The global plate grinder market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand from industries such as construction, manufacturing, and metal fabrication. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the industrial grinding equipment market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by advancements in automation and the need for precision surface finishing. As infrastructure development accelerates worldwide and manufacturers prioritize efficiency and quality, plate grinders have become essential tools for achieving flat, burr-free surfaces on large metal components. With rising investments in industrial modernization—particularly across Asia-Pacific and North America—procurement professionals are increasingly seeking reliable, high-performance suppliers. To support strategic sourcing decisions, this list presents the top 10 plate grinder manufacturers recognized for innovation, production capacity, global reach, and adherence to industry standards.
Top 10 Plate Grinder Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
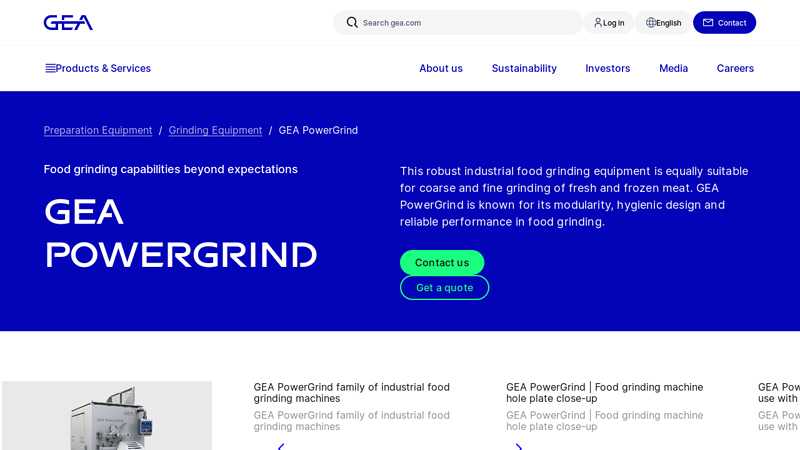
#1 GEA PowerGrind
Domain Est. 1995
Website: gea.com
Key Highlights: The GEA PowerGrind family is a new generation of robust food grinding machines that focuses on performance, hygiene, safety and modularity….
#2 Speco
Domain Est. 1996
Website: speco.com
Key Highlights: One of the largest manufacturers of Grinder Plates and Knives in the world. From meat grinder plates and knives to bone collector systems and insert blades….
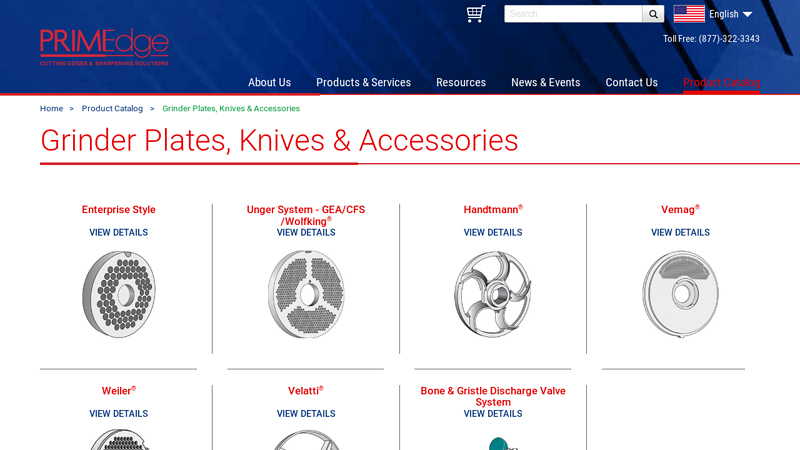
#3 Grinder Plates, Knives & Accessories
Domain Est. 2003
Website: primedge.com
Key Highlights: All items, parts, and accessories listed on the website of PRIMEdge, Inc., are manufactured by PRIMEdge, Inc., or manufactured to PRIMEdge, Inc.’s ……
#4 Grinder Knife and Plate Archives
Domain Est. 2019
Website: biroservice.com
Key Highlights: $12.99 deliveryGrinder Knife and Plate. Biro Service, Inc. Products Grinder Knife and Plate. Showing 1–9 of 31 resultsSorted by latest. Sort by popularity, Sort by latest ……
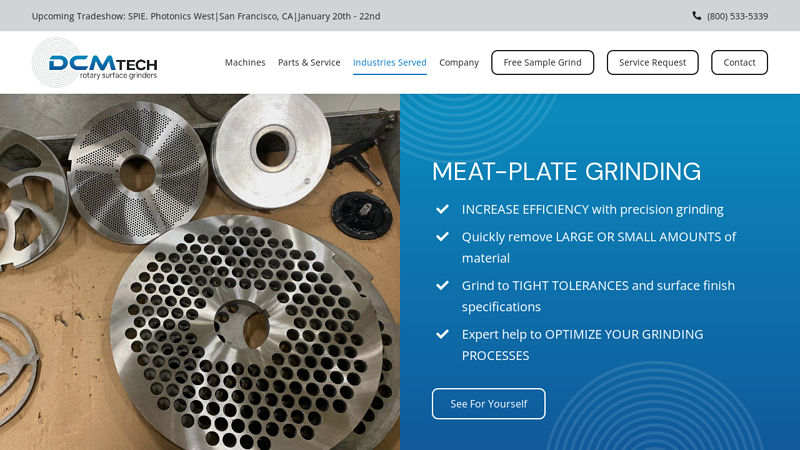
#5 DCM Introduces Meat Plate Grinders
Website: dcm-tech.com
Key Highlights: Made in the USA. DCM Tech designs and manufactures our products in Winona, MN. We provide factory direct sales and technical service….
#6 Grinder Plates & Knives
Domain Est. 1995
Website: kasco.com
Key Highlights: 4-day deliveryEngineered to excel in high-volume meat grinding … KASCO, with over 120 years of expertise, stands as the premier supplier of meat grinder plates and knives….
#7 Arrow Grinding, Expert Precision Grinding, CNC Machining, AS9100
Domain Est. 1996 | Founded: 1956
Website: arrowgrinding.com
Key Highlights: Since 1956, Arrow Grinding, a family-owned company, specializes in precision grinding services & close-tolerance part manufacturing, AS 9100, ISO 9001….
#8 Chopper Plates, Grinder Plates
Domain Est. 1997
Website: alfaco.com
Key Highlights: Alfa’s exclusive L&W chopper plates mean greater production and cooler, more efficient cutting. Made in Germany from a state-of-the-art chrome-vanadium steel….
#9 LEM Grinder Plates, Stainless #8
Domain Est. 1999
Website: pleasanthillgrain.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 5.0 (3) LEM makes their grinder knives with the highest standards for hardness and quality that are hard to find elsewhere. Made of stainless steel, each knife la…
#10 meat grinders
Domain Est. 2015
Website: westonbrands.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $200 Free 30-day returns…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Plate Grinder

2026 Market Trends for Plate Grinders
The plate grinder market is poised for notable shifts by 2026, driven by technological innovation, evolving industry needs, and growing emphasis on efficiency and sustainability. Here are the key trends expected to shape the sector:
H2: Advancements in Automation and Smart Technology Integration
Plate grinders are increasingly incorporating automation and smart features to enhance precision, reduce labor costs, and improve safety. By 2026, expect widespread adoption of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems, IoT-enabled monitoring, and AI-driven diagnostics. These technologies allow for real-time performance tracking, predictive maintenance, and remote operation, particularly in heavy industries such as shipbuilding, construction, and oil & gas. Manufacturers are investing in user-friendly interfaces and programmable settings to minimize operator error and ensure consistent surface finishes across large-scale projects.
H2: Rising Demand for Portable and Multi-Functional Grinders
There is a growing preference for compact, portable plate grinders that offer versatility across different materials and job sites. In 2026, the market will see a surge in lightweight models equipped with modular attachments for grinding, polishing, and beveling. This trend is fueled by the construction and fabrication sectors, where mobility and on-site adaptability are critical. Additionally, battery-powered grinders with extended runtimes and quick-charging capabilities are gaining traction, reducing dependency on power outlets and enhancing operational flexibility.
H2: Emphasis on Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing manufacturers to develop energy-efficient and eco-friendly plate grinders. By 2026, expect innovations in motor design—such as brushless DC motors—that reduce energy consumption and heat generation. Dust extraction and containment systems will become standard features to comply with workplace health and safety standards, especially in indoor or urban environments. Recycling of grinding abrasives and use of recyclable materials in grinder construction will also gain importance.
H2: Growth in Industrial Automation and Robotics Integration
The integration of plate grinders into robotic arms and automated production lines is accelerating, particularly in high-volume manufacturing settings. By 2026, robotic grinding cells will be more common in automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery industries, where consistency and repeatability are paramount. These systems use vision-guided grinding and adaptive force control to handle complex geometries and varying surface conditions, reducing cycle times and improving product quality.
H2: Regional Market Expansion and Infrastructure Development
Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa are expected to drive demand for plate grinders due to ongoing infrastructure projects and industrialization. Countries like India, Indonesia, and Brazil are investing heavily in transportation, energy, and urban development, creating a sustained need for metal fabrication and surface preparation tools. As a result, global manufacturers are tailoring product offerings to meet regional specifications and price sensitivities, including mid-range, durable models suited for challenging environments.
In summary, the 2026 plate grinder market will be defined by smarter, more efficient, and adaptable tools, supported by automation, portability, and sustainability trends. Companies that innovate in these areas will be well-positioned to capture growing demand across both mature and emerging industrial sectors.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing a Plate Grinder (Quality, IP)
Sourcing a plate grinder—especially one designed for industrial, laboratory, or high-precision applications—comes with several critical risks related to quality and intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to operational inefficiencies, safety hazards, legal disputes, and financial losses.
Poor Build Quality and Material Selection
A common issue when sourcing plate grinders is receiving units made from substandard materials or with inadequate engineering. Low-quality grinders may use inferior steel alloys for grinding plates, leading to rapid wear, warping, or contamination of processed materials. Poor manufacturing tolerances can result in inconsistent grinding performance, vibration, and premature mechanical failure. Additionally, inadequate sealing or cooling systems increase the risk of overheating and motor burnout. Always verify material certifications (e.g., stainless steel grade), inspect build quality firsthand or via third-party audits, and request performance data under load conditions.
Lack of Compliance with Safety and Industry Standards
Many suppliers, especially in unregulated markets, offer plate grinders that do not meet essential safety or industry standards (e.g., CE, UL, ISO). Non-compliant equipment may lack proper guarding, emergency stop mechanisms, or electrical safety features, posing serious risks to operators. In regulated industries like food, pharmaceuticals, or chemicals, using non-compliant grinders can invalidate certifications and result in regulatory penalties. Ensure all equipment adheres to relevant standards and request official compliance documentation before purchase.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Sourcing from suppliers offering “compatible” or “budget” versions of branded plate grinders raises significant IP concerns. Some manufacturers may reverse-engineer patented designs or use trademarked components without authorization. Purchasing such equipment—even unknowingly—can expose your organization to legal liability, shipment seizures, or reputational damage. Always vet suppliers for legitimate IP rights, request proof of licensing for branded technology, and avoid suppliers offering suspiciously low-priced replicas of well-known models.
Inadequate Documentation and Technical Support
Low-cost suppliers often provide minimal or poorly translated technical documentation, making installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting difficult. Missing or inaccurate manuals can compromise safe operation and lead to avoidable downtime. Additionally, limited technical support or unavailability of spare parts can render the equipment unusable over time. Confirm that the supplier offers comprehensive documentation in your language and has a reliable support network or local service partners.
Hidden Costs from Low Initial Pricing
While some plate grinders appear cost-effective upfront, hidden expenses often emerge post-purchase. These include frequent part replacements, higher energy consumption due to inefficient motors, or the need for retrofitting to meet safety or performance requirements. In extreme cases, poor-quality equipment may require complete replacement sooner than expected. Conduct a total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis—factoring in maintenance, energy use, and downtime—before making a decision.
Supply Chain and Warranty Reliability
Sourcing from distant or unknown manufacturers can lead to long delivery times, import delays, or difficulties enforcing warranty claims. Some suppliers may offer warranties that are difficult to redeem due to unclear terms or lack of local service centers. Verify the supplier’s track record for after-sales service, warranty coverage duration, and spare parts availability before committing.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—focusing on verifiable quality, regulatory compliance, IP legitimacy, and long-term support—organizations can mitigate risks and ensure reliable, legal, and efficient operation of their plate grinding equipment.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Plate Grinder
Overview
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe, efficient, and legal transport, handling, storage, and operation of plate grinders—industrial machinery used for surface preparation, material removal, or leveling metal plates. Adherence to this guide ensures regulatory compliance, worker safety, and equipment longevity.
Equipment Specifications and Handling
Ensure all logistics personnel are aware of the plate grinder’s:
– Weight, dimensions, and center of gravity
– Required lifting points or forklift entry locations
– Fragile components (e.g., grinding wheels, control panels)
Use proper lifting equipment (e.g., overhead crane, forklift with appropriate capacity) and secure the grinder during transport using straps or cradles to prevent shifting.
Packaging and Transportation
Package the plate grinder in a protective crate or palletized frame if shipped long-distance. Include:
– Moisture-resistant wrapping to prevent corrosion
– Shock-absorbing materials to protect sensitive parts
– Clearly labeled orientation arrows and “Fragile” warnings
Transport via freight carriers compliant with DOT (Department of Transportation) or equivalent regional regulations. Ensure carriers provide tracking and insurance for high-value equipment.
Import/Export Compliance
If moving across borders, verify:
– Harmonized System (HS) code for plate grinders (typically 8467.21 or similar)
– Import duties, tariffs, and required documentation (commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading)
– Export controls under EAR (Export Administration Regulations) if applicable
Obtain necessary export licenses for restricted destinations or dual-use technologies.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Ensure the plate grinder complies with:
– OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) standards for workplace machinery
– ANSI B7.1 (Safety Requirements for the Use, Care, and Protection of Abrasive Wheels)
– CE marking (for EU markets) per Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC
– CSA certification (for Canadian markets)
Retain all certification documents and user manuals for audit purposes.
Workplace Safety and Operational Compliance
Before use, confirm:
– Operators are trained and certified per company safety protocols
– Required PPE (personal protective equipment) is available: safety glasses, hearing protection, gloves, and respiratory protection if dust is generated
– Equipment is grounded and electrical components meet local codes (e.g., NEC in the U.S.)
Conduct routine safety inspections and maintain a log of maintenance and repairs.
Environmental and Waste Compliance
Grinding operations may produce metal dust or particulates. Comply with:
– EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) or local air quality regulations
– OSHA PELs (Permissible Exposure Limits) for airborne contaminants
– Proper disposal of used grinding wheels and metal waste as hazardous or non-hazardous per jurisdiction
Use dust extraction systems and conduct air monitoring where required.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain records of:
– Equipment purchase and maintenance history
– Safety inspections and operator training
– Shipping and customs documentation
– Incident reports or near-misses involving the grinder
Retain records for a minimum of five years or per local regulatory requirements.
Emergency Procedures
Establish protocols for:
– Equipment malfunction or kickback incidents
– Fire caused by sparks or electrical faults
– Exposure to hazardous dust or noise
Ensure emergency shut-offs are accessible and personnel know evacuation routes.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management for plate grinders reduces operational risks, ensures regulatory adherence, and promotes a safe working environment. Regular audits and staff training are essential to maintain compliance across the equipment lifecycle.
Conclusion:
After a thorough evaluation of various suppliers and models for sourcing a plate grinder, it is evident that selecting the right equipment involves balancing cost, quality, durability, and after-sales support. Based on performance reviews, technical specifications, and supplier reliability, it is recommended to partner with a supplier that offers a well-engineered plate grinder with robust construction, energy efficiency, and strong customer service. Prioritizing long-term value over initial cost will ensure operational efficiency, reduced downtime, and lower maintenance expenses. Ultimately, the selected plate grinder should align with the specific grinding requirements of the application, contributing to improved productivity and product consistency. A final decision should be supported by pilot testing, supplier references, and a clear understanding of warranty and service terms.