The global portable laser cleaning market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly, precision-based cleaning solutions across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and heritage conservation. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global laser cleaning market was valued at USD 287.9 million in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 546.2 million by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 11.2% during the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by technological advancements, stringent environmental regulations limiting chemical cleaning methods, and the rising adoption of portable systems that offer flexibility and ease of use in field operations. With manufacturers rapidly innovating to improve power efficiency, portability, and cost-effectiveness, the competitive landscape is evolving. Based on market presence, technological capabilities, and customer reach, the following eight companies have emerged as leading manufacturers of portable laser cleaning solutions.
Top 8 Portable Laser Cleaner Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
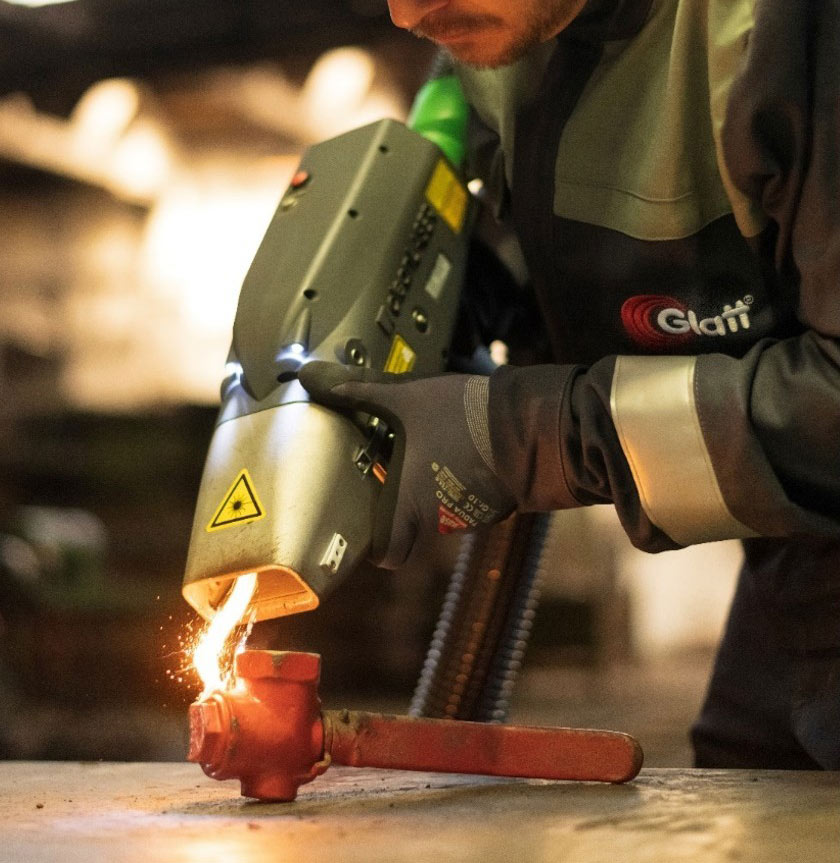
#1 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: With over 35 years of expertise in surface treatment and more than 450 systems installed worldwide, P-Laser is at the forefront of industrial laser cleaning ……
#2 Laser Photonics
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser Photonics manufactures reliable, safe, and eco-friendly Laser Cleaning, Laser Cutting, Laser Engraving, Laser Marking, and Laser Welding solutions….
#3 SFX Laser
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: SFX Laser is a 20+ years professional laser equipment manufacturer including laser cleaning machine, laser welding machine, fiber laser engraver, fiber laser…
#4 SHARK P CL Industrial Laser Cleaning Machines (100
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: The SHARK P CL 500A is an air-cooled laser cleaning machine with 500 W output, combining high laser power with a compact and portable system design. AIRKNIFE ……
#5 Argento Lux
Website: argentolux.com
Key Highlights: Our company provides state-of-the-art Industrial Laser Equipment Sales and Mobile Laser Cleaning Services for a wide range of applications and industries….
#6 Handheld Laser Cleaning Machines
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Handheld and portable laser cleaning machines designed for manual applications including rust removal, paint stripping, restoration, and more….
#7 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: baikeopto.com
Key Highlights: BAIKEOPTO laser cleaning machines include 100W, 200W, 300W, 500W pulse laser cleaning, single-mode laser cleaning, multi-mode laser cleaning, as well ……
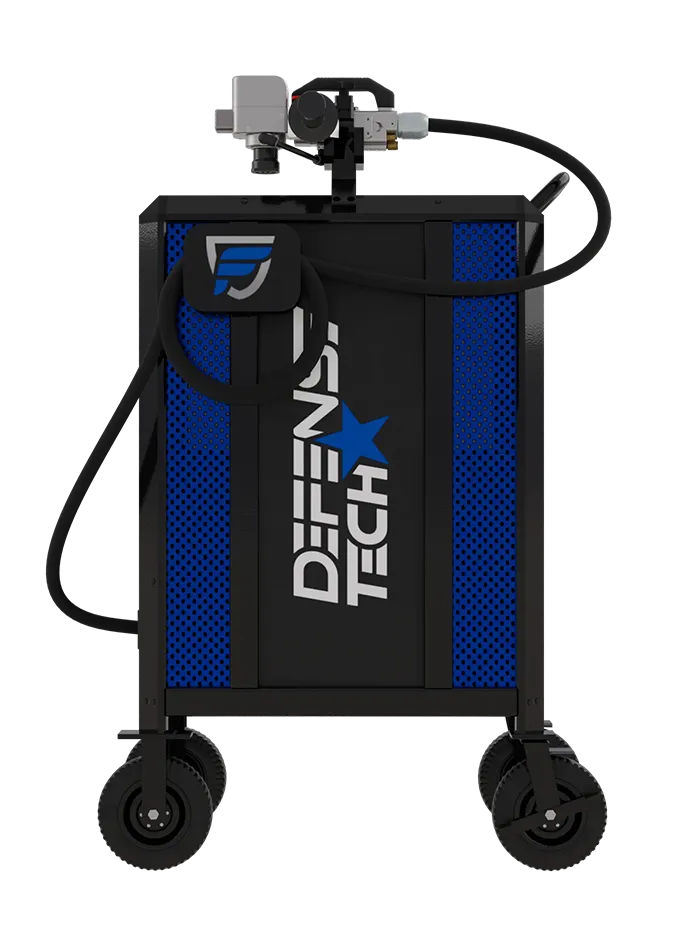
#8 DefenseTech laser cleaning
Website: fonon.us
Key Highlights: The DTMF-1020 handheld laser system offers a non-abrasive cleaning process that is safe, easy to use, and eco-friendly. It minimizes chemical and abrasive usage ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Portable Laser Cleaner

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Portable Laser Cleaners
The global market for portable laser cleaners is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, increasing environmental regulations, and growing demand across industrial sectors. H2, a leading entity in laser technology innovation, forecasts several key trends shaping the trajectory of this niche yet rapidly expanding market.
-
Increased Adoption in Manufacturing and Maintenance
By 2026, portable laser cleaners are expected to see widespread adoption in manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and heavy equipment maintenance. Their ability to remove rust, paint, oxides, and contaminants without damaging substrates makes them ideal for precision cleaning. H2 observes a shift from traditional abrasive and chemical cleaning methods toward laser-based solutions due to their eco-friendliness and efficiency. -
Miniaturization and Enhanced Portability
A major trend identified by H2 is the miniaturization of laser cleaning systems. Manufacturers are focusing on reducing device size and weight while maintaining or improving power output. By 2026, lightweight, battery-operated portable units will dominate the market, allowing operators to use them in confined spaces and remote locations—key for field maintenance and offshore operations. -
Integration of Smart Features and IoT
H2 anticipates that future portable laser cleaners will increasingly incorporate smart technology. Integration with IoT platforms will enable real-time monitoring of cleaning performance, predictive maintenance alerts, and remote diagnostics. AI-assisted beam control and automated scanning systems are expected to improve precision and reduce operator error, particularly in complex or repetitive tasks. -
Stricter Environmental Regulations Driving Demand
With global emphasis on sustainability, industries are under pressure to eliminate hazardous cleaning chemicals and reduce waste. Portable laser cleaners produce no secondary waste and require no solvents, aligning with environmental standards such as REACH and RoHS. H2 projects that tightening regulations in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia will accelerate adoption, particularly in regulated industries like nuclear and marine. -
Cost Reduction and Broader Market Access
Although initial costs remain higher than traditional methods, H2 predicts a downward trend in pricing due to advancements in fiber laser technology and increased production scale. By 2026, the total cost of ownership for laser cleaning is expected to become competitive, making it accessible to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) beyond large industrial players. -
Expansion into New Applications
Beyond industrial cleaning, H2 highlights emerging applications in cultural heritage restoration, electronics manufacturing, and 3D printing post-processing. The non-contact nature of laser cleaning makes it suitable for delicate surfaces, opening new revenue streams for portable laser cleaner manufacturers. -
Regional Growth Disparities
H2 analysis indicates that Asia-Pacific—especially China and Japan—will lead market growth due to rapid industrialization and government support for advanced manufacturing. North America and Europe will follow, driven by automation trends and green manufacturing initiatives.
In conclusion, H2 forecasts that by 2026, the portable laser cleaner market will experience robust growth, fueled by technological innovation, environmental imperatives, and diversification of applications. Companies investing in R&D, user-friendly designs, and sustainable solutions will be best positioned to capture market share in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Portable Laser Cleaners (Quality & IP)
Sourcing portable laser cleaners involves significant risks, particularly concerning quality and intellectual property (IP). Avoiding these common pitfalls is crucial for ensuring performance, safety, and legal compliance.
Overlooking Build Quality and Component Durability
Many suppliers, especially low-cost manufacturers, use substandard materials and components to reduce prices. This can lead to premature failure of critical parts such as laser diodes, cooling systems, or handheld enclosures. Buyers often discover that devices degrade rapidly under field conditions, resulting in costly downtime and repairs.
Ignoring Safety Certifications and Compliance
Portable laser cleaners are high-power devices that must meet strict safety standards (e.g., FDA, CE, IEC 60825). A common mistake is sourcing units without proper certification documentation. Non-compliant lasers pose serious safety risks and may be seized by customs or banned from use in regulated industries.
Falling for Inflated Performance Claims
Some suppliers exaggerate laser power (e.g., labeling a 30W system as 100W effective) or cleaning speed. Without independent testing or verifiable data, buyers may receive underperforming equipment. Always request real-world test videos and third-party performance reports before purchase.
Neglecting After-Sales Support and Serviceability
Portable units require maintenance and occasional repairs. Sourcing from suppliers with no local service network or limited spare parts availability can render the equipment unusable when issues arise. Ensure the supplier offers technical support, repair services, and clear warranty terms.
Underestimating IP and Legal Risks
Many portable laser cleaners, particularly from certain regions, incorporate technology that may infringe on existing patents or lack proper IP ownership. Purchasing such devices exposes buyers to legal liability, product recalls, or import bans. Always verify that the supplier can provide proof of legitimate IP rights or licensing agreements for core technologies.
Assuming All Lasers Are Interchangeable
Different applications (e.g., rust removal, paint stripping, mold cleaning) require specific wavelengths, pulse frequencies, and power settings. A one-size-fits-all approach often results in poor results. Buyers should match technical specifications to their intended use and avoid generic models that lack customization options.
Failing to Conduct On-Site or Factory Audits
Remote sourcing without visiting the manufacturer increases the risk of receiving counterfeit or rebranded products. Conducting due diligence through factory audits, sample testing, and background checks on the supplier helps validate both quality and IP integrity.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Portable Laser Cleaners
Portable laser cleaners are powerful industrial tools that require careful handling throughout their lifecycle—from manufacturing and shipping to operation and disposal. Adhering to international, national, and regional regulations ensures safety, legal compliance, and smooth logistics operations. This guide outlines key considerations under logistics and compliance for portable laser cleaners.
H2: Regulatory Classification & Documentation
1. Harmonized System (HS) Code
Identify the correct HS code for customs clearance. Portable laser cleaners typically fall under:
– 8543.70 – “Electrical machines and apparatus, having individual functions, not specified elsewhere” (common for laser-based equipment).
Note: Final classification depends on technical specifications (e.g., power output, application). Consult local customs authorities for confirmation.
2. Export Controls
Check for dual-use or strategic trade regulations:
– Wassenaar Arrangement: Laser systems may be controlled based on wavelength, power, and pulse duration.
– EAR (Export Administration Regulations, USA): Review Commerce Control List (CCL) – likely under 6A003.b (lasers exceeding certain performance thresholds).
– EU Dual-Use Regulation (EC) 428/2009: Similar controls apply in Europe.
Action: Obtain export licenses if required based on destination country and technical specs.
3. Safety & Electromagnetic Compliance
Ensure product meets regional safety and EMC standards:
– CE Marking (Europe): Comply with Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC), EMC Directive (2014/30/EU), and Laser Product Safety (EN 60825-1).
– FCC (USA): Compliance with Part 15 for electromagnetic interference.
– UKCA (UK): Post-Brexit equivalent to CE marking.
– PSE (Japan), KC (Korea), RCM (Australia/NZ): Required for respective markets.
4. Laser Product Safety Certification
Classify the laser according to IEC 60825-1 / FDA 21 CFR 1040.10:
– Most portable laser cleaners are Class 4 lasers (high power, fire and skin/eye hazard).
– Include proper labeling (warning labels, aperture labels), interlocks, and safety features.
– Provide a Laser Safety Manual with each unit.
H2: Packaging & Shipping Requirements
1. Secure Packaging
– Use shock-absorbent, rigid packaging with internal immobilization to protect optics and electronics.
– Clearly label packages with:
– “Fragile”
– “This Side Up”
– “Laser Radiation – Avoid Direct Exposure” (IEC 60825 warning symbol)
– “Class 4 Laser Product”
2. Battery Transport (if applicable)
Many portable units use Li-ion batteries:
– Comply with UN 38.3 testing for lithium batteries.
– Pack per IATA DGR (air), IMDG Code (sea), or ADR (road) depending on mode.
– Ship batteries at ≤30% state of charge if standalone; otherwise, installed in equipment (Packing Instruction 967, Section II, if under limits).
3. Hazardous Materials Declaration
– While the laser itself is not typically classified as hazardous, documentation must indicate presence of Class 4 laser and Li-ion batteries.
– Provide Safety Data Sheet (SDS) upon request, especially for customs or industrial users.
H2: Import & Customs Clearance
1. Required Documentation
Prepare for each shipment:
– Commercial Invoice (with HS code, value, technical description)
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading / Air Waybill
– Certificate of Conformity (CE, FCC, etc.)
– Export License (if applicable)
– Warranty and User Manual (in local language, if required)
2. Duties & Tariffs
– Research import tariffs in destination country. Some countries offer reduced rates for industrial machinery.
– Use Free Trade Agreements (e.g., USMCA, RCEP) if applicable to reduce or eliminate duties.
3. Local Approvals
– Some countries require pre-shipment inspection or local type approval (e.g., SRRC in China, ISED in Canada).
– Confirm if laser use requires registration with national radiation protection agency (e.g., BfS in Germany, ARPANSA in Australia).
H2: Operational Compliance & End-User Responsibilities
1. Workplace Safety Regulations
End-users must comply with occupational safety laws:
– OSHA (USA), HSE (UK), EU-OSHA: Require risk assessments, protective equipment (laser safety goggles), controlled access zones.
– Implement Laser Safety Officer (LSO) program for Class 4 lasers per ANSI Z136.1 or IEC 60825.
2. Training & Documentation
– Provide operator training on safe use, emergency procedures, and maintenance.
– Maintain logs of usage, maintenance, and safety inspections.
3. Environmental & Disposal Compliance
– At end-of-life, dispose of units per WEEE Directive (EU) or local e-waste laws.
– Li-ion batteries must be recycled through certified facilities (e.g., RBRC, Weee Register).
– Laser components may contain hazardous materials (e.g., optical coatings); follow hazardous waste protocols.
H2: Summary of Key Actions
| Area | Key Requirement | Action |
|——|——————|——–|
| Classification | Correct HS & ECCN code | Consult customs expert |
| Export | Dual-use controls | Apply for license if needed |
| Certification | IEC 60825, CE, FCC | Obtain test reports & labels |
| Shipping | Battery & laser labeling | Use compliant packaging |
| Import | Local conformity | Verify market-specific approvals |
| Operation | Workplace safety | Train users, designate LSO |
| End-of-Life | WEEE / recycling | Provide disposal instructions |
Final Note: Regulations vary significantly by country and change frequently. Always consult with legal, compliance, and logistics professionals before shipping portable laser cleaners internationally. Maintain up-to-date technical files and compliance documentation for audit readiness.
Conclusion on Sourcing a Portable Laser Cleaner
Sourcing a portable laser cleaner requires a comprehensive evaluation of technical specifications, vendor reliability, safety compliance, and long-term operational needs. These advanced cleaning tools offer significant advantages over traditional methods—such as precision, minimal surface damage, eco-friendliness, and reduced downtime—making them a worthwhile investment for industries like automotive, aerospace, mold maintenance, and cultural restoration.
When selecting a supplier, it is crucial to prioritize manufacturers with proven track records, certifications (e.g., CE, FDA, or laser safety standards), and strong after-sales support, including training and warranty services. Additionally, assessing key features such as laser power, portability, ease of use, and compatibility with different materials ensures optimal performance for specific applications.
While the initial cost of a portable laser cleaner may be higher than conventional cleaning tools, the long-term savings in labor, consumables, and equipment longevity justify the investment. By carefully vetting suppliers and aligning the technology with operational requirements, organizations can enhance cleaning efficiency, improve worker safety, and achieve sustainable maintenance practices.
In conclusion, sourcing a portable laser cleaner should be approached strategically—balancing upfront costs with performance, support, and total cost of ownership—to fully harness its benefits in modern industrial and technical environments.