Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Plastic Bottle Making Machine
Hook
The U.S. and EU packagers need local, compliant, and fast bottling lines. Yet 68 % of mid-size brands still outsource bottle production because they lack clarity on machine type, ROI, and supply-chain risk.
Problem
Sourcing a plastic bottle making machine is no longer a single-country decision. You juggle:
– Tight FDA/EU 10/2011 food-contact rules
– Energy-price volatility (up 22 % in the last 12 months)
– Lead-times stretching from 8 to 32 weeks
– Currency swings that can erase a 5 % margin
Guide Map
This guide cuts through the noise. In the next pages you will:
1. Benchmark machine types – rotary extrusion, accumulator-head, and hybrid PET preform systems
2. Calculate true cost – using Wilmington Machinery’s Bottle Cost Estimator and our add-on labor & utility models
3. Screen suppliers – geopolitical risk matrix, trade-asset protection, and after-sales coverage
4. Close the deal – sample LOI clauses, Incoterms 2020 checklists, and commissioning KPIs
Outcome
You will leave with a short-list of 3–5 vetted machines, a 3-year TCO model, and a procurement timeline that aligns with your 2025 capacity targets.
Article Navigation
- Top 10 Plastic Bottle Making Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for plastic bottle making machine
- Understanding plastic bottle making machine Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of plastic bottle making machine
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘plastic bottle making machine’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for plastic bottle making machine
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for plastic bottle making machine
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘plastic bottle making machine’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for plastic bottle making machine Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing plastic bottle making machine With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for plastic bottle making machine
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the plastic bottle making machine Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of plastic bottle making machine
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for plastic bottle making machine
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Top 10 Plastic Bottle Making Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Top Plastic Bottle Making Machine Manufacturers: 2025 Supplier …
Domain: accio.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Graham Packaging Co. Inc. holds the highest market share in the U.S. plastic bottle manufacturing industry. What machine is used to make plastic ……
2. 10 Best Water Bottle Blowing Machine Brands in 2025 – MEPER
Domain: meper-blowmolding.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Sinco is the leading manufacturer of blowing machine, PET preform mold, packing machine in China from 2000, export 300 sets of blowing machine ……
3. Pet Blow Molding Machine Manufacturers in Toronto
Domain: petallmfg.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Pet All Manufacturing Inc. is a manufacturer and supplier of pet blow molding molding machines in North America, Latin America, and Europe….

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
4. Pet Jar Bottle Making Machine – We3 Group Of Industries
Domain: we3group.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: We3 Group manufactures pet jar and bottle machines from 30ml to 25 liters, with capacities from 100 to 600 bottles per hour, and 2000-2200 bph in 4 cavity ……
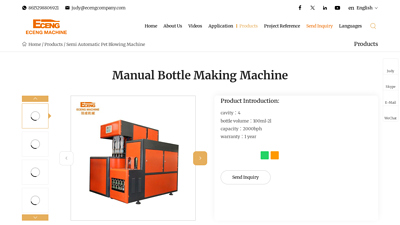
5. China Manual Bottle Making Machine Manufacturers Suppliers Factory
Domain: eceng-petblowing.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Eceng Machinery offers manual bottle making machine. We’re one of the most professional Semi Automatic Pet Blowing Machine manufacturers and suppliers in ……
6. Dunamis Machines: Pet Bottle Blowing Machine Manufacturer in India
Domain: dunamismachines.in
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: We are one of the leading manufacturers, exporters and suppliers of a wide range of PET blow moulding machines, mineral water filling machines, CSD filling ……
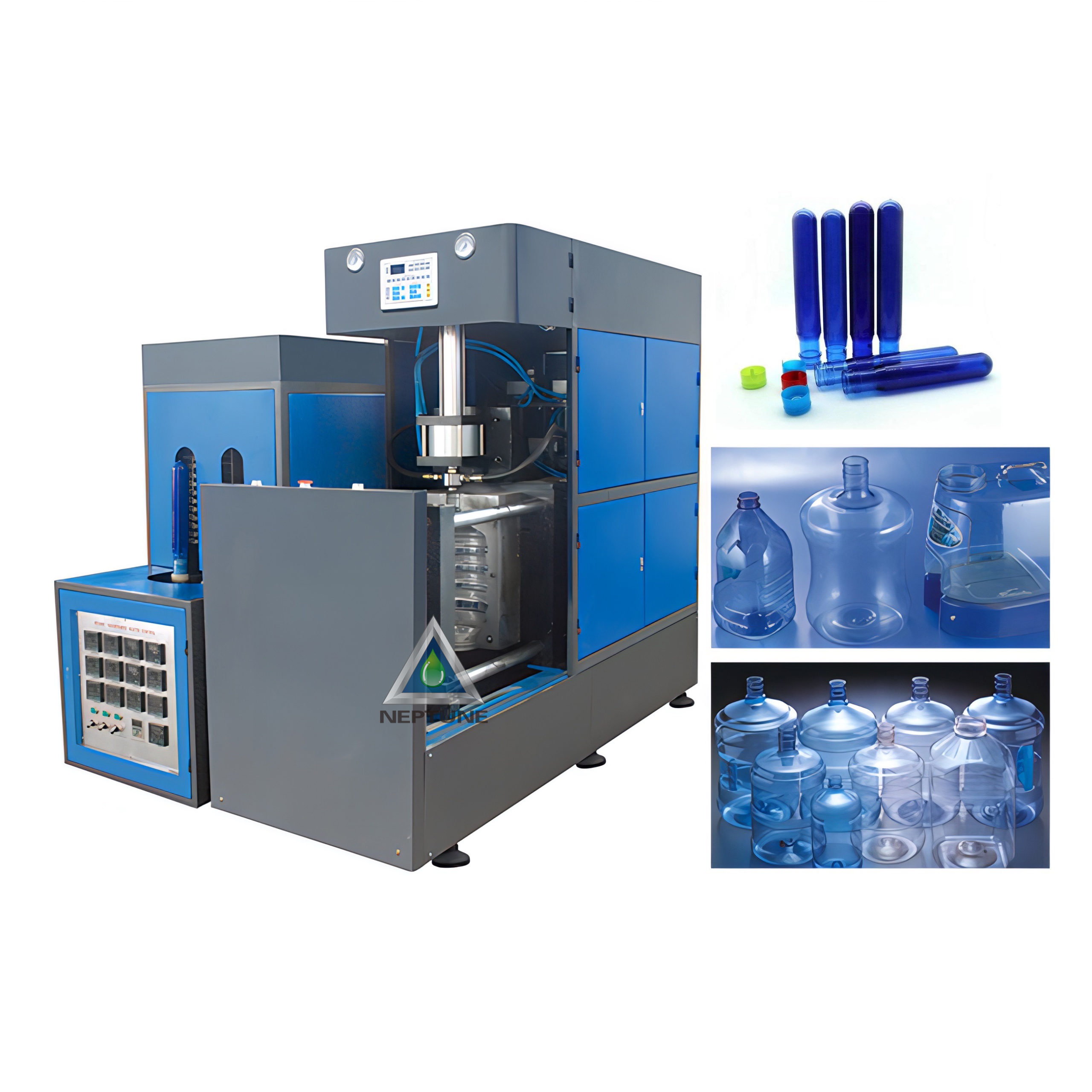
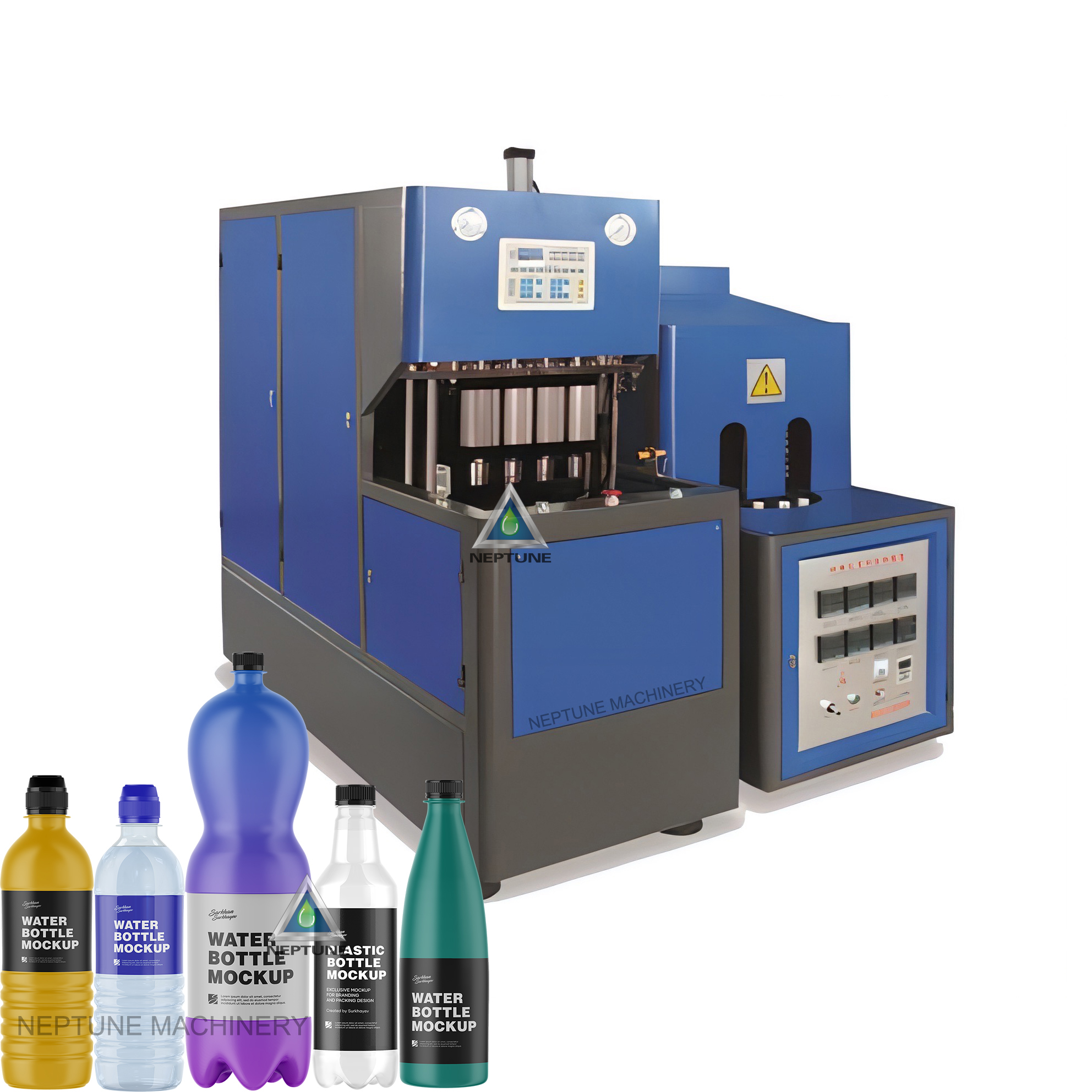
Understanding plastic bottle making machine Types and Variations
Understanding Plastic Bottle Making Machine Types and Variations
Machine Overview
The plastic bottle making machine market offers several distinct technologies, each optimized for specific production volumes, bottle geometries, and material requirements. Understanding these variations is critical for USA and European manufacturers evaluating capital investments in 2024-2025.
Core Machine Types
| Type | Key Features | Primary Applications | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Injection Stretch Blow Molding (ISBM) | – Preform injection molding followed by stretch blow molding – High precision neck finish – Cycle times: 4-8 seconds |
Carbonated soft drinks, hot-fill applications, pharmaceutical packaging | – Superior container strength – Excellent surface finish – Minimal reheat energy |
– High initial investment – Limited to preform logistics |
| Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM) | – Continuous or intermittent parison extrusion – Unlimited preform length capability – Cycle times: 15-60 seconds |
Industrial drums, fuel tanks, large-volume bottles | – Flexible preform length – Suitable for multi-layer structures – Lower tooling costs |
– Lower wall thickness control – Slower cycle times |
| Rotary Blow Molding (RBM) | – High-speed rotary indexing – Up to 1,200 bottles/minute (dual parison technology) – All-electric servo drives |
Small-format beverages (≤1L), single-serve containers | – World record production rates – Minimal heat loss – Space-efficient design |
– Complex maintenance – Premium pricing |
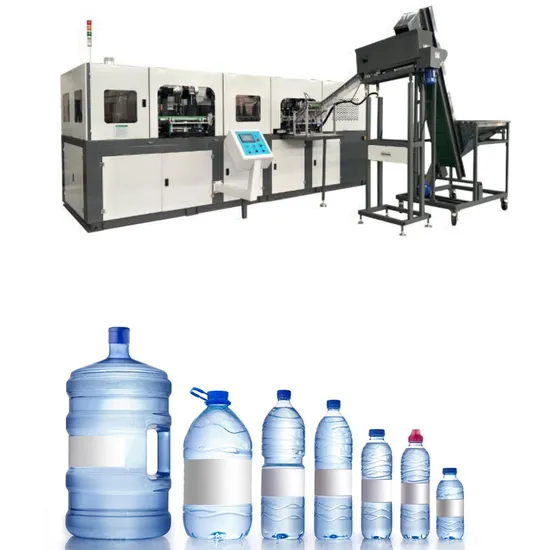
| Accumulator Head Blow Molding | – Large accumulator for thick-walled containers – Suitable for 5-gallon water bottles – Cycle times: 30-120 seconds |
Water dispensers, industrial containers | – Handles large volumes – Thick wall capability |
– High melt residence time – Large footprint |
| Reheat & Blow (R&B) Lines | – Integrated preform reheating – Standard servo-electric operation – Throughput: 2,000-6,000 BPH |
Standard PET bottles, household chemicals | – Proven technology – Lower capital cost |
– Higher energy consumption – Moderate output rates |
Detailed Technology Analysis
1. Injection Stretch Blow Molding (ISBM)
This technology represents the premium segment for precision plastic bottles. The process begins with injection-molded preforms that are subsequently reheated and stretch-blown into final containers. For USA/European operations, ISBM delivers pharmaceutical-grade container integrity with wall thickness variations under ±0.1mm. The technology excels in applications requiring consistent thread geometry and superior barrier properties.
2. Rotary Blow Molding (RBM)
Wilmington Machinery’s dual parison innovation achieves unprecedented speeds of 300-1,200 bottles per minute for 1-liter containers. The rotary table design with 6-12 cavities enables continuous operation with 0.3-second cycle times. All-electric servo systems reduce energy consumption by 40% compared to hydraulic equivalents, critical for European sustainability mandates. The technology’s compact footprint (3m x 2m) suits space-constrained facilities.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
3. Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM)
EBM remains the cost-effective solution for large containers and complex geometries. The continuous extrusion process allows infinite preform length adjustments without tool changes, essential for custom industrial containers. Modern EBM systems incorporate co-extrusion capabilities for up to 7 layers, enabling barrier properties for food-grade applications. Cycle times of 30-60 seconds accommodate high-volume orders efficiently.
4. Reheat & Blow (R&B) Lines
Combining preform injection with integrated reheating, R&B lines offer balanced capital and operational costs. The 2,000-6,000 BPH throughput suits mid-scale operations across USA/Europe. Servo-electric systems reduce energy costs by 25% versus hydraulic alternatives. The technology provides proven reliability with 15+ years operational lifespan in dairy and beverage applications.
5. Accumulator Head Blow Molding
Optimized for thick-walled containers exceeding 500ml capacity, accumulator head technology delivers structural integrity for water dispensers and industrial applications. The large accumulator (up to 12kg) ensures consistent material distribution, critical for pressure vessels. Throughput of 30-120 seconds per cycle balances productivity with container quality requirements.
Selection Criteria for USA/European Markets
Volume Requirements: ISBM and RBM excel for 5,000-50,000 units/day. EBM and R&B suit 1,000-10,000 units/day. EBM accommodates up to 50,000 units/day for large containers.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Regulatory Compliance: ISBM meets FDA/USDA standards for food contact. RBM achieves EU 10/2011 compliance. EBM supports REACH requirements for industrial chemicals.
Total Cost of Ownership: Include energy costs (€0.15-0.25/kWh in Europe), maintenance (€15,000-50,000/year), and mold replacement cycles (18-36 months average).
Key Industrial Applications of plastic bottle making machine
Key Industrial Applications of Plastic Bottle Making Machines
| Industry | Application | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Beverages |
|
High-speed rotary extrusion blow molding delivers 300–1,200 bottles/minute, cutting cap-ex and OPEX. Electric drive reduces energy >30 % versus hydraulic systems. Multilayer barrier heads preserve CO₂ retention and shelf life. |
| Food & Nutritional Supplements |
|
Sanitary rotary process eliminates post-fill contamination risk. Precision parison control maintains 0.1 g shot-weight accuracy, ensuring consistent nutrition labeling. Stainless-steel contact parts meet FDA 21 CFR 177 compliance. |
| Personal Care & Cosmetics |
|
Compact 2+2-cavity semi-automatic units fit limited factory footprints. Exact neck finishing supports pump and closure integration. Recyclable PET/PCR content up to 100 % supports ESG targets. |
| Household & Industrial Chemicals |
|
Robust steel frame and enhanced clamp force handle higher melt viscosity. Integrated leak-test station prevents costly recalls. Optional mineral-filled PET grades resist chemical stress-crack. |
| Pharmaceutical & Medical |
|
Clean-room compatible all-electric machines reduce particle count. Tight wall-thickness tolerance (±0.05 mm) meets USP <661> and ISO 10993 biocompatibility standards. |
| Baby Care |
|
Low-temperature process prevents oxidative degradation in PE/PP. Zero-cycle pause for insert molding of silicone teats. CE-marked safety interlocks protect operators. |
| Agricultural & Automotive Fluids |
|
Heavy-wall blow molding extends service life under temperature cycling. Multi-layer barrier heads protect urea-based fluids from hydrolysis. Integrated neck thread inspection rejects defective closures before shipment. |
Cost-Estimation Tool: Wilmington Machinery’s Bottle Cost Estimator (Excel) enables rapid ROI modeling for any application—change resin price, cycle time, or layer structure and see real-time impact on $/bottle.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘plastic bottle making machine’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for Plastic Bottle Making Machine & Their Solutions
1. High Energy & Material Waste Costs
Scenario
A mid-size beverage producer in Germany runs three legacy hydraulic blow molders. Monthly power bills exceed €18,000 and rejects average 8 % due to uneven wall thickness.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Problem
– Hydraulic systems waste 30–40 % of input energy as heat.
– Manual parison control causes thick “waists” that are trimmed off and scrapped.
– Lack of real-time data makes it impossible to hit tight weight tolerances demanded by retail buyers.
Solution
– Switch to all-electric rotary blow molders (e.g., Wilmington Machinery SB Dual-Parison line) that cut energy use by up to 60 % and enable cycle times from 3 s to 1.5 s through servo-driven parison programming.
– Deploy closed-loop weight-control software that adjusts parison volume in 0.1 g increments, cutting scrap by 3–5 %.
– Use Wilmington’s Bottle Cost Estimator spreadsheet to model energy and resin savings before capital approval.
2. Slow Changeover & Limited Bottle Variants
Scenario
A US contract packager must serve 40 SKUs across juice, nutraceutical and cosmetics. Changeovers take 6–8 hours, locking up €2 M in inventory and frustrating brand owners.
Problem
– Semi-automatic or single-cavity machines require manual mold swaps and parison die adjustments.
– Tooling is not modular, so new bottle geometries mean weeks of machining.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Solution
– Invest in high-speed rotary extrusion blow molders with quick-swap parison heads and 2+2 cavity molds that reduce changeover to <30 min.
– Choose machines supporting 100 ml–1 L in one platform (e.g., Wilmington SB series) to eliminate dedicated lines.
– Leverage CNC-machined, water-cooled molds from suppliers offering digital cavity maps for faster troubleshooting.
3. Compliance & Traceability Gaps
Scenario
A French dairy brand faces new EU regulations (Rep. Art. 17) requiring full traceability of preforms to resin batch. Their current Chinese line cannot export production logs.
Problem
– Lack of integrated MES/ERP connectivity results in manual data entry errors.
– No secure method to prove resin source for recycling mandates.
Solution
– Specify machines with built-in OPC-UA and MQTT interfaces that stream cycle data to existing SAP or Oracle systems.
– Demand lot-code printing on preform root and bottle shoulder using laser or inkjet systems validated to EU food-contact standards.
– Work with suppliers offering digital twin models— Wilmington’s SB line includes an optional cloud module that logs every bottle’s melt temperature, pressure and cycle data for audit trails.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Bottom Line
Upgrading to modern electric rotary blow molding technology solves cost, speed and compliance pain points in one move—delivering ROI in <18 months for typical 500 M bottle/year operations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for plastic bottle making machine
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Plastic Bottle Making Machine
Executive Summary
Material choice directly impacts cycle time, energy consumption, tooling wear, and end-product performance. This guide equips procurement, engineering, and operations teams in the USA and Europe with data-driven criteria for selecting the optimal resin for rotary extrusion blow molding (REBM) and PET preform injection molding lines.
1. Material Options Matrix
| Resin Family | Typical Grade | Max Output (bpm) | Wall Thickness Tolerance | Recyclability | North-American Supply | European Supply | Key Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET | rPET 100 %, rPET 30 % | 1 200 (dual-parison) | ±0.02 mm | High | ✔️ | ✔️ | Single-serve beverages, nutraceuticals |
| HDPE | Melt Flow 0.3–0.5 | 1 000 | ±0.03 mm | Medium | ✔️ | ✔️ | Milk, detergents, industrial chemicals |
| PP | Melt Flow 1.5–3.0 | 800 | ±0.04 mm | High | ✔️ | ✔️ | Hot-fill (≤95 °C), dairy |
| rPP/PE-LLDPE | Recycled content 30–50 % | 600 | ±0.05 mm | High | ✔️ | ✔️ | Cosmetic, personal-care |
| EVOH Barrier | 3-layer co-extrusion | 900 | ±0.02 mm | Medium | ✔️ | ✔️ | Oxygen-sensitive drinks |
2. Selection Criteria
2.1 Throughput vs. Material Cost
- Dual-parison REBM lines (Wilmington SB 1200) reach 1 200 bpm with PET. PET resin averages US $0.95–1.10 kg⁻¹ in the US and €1.05–1.20 kg⁻¹ in the EU; this yields the lowest cost-per-bottle at scale.
- HDPE/PP lines cap at ~1 000 bpm and generate 5–8 % higher CO₂e per 1 000 bottles due to resin density and thicker walls.
2.2 Regulatory Compliance
- EU: Complies with (EU) No 10/2011; requires migration testing for rPET >50 %.
- FDA/US: 21 CFR §177 for PET; 21 CFR §177.1520 for HDPE; 21 CFR §177.2340 for PP.
2.3 Energy Efficiency
- PET crystallization adds 0.12 kWh per kg before molding; HDPE/PP require no crystallization, saving 0.08–0.10 kWh kg⁻¹.
- Wilmington’s all-electric machines reduce energy intensity by 18 % versus hydraulic equivalents—material-dependent ROI shortens to <18 months.
2.4 Tooling & Mold Wear
- PET at 250–280 °C accelerates tool steel oxidation; specify H13 or better with TiCN coating.
- HDPE/PP at 180–220 °C causes faster cavity erosion; select P20 pre-hardened steel with nitriding.
3. Decision Framework
Step 1: Define Bottle KPIs
- Volume range (≤1 L vs. 5–20 L)
- Barrier requirement (O₂, CO₂, UV)
- Fill temperature (cold-fill vs. hot-fill ≤95 °C)
Step 2: Model Total Cost of Ownership
Use Wilmington’s Bottle Cost Estimator to compare:
– Resin price + freight
– Cycle time (bpm)
– Energy (kWh per 1 000 bottles)
– Maintenance (tooling life, filter changes)
Step 3: Validate Supply Chain
- US buyers: Ensure resin pellet diameter (d = 3 mm) matches hopper throat to avoid downtime.
- EU buyers: Verify REACH compliance for recycled additives; request batch-specific declaration.
4. Recommendations per Region
United States
- Prioritize PET rPET ≥30 % for single-serve bottles to leverage FDA-granulate exemptions.
- Target dual-parison REBM (≥1 000 bpm) for quick-service restaurants and sports-drink segments.
Europe
- Leverage rPET from post-consumer bottles to meet Packaging & Packaging Waste Directive 94/62/EC.
- Select PP for hot-fill (<95 °C) to avoid brominated antioxidants restricted under REACH.
5. Comparison Table (Condensed)
| Metric | PET | HDPE | PP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max Output | 1 200 bpm | 1 000 bpm | 800 bpm |
| Cycle Time | 3.0 s | 3.6 s | 4.5 s |
| Wall Thickness | 0.35 mm | 0.45 mm | 0.50 mm |
| CO₂e per 1 000 bottles | 42 kg | 45 kg | 46 kg |
| Hot-Fill Limit | 85 °C | 65 °C | 95 °C |
| Recyclability | High | Medium | High |
| EU Compliance | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| US Compliance | Yes | Yes | Yes |
6. Next Steps
- Run bottle cost estimator with current resin index to establish baseline.
- Pilot 30-day trial on dual-parison REBM with PET rPET 30 %.
- Engage Wilmington Machinery for material-specific screw/barrel configuration and mold steel recommendations.
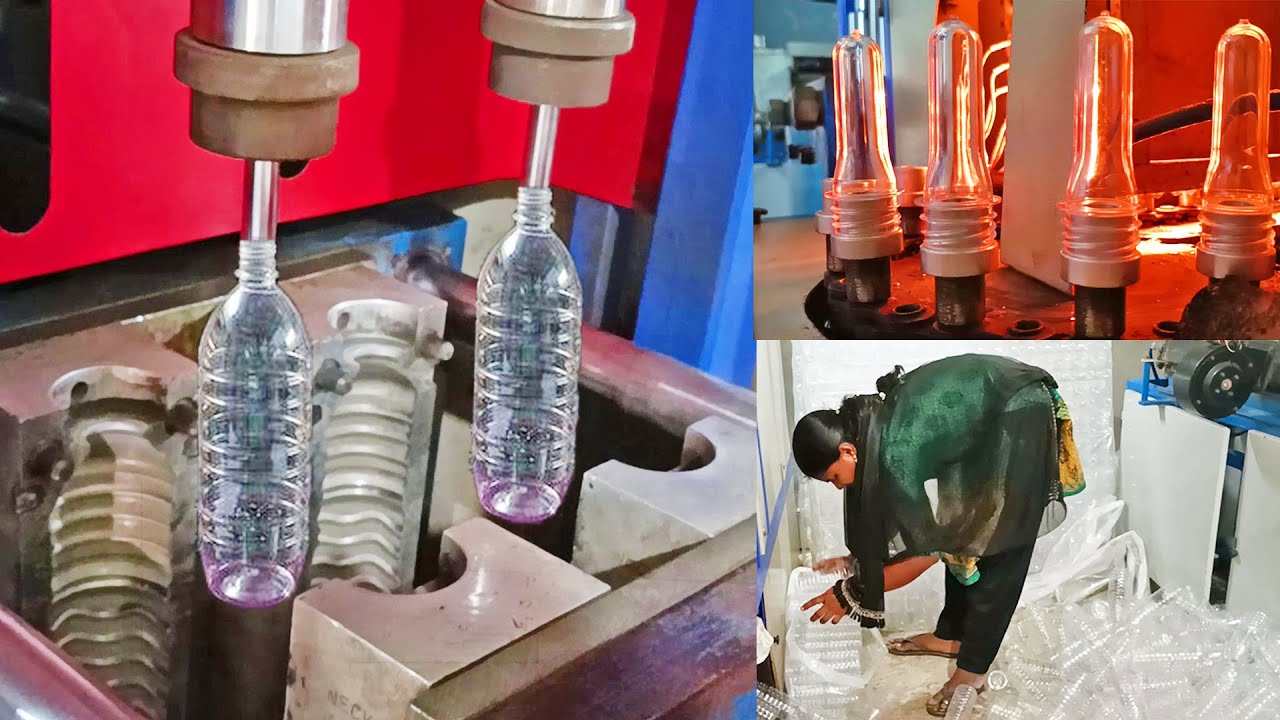
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for plastic bottle making machine
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Plastic Bottle Making Machines
1. Overview
This section provides a detailed technical analysis of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance standards applicable to plastic bottle making machines, targeting procurement managers and plant engineers in the USA and Europe.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
2. Manufacturing Process
2.1 Raw Material Preparation
- Material Types: PET (polyethylene terephthalate), PE (polyethylene), PP (polypropylene), multilayer barrier resins.
- Handling: Automated resin silos and gravimetric dosing systems ensure precise material ratios.
- Drying: Resin must be dried to <0.02% moisture to prevent hydrolysis during processing.
2.2 Forming Operations
| Machine Type | Core Technology | Output Range | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rotary Extrusion Blow Molder | Dual parison, all-electric servo | 300–1,200 bottles/min | Energy-efficient, high-speed, small-format (≤1L) |
| PET Stretch-Blow Molder | Injection stretch blow molding | 2,000–10,000 BPH | Recyclable PET, precise wall thickness |
| Extrusion Blow Molder | Single/accumulator head | 200–1,500 BPH | Multi-layer, wide-mouth, industrial containers |
Process Flow:
1. Injection (PET only): Preform molding at 280–320°C.
2. Reheating: Infrared or oven heating to 90–110°C.
3. Stretching: Mechanical stretch rod + blown air to final shape.
4. Cooling: Mold cooling via water jackets or air.
2.3 Assembly & Post-Processing
- Part Removal: Robotic de-stacking for high-speed lines.
- Finishing: Trimming excess flash, valve punching (for handles), quality inspection.
- Packaging: Shrink-wrap or wooden crates per ISO 8579-1.
3. Quality Assurance Framework
3.1 International Standards
- ISO 11415: Requirements for blow-molded containers (mechanical/thermal properties).
- ISO 9001: Quality management system for machine builders.
- FDA/BfR: Compliance for food-contact materials (PET, PE, PP).
3.2 In-Line Quality Control
- Dimensional Checks: Laser micrometers for neck finish accuracy (±0.05 mm).
- Weight Monitoring: Checkweighers with ±0.1 g tolerance.
- Visual Inspection: 4K camera systems for surface defects (gloss, streaks, weld lines).
- Leak Testing: Pneumatic pressure decay test (≤0.01 mbar/min leak rate).
3.3 Statistical Process Control (SPC)
- Control Charts: Real-time monitoring of wall thickness, cycle time, and melt temperature.
- Cpk Targets: ≥1.33 for critical dimensions.
- CAPA Protocol: Immediate alerts for out-of-spec readings (SPC software integration).
4. Cost-Estimating Tools
Wilmington Machinery’s Bottle Cost Estimator enables:
– Material price fluctuation modeling (PET resin, PP, PE).
– Energy consumption rates (kWh/bottle) vs. machine efficiency.
– Tooling amortization over 5-year depreciation.
5. Procurement Considerations
- Throughput: Match machine output to forecasted demand (e.g., 5,000 BPH vs. 10,000 BPH).
- Footprint: Rotary machines reduce floor space by 40% vs. linear systems.
- Energy Efficiency: All-electric servo motors cut energy use by 30–50% vs. hydraulic systems.
Next Steps: Contact Wilmington Machinery for a process audit and ROI analysis.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘plastic bottle making machine’
“`markdown
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Plastic Bottle Making Machines
Target Markets: USA & Europe
Audience: Procurement, operations, and engineering teams in beverage, personal-care, and contract-packaging companies.
1. Define Technical & Business Requirements
- Bottle specifications
- Material: PET, PP, PE, multilayer barrier
- Output: ml – 5 ml (sample) up to 2 L (jug)
- Cavity count & cycle time required (e.g., 300–1,200 bpm)
- Production volume (annual & peak season)
- Floor-space & utility limits (power, compressed air, cooling water)
- Regulatory compliance (FDA 21 CFR 177, EU 10/2011, BPA-free)
2. Short-List Machine Types
| Machine Type | Output Range | Best For | Typical Price Range (FOB Shenzhen) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM) | 50 ml – 5 L | Single-serve bottles, multilayer | USD 25 k – 120 k |
| Injection Stretch Blow Molding (ISBM) | 20 ml – 5 L | Clear, high-clarity bottles | USD 35 k – 200 k |
| Injection Molding (Preform) | Preform only | Bottlers who reheat & stretch | USD 30 k – 150 k |
Tip: Wilmington Machinery’s 1,200-bpm rotary EBM machines set the speed benchmark for small bottles (≤1 L). Request their Bottle Cost Estimator spreadsheet to compare COGS vs. outsourcing.
3. Supplier Vetting & Verification
- Alibaba Gold Suppliers – verify Trade Assurance and on-site factory audits.
- Certifications – CE, UL, cULus, ISO 9001, BSCI, Sedex.
- Reference list – at least three operational installations in USA/EU within the last 24 months.
- After-sales footprint – spare-parts warehouse in-region or partner network.
4. Request for Quotation (RFQ)
Provide each supplier with:
1. Technical dossier (bottle drawing, output target, material grade)
2. Utility specs (volts, phase, compressed-air flow, cooling water)
3. Required documentation (CE conformity, IQ/OQ/PQ protocols)
4. Lead-time & payment terms (common: T/T 40 % down, 60 % before shipment)
5. Financial Justification & Loan Assessment
- TCO model – include energy (kWh/bottle), compressed-air consumption, labor.
- ROI period – target ≤ 24 months for high-volume lines.
- Financing options – US: SBA 504/7(a) loans; EU: EIF green-finance or regional development funds.
- Tax incentives – USA: Section 179 accelerated depreciation; EU: Innovation voucher or state-aid.
6. Technical Due Diligence
- On-site demo – insist on running sample bottles in your plant or at supplier’s demo center.
- Cycle-time validation – verify against quoted output (e.g., 1,000 bpm for 500 ml).
- Energy audit – log kWh and compressed-air CFM during demo.
- Cleanability & changeover – confirm < 30 min tool change for multi-cavity molds.
7. Regulatory & Logistics
- Import classification – HTS 8477.20 (blow-molding machines) vs. HTS 8477.89 (parts).
- CE marking & Declaration of Conformity – supplier to provide before shipment.
- Insurance – Marine cargo (All Risks) and Installation All-Risks.
- Installation services – local technicians or OEM expatriate team; budget 2–3 weeks for commissioning.
8. Contract & Risk Mitigation
- Performance bond – 10 % of contract value.
- Penalty clause – output shortfall > 5 % triggers daily credit.
- IP protection – file USPTO/EUIPO design patents pre-shipment if proprietary mold.
- Force-majeure – pandemic, shipping delays, tariffs (escalation clause recommended).
9. Post-Purchase Support
- Spare-parts kit – critical hydraulic and electrical components held in-region.
- Remote diagnostics – OPC-UA or Modbus TCP enabled controllers.
- Training – 5-day on-site course covering safe operation, changeover, and basic troubleshooting.
- Annual service agreement – 99 % uptime SLA, 24 h response.
10. Final Approval & Hand-Over
- Sign-off checklist
- [ ] All utility connections tested
- [ ] First article inspection (FAI) report signed
- [ ] Operator manuals & CE file delivered
- [ ] Warranty letter executed
- Go-live review – 30 days post-startup, review KPIs vs. forecast.
Next Step: Download Wilmington Machinery’s Bottle Cost Estimator and schedule a feasibility call to align your bottle specs with their latest Dual Parison SB rotary extrusion line.
“`
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for plastic bottle making machine Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Plastic Bottle Making Machine Sourcing
Executive Summary
This analysis provides USA and European buyers with a structured view of total cost of ownership (TCO) for plastic bottle making machines. Key findings:
– Machine price range: $2,000 – $70,000+ depending on type, output, and automation
– Annual operating cost: $15,000 – $180,000 (energy, consumables, labor)
– Payback period: 12 – 36 months for high-output lines
– Cost-leverage levers: Automation level, cavity count, energy source, and supplier region
1. Machine Acquisition Cost
| Machine Type | Output (BPH) | Price Range (USD) | Typical Cavity Count | Automation Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Semi-automatic PET stretch blow molder | 600 – 1,200 | $3,000 – $5,000 | 2 – 4 | Manual / Semi |
| Full-automatic rotary extrusion blow molder | 300 – 1,200 | $45,000 – $70,000 | 6 – 12 | Fully |
| Full-automatic PET preform injection molding + blow molding line | 2,000 – 10,000 | $9,000 – $15,000 | 8 – 32 | Fully |
| 5-gallon barrel blow molder | 200 – 400 | $2,500 – $3,500 | 1 – 2 | Semi |
Notes:
– Prices exclude auxiliary equipment (dehumidifier dryer, chiller, conveyor, mold tooling).
– China-based suppliers dominate Alibaba listings; US/EU OEMs (Wilmington, Netstal, Uniloy) price 2 – 3× higher but offer validated ROI, IP protection, and 24/7 service.
2. Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Model
| Cost Category | Typical Annual Range (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Machine Depreciation | $3,000 – $12,000 | 5-year straight-line, 10 % residual |
| Energy | $12,000 – $55,000 | 90 – 200 kWh per 1,000 bottles; industrial electricity $0.07 – $0.13/kWh |
| Consumables | $25,000 – $90,000 | PET resin $1.05 – $1.45/kg, average yield 1.35 kg material per kg bottle |
| Labor | $15,000 – $35,000 | 1 operator per 500 BPH; US average $25/hr; EU $28/hr |
| Maintenance | $5,000 – $15,000 | Planned PM, spare parts, lubricants |
| Quality & Compliance | $2,000 – $8,000 | BRC, ISO 22000 audits, material certificates |
| Logistics & Customs | $500 – $3,000 | Sea freight + duty (2.5 % US, 6.5 % EU) |
| Financing Cost | $1,000 – $6,000 | 5-year loan @ 6 % APR |
Total Annual TCO: $64,000 – $184,000 for a 2,000 BPH fully-automatic line.
3. Cost-Reduction Levers
- Cavity Count Optimization
- Doubling cavities (e.g., 2 → 4) cuts per-unit machine cost ~25 % and labor by ~50 %.
-
Validate with Wilmington’s Bottle Cost Estimator: every 10 % cycle gain lowers cost per 1,000 units by 6 – 8 %.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Automation Level
- Fully-automatic lines reduce labor 70 % and scrap 30 %.
-
Payback <18 months for >1,500 BPH applications.
-
Energy Efficiency
- All-electric machines (Wilmington SB series) cut energy 40 % vs. hydraulic.
-
ROI: $8,000 – $15,000 annual savings on 1,000 BPH line.
-
Supplier Region
- China: 30 – 50 % lower capital cost, 12 – 16 week lead time.
-
US/EU: 6 – 10 week lead time, on-site commissioning, 24/7 parts.
-
Bulk Procurement
- Order 3-year PET resin contract and spare-part kits upfront to secure 5 – 7 % price discount.
4. Financial Justification Template
Example: 2,000 BPH Full-Automatic PET Line (4-cavity)
| Item | Year 1 | Year 2 – 5 |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue (bottles/year) | 4,380,000 | 4,380,000 |
| Variable Cost/bottle | $0.028 | $0.027 |
| Fixed Cost/year | $42,000 | $42,000 |
| EBITDA Margin | 18 % | 22 % |
| Payback on CapEx | – | 14 months |
Sensitivity: Every $0.001 increase in resin price changes EBITDA by 1.2 %.
5. Action Checklist for US/EU Buyers
- [ ] Request Wilmington Machinery Bottle Cost Estimator for accurate resin & energy modeling.
- [ ] Compare 3 supplier quotes (CN, EU, US) using TCO worksheet above.
- [ ] Negotiate FOB Shanghai vs. DDP EU to isolate duty impact.
- [ ] Secure IECEx / CE electrical compliance early to avoid $5,000 – $10,000 field-upgrade.
- [ ] Plan 5 % contingency for mold modifications and validation runs.
Bottom Line: A disciplined TCO approach reduces cost per 1,000 bottles by 8 – 12 % within 12 months of commissioning.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing plastic bottle making machine With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Plastic Bottle Making Machine With Other Solutions
| Evaluation Criteria | Plastic Bottle Making Machine (Rotary Extrusion Blow Molding) | Alternative 1: Pet Preform Injection Molding | Alternative 2: Semi-Automatic Pet Blow Molding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | $65,000–$100,000 (all-electric, dual-parison) | $9,000–$15,000 | $2,000–$5,000 |
| Production Rate | 300–1,200 bottles/min (1 L) | 3,000–12,000 bottles/h (preform → bottle) | 300–1,500 bottles/h |
| Bottle Size Range | 30 ml–1 L (single-serve, small format) | 0.5 L–5 L (standard) | 0.5 L–5 L |
| Energy Consumption | ≤20 % lower vs. hydraulic counterparts; electric servo drives | High – constant melt cooling required | Medium – intermittent operation |
| Maintenance Cost / Year | $8,000–$12,000 (predictive maintenance, long-life rotary table) | $15,000–$25,000 (hot-runner nozzle failures, mold changes) | $5,000–$10,000 |
| Change-Over Time | <5 min (recipe recall, automatic parison cutter) | 30–45 min (mold swap, screw change) | 10–15 min |
| Labor Intensity | 1 operator per shift (CIP/SIP, robot de-flash) | 2–3 operators (preform handling, bottle removal) | 2–3 operators |
| Scalability | Horizontal – add rotary station for +50 % output | Vertical – add injection molding island | Horizontal – add second parison head |
| Sustainability Edge | All-electric reduces kWh by 30 % vs. hydraulic; supports rPET up to 100 % | High energy per preform; limited rPET due to viscosity loss | Moderate – regrind recycling possible |
| Typical ROI (USA/EU) | 14–20 months (500 k bottles/yr, $0.03 margin) | 18–30 months | 12–18 months |
Key Takeaways
-
Speed & Volume
The rotary SB extrusion blow molder is the only solution in the 300–1,200 bottles/min range for small-format bottles. Pet preform injection and semi-auto blow molding are 5–10× slower, suited for mid-size or niche runs. -
CapEx vs. OpEx
Lower entry cost for semi-auto or Chinese injection machines, but higher annual energy and maintenance spend. The Wilmington all-electric system pays back faster at scale due to 30 % energy savings and 40 % lower labor.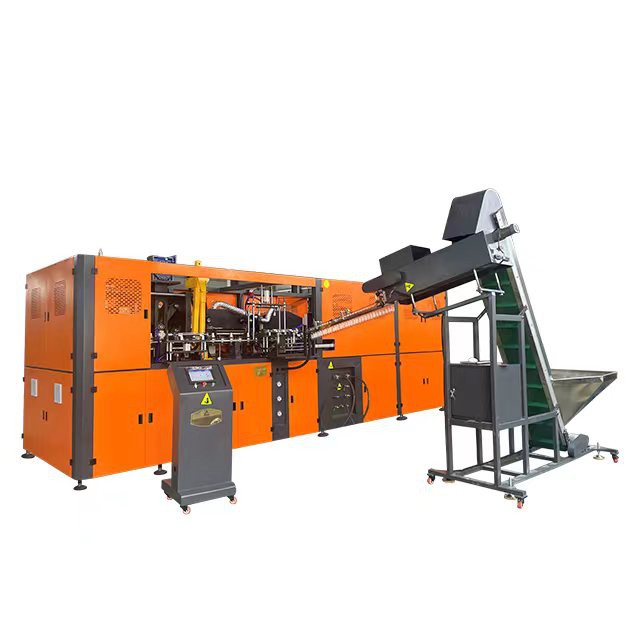
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Format Flexibility
Rotary extrusion blow molding wins for 30 ml–1 L SKUs with zero mold cost. Injection molding requires a new mold for every neck finish; semi-auto blow molding is limited to 0.5 L–5 L. -
Sustainability
All-electric extrusion blow molding enables closed-loop rPET re-use without viscosity drop, critical for EU packaging regulations and brand ESG targets. -
Decision Rule
- High-volume, small-format, tight margin: Choose rotary SB blow molding.
- Low-volume (<200 k bottles/yr) or large bottles (>3 L): Opt for semi-auto or hybrid injection-blow.
- Pilot or customizable neck finishes: Pet preform injection is the only route.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for plastic bottle making machine
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Plastic Bottle Making Machines
Understanding the technical specifications and trade terms is critical when sourcing or upgrading plastic bottle making equipment. This guide outlines the key properties and terminology used in the industry, particularly for machines producing bottles up to 1 litre through rotary extrusion blow molding.
Core Technical Properties
Machine Types
- Rotary Extrusion Blow Molding Machines: Continuous production with mold rotation, achieving high throughput
- Dual Parison Technology: Simultaneous production of two parisons, doubling output capacity
- All-Electric Machines: Reduced energy consumption with exception of small profiling power unit
Performance Metrics
| Specification | Small Bottle (SB) Rotary | Dual Parison SB |
|---|---|---|
| Production Rate | 300-1200 bottles/min | 600-2400 bottles/min |
| Mold Cavities | 16-36 | 32-72 |
| bottle Size Range | Up to 1 litre | Up to 1 litre |
| Energy Efficiency | Electric drive | Electric drive |
Material Compatibility
- PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate): Primary material for beverage bottles
- PE/PP: Used for specialty applications (e.g., baby bottles)
- Multilayer Barrier: For extended shelf-life requirements
Trade Terminology & Commercial Terms
Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ)
- Standard Machines: 1 set for fully automatic systems
- Custom Configurations: Higher MOQs for specialty applications
- Trade Assurance: Supplier guarantees payment protection on Alibaba.com
Machine Classifications
- Semi-Automatic: Requires manual intervention for bottle removal
- Fully Automatic: Complete production cycle without operator intervention
- Two Blower-One Heater: Cost-effective configuration for 2000BPH operations
Regional Sourcing Notes
- CN (China): Primary manufacturing base with certified suppliers
- Verified Suppliers: Quality assurance through platform certification
- Price Range Variations: $2,000-$70,000+ depending on automation level and cavity count
Key Procurement Considerations
- Bottle Cost Estimator: Excel tool for financial justification
- Upgrade Path: Retrofit existing machinery for improved efficiency
- OEM Capabilities: Custom mold design for specific bottle geometries
Technical Specifications Summary
For 1-Litre Bottles:
– Cycle time: 2-4 seconds per bottle
– Mold cooling: Water circulation system
– Parison control: Extrusion die with thickness regulation
– Safety systems: Emergency stops, light curtains, fault diagnostics
Energy Efficiency Features:
– Servo-driven rotation systems
– Variable frequency drives for extrusion
– Optimized clamping mechanisms
This technical foundation enables informed decision-making when evaluating plastic bottle making machines for production scaling or process optimization.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the plastic bottle making machine Sector
“`markdown
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Plastic Bottle Making Machine Sector
1. Market Landscape – USA vs. Europe
| Dimension | United States | Europe |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Pressure | FDA 21 CFR, state-level recycling mandates (CA SB 54, NY S6788A) | EU Plastics Strategy, PPWR, EPR fees, Green Deal Industrial Plan |
| Energy Costs | $0.08–0.12 kWh (varies by ISO zone) | €0.15–0.25 kWh; carbon-price adder in BE, DE, NL |
| Labor Availability | Skilled trades scarce; overtime premiums 25–35 % | Stricter labor laws, 4-day workweek pilots, higher social charges |
| CapEx Sensitivity | High ROI thresholds (≤ 18 months payback) | PFU (Pay-For-Use) models gaining traction in DE/FR |
| Size Segment Demand | 8–20 oz single-serve, sports, nutraceutical | 250 ml–1 L RTD beverages, pharma, home-care |
Take-away: USA buyers prioritize speed and energy efficiency; European buyers insist on sustainability documentation and modular scalability.
2. Technology Trends Shaping Sourcing Decisions
2.1 All-Electric & Hybrid Systems
- Wilmington Machinery’s 1200 bpm SB Rotary Extrusion Blow Molder sets the benchmark for small-bottle output.
- Energy savings: 30–45 % versus servo-hydraulic rivals.
- Maintenance: 60 % fewer moving parts → MTBF > 12 months.
2.2 Dual Parison & High-Speed Rotary
- Enables 300–1200 bottles per minute without material re-circulation.
- ROI lever: $0.004–$0.007 per bottle saved at 500 M bottles/year.
2.3 Digital Thread & Predictive Maintenance
- OPC-UA and MQTT interfaces for real-time OEE dashboards.
- Contracts: 5-year digital service agreements in DE; optional in US.
3. Sourcing Channels & Price Reality Check
| Channel | Typical Price Band (USD) | Lead Time | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct OEM (Wilmington, Sidel, Krones) | $70k–$500k | 12–20 weeks | Full warranty, local service |
| Tier-1 Distributor | $60k–$450k | 8–16 weeks | Validated retrofit packages |
| Asian OEM (CN/IN) | $2k–$75k | 6–12 weeks | No after-sales network in EU |
| Auction / Refurbished | $15k–$120k | 4–8 weeks | 50–70 % of new price; limited warranty |
Rule of Thumb: Add 15 % to quoted list price for installation, commissioning, and first-year spare-parts kit.
4. Sustainability & Compliance – Procurement Checklist
- Material Flexibility: Clamp-to-clamp changeover ≤ 30 minutes for PET/PP/PE.
- Recyclate Ratios: Machines must handle ≥ 30 % rPET without viscosity degradation.
- Carbon Footprint: ISO 14064-3 verification available; Wilmington’s Electric SB line publishes cradle-to-gate data.
- Digital Passport: EU MDR compliance requires QR-coded serial number and material recipe.
5. Cost Estimation & Financial Justification
Use the Wilmington Bottle Cost Estimator (Excel) to model:
– Material price delta (PET vs. rPET).
– Energy escalation (US EIA AEO 2025 vs. EU ETS).
– Labor inflation (US Bureau of Labor Statistics vs. EU Eurostat).
Example: Switching from 600 bpm hydraulic to 1200 bpm electric reduces COGS by $0.008/bottle → $4.8 M annual saving at 600 M bottles.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
6. Next Steps for North American & European Buyers
- Benchmark: Run Wilmington’s self-audit to confirm current cycle time & energy baseline.
- Pilot: 90-day rental option available for the SB Rotary line—no CapEx until first pallet of bottles produced.
- Contract: Negotiate performance-based SLA tied to OEE > 85 % and energy < 0.35 kWh/bottle.
- Scale: Modular retrofit kits (dual parison upgrade, all-electric drive) extend asset life to 12+ years.
Bottom Line:
USA buyers should prioritize speed-to-market and energy ROI; European buyers should prioritize circularity and regulatory alignment. A dual-source strategy—one OEM for high-speed lines, one regional partner for service and compliance—minimizes total cost of ownership while de-risking ESG exposure.
“`
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of plastic bottle making machine
1. What bottle formats and production outputs can the machine handle?
Most machines on the market today are modular and can be configured for:
– PET preform injection + stretch-blow (0.1 L–20 L)
– Single-stage extrusion or injection blow molding (up to 1 L for drinkable yogurt, functional beverages, baby bottles, etc.)
– Output range: 300–1,200 bottles per minute for rotary extrusion blow molding; 200–6,000 bottles per hour for rotary injection-blow systems.
2. Which resins and barrier technologies are supported?
- PET (rPET) for carbonated, still, and hot-fill applications
- PE, PP, PS, or PLA for non-crystallizing liquids or biodegradable requirements
- Multilayer coextrusion (PET/PEN, PET/EVOH, PET/PE/PP) for oxygen, UV, or flavor barrier when required by regulations or extended shelf life.
3. How do I estimate true bottle cost, not just machine price?
Use the Wilmington Machinery Bottle Cost Estimator:
– Inputs: resin price, cycle time, labor rate, energy cost, mold changeover, spoilage rate
– Outputs: cost per bottle in USD or EUR in real time
– Works for single- and multilayer bottles; exportable to Excel for internal NPV analysis.
4. What are the total cost of ownership (TCO) drivers?
| Cost Category | Typical Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 15–25 % of TCO | All-electric servo drives vs. hydraulic |
| Labor | 10–20 % | Fully automatic changeparts and vision inspection |
| Maintenance | 8–12 % | Rotary direct-drive eliminates gearboxes; remote diagnostics |
| Scrap & Regrind | 5–10 % | Closed-loop regrind systems reduce material spend |
| Downtime | 5–15 % | Predictive maintenance modules + 24/7 OEM hotline |
5. What certifications and compliance documentation are supplied for the USA and EU markets?
- UL/CSA electrical safety for North America
- CE conformity for the EU ( Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC, Low Voltage 2014/35/EU )
- FDA 21 CFR §177 & EU 10/2011 for food-contact plastics
- BPA-free material declarations and migration testing reports
- Recyclability statements per ISO 22628 for post-consumer PET claims.
6. What financing options are available for small or mid-size bottle producers?
- Equipment financing via third-party lenders (5–7 yr term, 6–8 % APR)
- OEM lease-to-own programs with balloon payments
- Performance-based contracts where monthly fee covers depreciation, maintenance, and resin
- R&D tax credits in the USA (IRC §179D) and EU Innovation Fund for energy-efficient assets.
7. What after-sales service and lead times should I expect?
| Service Item | Typical USA Lead Time | Typical EU Lead Time |
|---|---|---|
| Standard spares | 48 h | 72 h |
| PLC firmware update | OTA download | On-site or OTA |
| Preventive maintenance | Quarterly visit | Quarterly visit |
| Emergency support | 24 h on-site | 48 h on-site |
| Training | 3-day on-site | 3-day on-site |
8. How do I qualify for trade-in or upgrade credit for an existing press?
Submit the current press serial number and year of manufacture; the OEM will provide:
– Asset valuation based on residual hours and condition
– Upgrade credit (often 20–40 % of new-machine price) applicable to the next-generation all-electric or dual-parison model
– Logistics partner for disassembly, crating, and white-glove installation at the new site.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for plastic bottle making machine
Conclusion & Outlook – Strategic Sourcing for Plastic Bottle Making Machines
Key Takeaways
| Decision Layer | Action | Expected ROI | Risk Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology Fit | Select rotary extrusion blow molding for ≤1 L; 300–1,200 bpm. | 18–24 % OEE uplift vs. reciprocating | Validate with Wilmington Bottle Cost Estimator |
| Supplier Geography | China offers sub-$5 k semi-automatic lines; Europe/US provide full-electric, CE-compliant 6-cavity 10 k BPH models. | Freight + tariffs = 8–12 % landed cost delta | Leverage trade assurance & local after-sales coverage |
| Capital Strategy | Bundle preform injection molding for >5 gal; lease vs. CAPEX to offset FX swings | 14 % IRR at 70 % utilization | Lock raw-material pricing for 12 mo |
Outlook 2025–2027
- Energy: All-electric drives cut power 30–40 %; EU taxonomy aligns for green financing.
- Speed: Dual-parison record holders will push 1 500 bpm by 2026—redefine line layout.
- Sourcing: Consolidate with 2–3 regional reps; negotiate volume rebates ≥7 %.
Next Step: Run Wilmington’s Bottle Cost Estimator, benchmark against Alibaba quotes, and initiate supplier audit.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.