The global polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) market has experienced steady expansion, driven by rising demand across industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and chemical processing, where PTFE’s exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and low friction properties are highly valued. According to Mordor Intelligence, the PTFE market was valued at approximately USD 2.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% through 2029. This growth is fueled by advancements in manufacturing technologies, increased adoption of high-performance polymers in emerging economies, and a shift toward lightweight, durable materials in industrial applications. As demand for PTFE rods—used in seals, bearings, and insulating components—continues to rise, a competitive landscape of manufacturers has emerged globally, focusing on product quality, regulatory compliance, and innovation. The following list highlights the top 10 PTFE rod manufacturers shaping this expanding market.
Top 10 Polytetrafluoroethylene Rod Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Fluoro
Domain Est. 2001
Website: fluoropolymerproducts.com
Key Highlights: 1-800-262-1910 [email protected] usa-flag Fluoro-Plastics is a US based manufacturer of Teflon and PTFE products….
#2 PTFE Teflon Rod Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2017
Website: jfeindia.com
Key Highlights: JFE has built up itself as a main producer and provider of prevalent quality PTFE Teflon Rod. This item utilizes a two-coat (primer/topcoat) framework….
#3 PTFE Plastic Sheet & Rod
Domain Est. 1996
Website: piedmontplastics.com
Key Highlights: Shop PTFE plastic sheet and rod from Piedmont Plastics. Strong, chemical-resistant, and versatile for industrial and electrical applications….
#4 A Leading PTFE Products Manufacturers and Exporter
Domain Est. 2003
Website: hindustan-nylons.com
Key Highlights: Hindustan Nylons is India’s premium quality manufacturer & major exporter of PTFE & filled PTFE products such as PTFE Rods, PTFE Bushes, PTFE Moulded Sheets….
#5 PTFE Rod MRF-100
Domain Est. 2008
Website: chukoh.com
Key Highlights: PTFE Rod MRF-100 is a product made by extruding fluoroplastic (PTFE) into a rod shape. It is used as a material for processing electrical parts, …Missing: polytetrafluoroethylen…
#6 PTFE Rods
Domain Est. 2012
Website: ptfemanufacturer.com
Key Highlights: We are one of the leading supplier and exporter of the ptfe rods in India. The ptfe rods are acknowledged for their property of very low coefficient for the ……
#7 Virgin PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) rod
Domain Est. 1997
Website: cshyde.com
Key Highlights: PTFE Rod. CS Hyde Company stocks Virgin PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) rod in a wide range of thicknesses. Rods are readily available in diameters from 1/8 ……
#8 PTFE Sheets & Rods (Mechanical Grade)
Domain Est. 1997
Website: professionalplastics.com
Key Highlights: PTFE is a self-lubricating material that provides a low friction coefficient, and is ideally suited for the manufacture of corrosion-resistant gaskets & seals….
#9 PTFE
Domain Est. 2012
Website: standard-ptfe.com
Key Highlights: Standard Fluoromers Private Limited manufactures PTFE Rods – Moulded by Compression Moulding process in variety of standard sizes….
#10 PTFE Rod
Domain Est. 2022
Website: interstateam.com
Key Highlights: In stock 6–7 day deliveryPTFE is a soft fluoropolymer mechanical plastic with exceptional resistance to high temperatures, chemicals, corrosion and stress cracking….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Polytetrafluoroethylene Rod

H2: Projected Market Trends for Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Rod in 2026
The global market for Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) rods is expected to experience steady growth by 2026, driven by expanding industrial applications, technological advancements, and rising demand across key end-use sectors. PTFE rods—known for their exceptional chemical resistance, low friction, thermal stability, and electrical insulation properties—are critical components in industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, chemical processing, and medical devices.
-
Increased Demand in High-Performance Industries
By 2026, the aerospace and defense sectors are anticipated to be major drivers of PTFE rod consumption. The need for lightweight, durable, and heat-resistant materials in aircraft components, seals, and gaskets will boost demand. Similarly, the automotive industry’s shift toward electric vehicles (EVs) will increase the need for PTFE rods in battery systems, fuel cell components, and under-the-hood applications due to their reliability in high-temperature and corrosive environments. -
Growth in Semiconductor and Electronics Manufacturing
The global expansion of semiconductor fabrication, especially in Asia-Pacific regions like China, South Korea, and Taiwan, will significantly influence PTFE rod demand. PTFE’s non-contaminating and insulative properties make it ideal for use in wafer handling equipment and cleanroom components, where purity and precision are paramount. As chip manufacturing advances toward smaller nodes, the reliance on high-purity PTFE materials is expected to grow, positively impacting the rod segment. -
Advancements in Material Engineering and Customization
Manufacturers are increasingly investing in modified PTFE formulations, such as filled PTFE rods (with glass, carbon, or bronze reinforcements), to enhance mechanical strength and wear resistance. By 2026, customization will become a competitive differentiator, with companies offering tailored PTFE rods for specific industrial requirements, supporting market diversification and premium pricing. -
Environmental Regulations and Sustainability Challenges
Environmental concerns related to the production of fluoropolymers, particularly per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), may constrain market growth in North America and Europe. Regulatory scrutiny is expected to intensify, prompting manufacturers to adopt more sustainable production practices and explore PFAS-free alternatives. However, PTFE remains essential in critical applications, so innovation in eco-friendly manufacturing will be key to maintaining market access. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is projected to dominate the PTFE rod market by 2026, fueled by rapid industrialization, infrastructure development, and strong manufacturing bases in countries like China and India. North America and Europe will maintain steady demand, supported by high-tech industries and strict performance standards. Meanwhile, the Middle East and Latin America may see emerging opportunities in oil & gas and chemical processing sectors. -
Supply Chain Resilience and Raw Material Costs
The market will continue to face volatility in raw material prices, particularly for fluorite and hydrofluoric acid. Geopolitical factors and supply chain disruptions may influence production costs. As a result, key players are likely to pursue vertical integration and regional sourcing strategies to ensure supply stability and cost efficiency by 2026.
In summary, the PTFE rod market in 2026 will be shaped by rising demand from advanced manufacturing and high-tech industries, ongoing material innovations, and evolving regulatory landscapes. While sustainability concerns pose challenges, the unique performance characteristics of PTFE will sustain its critical role across diverse industrial applications, underpinning moderate to strong global market growth.
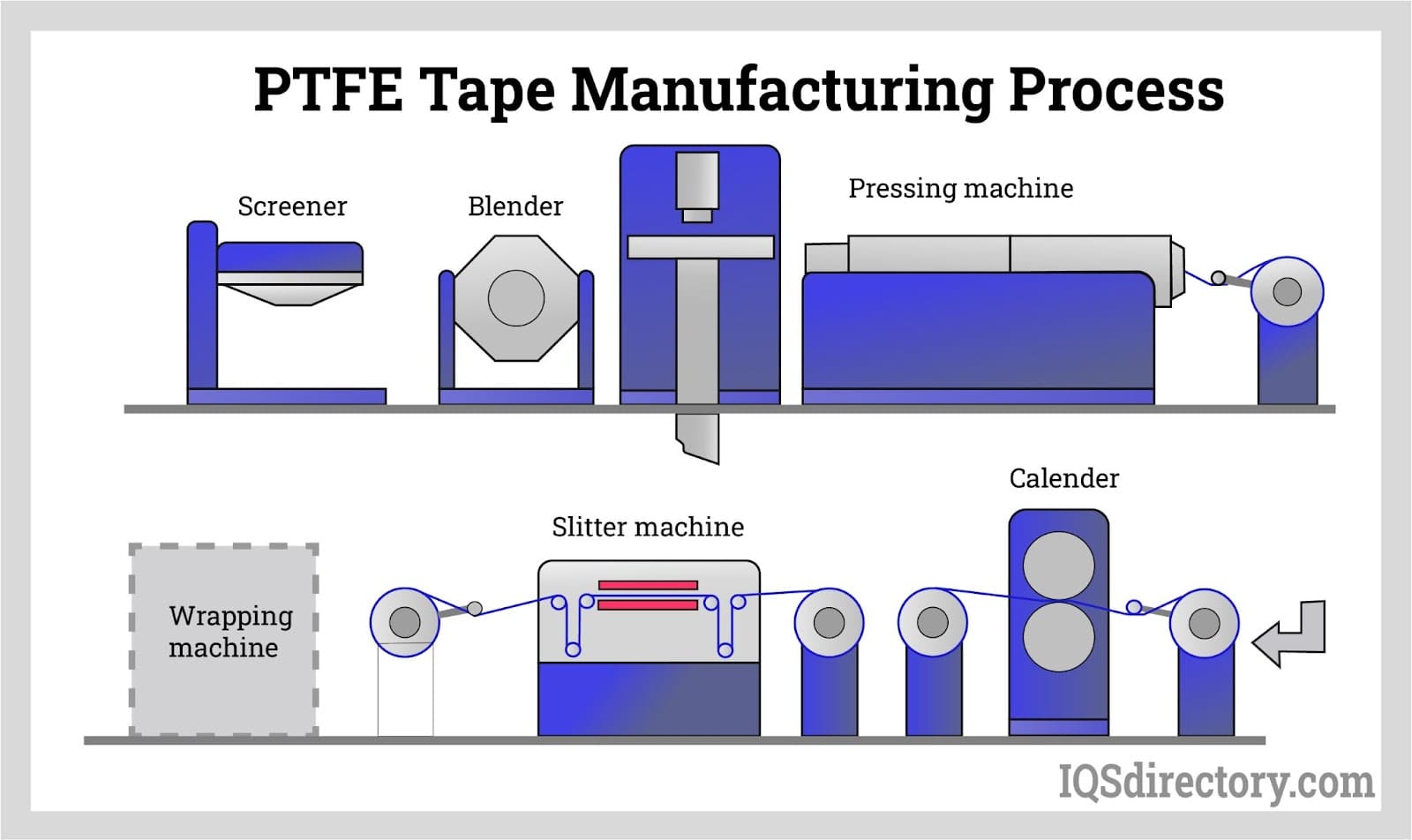
H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Rod – Quality & Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) rod, especially high-performance grades, involves significant risks related to material quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these can lead to product failure, safety hazards, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Here are the key pitfalls to avoid:
1. Substandard Material Quality & Impurities
- Pitfall: Receiving rods made from recycled, contaminated, or off-spec PTFE resin (e.g., incorrect molecular weight, high ash content, or fillers not disclosed).
- Consequence: Reduced chemical resistance, lower thermal stability, poor mechanical strength, and premature failure in critical applications (e.g., seals, bearings, or chemical processing).
- Mitigation: Specify resin grade (e.g., virgin Teflon™ PTFE 7A), require material certifications (CoC), and conduct independent testing (FTIR, DSC, density checks).
2. Misrepresentation of Material Origin & Brand
- Pitfall: Suppliers falsely claiming to supply branded PTFE (e.g., Chemours Teflon™, Daikin Neoflon™) when delivering generic or counterfeit material.
- Consequence: Loss of performance guarantees, voided equipment warranties, and potential IP infringement if branded names are used without authorization.
- Mitigation: Verify supplier authorization from original manufacturers and audit supply chain transparency. Avoid suppliers offering “Teflon™ equivalent” at suspiciously low prices.
3. Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
- Pitfall: Unknowingly sourcing PTFE rods that infringe on patented manufacturing processes, formulations, or product designs.
- Consequence: Legal liability, shipment seizures, and supply chain disruption. End-users may be named in infringement lawsuits.
- Mitigation: Require suppliers to warrant IP compliance. Conduct due diligence on proprietary tech (e.g., enhanced creep resistance, filled composites) and avoid gray-market sources.
4. Inconsistent Dimensional Accuracy & Tolerances
- Pitfall: Rods outside specified tolerances (e.g., diameter, straightness, roundness), especially in extruded or skived rods.
- Consequence: Poor fit in machining or assembly, increased scrap rates, and compromised performance in precision applications.
- Mitigation: Define strict dimensional tolerances in procurement specs (e.g., ASTM D4894) and perform incoming inspection.
5. Lack of Traceability & Documentation
- Pitfall: Inadequate batch traceability, missing CoCs, or falsified test reports.
- Consequence: Inability to verify material history during audits, recalls, or failure investigations. Non-compliance in regulated industries (e.g., aerospace, medical).
- Mitigation: Require full traceability (batch/lot numbers), authentic CoCs, and third-party test reports. Prefer suppliers with quality management systems (ISO 9001).
6. Unverified Filler Content & Homogeneity
- Pitfall: For filled PTFE rods (e.g., with glass, carbon, or bronze), inconsistent filler dispersion or undisclosed additives.
- Consequence: Non-uniform wear resistance, thermal conductivity, or electrical properties—leading to unpredictable performance.
- Mitigation: Specify filler type, %, and dispersion requirements. Request microstructure analysis (SEM) for critical applications.
7. Counterfeit or Diverted Goods
- Pitfall: Purchasing counterfeit PTFE rods or genuine products diverted from authorized channels.
- Consequence: Unknown material history, potential degradation, and voided manufacturer support.
- Mitigation: Source only from authorized distributors or directly from OEMs. Authenticate packaging and labels.
Best Practice: Establish long-term partnerships with reputable, certified suppliers, conduct regular audits, and invest in material verification to ensure both quality integrity and IP compliance.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Rod
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) rod, commonly known by the brand name Teflon™, is a high-performance thermoplastic polymer valued for its chemical resistance, low friction, and thermal stability. While PTFE itself is chemically inert and non-hazardous under normal conditions, proper logistics and regulatory compliance are essential throughout its handling, transportation, storage, and documentation. This guide outlines key considerations for the safe and compliant management of PTFE rods.
1. Regulatory Classification
- Chemical Identity: Polytetrafluoroethylene (CAS No. 9002-84-0)
- Hazard Classification (GHS/CLP):
- PTFE in solid form (e.g., rods) is not classified as hazardous under GHS (Globally Harmonized System) or EU CLP Regulation.
- It is non-flammable, non-reactive, and non-toxic under normal handling conditions.
- Note: During thermal decomposition (above 300°C), PTFE can release toxic fumes (e.g., hydrogen fluoride, perfluoroisobutylene). However, this does not affect transportation or storage under standard conditions.
2. Transportation
- Mode of Transport:
- Road (ADR): Not regulated as dangerous goods.
- Air (IATA): Not classified as hazardous; no special labeling required.
- Sea (IMDG): Exempt from dangerous goods regulations.
- Packaging:
- Use durable, moisture-resistant packaging (e.g., sealed plastic wraps, wooden crates, or cardboard boxes).
- Protect rods from physical damage, dust, and contamination.
- Ensure stacking stability during transit.
- Labeling:
- No hazardous labels required.
- Include product name, batch number, net weight, manufacturer details, and handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Protect from UV”).
3. Storage
- Conditions:
- Store in a dry, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight and UV exposure.
- Avoid temperatures above 260°C to prevent degradation.
- Keep away from strong oxidizing agents (though reactivity is minimal).
- Shelf Life:
- PTFE rods have an indefinite shelf life if stored properly.
- Segregation:
- No special segregation required from other materials.
4. Handling & Worker Safety
- PPE Recommendations:
- Gloves (to prevent surface contamination).
- Safety glasses (if cutting or machining).
- Dust mask (during machining to avoid inhalation of fine particles).
- Machining Precautions:
- Use proper ventilation or dust extraction when cutting, drilling, or grinding.
- Avoid generating fine dust; while PTFE dust is not highly toxic, inhalation should be minimized.
- Never overheat PTFE during processing (keep below 260°C).
5. Environmental & Disposal Compliance
- Environmental Impact:
- PTFE is inert and does not readily degrade; it is not considered an environmental pollutant in solid form.
- Disposal:
- Dispose of as non-hazardous industrial waste in accordance with local regulations.
- Incineration should only be conducted in facilities equipped to handle fluorinated compounds (to avoid toxic emissions).
- Recycling is limited but possible through specialized polymer recyclers.
6. Documentation & Compliance
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS):
- Provide a compliant SDS (in accordance with REACH, OSHA HazCom 2012, or local regulations).
- Although PTFE rods are non-hazardous, an SDS is still required under most jurisdictions.
- REACH (EU):
- PTFE is registered under REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals).
- No SVHC (Substances of Very High Concern) obligations apply.
- TSCA (USA):
- PTFE is listed on the TSCA Inventory; compliant for commercial use.
- Export Controls:
- PTFE rods are not subject to ITAR, EAR, or other export control regimes unless part of a controlled system or application.
7. Special Considerations
- Food & Medical Grades:
- If PTFE rods are intended for food contact (FDA 21 CFR 177.1550) or medical use, ensure compliance with relevant standards and certifications.
- Maintain traceability and appropriate documentation (e.g., FDA compliance letter, USP Class VI).
- Customs & Import:
- HS Code Example: 3909.40 (Polymers of tetrafluoroethylene).
- Confirm tariff classification with local customs authority.
- No special import permits required in most countries.
Summary
PTFE rods are non-hazardous, chemically stable materials that require minimal regulatory oversight during transport and storage. However, proper handling, documentation, and adherence to environmental and occupational safety practices are essential. Always ensure that product-specific grades (e.g., FDA-compliant, conductive, filled) meet the intended application’s regulatory requirements.
For further compliance support, consult the manufacturer’s SDS and local regulatory authorities.
Conclusion for Sourcing Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Rod:
Sourcing polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) rod requires a strategic approach that balances material quality, supplier reliability, cost-efficiency, and compliance with industry standards. PTFE’s exceptional chemical resistance, thermal stability, low friction, and electrical insulation properties make it a critical material across industries such as aerospace, automotive, semiconductor, chemical processing, and medical devices. Therefore, selecting the right supplier is vital to ensure consistent performance and regulatory compliance.
Key considerations in the sourcing process include verifying the PTFE grade (e.g., virgin, filled, or modified), dimensional accuracy, certification (such as ASTM or ISO standards), and the supplier’s manufacturing capabilities and quality control procedures. Additionally, evaluating lead times, scalability, and technical support is essential for maintaining efficient production workflows.
Establishing long-term partnerships with reputable suppliers who offer traceability, customization options, and responsive service can enhance supply chain resilience. In conclusion, a well-structured sourcing strategy for PTFE rods ensures operational reliability, product integrity, and cost-effective procurement, ultimately supporting the success of high-performance engineering applications.