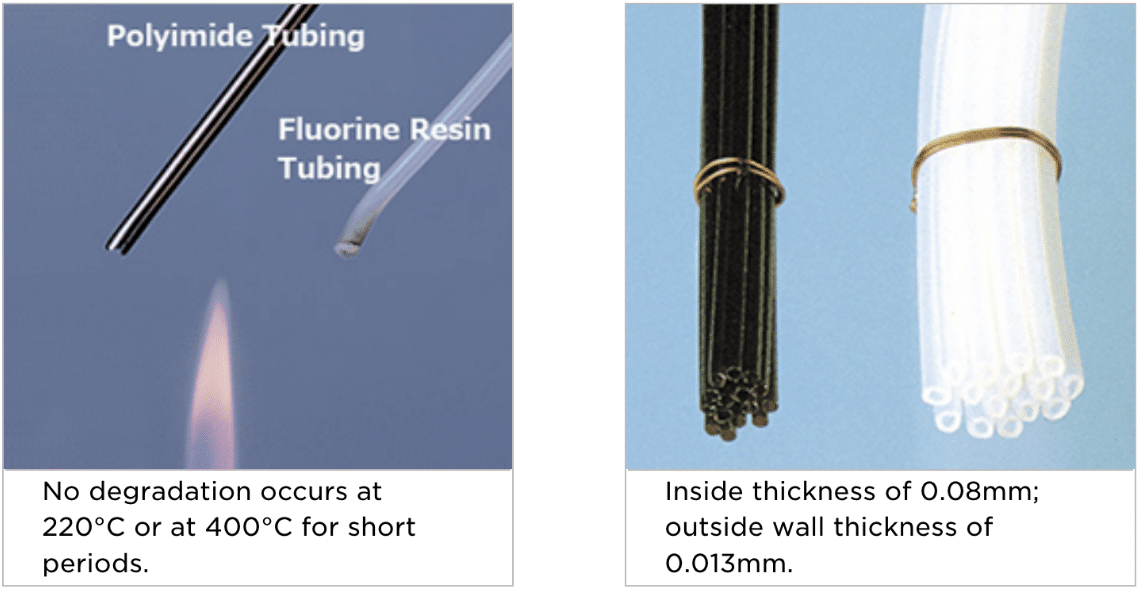
The global polyimide tubing market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand in aerospace, medical devices, automotive, and semiconductor industries. According to Grand View Research, the global polyimide market size was valued at USD 3.6 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by polyimide’s exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical performance in extreme environments. As industries increasingly prioritize high-performance materials, polyimide tubing has become a critical component in applications ranging from jet engines to minimally invasive medical devices. With expanding R&D initiatives and growing industrialization in Asia-Pacific and North America, the demand for reliable, high-quality tubing solutions continues to rise. Against this backdrop, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders in innovation, scalability, and technical expertise—shaping the future of one of the most resilient polymers in modern engineering.
Top 9 Polyimide Tubing Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Polyimide Tubing Archives
Domain Est. 1998
Website: americandurafilm.com
Key Highlights: American Durafilm Co., Inc. Tubing Division is a custom manufacturer of seamless, heat resistant, and chemically inert thermo- set polyimide tubing….
#2 Polyimide Tubing, Reinforced PI Tubing, & PI Coated Wire
Domain Est. 1996
Website: zeusinc.com
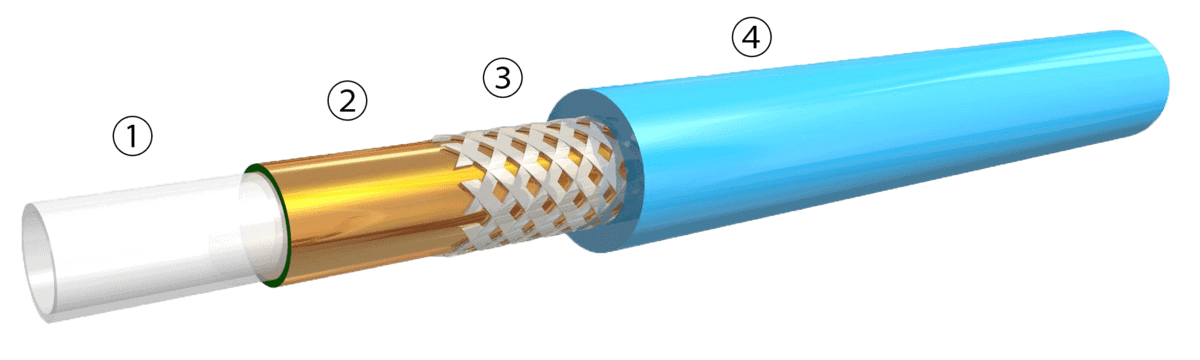
Key Highlights: Polyimide tubing can be produced in a range of ID sizes with super-thin walls and extremely tight tolerances. Polyimide tubing can also be provided in multi- ……
#3 Polyimide Tubing
Domain Est. 1996
Website: optima.se
Key Highlights: The MicroLumen Polyimide tubing is ideal for applications requiring thin walls, small diameters, and high dielectric strength. Reinforced Polyimide tubing has ……
#4 Polyimide Tubing
Domain Est. 1997
Website: microlumen.com
Key Highlights: Polyimide tubing is a polymer thermoset plastic, ideally suited for the stability required for surgical and medical tubing….
#5 Polyimide Medical Tubing
Domain Est. 1997
Website: putnamplastics.com
Key Highlights: What is polyimide tubing? Polyimides are used to manufacture vascular catheters for insertion into small vessels in the neck, head and brain….
#6 POLYIMIDE Tubing
Domain Est. 1997
Website: professionalplastics.com
Key Highlights: Polyimide Tubing (aka Kapton®) Micro Tubing features include: superior pushability and tractability, flexibility, ink resistance, and column strength….
#7 Confluent Opens Specialty Medical Polymer Tubing Center of …
Domain Est. 2015
Website: confluentmedical.com
Key Highlights: Confluent Medical’s New Center of Excellence Offers Component Design Support, PTFE Liners, Polyimide Tubing and Multi-layer Composite Tubing….
#8 Polyimide Tubing
Domain Est. 2016
Website: essexsolutions.com
Key Highlights: Essex Solutions Polyimide Tubing is a seamless tubing fabricated by special processes using polyimide resin, which has excellent heat and chemical resistance….
#9 Polyimide Tubing
Domain Est. 2017
Website: chamfr.com
Key Highlights: $0.01 delivery 7-day returnsPolyimide Tubing. Polyimide is a high performance thermoset material which offers very high tensile strength even with extremely thin walls….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Polyimide Tubing

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Polyimide Tubing
The global polyimide tubing market is poised for significant transformation and growth by 2026, driven by escalating demand from high-performance industries, technological advancements, and evolving material science. Key trends shaping the market include:
1. Surging Demand from Aerospace & Defense: The relentless pursuit of weight reduction, fuel efficiency, and enhanced performance in commercial and military aerospace will be a primary growth driver. Polyimide tubing’s exceptional combination of lightweight properties, extreme temperature resistance (cryogenic to over 400°C), high strength-to-weight ratio, and low outgassing makes it indispensable for critical applications in jet engines (fuel lines, bleed air systems), avionics cooling, and spacecraft thermal management. The rise of electric and hybrid-electric propulsion concepts will further increase demand for reliable, high-temperature insulation tubing.
2. Expansion in Medical & Life Sciences: The medical device sector, particularly minimally invasive surgery (MIS) and advanced diagnostics, will see accelerated adoption. Polyimide tubing’s biocompatibility, flexibility, kink resistance, and ability to be manufactured in ultra-thin walls (down to microns) are crucial for neurovascular, cardiovascular, and endoscopic catheters. Advancements in coating technologies (e.g., hydrophilic, antimicrobial) applied to polyimide substrates will enhance device performance and safety, driving market penetration.
3. Critical Role in Semiconductor & Electronics Manufacturing: The ongoing miniaturization of electronics and the push towards next-generation semiconductor nodes (3nm, 2nm) demand materials with superior thermal stability, dielectric strength, and dimensional stability. Polyimide tubing is essential for high-precision fluid handling (ultra-pure chemicals, deionized water) in wafer fabrication tools, photolithography equipment, and as insulating sleeves for delicate wiring in high-heat environments like reflow ovens. Demand will grow with global semiconductor capacity expansion.
4. Growth in Renewable Energy & Electric Vehicles (EVs): The transition to EVs fuels demand for components handling high-voltage systems and battery thermal management. Polyimide tubing’s high dielectric strength and thermal stability make it suitable for insulation in battery packs, power electronics (inverters, converters), and high-voltage cabling. In concentrated solar power (CSP) and next-generation nuclear (e.g., fusion research), its ability to withstand extreme temperatures and radiation is increasingly valuable.
5. Technological Advancements & Material Innovation: Key trends include:
* Enhanced Performance Grades: Development of polyimides with even higher continuous use temperatures, improved chemical resistance (especially to strong bases), lower moisture absorption, and higher tensile strength.
* Multi-Layer & Composite Tubing: Integration of polyimide with other polymers (e.g., PTFE liners for lubricity, ETFE for chemical resistance) or reinforcement layers (e.g., braided fibers) to create hybrid solutions offering optimized performance profiles.
* Precision Manufacturing: Advancements in extrusion and drawing techniques enabling tighter tolerances, more complex geometries, and consistent quality for micro-bore applications.
* Sustainable Production: Increased focus on developing more environmentally friendly synthesis routes and exploring recyclability pathways, though challenges remain.
6. Supply Chain Dynamics & Regional Shifts: Geopolitical factors and supply chain resilience concerns will drive some regionalization of production, particularly in North America and Europe, alongside continued strong manufacturing in Asia-Pacific (especially China and Japan). Securing stable raw material (dianhydrides, diamines) supply chains will be a critical focus for manufacturers.
7. Price Pressure & Cost Optimization: While demand grows, intense competition and pressure from end-users for cost reduction will push manufacturers to optimize production processes, improve yield rates, and potentially explore alternative (though likely lower-performing) materials for less demanding applications. However, the unique performance envelope of polyimide ensures its premium position in critical sectors.
Conclusion: By 2026, the polyimide tubing market will be characterized by robust growth, primarily fueled by technological imperatives in aerospace, healthcare, semiconductors, and clean energy. Success will depend on continuous innovation in material properties and manufacturing, strategic supply chain management, and the ability to meet the increasingly demanding performance and reliability requirements of cutting-edge applications across these high-growth industries.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Polyimide Tubing (Quality & IP)
Sourcing high-performance materials like polyimide tubing requires careful evaluation to avoid costly mistakes related to quality inconsistencies and intellectual property (IP) risks. Below are key pitfalls to watch for:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Material Properties
Polyimide tubing performance hinges on precise manufacturing controls. Suppliers may offer tubing with variable wall thickness, dimensional tolerances, or mechanical strength due to inconsistent extrusion or curing processes. This variability can lead to failures in critical applications such as aerospace or medical devices.
Substandard Raw Materials
Some suppliers may use lower-grade or recycled polyimide resins to cut costs. This compromises thermal stability, chemical resistance, and long-term durability—especially under high-temperature or aggressive chemical environments.
Lack of Traceability and Certification
Reputable applications require full material traceability (e.g., lot numbers, test reports) and certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, ASTM standards). Sourcing from vendors without these systems increases the risk of non-compliance and quality disputes.
Insufficient Testing and Validation
Suppliers might provide tubing without comprehensive performance data (e.g., dielectric strength, burst pressure, biocompatibility). Assuming performance based on datasheets alone—without independent validation—can lead to field failures.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Products
Unscrupulous suppliers may produce tubing that mimics patented designs or infringes on proprietary manufacturing processes (e.g., specific heat-treatment or coating technologies). Using such products exposes buyers to legal liability and supply chain disruption.
Unclear IP Ownership in Custom Designs
When sourcing custom-dimensioned or modified tubing, failure to clarify IP ownership in contracts may result in the supplier claiming rights to the design, limiting your freedom to manufacture or source elsewhere.
Lack of Freedom-to-Operate Analysis
Some polyimide formulations and tubing geometries are protected by patents. Sourcing without verifying freedom-to-operate (FTO) can lead to infringement claims, especially in regulated industries like medical devices or defense.
Mitigation Strategies
- Audit suppliers for quality systems and production controls.
- Require material certifications and batch-specific test reports.
- Conduct independent testing on initial and periodic shipments.
- Perform IP due diligence, including patent landscape reviews.
- Include clear IP clauses in supply agreements, especially for custom designs.
- Source from established manufacturers with proven IP compliance records.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures reliable performance and legal safety in demanding applications of polyimide tubing.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Polyimide Tubing
Overview
Polyimide tubing is a high-performance polymer tubing widely used in aerospace, medical devices, semiconductor manufacturing, and industrial applications due to its excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength. Due to its specialized nature and use in regulated industries, logistics and compliance are critical throughout its supply chain.
Transportation & Handling
Storage Conditions
- Temperature: Store in a cool, dry environment, ideally between 15°C and 30°C (59°F to 86°F).
- Humidity: Maintain relative humidity below 60% to prevent moisture absorption, which can affect dimensional stability.
- Light: Protect from prolonged exposure to direct sunlight or UV radiation to prevent surface degradation.
- Packaging: Keep tubing in original sealed packaging until use. Use moisture-barrier bags when necessary, especially for extended storage.
Handling Precautions
- Avoid kinking or sharp bends during handling; polyimide tubing is stiff and may crack under stress.
- Use clean gloves to prevent contamination, especially in medical or semiconductor applications.
- Do not drag or drop spools or reels; use appropriate lifting equipment for large quantities.
Shipping Requirements
- Use protective packaging (e.g., rigid boxes, foam inserts) to prevent physical damage.
- Clearly label packages as “Fragile” and “Do Not Crush.”
- For international shipments, ensure compliance with carrier-specific regulations for polymer materials.
- Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures during transit (e.g., non-climate-controlled containers).
Regulatory Compliance
International Trade & Customs
- HS Code: Typically classified under 3917.33 (Plastic tubes, of polyamides) or 3917.40 (Other plastic tubes). Confirm with local customs authorities; polyimide may fall under 3926.90 (Other articles of plastics) depending on form and use.
- Export Controls: Check for ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) or EAR (Export Administration Regulations) requirements if used in aerospace or defense applications.
- REACH & RoHS Compliance: Polyimide tubing must comply with EU REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directives, particularly if used in electronics or medical devices.
- Ensure no SVHCs (Substances of Very High Concern) are present above threshold levels.
- Confirm lead, cadmium, mercury, and other restricted substances are absent or within allowable limits.
Industry-Specific Standards
- Medical Devices (FDA): If used in medical applications, tubing must comply with FDA 21 CFR Part 820 (Quality System Regulation) and may require biocompatibility testing per ISO 10993.
- Aerospace (AS/EN Standards): Comply with AS9100 for quality management and specific material standards such as AMS (Aerospace Material Specifications).
- Semiconductor Industry: Must meet high-purity standards; verify low outgassing properties per ASTM E595 for vacuum environments.
Documentation & Traceability
Required Documentation
- Certificate of Conformance (CoC): Must accompany each batch, including material grade, lot number, dimensions, and compliance with relevant standards.
- Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS/SDS): Provide updated SDS detailing handling, storage, and disposal per GHS (Globally Harmonized System).
- Test Reports: Include mechanical, thermal, and chemical resistance data as applicable.
- Origin Documentation: For customs clearance, include commercial invoice, packing list, and bill of lading.
Traceability
- Implement full lot traceability from raw material to finished product.
- Maintain records for a minimum of 10 years for medical and aerospace applications.
- Use unique batch/lot numbering and barcoding for inventory and quality tracking.
Environmental & Disposal Considerations
Waste Management
- Polyimide is not biodegradable. Dispose of according to local hazardous waste regulations.
- Incineration should be conducted in facilities equipped to handle high-temperature polymer combustion, with emissions controls.
- Recycling options are limited; consult specialized polymer recyclers for feasibility.
Sustainability Compliance
- Monitor compliance with environmental regulations such as EU WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) if used in electronic assemblies.
- Consider lifecycle analysis and environmental impact during sourcing and procurement.
Summary
Proper logistics and compliance for polyimide tubing require careful attention to storage, handling, regulatory standards, and documentation. Adherence to industry-specific requirements and international regulations ensures product integrity, legal compliance, and supply chain reliability. Always consult applicable local and international regulations based on the end-use and destination market.
Conclusion for Sourcing Polyimide Tubing:
Sourcing polyimide tubing requires a strategic approach that balances performance requirements, cost efficiency, and supplier reliability. Due to its exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and flexibility at high temperatures, polyimide tubing is ideal for demanding applications in aerospace, semiconductor manufacturing, medical devices, and industrial systems. However, its high-performance characteristics come at a premium, making supplier selection and material specifications critical.
After evaluating multiple suppliers, the recommended approach is to partner with established manufacturers or distributors that offer consistent quality, compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO, ASTM), and the ability to customize dimensions and tolerances as needed. Additionally, considerations such as lead times, minimum order quantities, and technical support should factor into the final decision.
In conclusion, while polyimide tubing is a specialized and relatively costly material, sourcing from qualified, reputable suppliers ensures long-term reliability, performance, and cost-effectiveness across critical applications. Investing in thorough due diligence during the supplier qualification phase will mitigate risks and support supply chain resilience.