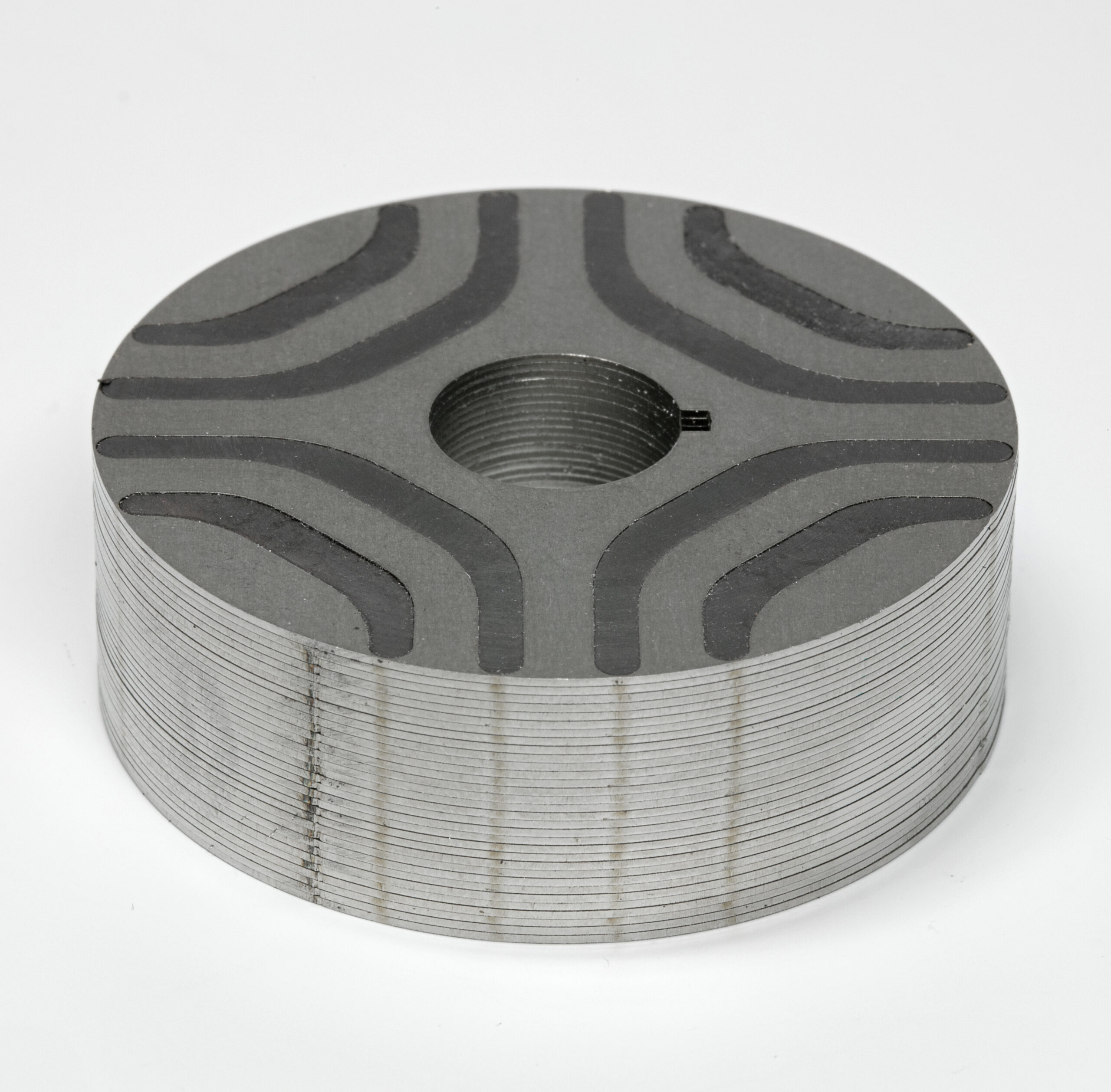
The global plastics industry continues to expand rapidly, driven by increasing demand across automotive, electronics, packaging, and consumer goods sectors. A critical yet often overlooked segment within this ecosystem is plastic magnet manufacturing—specialized composites combining magnetic materials with polymer matrices to deliver lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easily moldable solutions. According to Grand View Research, the global magnetic materials market size was valued at USD 33.8 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.2% from 2024 to 2030, fueled by advancements in electric vehicles, miniaturized electronics, and renewable energy systems—all of which rely heavily on high-performance plastic magnets. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects steady growth in functional polymer composites, citing increased R&D investments and strategic partnerships among key players to enhance material efficiency and thermal stability. As demand for customized, cost-effective magnetic solutions rises, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders in innovation, production scale, and material science expertise. Here’s a data-driven look at the top 10 plastic magnet manufacturers shaping the future of the industry.
Top 10 Plastic Magnet Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Unlock Plastic Processing Success with…
Domain Est. 1995
Website: magnetics.com
Key Highlights: Master metal separation with IMI magnets for the plastic processing industry. Explore IMI’s range of products that improve purity and create efficiency….
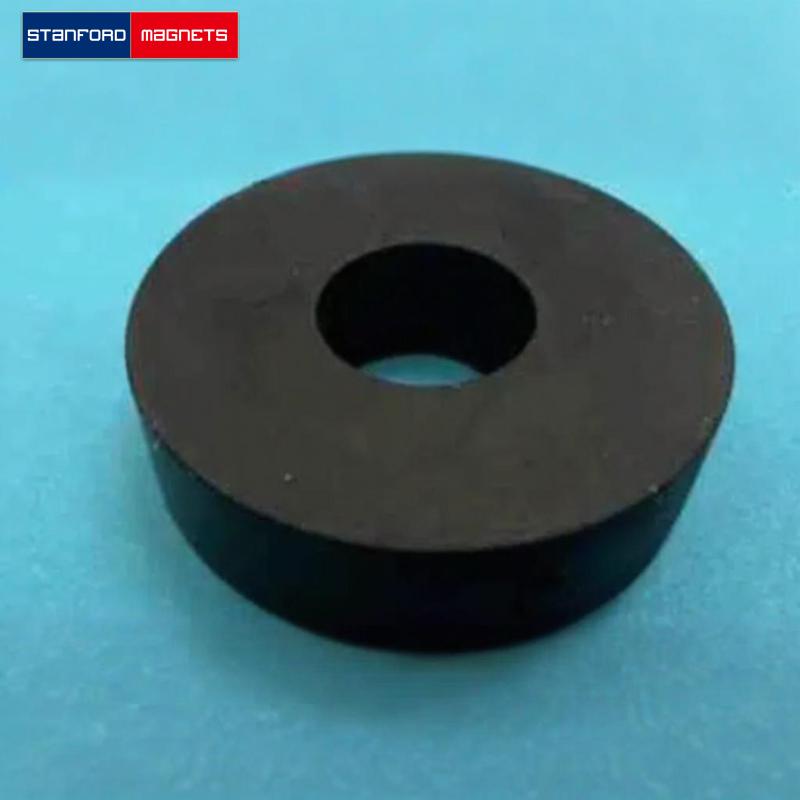
#2 Stanford Magnets
Domain Est. 1998
Website: stanfordmagnets.com
Key Highlights: Stanford Magnets is a rare earth magnet manufacturer including various custom magnets, specializes in the design, engineering, and manufacture of custom ……
#3 Specialists in magnetic sensor & plastic bonded magnets
Domain Est. 1999
Website: suramagnets.se
Key Highlights: We are a well-known top quality supplier to customers throughout the world and in Scandinavia, where we are the largest manufacturer of plastic-bonded magnets….
#4 Eclipse Magnetics
Domain Est. 2002
Website: eclipsemagnetics.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture high quality magnets, supporting various industries with advanced magnetic technology and equipment….
#5 IBS MAGNET
Domain Est. 2005
Website: ibsmagnet.com
Key Highlights: We specialise in the manufacture and supply of permanent magnets from any magnetic material, particularly from the high-energy magnetic materials NdFeB and SmCo ……
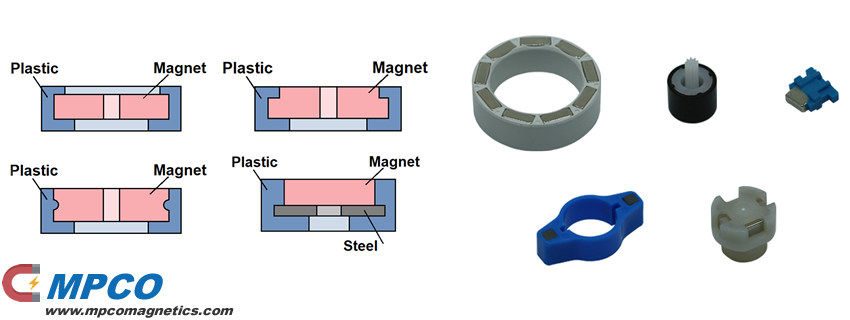
#6 Plastic Integrated Magnet
Domain Est. 2013
Website: magnet-sdm.com
Key Highlights: A plastic integrated magnet combines permanent magnets with plastics to deliver versatile, efficient solutions for diverse applications….
#7 Permanent Magnets and Magnet
Domain Est. 1999
Website: calamit.com
Key Highlights: Production and sale of permanent magnets and magnets of any type, including Bonded and rubber magnets. See our catalogue!…
#8 Product Injection Molded Magnets
Domain Est. 2001
Website: arnoldmagnetics.com
Key Highlights: Our injection molded magnets include a variety of polymer base materials blended with fully dense magnetic powders in simple and complex shapes. Learn more….
#9 Plastic Bonded Magnets Archives
Domain Est. 2018
Website: imamagnets.com
Key Highlights: Plastic magnets can be injected, over-injected or pressed. We have a technical team of engineers responsible for the manufacture of plastic molds….
#10 Magnetic solutions for lifting and …
Domain Est. 2021
Website: mag-tecnomagnete.com
Key Highlights: We design, manufacture and market electropermanent magnetic systems for industry, offering highly costumed and constantly improved solutions. To effectively and ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Plastic Magnet
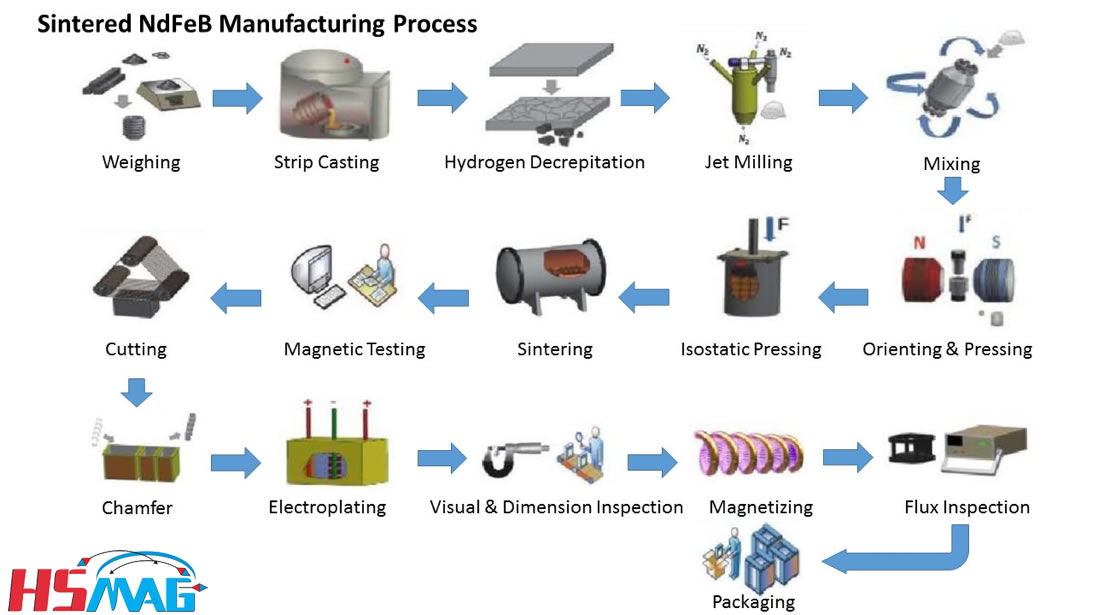
H2: Market Trends for Plastic Magnets in 2026
As we approach 2026, the plastic magnet market is undergoing a significant transformation driven by technological innovation, environmental regulations, and shifting industrial demand. Plastic magnets—also known as polymer-based magnetic composites or bonded magnets—combine magnetic powders (typically neodymium-iron-boron or ferrite) with plastic binders such as nylon, polypropylene, or PPS. This hybrid structure offers design flexibility, corrosion resistance, and cost-effective manufacturing, positioning plastic magnets as a critical component across various advanced industries.
1. Growth in Electric Vehicles (EVs) and E-Mobility
One of the dominant forces shaping the 2026 market is the surge in electric vehicle (EV) production. Plastic magnets are increasingly used in EV subsystems such as sensors, actuators, traction motors, and auxiliary motors (e.g., in HVAC, power steering, and braking systems). Their lightweight nature and ability to be injection-molded into complex geometries reduce overall vehicle weight and improve energy efficiency. OEMs are prioritizing materials that support miniaturization and integration, giving plastic magnets a competitive edge over traditional sintered magnets.
2. Expansion in Consumer Electronics and IoT Devices
The proliferation of smart devices, wearables, and IoT sensors continues to drive demand. In 2026, plastic magnets are essential in haptic feedback systems, micro-motors, and compact speakers due to their precision molding capabilities and electromagnetic performance. With trends toward thinner, lighter gadgets, manufacturers increasingly adopt bonded solutions that allow for customized magnetic fields and spatial integration.
3. Sustainability and Recyclability as Market Drivers
Environmental regulations, especially in Europe and North America, are pushing for sustainable material use. Plastic magnets offer advantages in recyclability compared to sintered counterparts, particularly when using thermoplastic binders. In 2026, leading producers are investing in closed-loop recycling systems and bio-based polymer matrices to meet ESG goals and comply with directives such as the EU Circular Economy Action Plan.
4. Supply Chain Resilience and Rare Earth Diversification
Geopolitical tensions and supply chain vulnerabilities related to rare earth elements (e.g., neodymium, dysprosium) are prompting innovation. In 2026, there is a noticeable shift toward ferrite-based plastic magnets and hybrid designs that reduce reliance on critical raw materials. Additionally, advancements in magnetocaloric and organic-based magnetic polymers—though still largely in R&D—are beginning to influence long-term material strategies.
5. Advancements in Manufacturing Technologies
The adoption of 3D printing and multi-material injection molding is accelerating in 2026. These technologies allow for the production of functionally graded magnets and integrated magnetic assemblies, reducing part count and assembly costs. Digital twin simulations and AI-driven material optimization are enabling faster development cycles for custom magnetic solutions tailored to specific applications.
6. Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific remains the largest market for plastic magnets, led by China, Japan, and South Korea, due to robust electronics and automotive manufacturing. However, North America and Europe are witnessing accelerated growth due to onshoring initiatives and investments in clean energy and smart infrastructure. Localized production is expected to rise, supported by government incentives for domestic magnet supply chains.
7. Price Volatility and Material Innovation
Fluctuations in rare earth prices continue to impact production costs. In response, 2026 sees increased R&D in alternative magnetic fillers and nano-composite structures that enhance magnetic performance without increasing rare earth content. Companies are also exploring hybrid systems that combine plastic magnets with soft magnetic composites for improved efficiency.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the plastic magnet market is characterized by rapid innovation, sustainability integration, and deep penetration into high-growth sectors like EVs, consumer tech, and industrial automation. While challenges related to material supply and performance limitations persist, ongoing advancements in materials science and manufacturing are positioning plastic magnets as a cornerstone of next-generation electromechanical systems. Companies that invest in scalable, eco-friendly production and application-specific design will lead the market in this pivotal year.
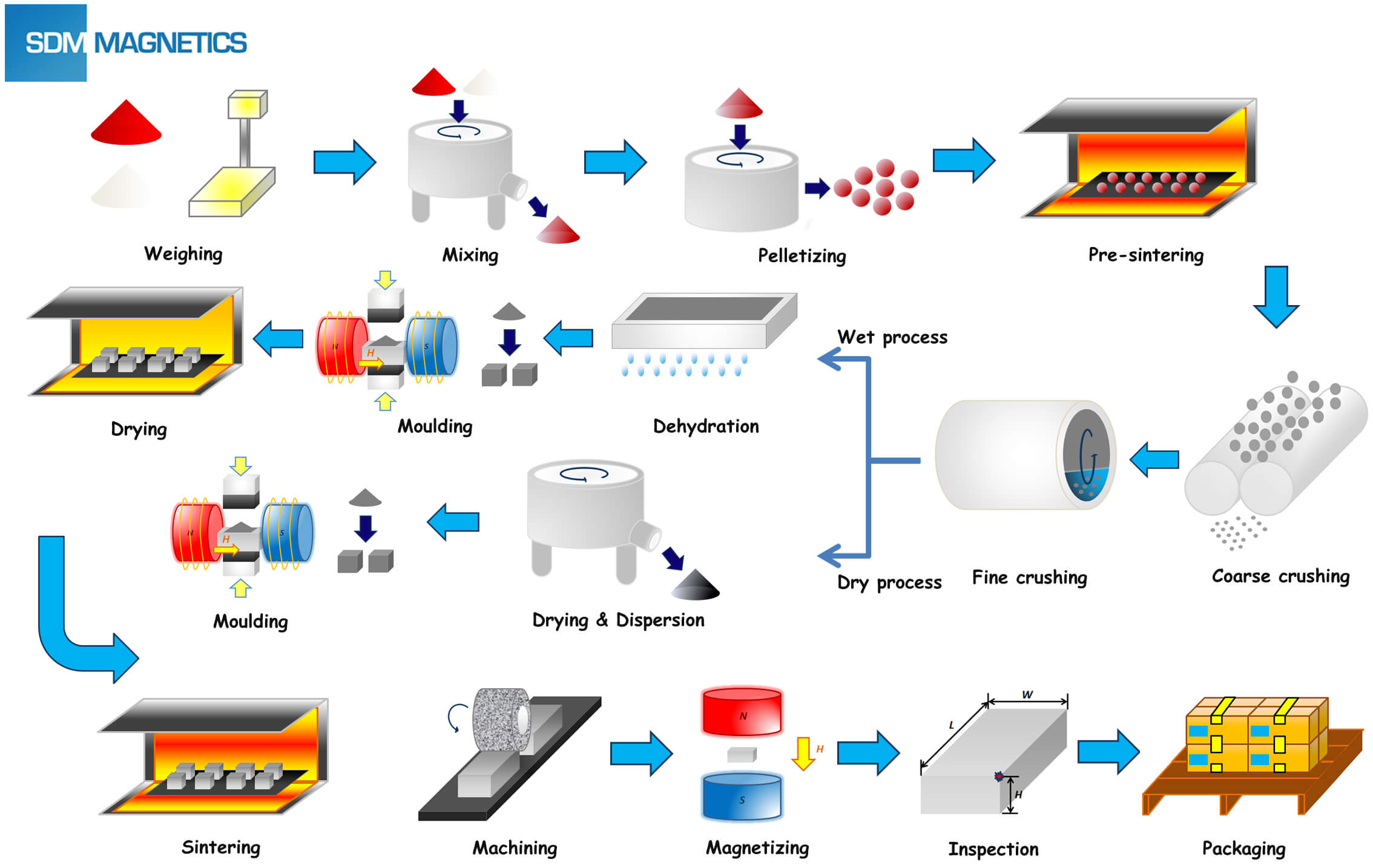
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Plastic Magnets (Quality, IP)
Sourcing plastic magnets—also known as bonded magnets or magnetic plastics—requires careful attention due to their composite nature and specialized applications. Companies often encounter significant challenges related to quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these pitfalls can result in product failures, supply chain disruptions, or legal exposure.
Quality Inconsistencies Due to Material and Process Variability
Plastic magnets are typically made by combining magnetic powder (e.g., NdFeB, ferrite) with a polymer binder, processed via injection molding, compression bonding, or extrusion. This hybrid manufacturing introduces several quality risks:
- Inhomogeneous Magnetic Powder Distribution: Poor dispersion of magnetic particles in the polymer matrix can lead to weak spots, inconsistent magnetic performance, and premature failure.
- Variability in Magnetic Properties: Differences in powder grade, loading percentage, and alignment during molding affect key metrics like remanence and coercivity. Suppliers may not provide full test data, leading to performance gaps in end applications.
- Dimensional Instability and Warping: Shrinkage during cooling and anisotropic behavior in molded parts can result in out-of-spec components, especially in complex geometries.
- Thermal and Environmental Degradation: Many plastic magnets degrade under high temperatures or exposure to moisture and chemicals. Suppliers may overstate performance limits without proper validation.
- Lack of Standardized Testing and Documentation: Some suppliers provide incomplete or inconsistent quality certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), making it difficult to verify batch-to-batch reliability.
Mitigation Tip: Require detailed material specifications, conduct on-site audits of supplier facilities, and implement incoming inspection protocols with third-party testing for magnetic and mechanical properties.
Intellectual Property Risks and Design Leakage
Plastic magnets are often custom-engineered for specific applications, making IP protection critical. Sourcing from low-cost or offshore suppliers increases the risk of:
- Design Replication and Reverse Engineering: Detailed CAD files, tooling designs, and material formulations provided to suppliers can be copied or sold to competitors.
- Weak or Unenforceable IP Clauses in Contracts: Generic NDAs or manufacturing agreements may lack jurisdiction-specific enforceability or fail to cover derivative designs.
- Joint Development Ambiguities: If the supplier contributes to design optimization, unclear IP ownership can lead to disputes over patent rights or usage rights.
- Supply Chain Transparency Gaps: Sub-tier suppliers or subcontractors involved in production may not be bound by the same IP protections, increasing exposure.
Mitigation Tip: Use jurisdiction-specific IP agreements, limit technical data disclosure to only what is necessary, and audit supplier compliance with confidentiality and IP clauses. Consider dual-sourcing or patenting critical designs before engagement.
Proactively addressing these pitfalls ensures reliable performance of plastic magnets in final products while safeguarding proprietary innovations.
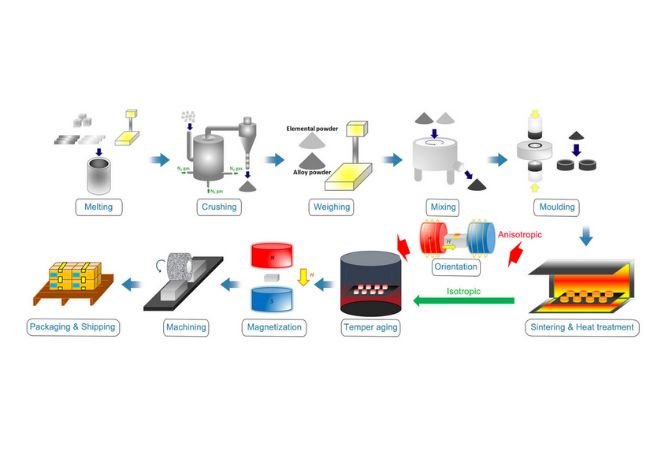
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Plastic Magnet
This guide outlines essential logistics and compliance considerations for the manufacturing, handling, transportation, and distribution of Plastic Magnet — a composite material combining plastic with magnetic properties, commonly used in consumer electronics, automotive components, and industrial applications.
Material Classification and Regulatory Compliance
Plastic Magnet is classified as a composite material under international regulations. Compliance with environmental, safety, and trade standards is mandatory.
- REACH (EU Regulation): Ensure full compliance with REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of Chemicals). Declare all substances of very high concern (SVHCs) present above threshold levels.
- RoHS Directive (EU): Verify that Plastic Magnet complies with RoHS restrictions on hazardous substances such as lead, cadmium, mercury, and certain flame retardants.
- REACH SVHC Disclosure: Maintain up-to-date documentation for any SVHCs in the material composition and provide to downstream customers upon request.
- Proposition 65 (California, USA): Confirm that Plastic Magnet does not contain chemicals listed under California’s Proposition 65 without proper warning labels.
- TSCA (USA): Comply with the Toxic Substances Control Act by confirming all chemical components are pre-manufactured notified or exempt.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Proper packaging and labeling ensure safe handling and regulatory adherence during storage and transport.
- Packaging: Use anti-static and moisture-resistant packaging to prevent degradation of magnetic properties and contamination. Secure packaging to minimize movement during transit.
- UN/DOT Labels: If classified as non-hazardous, standard commercial packaging applies. If magnetic field strength exceeds 0.159 A/m at 2.1 meters, classify as “Magnetized Material” (UN2807) under IATA/IMDG regulations.
- GHS Labeling: Apply GHS-compliant labels if any hazardous components are present, including signal words, hazard statements, and precautionary measures.
- Country-Specific Labels: Include CE marking for EU, FCC IDs if applicable for electromagnetic interference, and other region-specific compliance marks.
Transportation and Shipping
Transportation of Plastic Magnet must follow international and regional regulations based on its physical and magnetic properties.
- Air Transport (IATA): If magnetic field strength exceeds limits, submit a “Magnetized Material” declaration and undergo testing per IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR) Section II.
- Marine Transport (IMDG Code): Declare as “Magnetized Material, UN2807” if applicable. Follow stowage and segregation rules to prevent interference with navigation systems.
- Ground Transport (ADR/RID): Apply relevant regulations in Europe for road and rail; declare if magnetic field strength requires classification.
- Non-Hazardous Classification: If below magnetic thresholds, ship as general freight with standard documentation (commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading).
Customs and Trade Compliance
Ensure smooth cross-border movement by maintaining accurate documentation and tariff classification.
- HS Code: Use appropriate Harmonized System code (e.g., 3916.20 for plastic semi-finished products or 8505.11 for permanent magnets, depending on form and composition).
- Country of Origin: Clearly declare the manufacturing origin to comply with trade agreements and anti-dumping regulations.
- Export Controls: Verify that Plastic Magnet is not subject to dual-use export controls (e.g., EU Dual-Use Regulation or U.S. EAR) unless embedded in controlled end-use devices.
- Customs Documentation: Provide commercial invoice, certificate of origin, material safety data sheet (MSDS/SDS), and compliance declarations as required.
Storage and Handling
Implement best practices for safe and effective storage and handling.
- Environment: Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment (15–25°C recommended) to prevent warping or magnetic degradation.
- Static Control: Use grounded workstations and anti-static materials during handling, especially in dry environments.
- Segregation: Keep away from sensitive electronic devices, pacemakers, and magnetic storage media due to residual magnetic fields.
- Stacking Limits: Adhere to manufacturer-recommended stacking heights to prevent deformation.
Environmental and Sustainability Compliance
Adhere to waste and recycling regulations to support circular economy goals.
- WEEE Compliance (EU): If used in electrical/electronic equipment, ensure end-of-life take-back and recycling under WEEE Directive.
- Recycling Instructions: Provide clear guidance for disassembly and material separation (plastic vs. magnetic components).
- End-of-Life Management: Partner with certified recyclers capable of processing composite magnetic plastics.
- Carbon Footprint Reporting: Track and report emissions across the supply chain in alignment with GHG Protocol standards.
Audit and Documentation
Maintain records to demonstrate compliance and support supply chain transparency.
- Compliance Dossier: Keep a master file including SDS, test reports (e.g., magnetic flux, RoHS, REACH), and certifications.
- Supplier Declarations: Obtain material compliance statements from raw material suppliers.
- Internal Audits: Conduct regular audits of logistics and compliance procedures to ensure ongoing adherence.
- Traceability: Implement batch-level traceability from raw materials to finished goods for recall readiness.
Summary
Plastic Magnet requires careful attention to material regulations, transport classifications, and environmental standards. By following this guide, manufacturers and distributors can ensure compliant, efficient, and safe logistics operations across global markets. Regular updates to regulatory changes are strongly recommended.
Conclusion for Sourcing Plastic Magnets
In conclusion, sourcing plastic magnets (also known as flexible or magnetic rubber materials) requires a strategic approach that balances performance requirements, cost-efficiency, and supplier reliability. These composite materials—typically made by embedding magnetic powders such as strontium or barium ferrite into a flexible polymer matrix—offer unique advantages including flexibility, ease of fabrication, and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for applications in signage, displays, gaskets, and consumer electronics.
Successful sourcing involves identifying suppliers capable of delivering consistent material quality, custom shapes, and magnetization patterns tailored to specific needs. Key considerations include magnetic strength (flux density), temperature resistance, durability, and compliance with industry standards. Additionally, evaluating lead times, minimum order quantities, and geographic logistics can significantly impact overall supply chain efficiency.
Ultimately, building strong relationships with reputable manufacturers, conducting rigorous material testing, and staying informed on advancements in magnetic composites will ensure reliable and cost-effective sourcing of plastic magnets for both current and future applications.