The global plastic machining industry is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for precision-engineered plastic components across aerospace, medical, automotive, and semiconductor sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global plastic injection molding market—which closely intersects with precision machining—is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.3% from 2023 to 2028, reaching a valuation of over USD 350 billion. Meanwhile, Grand View Research reports that the broader engineered plastics market is expected to expand at a CAGR of 6.5% from 2022 to 2030, underscoring the increasing adoption of high-performance polymers like PEEK, PTFE, and ULTEM in critical applications. As industries prioritize lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and electrically insulating materials, the need for advanced plastic machining capabilities has intensified. In this competitive landscape, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining tight-tolerance CNC machining, material expertise, and ISO-certified processes to serve high-tech sectors. Below are the top 10 plastic machining manufacturers leading innovation and reliability in this expanding market.
Top 10 Plastic Machining Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 ConMet
Domain Est. 1996
Website: conmet.com
Key Highlights: We supply the commercial vehicle industry with wheel ends, hub assemblies, brake drums, hubs, rotors, aftermarket wheel products & OEM genuine products….
#2 Precision CNC Machining Services
Domain Est. 1997
Website: emcoplastics.com
Key Highlights: At Emco Industrial Plastics, we offer CNC machining services for different plastic materials. We also provide a variety of finishes….
#3 Plastic Machining Company
Domain Est. 2008
Website: plasticmachiningcompany.com
Key Highlights: Plastic Machining Company is your one-stop fabricator for custom UHMW, nylon, and acetal parts including bearings, bushings, collars, guides, pulleys, ……
#4 Plastic Machining Solutions
Domain Est. 1997 | Founded: 1976
Website: mcneal.com
Key Highlights: Founded in 1976, McNeal is a leader in custom machined, fabricated, and thermoformed plastic components. From design to assembly, our full range of services…
#5 Precision Plastic & CNC Machining
Domain Est. 1998
Website: insulfab.net
Key Highlights: Expert plastics machining and CNC machining plastics in a climate-controlled facility. For precision machined plastics, contact us for a custom quote….
#6 Plastic CNC Machining & Fabrication
Domain Est. 1999
Website: seagateplastics.com
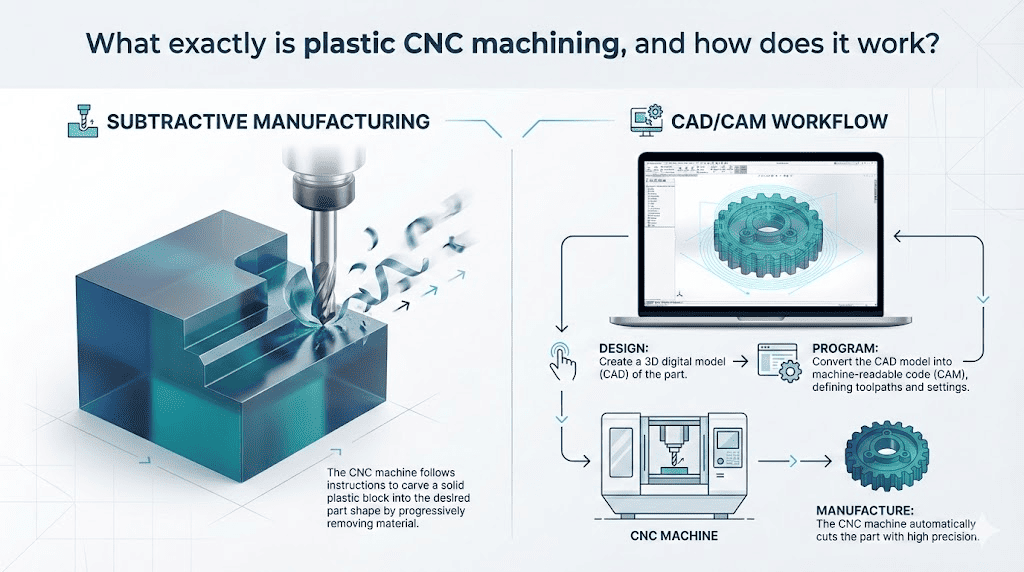
Key Highlights: CNC plastic machining is a manufacturing process that uses computer-controlled tools to shape plastic components with high precision. Unlike metal machining, ……
#7 Plastic Machining Services
Domain Est. 2001
Website: americanmicroinc.com
Key Highlights: American Micro Industries fabricates a variety of machined plastics. Learn more about our capabilities with polymer, Lexan, & more. Get a free quote today!…
#8 Plastic Fabrication Company
Domain Est. 2006
Website: plasticmachininginc.com
Key Highlights: PMI is home to a top-tier plastic machining workshop, equipped with a wide array of advanced machinery capable of producing diverse plastic machined parts….
#9 Plastic Machining & Polishing Services
Domain Est. 2006
Website: eastcoastmfg.com
Key Highlights: We machine all types of plastics. Our experienced professionals can help you select the proper material for your component and provide special machining ……
#10 Controlled Fluidics
Domain Est. 2010
Website: controlledfluidics.com
Key Highlights: Controlled Fluidics specializes in precision plastic machining and bonded fluidic manifolds for aerospace, medical, life sciences, defense and research ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Plastic Machining

2026 Market Trends in Plastic Machining: Shaping the Future of Precision Manufacturing
As we approach 2026, the plastic machining industry is undergoing significant transformation, driven by technological advancements, evolving material science, and shifting demands across key end-use sectors. This analysis explores the pivotal trends shaping the market landscape, revealing opportunities for innovation and growth.
Rising Demand from High-Growth Industries
The primary driver of the 2026 plastic machining market is the escalating demand from industries requiring high-precision, complex, and reliable non-metallic components. The medical technology sector continues to lead, necessitating machined parts for surgical instruments, diagnostic devices, and implantable components due to the biocompatibility and sterilizability of advanced engineering plastics. Simultaneously, the aerospace and defense industries are increasingly substituting metal with lightweight, high-strength plastics like PEEK and PEI for interior components, avionics housings, and drone parts, driven by fuel efficiency and performance requirements. The semiconductor and electronics manufacturing sectors also demand ultra-pure, dimensionally stable machined plastic components for wafer handling, cleanroom fixtures, and test equipment, further fueling market expansion.
Advancements in Material Science and Engineering Plastics
Material innovation is a cornerstone of the 2026 trend landscape. The market is shifting decisively towards high-performance thermoplastics (HPTs) such as Polyetheretherketone (PEEK), Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS), Polyamide-imide (PAI), and Polyetherimide (PEI). These materials offer exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and low outgassing, making them indispensable for demanding applications. Furthermore, the development of reinforced and specialty grades—filled with carbon fiber, glass fiber, or PTFE for enhanced properties like wear resistance and conductivity—is enabling machinists to meet increasingly stringent application requirements. The focus is on materials that push the boundaries of performance while maintaining machinability.
Integration of Automation and Smart Manufacturing
Automation is rapidly moving from a competitive advantage to a necessity in the 2026 plastic machining environment. CNC machining centers are increasingly being integrated with robotic loading/unloading systems, automated tool changers, and in-process inspection technologies to maximize uptime, ensure consistency, and address labor shortages. The adoption of Industry 4.0 principles is gaining momentum, with machine monitoring, predictive maintenance, and digital twins being implemented to optimize production efficiency, reduce waste, and enable real-time data-driven decision-making. This trend towards “lights-out” manufacturing is particularly crucial for high-volume, high-precision production runs.
Focus on Sustainability and Efficient Processes
Sustainability is becoming a critical competitive factor. Customers and regulators are demanding more environmentally responsible practices. This is driving innovation in machining processes to minimize material waste through optimized nesting software and near-net-shape machining. There is also growing interest in the machining of recycled engineering plastics, although challenges related to material consistency and performance remain. Furthermore, manufacturers are investing in energy-efficient machine tools and exploring closed-loop coolant systems to reduce their environmental footprint. The ability to demonstrate sustainable practices will be a key differentiator.
Expansion of Additive Manufacturing Synergy
While subtractive machining remains dominant for high-precision parts, the relationship with additive manufacturing (3D printing) is evolving into a synergistic one by 2026. Additive processes are increasingly used to produce complex near-net-shape parts or prototypes, which are then finished to tight tolerances using precision CNC machining. This hybrid approach leverages the design freedom of 3D printing with the superior surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and material properties achievable through machining. Service providers offering integrated additive-subtractive solutions are gaining a competitive edge in the market.
Geopolitical Shifts and Supply Chain Resilience
Geopolitical uncertainties and past supply chain disruptions have prompted a strategic reevaluation. There is a noticeable trend towards regionalization and nearshoring of manufacturing, particularly in North America and Europe, for critical components in medical, aerospace, and defense. This shift favors local and agile plastic machining suppliers capable of short lead times, stringent quality control, and responsive engineering support. Building resilient, diversified, and transparent supply chains is a top priority for both machinists and their customers heading into 2026.
In conclusion, the 2026 plastic machining market is characterized by a confluence of technological sophistication, material innovation, and strategic adaptation. Success will belong to companies that embrace automation, master advanced materials, prioritize sustainability, leverage digitalization, and offer flexible, resilient manufacturing solutions to serve the evolving needs of high-tech industries.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Plastic Machining (Quality, IP)
Inadequate Quality Control Processes
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing plastic machining is partnering with suppliers that lack robust quality control systems. Without proper in-process inspections, material traceability, and final product validation, defects such as dimensional inaccuracies, surface imperfections, or material inconsistencies can go undetected. This often leads to part failure in end-use applications, especially in industries like medical or aerospace where precision is critical.
Poor Material Selection and Traceability
Suppliers may use substandard or incorrect grades of plastic to cut costs, resulting in compromised mechanical, thermal, or chemical performance. Lack of material certification or traceability documentation increases the risk of non-compliance with industry standards (e.g., FDA, USP Class VI, or UL). Always verify that the machined parts are made from the specified grade and come with proper material test reports.
Insufficient Expertise with Engineering Plastics
Not all plastic machining suppliers are equally skilled in handling high-performance polymers like PEEK, PTFE, or ULTEM. These materials require specialized tooling, machining parameters, and environmental controls to prevent warping, cracking, or internal stresses. Choosing a supplier without proven experience can lead to poor part integrity and increased scrap rates.
Intellectual Property (IP) Exposure Risks
Sharing detailed CAD files and proprietary designs with third-party machinists can expose your IP to theft or unauthorized replication, especially when sourcing internationally. Suppliers in regions with weak IP enforcement may duplicate and sell your designs without consent. Always use strong non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and consider watermarking or segmenting design files.
Lack of IP Protection in Contracts
Even with an NDA, contracts often fail to clearly define ownership of tooling, design modifications, or production data. Without explicit clauses stating that IP remains with the client, suppliers may claim partial rights or reuse design elements for other customers, creating legal and competitive risks.
Inconsistent Documentation and Compliance
Missing or incomplete documentation—such as inspection reports, process validations, or compliance certificates—can hinder regulatory approvals and quality audits. Ensure that suppliers provide full documentation packages aligned with your industry requirements to avoid delays or rejections in certification processes.
Overlooking Post-Machining Processes
Critical secondary operations like stress relieving, precision polishing, or cleaning are often underestimated. Poor execution of these steps can introduce contaminants, residual stresses, or dimensional changes that affect part performance. Verify that the supplier controls the entire process chain, not just the initial cut.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—through supplier audits, clear contractual terms, and rigorous quality oversight—companies can mitigate risks and ensure reliable, IP-secure plastic machining outcomes.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Plastic Machining
Overview
This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations specific to the plastic machining industry. It is designed to help manufacturers, suppliers, and distributors ensure smooth operations while meeting regulatory, safety, and environmental standards.
Raw Material Sourcing & Handling
- Source engineering-grade plastics (e.g., PEEK, PVC, Acetal, Polycarbonate) from certified suppliers adhering to ISO 9001 or equivalent standards.
- Maintain material certifications (e.g., RoHS, REACH, UL 94 flammability ratings) for traceability.
- Store plastics in climate-controlled environments to prevent moisture absorption, warping, or degradation.
- Label all stock with material type, batch number, and date of receipt.
Inventory Management
- Implement a First-In, First-Out (FIFO) inventory system to prevent aging of hygroscopic or UV-sensitive materials.
- Use barcode or RFID tracking for raw materials and work-in-progress (WIP) components.
- Conduct regular cycle counts to ensure accuracy and reduce waste.
Machining Process Controls
- Follow documented procedures compliant with ISO 13485 (for medical) or AS9100 (for aerospace), where applicable.
- Calibrate CNC machines, lathes, and measuring equipment on a routine basis.
- Monitor cutting parameters (speed, feed, coolant use) to minimize material stress and maintain dimensional accuracy.
Waste Management & Environmental Compliance
- Segregate plastic waste by resin type (e.g., ABS, HDPE) for proper recycling.
- Comply with local and federal regulations (e.g., EPA, OSHA) for handling machining byproducts such as chips and coolant.
- Use closed-loop coolant systems to reduce hazardous waste and environmental impact.
- Dispose of non-recyclable waste through licensed hazardous waste handlers if contaminated.
Shipping & Transportation
- Package machined parts in anti-static or protective materials to prevent scratches, static discharge, or contamination.
- Use moisture-barrier bags for sensitive components, especially in humid environments.
- Label shipments with proper handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”).
- Partner with freight carriers experienced in handling precision plastic components.
Regulatory Compliance
- Ensure product compliance with relevant standards:
- RoHS/REACH: Restriction of hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment.
- FDA 21 CFR: For plastics used in food contact or medical devices.
- UL Certification: For flame-resistant materials used in electrical enclosures.
- Maintain technical documentation, including Declarations of Conformity and material test reports.
Export Controls & Documentation
- Verify export regulations (e.g., ITAR, EAR) when shipping to international markets.
- Prepare accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin.
- Classify products under the correct Harmonized System (HS) code for customs clearance.
Quality Assurance & Traceability
- Perform in-process and final inspections using calibrated tools (micrometers, CMMs).
- Maintain lot traceability from raw material to finished part.
- Implement corrective and preventive action (CAPA) processes for non-conformances.
Worker Safety & Training
- Train machinists on safe handling of plastics, machine operation, and emergency procedures.
- Provide appropriate PPE (gloves, eye protection, respirators) when machining plastics that generate fine dust or fumes.
- Ensure proper ventilation and dust extraction systems are in place.
Continuous Improvement
- Audit logistics and compliance procedures annually or after major process changes.
- Stay updated on changes in environmental regulations, material standards, and industry best practices.
- Engage in supplier and customer feedback loops to refine compliance and delivery performance.
In conclusion, sourcing plastic machining requires a careful evaluation of material properties, machining capabilities, supplier expertise, and quality standards. Selecting the right plastic material—such as acrylic, polycarbonate, PEEK, or nylon—is critical to ensuring performance in the intended application. Partnering with a reliable machining provider that offers precision, experience with engineering plastics, and adherence to industry specifications enhances product quality and reduces lead times. Additionally, considering factors like cost-efficiency, scalability, and post-processing needs contributes to a successful sourcing strategy. Ultimately, effective plastic machining sourcing balances technical requirements with operational efficiency, supporting innovation and reliability across industries such as medical, aerospace, automotive, and electronics.