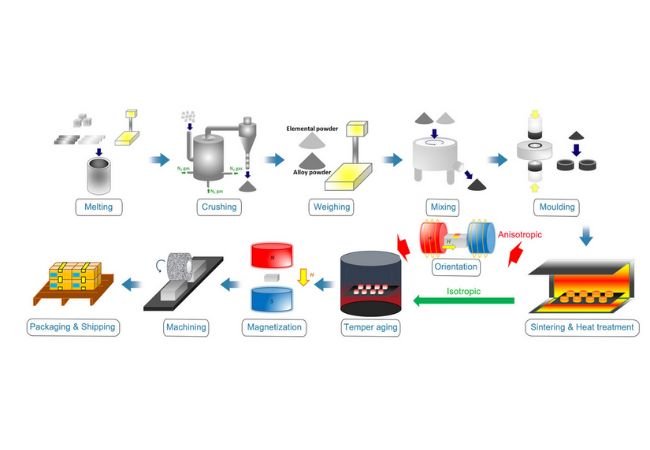
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Pot Magnets
Overview of Pot Magnets
Pot magnets are permanent magnets encased in a steel shell or “pot,” typically made of ferromagnetic materials such as iron or steel. This design enhances their magnetic strength and provides mechanical protection. Commonly used in industrial, automotive, and consumer applications, pot magnets are subject to specific logistics and regulatory considerations due to their magnetic properties and material composition.
Classification and Shipping Regulations
International Air Transport Association (IATA) Guidelines
Pot magnets are classified as dangerous goods under IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR) if their magnetic field strength exceeds specified thresholds. Specifically:
– If the magnetic field at a distance of 2.1 meters (7 feet) from any point on the surface of the assembled package exceeds 0.159 A/m (0.002 Gauss), the shipment must be classified as UN2807, Magnetized Material.
– Proper testing using a gauss meter is required to determine classification.
– Packages must be labeled with the Class 9 Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods label and include a Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods when applicable.
International Maritime Organization (IMO) – IMDG Code
Under the IMDG Code, magnetized materials that can affect navigational instruments are similarly regulated:
– UN2807, Magnetized Material, Class 9.
– Packages must be stowed away from sensitive navigation equipment.
– Documentation must include proper shipping name, UN number, class, and emergency contact information.
Ground Transport (e.g., ADR in Europe, 49 CFR in the U.S.)
- 49 CFR (U.S. DOT): Regulates domestic transport of hazardous materials. Magnetized materials must comply with hazardous materials regulations if they meet the magnetic field criteria.
- ADR (Europe): Similar to IATA and IMDG, requires classification, labeling, and documentation for Class 9 materials.
Packaging Requirements
Magnetic Shielding and Containment
- Use steel-lined packaging or magnetic shielding materials to reduce external magnetic fields below regulatory thresholds.
- Secure magnets to prevent movement during transit, which could compromise shielding.
- Individual pot magnets should be spaced or isolated to prevent magnetic interaction and demagnetization.
Marking and Labeling
- Packages must display the Class 9 hazard label if classified as dangerous goods.
- Include proper shipping name: “Magnetized Material”, UN2807.
- Add orientation arrows if required (e.g., “This Way Up”).
- Include shipper and consignee contact details and emergency information.
Documentation
Required Shipping Documents
- Air Waybill (AWB) or Bill of Lading (BOL) with accurate commodity description.
- Dangerous Goods Declaration when shipping by air or sea (if UN2807 applies).
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS): While not always required for pot magnets, it may be provided upon request, particularly if nickel-plated or containing hazardous coatings.
Customs and Import Compliance
- HS Code Classification: Pot magnets typically fall under HS code 8505.11 (permanent magnets, including parts) or 8505.19 (other).
- Accurate declaration of value, origin, and quantity is required.
- Some countries may impose restrictions on imports of magnetic materials due to security or regulatory concerns (e.g., aviation safety).
Handling and Storage
Safety Precautions
- Use non-magnetic tools to handle strong pot magnets.
- Keep magnets away from electronic devices, pacemakers, credit cards, and mechanical watches.
- Provide personnel with training on safe handling to avoid pinching injuries.
Storage Conditions
- Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment to prevent corrosion, especially for nickel- or zinc-coated magnets.
- Keep away from demagnetizing fields (e.g., AC coils) and high temperatures.
Environmental and Regulatory Compliance
REACH and RoHS (EU)
- Ensure compliance with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) if pot magnets contain restricted substances (e.g., lead, cadmium).
- REACH compliance requires declaration of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) if present above thresholds, particularly in coatings or platings.
Conflict Minerals (U.S. Dodd-Frank Act)
- If applicable, disclose the use of tin, tantalum, tungsten, or gold (3TG) in manufacturing components, although rare in standard pot magnets.
Special Considerations for Air Freight
- Airlines may impose additional restrictions on magnetic materials.
- Prior notification and approval may be required.
- Use of IATA-certified packaging and trained personnel (IATA DGR certified) is mandatory for dangerous goods shipments.
Best Practices Summary
- Test magnetic field strength before shipping.
- Classify correctly under IATA, IMDG, or national regulations.
- Use compliant packaging with adequate shielding.
- Provide complete and accurate documentation.
- Train staff in hazardous materials handling if applicable.
- Stay updated on regulatory changes in target markets.
By following this guide, businesses can ensure safe, compliant, and efficient logistics for pot magnet shipments across global supply chains.
Conclusion for Sourcing Pot Magnets
In conclusion, sourcing pot magnets requires a careful evaluation of several key factors including magnetic strength, size, coating, operating temperature, and pull force requirements, all aligned with the intended application. It is essential to work with reputable suppliers who provide consistent quality, technical expertise, and compliance with relevant industry standards. Comparing options based on performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness ensures optimal value and reliability. Additionally, considering customization capabilities and supply chain reliability can further enhance long-term success. By following a structured sourcing strategy, businesses can secure high-performance pot magnets that meet their technical needs while maintaining efficiency and cost control.