The global polyester powder coating market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for durable, eco-friendly, and cost-effective finishing solutions across industries such as automotive, construction, and appliances. According to Grand View Research, the global powder coatings market size was valued at USD 13.3 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2024 to 2030, with polyester-based formulations accounting for a significant share due to their excellent weather resistance and performance in outdoor applications. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects a CAGR of over 6.5% during the forecast period 2024–2029, citing increasing regulatory pressure to reduce VOC emissions as a key factor favoring powder coating adoption over traditional liquid paints. As demand continues to rise, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders in innovation, production capacity, and global reach—shaping the competitive landscape of the polyester powder coating industry.
Top 10 Polyester Powder Coating Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Industrial Powder Coatings
Domain Est. 1990
Website: ppg.com
Key Highlights: A pioneering powder coatings partner for over 30 years. Realize next-layer brilliance with customizable powder coatings in a spectrum of over 200 shades….
#2 » Cardinal Paint
Domain Est. 1996
Website: cardinalpaint.com
Key Highlights: Cardinal Paint is a premier manufacturer of high quality liquid & powder coatings which include primers, top coats, aerosols, and various powder products….
#3 Powder Coatings Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2001
Website: ifscoatings.com
Key Highlights: IFS Coatings is a leading powder coatings manufacturer for all applications. Find the perfect color and powder chemistry for your project with IFS….
#4 Powder Coatings
Domain Est. 1994
Website: stepan.com
Key Highlights: Stepan provides a broad range of high-quality RUCOTE® powder coating resins, manufactured to demanding ISO quality standards and backed by focused technical ……
#5 Powder
Domain Est. 1995
Website: akzonobel.com
Key Highlights: As well as an incredible range of colors, Interpon powder coatings offer a choice of stunning finishes including gloss, matt, structured and metallic….
#6 Powder Coatings by AkzoNobel
Domain Est. 1997
Website: interpon.com
Key Highlights: Discover Interpon, AkzoNobel’s brand transforming powder coatings. Explore innovative solutions tailored to every need and join the powder revolution!…
#7 TCI Powder Coatings
Domain Est. 1998
Website: tcipowder.com
Key Highlights: TCI stocks hundreds of products available in a variety of colors, textures, and effects ready to ship. Our portfolio also includes 150+ Super Durable Polyester ……
#8 Powder Coating & Surface Finishing Solutions
Domain Est. 2000
Website: tiger-coatings.com
Key Highlights: FOR A BETTER WORLD. Discover more than 1,500 powder coating products with endless possibilities for surface finishing….
#9 Prismatic Powders
Domain Est. 2001
#10
Domain Est. 2004
Website: axalta.com
Key Highlights: Axalta powder coatings offer you an extensive range of polyester products for the architectural field. These products have been specifically developed for ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Polyester Powder Coating
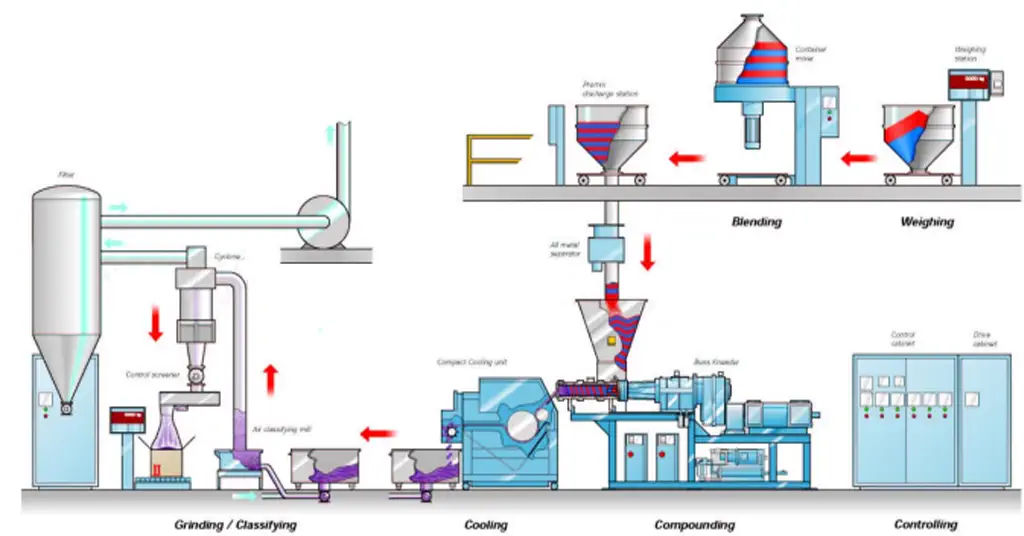
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Polyester Powder Coating
The global polyester powder coating market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by increasing environmental regulations, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences toward sustainable and durable finishes. As one of the most widely used powder coating types—particularly for outdoor applications due to its excellent UV resistance and weatherability—polyester powder coatings are expected to witness steady growth across key industries such as construction, automotive, and appliances.
A major trend shaping the 2026 market landscape is the tightening of volatile organic compound (VOC) regulations worldwide. With governments in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia enacting stricter environmental policies, industries are rapidly transitioning from solvent-based coatings to eco-friendly alternatives like polyester powder coatings. These powder coatings are inherently low in VOC emissions, aligning with sustainability goals and corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) commitments.
Additionally, innovations in formulation are enhancing the performance of polyester powder coatings. Manufacturers are developing hybrid resins and improving weather resistance, chalk resistance, and color retention to meet demanding specifications in architectural and infrastructure projects. By 2026, premium-grade polyester powders with extended durability (e.g., 10+ years of exterior performance) are expected to gain traction, especially in regions with harsh climatic conditions.
The construction sector remains a key growth driver, particularly in emerging economies where urbanization is accelerating demand for durable, low-maintenance building materials such as aluminum windows, roofing, and cladding. The rise in prefabricated construction and modular building techniques also favors powder-coated components due to their consistent finish and rapid application.
In the automotive industry, while epoxy and epoxy-polyester hybrids dominate under-the-hood applications, polyester powders are increasingly being adopted for exterior trim, wheels, and undercarriage parts due to their corrosion resistance and aesthetic versatility. Electric vehicle (EV) manufacturers are also exploring powder coatings for battery enclosures and structural components, further expanding market opportunities.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is expected to lead market growth by 2026, fueled by industrial expansion in China, India, and Southeast Asia. Europe will maintain strong demand due to regulatory support and a mature construction sector, while North America sees growth from infrastructure renewal projects and the adoption of sustainable manufacturing practices.
In summary, by 2026, the polyester powder coating market will be characterized by innovation, sustainability, and regional diversification. Strategic investments in R&D, coupled with a focus on circular economy principles—such as recyclable powders and reduced overspray waste—are likely to define competitive advantage in this maturing yet dynamic market segment.
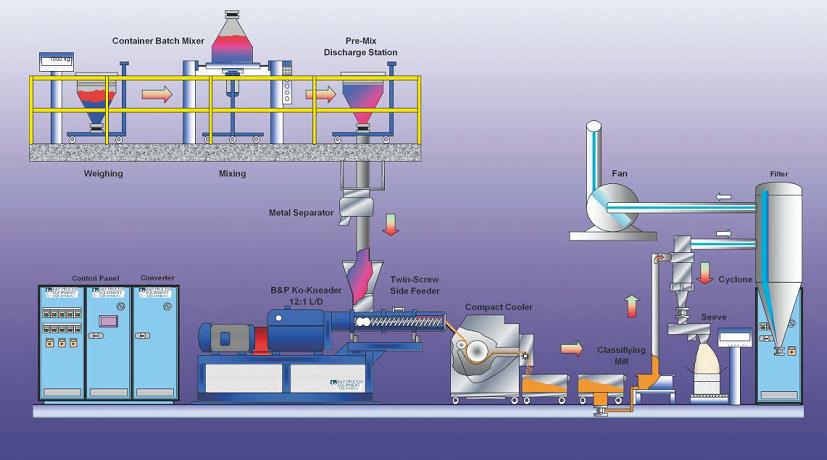
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Polyester Powder Coating: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
Sourcing polyester powder coating can be cost-effective, but it carries significant risks related to quality consistency and intellectual property. Understanding these pitfalls is essential for maintaining product performance and protecting your brand.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Inconsistent Raw Material Sourcing
Suppliers may source raw materials (resins, pigments, additives) from multiple low-cost vendors without rigorous quality controls. This leads to batch-to-batch variability in color, gloss, flow, and curing behavior, resulting in coating defects and production delays. -
Insufficient Performance Testing
Many suppliers—especially low-cost or emerging ones—lack comprehensive testing facilities. They may not conduct critical tests (e.g., QUV accelerated weathering, salt spray corrosion, impact resistance), leading to premature coating failures in real-world applications. -
Poor Process Control and Contamination
Inadequate production practices can introduce contaminants or cause improper curing during manufacturing. This affects coating adhesion, durability, and appearance, particularly in sensitive environments like outdoor or industrial settings. -
Misrepresentation of Specifications
Some suppliers exaggerate performance claims (e.g., 10-year exterior durability) without third-party validation. Buyers may receive coatings that degrade rapidly under UV exposure or fail to meet industry standards like AAMA 2604 or Qualicoat. -
Lack of Technical Support
Low-cost suppliers often provide minimal technical guidance. This can lead to incorrect application parameters (curing temperature, film thickness), resulting in poor finish quality and increased rework costs.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
-
Reverse-Engineered Formulations
Unethical suppliers may illegally reverse-engineer proprietary formulations from market leaders. Using such coatings exposes buyers to legal risks, including infringement claims from original manufacturers. -
Trademark and Brand Infringement
Some suppliers falsely label their products with well-known brand names or use similar packaging to mislead buyers. This not only violates trademark laws but also compromises reliability and traceability. -
Lack of IP Ownership Clarity
When developing custom formulations, suppliers may retain IP rights or use shared recipes. Buyers risk losing exclusivity and may face supply chain vulnerabilities if the supplier sells the same formulation to competitors. -
No Confidentiality Agreements
Reputable suppliers sign NDAs to protect client-specific formulations and applications. Sourcing from vendors who refuse such agreements increases the risk of sensitive information being shared or exploited. -
Grey Market and Unauthorized Distribution
Purchasing through unauthorized distributors may result in counterfeit or diverted products. These lack quality assurance and can void warranties, while also exposing companies to indirect IP liability.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, conduct thorough due diligence: audit supplier facilities, request certified test reports, verify IP ownership, and use legally binding agreements. Prioritize long-term reliability over short-term savings to protect product integrity and brand reputation.
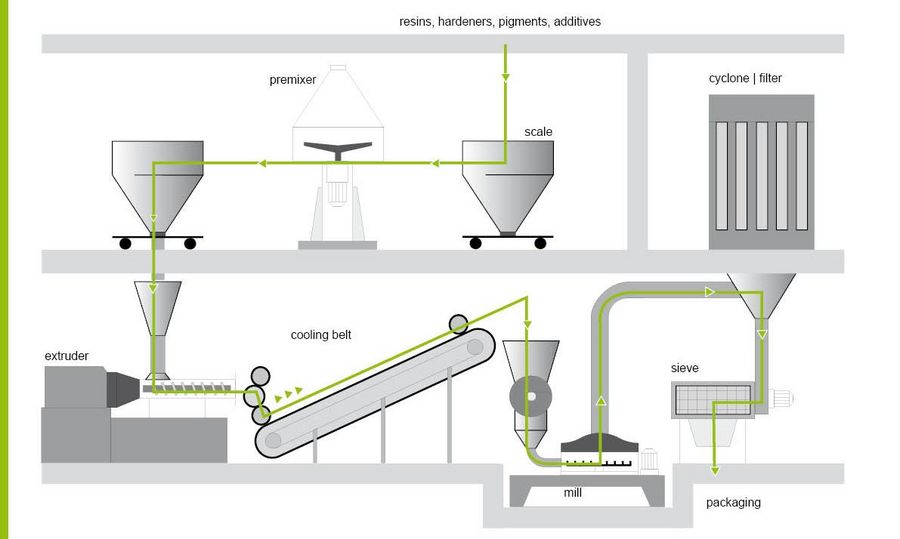
H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Polyester Powder Coating
This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for the safe handling, transportation, storage, and regulatory adherence related to polyester powder coating products. Adherence to these guidelines ensures operational efficiency, personnel safety, and legal compliance.
H2: Regulatory Compliance
1. Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
– Always maintain up-to-date Safety Data Sheets (SDS) in accordance with the Globally Harmonized System (GHS) of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals.
– SDS must be readily accessible to all personnel involved in handling, storing, or transporting the powder.
– Review Section 2 (Hazard Identification), Section 7 (Handling and Storage), and Section 14 (Transport Information) regularly.
2. Classification and Labeling
– Polyester powder coatings are generally classified as non-hazardous under transport regulations but may contain components that require labeling.
– Ensure all containers are properly labeled with product name, batch number, manufacturer details, and any applicable GHS pictograms (e.g., if dust is combustible).
– Dust explosion potential may require labeling such as “May form combustible dust concentrations in air.”
3. Environmental Regulations
– Comply with local and international environmental standards (e.g., REACH in the EU, TSCA in the US).
– Verify that formulations are free from restricted substances (e.g., heavy metals like lead or cadmium).
– Maintain documentation of compliance certifications (e.g., RoHS, REACh SVHC declarations).
4. Workplace Safety Standards
– Adhere to OSHA (US), COSHH (UK), or equivalent national occupational health and safety regulations.
– Implement measures to control inhalation and skin contact (e.g., PPE, ventilation systems).
– Conduct regular risk assessments for dust exposure and explosion hazards.
H2: Transportation & Logistics
1. Packaging Requirements
– Use sealed, moisture-resistant packaging (e.g., polyethylene-lined cardboard drums or plastic pails).
– Ensure containers are robust to withstand stacking and transit without rupture.
– Label packages with proper product identification and handling instructions (e.g., “Keep Dry,” “Protect from Moisture”).
2. Transport Classification
– Polyester powder coatings are typically not classified as dangerous goods under ADR/RID (road/rail in Europe), IMDG (sea), or IATA (air) regulations.
– Confirm classification via SDS Section 14; most powders are transported as “Not Regulated” or UN3077 (Environmentally hazardous substance, solid, n.o.s.).
– If dust explosion risk is significant, consider UN3175 (Combustible solid, organic, n.o.s.) with appropriate precautions.
3. Handling & Loading
– Use mechanical handling equipment (e.g., pallet jacks) to avoid manual strain.
– Prevent package damage during loading/unloading.
– Segregate from incompatible materials (e.g., strong oxidizers, acids) during transport.
4. Temperature & Environmental Controls
– Avoid exposure to high temperatures (>40°C / 104°F) to prevent caking or pre-reaction.
– Protect from direct sunlight and freezing conditions during transport.
– Ensure vehicles are clean, dry, and well-ventilated.
H2: Storage & Handling
1. Storage Conditions
– Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area with temperatures between 15–25°C (59–77°F).
– Keep away from heat sources, ignition points, and direct sunlight.
– Use elevated pallets to prevent moisture absorption from floors.
2. Shelf Life & Inventory Management
– Observe manufacturer-stated shelf life (typically 6–12 months from production date).
– Implement FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory rotation.
– Monitor for clumping, discoloration, or odor changes indicating degradation.
3. Dust Control & Explosion Prevention
– Install local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems in mixing and handling areas.
– Use explosion-proof electrical equipment in storage and processing zones.
– Implement grounding and bonding procedures to prevent static discharge.
– Comply with NFPA 652 (Standard on the Fundamentals of Combustible Dust) or ATEX directives (EU).
4. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
– Required PPE includes:
– Dust mask/respirator (NIOSH-approved N95 or equivalent)
– Safety goggles or face shield
– Gloves (nitrile or similar)
– Anti-static workwear
– Provide training on proper PPE use and maintenance.
H2: Emergency Preparedness
1. Spill Response
– For small spills: Carefully collect powder using non-sparking tools; avoid creating dust clouds.
– For large spills: Evacuate area, ventilate, and use ATEX-rated vacuum systems.
– Never use compressed air for cleanup—this increases explosion risk.
– Dispose of contaminated material as per local regulations.
2. Fire Response
– Polyester powders may burn if ignited; use dry chemical, CO₂, or foam extinguishers.
– Do not use water jets, as they may disperse dust and worsen the situation.
– Evacuate and call emergency services if fire involves large quantities.
3. Health Exposure
– Inhalation: Move to fresh air; seek medical attention if respiratory irritation persists.
– Skin contact: Wash with soap and water; remove contaminated clothing.
– Eye contact: Rinse thoroughly with water for at least 15 minutes; consult a physician.
H2: Disposal & Sustainability
1. Waste Management
– Unused or expired powder must be disposed of in accordance with local hazardous waste regulations.
– Contact licensed waste disposal contractors for proper handling.
– Recycle overspray powder where possible using recovery systems (e.g., cartridge collectors).
2. Sustainability Practices
– Optimize application processes to minimize waste.
– Choose powder coatings with high transfer efficiency and low environmental impact.
– Partner with suppliers offering take-back or recycling programs.
Note: Regulations vary by country and region. Always consult local authorities and the product manufacturer for specific compliance requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing Polyester Powder Coating
Sourcing polyester powder coating requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, sustainability, and supply chain reliability. As a durable, weather-resistant, and environmentally friendly finishing solution, polyester powder coating is ideal for outdoor and industrial applications such as architectural components, automotive parts, and fencing.
To ensure a successful sourcing process, it is essential to evaluate suppliers based on technical capabilities, consistency in pigment dispersion and curing performance, certifications (such as ISO, AAMA, or Qualicoat), and their ability to meet regulatory standards (including REACH and RoHS). Additionally, considering lead times, logistical support, and the capacity for customization can greatly impact long-term operational efficiency.
Emphasis on sustainable practices—such as low-cure formulations, recyclable packaging, and reduced VOC emissions—further aligns sourcing decisions with environmental goals. Building strong partnerships with reliable suppliers who offer technical support and continuous innovation will ultimately enhance product performance and competitiveness in the market.
In conclusion, a well-structured sourcing strategy for polyester powder coating not only ensures superior finish quality and durability but also supports cost-effectiveness and sustainability objectives across the supply chain.