The global carbon steel plate market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising infrastructure development, growing demand from the construction, automotive, and energy sectors, and increased investment in industrial manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the global carbon steel market was valued at USD 117.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.1% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects sustained growth in carbon plate demand, particularly in Asia-Pacific—home to major industrial hubs—where urbanization and government-led infrastructure initiatives are key catalysts. As competition intensifies and quality standards evolve, identifying leading plate carbon manufacturers becomes critical for supply chain optimization and project reliability. Below, we highlight the top nine manufacturers shaping the industry through innovation, scale, and material performance.
Top 9 Plate Carbon Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Carbon Steel Profiles Limited
Domain Est. 2000
Website: carbon.ca
Key Highlights: Carbon Steel Profiles Limited is ISO 9001:2015 certified in CNC Technology used in Plate Burning, Plasma Cutting, Milling and Blanchard Grinding….
#2 Carbon plates
Domain Est. 2001
Website: carbon-composite.com
Key Highlights: Free deliveryHere you will find carbon plates from Carbon Composite. Delivery from stock directly from the manufacturer….
#3 Toray
Domain Est. 2012
Website: toray-cfe.com
Key Highlights: Recognised for the quality, reliability and performance of its carbon fibers and composite materials, Toray brings its technical expertise to its customers….
#4 OEM 100% Carbon Fiber Plate Supplier, Service
Domain Est. 2021
Website: fmscarbon.com
Key Highlights: We produce carbon fiber board through the autoclave process, which makes the surface of the carbon fiber more smooth and the texture more regular. We are high ……
#5 DragonPlate
Domain Est. 2003
Website: dragonplate.com
Key Highlights: DragonPlate is a leading innovator in high performance carbon fiber-reinforced composites. From custom carbon fiber shapes, to products including tubes, ……
#6 Universal Steel America: Steel Plate Distributor
Domain Est. 2005
Website: universalsteelamerica.com
Key Highlights: Universal Steel is a specialty steel plate distributor and processor built on superior service and quality. Offering an inventory of carbon & alloy plates….
#7 Rock West Composites Page
Domain Est. 2009
Website: rockwestcomposites.com
Key Highlights: Shop Tubes By Shape · Carbon Fiber Tubes · Fiberglass Tubes · Kevlar Tubes · Telescoping Tubes · Tube Samples · Build Your Own Tube. Shop Tubes By Shape….
#8 Fatcarbon® Materials
Domain Est. 2017
Website: fatcarbonmaterials.com
Key Highlights: Fatcarbon is the pioneer in offering machinable colored carbon fiber composite billets with a unique look and exceptional properties….
#9 Carbon Fiber Composite Materials
Website: cf-composites.toray
Key Highlights: Toray group supplies the most comprehensive range of carbon fiber materials in the market, from high-performance premium fiber for aircraft applications….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Plate Carbon
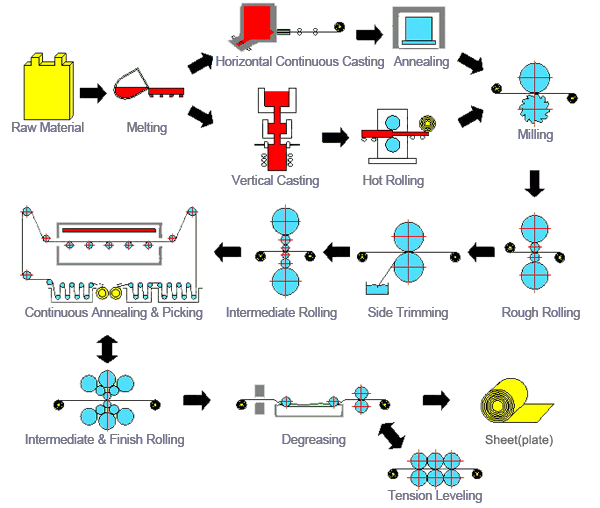
As of now, the year 2026 is in the future, and definitive market data for plate carbon (carbon steel plate) in that year is not yet available. However, based on current industry trajectories, macroeconomic factors, technological developments, and policy directions as of H2 2024 (the second half of 2024), we can project informed trends and outlooks for the plate carbon market in 2026. Below is a comprehensive analysis of expected market dynamics for carbon steel plate in 2026, leveraging H2 2024 insights.
Market Analysis: Carbon Steel Plate – Outlook for 2026
1. Global Demand Drivers
By 2026, demand for carbon steel plate is expected to be shaped by several key sectors:
-
Infrastructure & Construction: Major government-led infrastructure initiatives in the U.S. (e.g., IIJA – Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act), EU (Green Deal investments), and China (continued urbanization and regional development) will sustain demand for structural steel, including carbon plate.
-
Energy Sector:
- Oil & Gas: Despite energy transition efforts, carbon steel plate remains critical for pipelines, pressure vessels, and offshore platforms. Short-term volatility in oil prices (observed in H2 2024) may lead to cautious capital spending, but long-term projects in LNG and petrochemicals will support stable demand.
-
Renewables: Wind turbine towers (especially for offshore wind) and hydroelectric projects require large volumes of heavy plate, boosting demand in North America and Europe.
-
Heavy Industries & Machinery: The global push for nearshoring and industrial resilience (e.g., in U.S. manufacturing, German Industrie 4.0) will increase demand for fabricated equipment and machinery—key consumers of carbon plate.
-
Shipbuilding & Offshore: A resurgence in global shipping and offshore energy projects (e.g., floating wind, subsea infrastructure) will drive demand, particularly in South Korea, China, and Japan.
2. Supply Chain & Production Trends
– Regional Shifts:
– China remains the largest producer, but overcapacity concerns and export restrictions may limit global oversupply.
– The U.S. and EU are investing in domestic steel resilience (e.g., U.S. BOEING Act incentives, EU Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism – CBAM), potentially increasing localized production of carbon plate.
- Raw Material Costs:
- Iron ore and coking coal prices, volatile in H2 2024, are expected to stabilize by 2026 due to improved supply logistics and inventory management.
- Scrap availability may rise with increased end-of-life equipment recycling, supporting electric arc furnace (EAF) production, though carbon plate is still largely produced via blast furnaces.
3. Pricing Outlook
– Moderate Price Stability: After the volatility seen in 2022–2024, prices for carbon steel plate are expected to stabilize in 2026 due to:
– Balanced demand-supply dynamics.
– Improved forecasting and inventory strategies by manufacturers.
– Long-term contracts becoming more common to hedge against macroeconomic risks.
- Regional Differentials:
- Prices in North America may remain higher due to protectionist policies and higher input costs.
- Asian markets (especially India and Southeast Asia) could see competitive pricing due to expanding capacity.
4. Technological & Environmental Pressures
– Decarbonization Efforts:
– Steelmakers are investing in low-carbon technologies (e.g., hydrogen-based DRI, carbon capture). While these focus initially on flat products and long steel, carbon plate production will face increasing regulatory pressure.
– By 2026, “green steel” premiums may emerge, potentially creating a two-tier market: standard carbon plate vs. low-emission plate.
- Digitalization & Efficiency:
- Adoption of AI in production planning, predictive maintenance, and quality control will improve yield and reduce waste in plate manufacturing.
- Smart factories will allow faster response to custom orders, especially for specialized grades (e.g., high-strength, wear-resistant plate).
5. Trade & Geopolitical Factors
– Trade Barriers:
– U.S. Section 232 tariffs and EU CBAM will continue to influence import flows. Chinese exports may be rerouted through Southeast Asia, prompting anti-circumvention measures.
– Regional Free Trade Agreements (e.g., USMCA, RCEP) will support intra-regional carbon plate trade.
- Geopolitical Risks:
- Tensions in Eastern Europe, the South China Sea, and the Middle East could disrupt supply chains or spur defense-related steel demand (e.g., naval vessels, armored structures).
6. Competitive Landscape
– Consolidation: Mergers and partnerships among global steel producers (e.g., Tata-Bhushan, ArcelorMittal-Joint Ventures) will increase scale and competitiveness.
– Niche Players: Smaller mills focusing on high-value, customized carbon plate (e.g., abrasion-resistant, low-temperature toughness) will gain market share in specialized sectors.
Conclusion: 2026 Carbon Steel Plate Market Outlook
By 2026, the global carbon steel plate market is expected to achieve moderate growth (CAGR ~2.5–3.5% from 2024), driven by infrastructure, energy, and industrial modernization. While the long-term shift toward green materials and alternative alloys continues, carbon steel plate will remain indispensable due to its strength, cost-effectiveness, and recyclability.
Key Trends Summary:
– Stable demand from construction, energy, and heavy equipment.
– Regional production growth in the U.S. and EU, countering Chinese export dominance.
– Price stabilization with regional disparities.
– Increasing pressure to decarbonize production processes.
– Digital transformation improving efficiency and customization.
Strategic Implications for Stakeholders:
– Producers: Invest in low-carbon tech and digitalization to remain competitive.
– Buyers: Lock in long-term contracts to manage price volatility.
– Policymakers: Balance industrial protection with sustainability goals.
While uncertainties remain—especially regarding global economic growth and climate policy enforcement—the fundamentals for carbon steel plate remain resilient heading into 2026.
Note: This analysis is based on H2 2024 data and forward-looking projections. Actual 2026 market conditions may vary with unforeseen economic, geopolitical, or technological developments.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Plate Carbon (Quality, IP)
Sourcing plate carbon involves critical considerations around material quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to project delays, safety risks, legal disputes, and financial losses. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Specification of Material Grade and Standards
Failing to clearly define the required carbon steel grade (e.g., ASTM A36, A516, A572) and relevant industry standards can result in receiving substandard or non-compliant material. Suppliers may deliver plates that meet general carbon steel criteria but fall short of project-specific mechanical or chemical requirements.
2. Insufficient Testing and Certification Requirements
Accepting material without proper mill test reports (MTRs) or third-party certifications (e.g., EN 10204 3.1 or 3.2) increases the risk of receiving counterfeit or off-spec plate. Skipping independent testing (e.g., tensile, impact, chemical analysis) can allow defective materials to enter fabrication.
3. Poor Control Over Heat Treatment and Processing History
Carbon plate properties depend heavily on processing (e.g., hot-rolled, normalized, quenched & tempered). Sourcing without verifying the processing history may result in inconsistent mechanical properties, reduced weldability, or poor performance in service.
4. Inconsistent Thickness and Dimensional Tolerances
Neglecting to specify dimensional tolerances per standards (e.g., ASTM A6) can lead to plates that are out of flat, have variable thickness, or require costly rework—impacting fit-up and structural integrity.
5. Overlooking Traceability and Batch Consistency
Without full traceability (heat number, batch records), it becomes difficult to investigate failures or ensure consistency across large projects. This is especially critical in pressure vessels, bridges, or structural applications.
IP-Related Pitfalls
1. Unprotected Design and Technical Specifications
Sharing detailed engineering drawings, performance specs, or proprietary designs with suppliers without non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) exposes IP to misuse or unauthorized replication, especially in high-value or innovative applications.
2. Lack of Clarity on IP Ownership in Custom Orders
When sourcing custom-forged or processed carbon plates, failure to define IP ownership in contracts can lead to disputes. For example, tooling, molds, or process innovations developed during manufacturing may be claimed by the supplier.
3. Unauthorized Reverse Engineering or Copying
Suppliers in certain jurisdictions may reverse engineer plates or replicate proprietary alloys or treatments. Without IP safeguards, competitors could gain access to unique material formulations or manufacturing processes.
4. Inadequate Protection in International Sourcing
Sourcing from regions with weak IP enforcement increases the risk of counterfeit materials or IP theft. Differences in legal frameworks can make it difficult to pursue remedies if proprietary processes or designs are misappropriated.
5. Failure to Audit Supplier Compliance
Not conducting periodic audits of supplier facilities and documentation practices may allow IP leaks or quality deviations to go undetected. Suppliers might inadvertently or deliberately use unauthorized subcontractors or processes.
Best Practices to Mitigate Risks
- Define clear technical specifications and quality control protocols upfront.
- Require full material traceability and certified test reports.
- Use legally binding NDAs and IP clauses in procurement contracts.
- Conduct supplier qualification and periodic audits.
- Partner with reputable, certified suppliers with transparent processes.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls, organizations can ensure both the quality integrity of sourced carbon plate and the protection of their intellectual property.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Plate Carbon
Understanding Plate Carbon: Definition and Applications
Plate carbon refers to carbon steel plates manufactured in standardized thicknesses and dimensions for industrial use. These plates are widely used in construction, shipbuilding, pressure vessels, heavy machinery, and structural applications due to their strength, durability, and weldability. Plate carbon is typically categorized by grades (e.g., ASTM A36, A516, A572) that specify chemical composition, mechanical properties, and intended use.
Regulatory and Industry Standards Compliance
Compliance with international and regional standards is critical when handling, transporting, and utilizing plate carbon. Key standards include:
- ASTM International: Governs material specifications (e.g., ASTM A36 for structural steel).
- ISO 9001: Quality management systems for manufacturing and supply chain processes.
- EN Standards (Europe): Such as EN 10025 for hot-rolled structural steel products.
- AS/NZS Standards (Australia/New Zealand): Including AS/NZS 3678 for structural steel.
- API Standards (Oil & Gas): API 5L for line pipe materials, often requiring carbon plate inputs.
Ensure all supplied plate carbon is certified with Mill Test Certificates (MTCs) conforming to EN 10204 Type 3.1 or equivalent, verifying chemical and mechanical compliance.
Packaging, Handling, and Storage Requirements
Proper packaging and handling prevent corrosion, deformation, and safety hazards:
- Packaging: Plates should be bundled securely using steel strapping, with protective edge guards and moisture-resistant wrapping (e.g., VCI paper) for long-term storage or marine transport.
- Handling: Use appropriate lifting equipment (e.g., magnetic lifters, spreader beams) to avoid edge damage. Never drag plates across surfaces.
- Storage: Store indoors on level, well-drained surfaces. Elevate bundles off the ground using wood dunnage to prevent water accumulation. Ensure ventilation to reduce moisture buildup and rust formation.
Transportation and Logistics Planning
Transporting plate carbon requires careful planning due to weight, dimensions, and load security:
- Mode of Transport: Typically shipped via flatbed trucks, railcars, or break-bulk vessels. Oversized or heavy loads may require special permits.
- Load Securing: Use chains, binders, or lashing straps rated for the load weight. Follow guidelines from the FMCSA (USA) or ADR (Europe) for road transport.
- Weight and Dimension Limits: Confirm compliance with local regulations (e.g., bridge laws, axle weight limits) to avoid penalties.
- Documentation: Provide accurate shipping manifests, packing lists, and hazardous material disclosures if coatings or treatments involve regulated substances.
Import/Export and Customs Compliance
Cross-border shipments of plate carbon are subject to customs regulations and trade policies:
- HS Code Classification: Use correct Harmonized System codes (e.g., 7208.51–7208.54 for flat-rolled carbon steel) to determine tariffs and duties.
- Trade Agreements: Leverage preferential tariffs under agreements like USMCA, EU-Canada CETA, or ASEAN FTAs, if applicable.
- Export Controls: Verify if the material or end-use triggers export restrictions (e.g., dual-use applications under EAR or ITAR).
- Import Documentation: Provide commercial invoices, bills of lading, certificates of origin, and regulatory compliance statements.
Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) Considerations
Ensure adherence to EHS regulations throughout the logistics chain:
- Dust and Fumes: Cutting or grinding carbon plate generates particulates; use PPE and ventilation per OSHA or EU Directive 2004/37/EC.
- Chemical Treatments: If plates are coated (e.g., primers), comply with REACH (EU) or TSCA (USA) for chemical registration.
- Waste Management: Recycle scrap metal according to local environmental regulations (e.g., RCRA in the U.S.).
- Spill Prevention: Store treated plates away from drains; contain any oil or protective coatings that may leach.
Traceability and Documentation Management
Maintain full traceability from mill to end-user:
- Batch/Lot Tracking: Assign unique identifiers to each plate or bundle.
- Digital Records: Use ERP or SCM systems to store MTCs, shipping logs, and compliance certificates.
- Audit Readiness: Ensure documentation supports quality audits, customer requests, or regulatory inspections.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance for plate carbon require a structured approach to standards adherence, safe handling, regulatory documentation, and environmental responsibility. By integrating these practices, organizations can ensure product integrity, avoid delays, and maintain compliance across global supply chains.
Conclusion for Sourcing Carbon Steel Plates
In conclusion, sourcing carbon steel plates requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, reliability, and compliance with industry standards. Selecting the right supplier involves thorough evaluation of material specifications, certifications (such as ASTM, ASME, or EN), and the supplier’s track record for consistency and on-time delivery. Factors such as plate thickness, dimensions, grade (e.g., ASTM A36, A516, A572), and intended application—whether for construction, manufacturing, or pressure vessels—must be clearly defined to ensure performance and safety.
Proactive supply chain management, including supplier diversification and long-term agreements, can mitigate risks related to market volatility and lead times. Additionally, sustainable sourcing practices and attention to environmental impact are increasingly important considerations in today’s industrial landscape.
Ultimately, successful sourcing of carbon steel plates hinges on strong supplier relationships, rigorous quality assurance, and continuous market monitoring to adapt to changing demands and conditions. By adopting a comprehensive sourcing strategy, organizations can ensure reliable access to high-quality materials while optimizing cost-efficiency and project timelines.