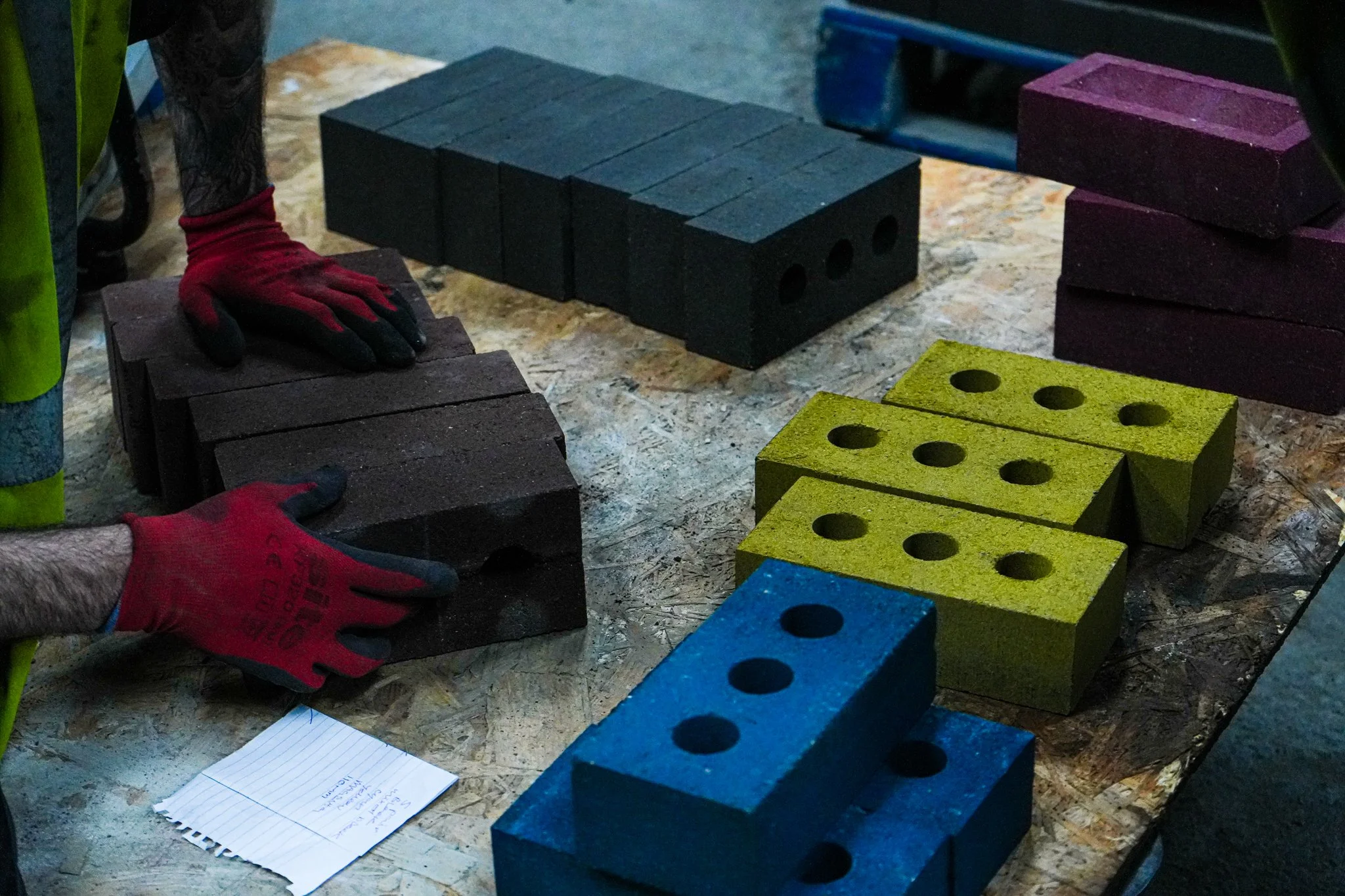
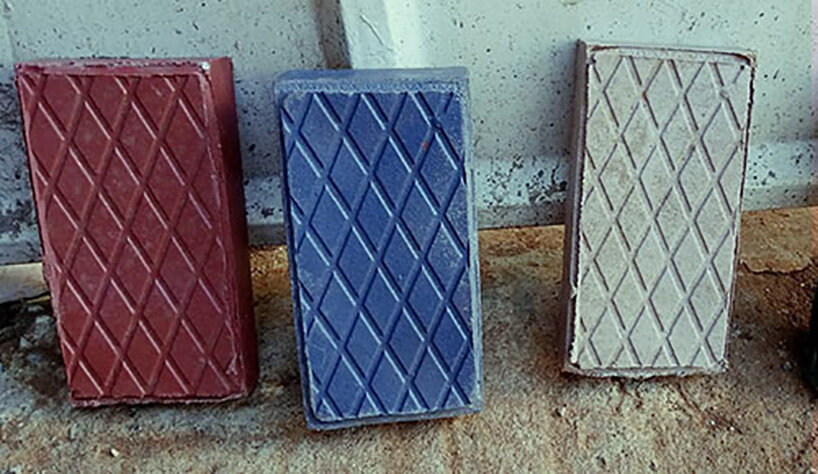
The global plastic bricks market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for sustainable construction materials and rapid urbanization. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global recycled plastic market—of which plastic bricks are a key application—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2023 to 2028. Additionally, Grand View Research estimates that the global construction plastics market size was valued at USD 357.9 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 6.3% through 2030, fueled by innovations in eco-friendly building solutions. In this context, plastic bricks have emerged as a viable alternative to traditional masonry, offering durability, thermal insulation, and reduced environmental impact. As the construction industry shifts toward circular economy principles, leading manufacturers are scaling production and investing in R&D to meet rising demand. Here are the top 10 plastic bricks manufacturers shaping the future of sustainable construction.
Top 10 Plastic Bricks Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 LyondellBasell (LYB)
Domain Est. 2007
Website: lyondellbasell.com
Key Highlights: LyondellBasell creates solutions for everyday sustainable living as the global chemical industry leader & leading polymer producer….
#2 Resco Products
Domain Est. 1999
Website: rescoproducts.com
Key Highlights: As a leading refractory manufacturer Resco Products provides refractory brick, mortar, precast, preshape, clay & minerals, and castable refractory products….
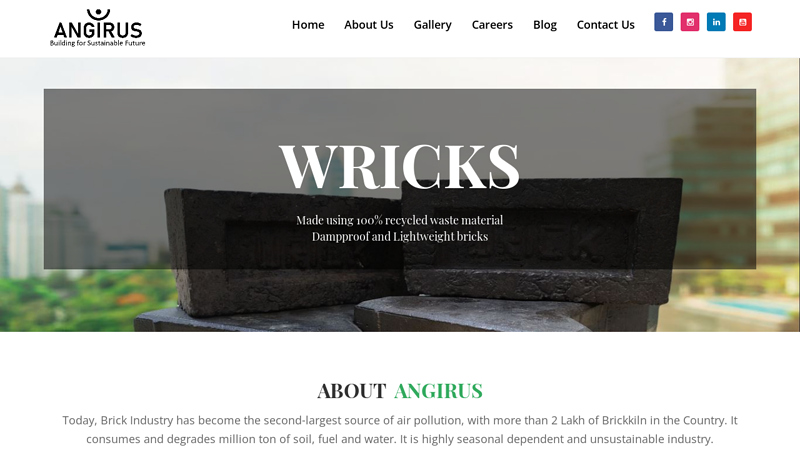
#3 Angirus
Domain Est. 2020
Website: angirusind.com
Key Highlights: Angirus provides Eco-friendly and sustainable Technology to make Bricks and Paver blocks that are Damp-proof and Lightweight. Angirus products are 100% made ……
#4 Ecobrick
Domain Est. 2023
Website: theecobricks.com
Key Highlights: Our technology that cures low-value waste into a eco-friendly product that is alternative to concrete products such as paving tiles, recycled containers, ……
#5 ByFusion
Domain Est. 2001
Website: byfusion.com
Key Highlights: ByFusion designs advanced construction materials and scalable polymer manufacturing solutions, delivering engineered building products with lower embodied ……
#6 to Ecobricks.org
Domain Est. 2013
Website: ecobricks.org
Key Highlights: Ecobricking is a simple, non-capital methodology to keep your plastic safe and secure so that it can be put to good, green use….
#7 Conceptos Plasticos
Domain Est. 2014
Website: conceptosplasticos.com
Key Highlights: We produce a 100% recycled plastic construction system [Bricks & Blocks] used to assemble houses and schools for vulnerable people….
#8 Kenoteq Ltd
Domain Est. 2015
Website: kenoteq.com
Key Highlights: Discover Kenoteq, pioneering the sustainable construction revolution with our innovative, ultra low-carbon building materials….
#9 Gjenge Makers
Domain Est. 2019
Website: gjenge.co.ke
Key Highlights: Gjenge plastic bricks serve as an illustration of what quality is; they have a compression strength that is three times more than that of conventional concrete ……
#10 Ramtsilo
Domain Est. 2019
Website: ramtsilo.com
Key Highlights: Introducing our Eco Plastic Bricks, a revolutionary building material that outperforms conventional bricks. With superior strength, a lower water absorption ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Plastic Bricks

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Plastic Bricks
The global plastic bricks market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by escalating environmental concerns, technological advancements, and evolving construction demands. Here’s a detailed analysis of the key trends expected to shape the industry in this pivotal year:
1. Accelerated Adoption Driven by Sustainability Mandates
By 2026, stringent government regulations on carbon emissions and plastic waste will be a primary catalyst for plastic brick adoption. Countries within the EU, North America, and parts of Asia-Pacific will enforce stricter building codes favoring sustainable materials. The circular economy model will gain traction, with plastic bricks offering a viable solution to manage non-recyclable plastic waste—projected to reach 34 billion tons globally by 2026. Public and private infrastructure projects will increasingly specify plastic bricks to meet ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) benchmarks.
2. Technological Innovation in Material Composition and Manufacturing
Advancements in polymer science and 3D printing will enable the production of plastic bricks with enhanced structural integrity, UV resistance, and thermal insulation. Hybrid composites—blending recycled plastics with additives like fly ash or bio-based polymers—will improve durability and fire resistance, addressing key concerns about safety and longevity. Automated, modular manufacturing units will lower production costs and enable localized, on-demand fabrication, reducing transportation emissions and lead times.
3. Expansion into Mainstream Construction
While initially used in low-cost housing and emergency shelters, plastic bricks will gain credibility in commercial and mid-rise residential construction by 2026. Certification bodies will finalize standardized testing protocols for load-bearing capacity and seismic resistance, facilitating wider regulatory approval. Partnerships between plastic brick manufacturers and established construction firms will accelerate market penetration, particularly in developing regions facing housing shortages.
4. Regional Market Diversification and Growth Hotspots
Asia-Pacific will remain the fastest-growing market, with India, Indonesia, and the Philippines leading adoption due to urbanization and plastic pollution challenges. Africa will emerge as a key frontier, supported by international development funding and NGO-led housing initiatives. Latin America will see increased investment, especially in countries like Colombia and Mexico, where informal settlements drive demand for affordable, resilient building solutions.
5. Challenges: Perception, Recycling Infrastructure, and Long-Term Durability
Despite progress, skepticism around the long-term performance and aesthetic appeal of plastic bricks will persist. Misconceptions about structural weakness and off-gassing could hinder mainstream acceptance. Additionally, inconsistent global recycling systems may impact the quality and availability of feedstock. Industry stakeholders will need to invest in public education, lifecycle assessments, and closed-loop recycling programs to build trust.
6. Investment and Market Valuation Surge
The global plastic bricks market, valued at approximately USD 1.2 billion in 2023, is projected to exceed USD 3.5 billion by 2026, reflecting a CAGR of over 40%. Venture capital and green infrastructure funds will increasingly back scalable startups and R&D initiatives. Strategic alliances between waste management companies and construction material producers will create vertically integrated supply chains, enhancing profitability and sustainability.
Conclusion:
By 2026, plastic bricks will transition from a niche eco-alternative to a mainstream construction material, driven by policy support, technological maturity, and urgent environmental imperatives. While challenges remain, the convergence of innovation and sustainability will position plastic bricks as a cornerstone of the future built environment—turning plastic waste into resilient, affordable infrastructure.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Plastic Bricks: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing plastic bricks—whether for construction, toys, or industrial applications—can present significant challenges, particularly concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) rights. Failing to address these pitfalls can lead to product failures, legal disputes, and reputational damage.
Quality Inconsistencies
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing plastic bricks is inconsistent quality across production batches. Variations in raw material composition, manufacturing processes, and colorants can result in bricks that differ in strength, durability, dimensional accuracy, and appearance. Poor quality control may lead to bricks that are brittle, warp under heat, or fail to interlock properly. Additionally, suppliers may use recycled plastics without adequate testing, introducing contaminants or weakening structural integrity. To mitigate this, buyers should require material certifications, conduct third-party inspections, and establish clear quality benchmarks in supplier agreements.
Intellectual Property Infringement
Another critical risk involves intellectual property violations, particularly when sourcing generic or imitation plastic bricks that resemble well-known branded products (e.g., toy building blocks). Many established brands hold design patents, trademarks, and copyrights on their brick shapes, logos, and packaging. Sourcing look-alike products—even if functionally similar—can expose buyers to legal action for trademark or design patent infringement. This is especially prevalent in regions with lax IP enforcement. To avoid litigation, buyers must verify that sourced products do not mimic protected designs and should obtain IP indemnification clauses from suppliers. Conducting thorough IP due diligence before placing orders is essential to ensure compliance and protect against costly legal consequences.
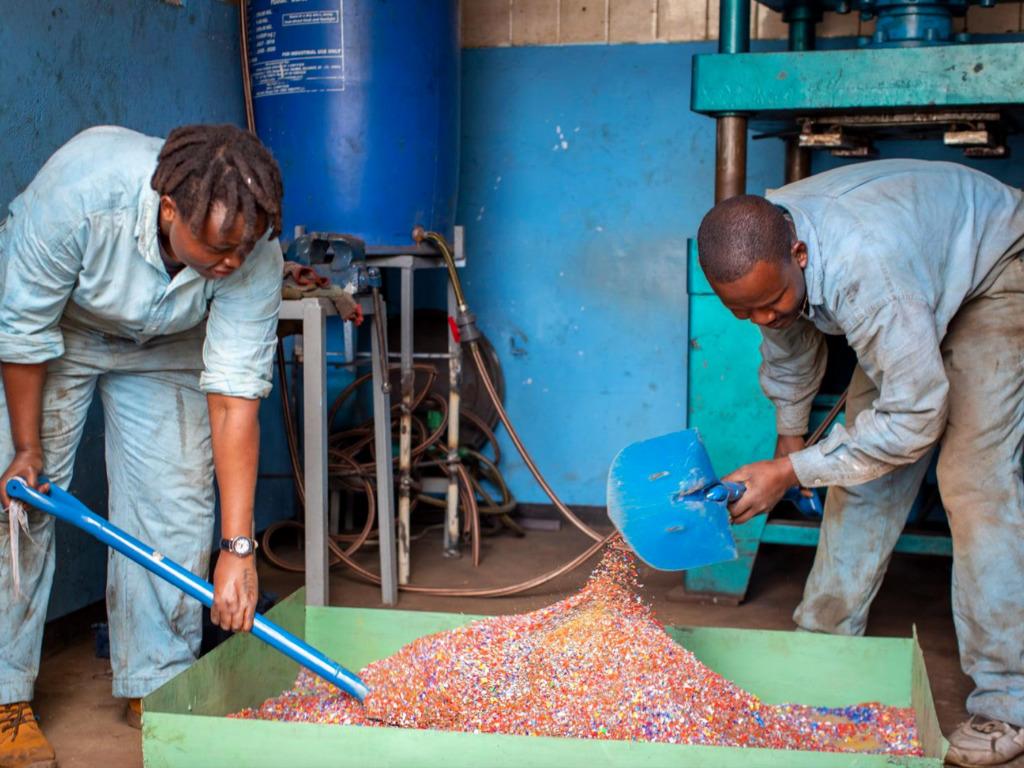

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Plastic Bricks
Plastic bricks—recycled building blocks made from post-consumer or industrial plastic waste—are gaining traction as sustainable construction materials. However, their transport, storage, and regulatory compliance require careful planning. This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations to ensure safe, legal, and efficient handling of plastic bricks.
Classification and Regulatory Compliance
Plastic bricks may be subject to various regulatory frameworks depending on their composition, origin, and destination. Key compliance areas include:
- Waste Classification: If made from recycled waste plastic, plastic bricks may fall under waste shipment regulations (e.g., Basel Convention, EU Waste Shipment Regulation). Ensure materials meet end-of-waste criteria to avoid classification as hazardous or controlled waste.
- REACH & RoHS Compliance (EU): Verify that plastic bricks do not contain restricted substances (e.g., phthalates, heavy metals) above permissible levels.
- Country-Specific Standards: Check local construction material standards (e.g., ASTM in the U.S., BSI in the UK) for mechanical strength, fire resistance, and durability.
- Customs Documentation: Provide accurate HS codes (typically under 3926.90 for plastic articles of construction) and material safety data sheets (MSDS) where required.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging protects product integrity and ensures safety during transport:
- Stackable Pallets: Use standardized pallets (e.g., EUR/ISO) wrapped in stretch film to prevent shifting. Plastic bricks should be uniformly packed to avoid overhang.
- Moisture Protection: Use waterproof covers or sealed packaging if stored or shipped in humid environments.
- Labeling: Clearly label packages with product type, weight, batch number, handling instructions (e.g., “Stack Max 5 High”), and any recycling or safety symbols.
- Load Securing: Use dunnage, straps, or air bags in shipping containers or trucks to prevent movement during transit.
Transportation and Shipping
Efficient logistics planning minimizes cost and environmental impact:
- Modal Selection: Choose transport modes based on distance and volume—road for regional distribution, rail or sea for long-haul or international shipments.
- Container Optimization: Maximize container load (e.g., 20’ or 40’ dry van) by calculating brick dimensions and weight to avoid underutilization or overloading.
- Temperature Considerations: Avoid prolonged exposure to extreme heat, which may deform plastic bricks. Ventilated containers or shaded storage areas are recommended.
- Last-Mile Delivery: Coordinate with local distributors for efficient offloading and site delivery, especially to remote or urban construction zones.
Storage and Inventory Management
Safe and organized storage maintains product quality:
- Indoor Storage Preferred: Store in dry, covered areas away from direct sunlight to prevent UV degradation.
- Pallet Racking: Use racking systems to allow for good airflow and easy access. Limit stack height per manufacturer specifications.
- Inventory Tracking: Implement barcode or RFID systems to manage stock levels, batch traceability, and expiration dates (if applicable).
- Fire Safety: Although non-combustible in some forms, plastic materials can melt or emit fumes. Store away from ignition sources and comply with local fire codes.
Environmental and Sustainability Reporting
Demonstrate compliance with green building standards and ESG goals:
- Recycled Content Certification: Provide documentation (e.g., third-party verification) of the percentage of post-consumer or post-industrial recycled plastic used.
- Carbon Footprint Tracking: Measure and report emissions associated with production and transport (e.g., using tools like EPDs—Environmental Product Declarations).
- End-of-Life Management: Offer guidance on recyclability or reuse to support circular economy principles.
Import/Export Considerations
Cross-border shipments require additional diligence:
- Export Controls: Confirm whether plastic bricks are subject to export restrictions, especially if derived from mixed waste streams.
- Import Permits: Some countries require permits or pre-approval for importing recycled materials. Check destination country regulations (e.g., China’s “Green Fence” policy).
- Language and Labeling: Provide multilingual labels and documentation if shipping internationally.
Quality Assurance and Documentation
Maintain trust and traceability across the supply chain:
- Batch Testing Reports: Keep records of compressive strength, dimensional accuracy, and fire resistance tests.
- Certificates of Conformity: Issue or obtain CoCs for each shipment to verify compliance with agreed specifications.
- Incident Reporting: Establish procedures for handling damaged goods, delays, or non-compliance issues.
By adhering to this logistics and compliance framework, manufacturers, distributors, and builders can ensure the safe, legal, and sustainable use of plastic bricks in construction projects worldwide.
In conclusion, sourcing plastic bricks presents a promising and sustainable solution for both construction and environmental challenges. By repurposing waste plastic into durable, lightweight, and cost-effective building materials, plastic bricks contribute to waste reduction, lower carbon emissions, and resource conservation. However, successful sourcing requires careful consideration of material quality, supplier reliability, certification standards, and long-term performance. Collaboration with ethical suppliers, adherence to regulatory guidelines, and investment in innovation are essential to ensure the viability and scalability of plastic bricks in the construction industry. As global awareness of sustainability grows, integrating plastic bricks into building projects not only supports circular economy principles but also positions organizations at the forefront of eco-friendly construction practices.