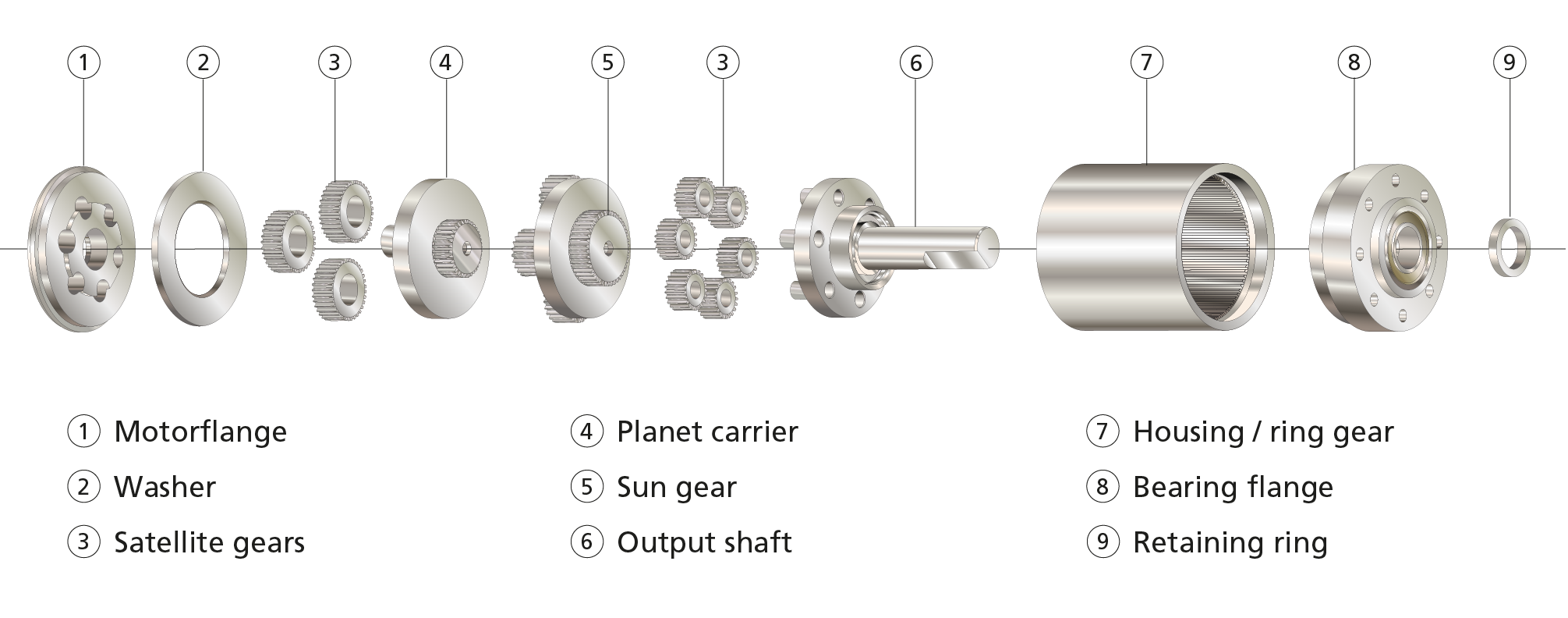
The global planetary gear reducer market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for precision motion control across industrial automation, robotics, and renewable energy sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global gearboxes market size was valued at USD 105.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.7% from 2023 to 2030, with planetary gear reducers representing a significant and growing segment due to their high torque density and efficiency. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects a steady CAGR of over 6% through 2029, citing increased adoption in wind turbines, electric vehicles, and automated manufacturing as key growth drivers. As industries prioritize compact, high-performance transmission solutions, leading manufacturers are investing in advanced materials, precision engineering, and smart integration capabilities. In this competitive landscape, the top 10 planetary gear reducer manufacturers stand out through innovation, global supply chain reach, and consistent performance across mission-critical applications.
Top 10 Planetary Gear Reducer Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 STOBER
Domain Est. 1996
Website: stober.com
Key Highlights: Right Angle Geared Motors. From helical gearboxes to planetary gearboxes, STOBER has geared motor options that fit your requirements….
#2 Matex Co., Ltd.
Domain Est. 2001 | Founded: 1921
Website: matex-japan.com
Key Highlights: Matex Co., Ltd. is a professional company for planetary gear systems and gear reducers since 1921. We can assist you in every phase from design to mass ……
#3 ZD Precision Gearboxes, Planetary Gear Reducers Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2019 | Founded: 2006
Website: zddriver.com
Key Highlights: Ningbo Zhongda Leader Intelligent Transmission Co., Ltd. is professional planetary gearbox manufacturers, established in 2006, we have more than 1500 employees, ……
#4 Neugart
Domain Est. 1997
Website: neugart.com
Key Highlights: Discover the high-quality planetary and custom gearboxes from Neugart GmbH. As one of the leading gearbox manufacturers, we offer innovative drive solutions ……
#5 Products
Domain Est. 2001
Website: deltaww.com
Key Highlights: Home > · Products > · Industrial Automation > · Motion > · Planetary Gearbox >….
#6 Planetary Gearbox Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2003
Website: apexdynamicsusa.com
Key Highlights: Apex Dynamics is a worldwide name in planetary gearbox manufacturing with over 20 years of accumulated experience producing high-quality components….
#7 Nidec Drive Technology Corporation
Domain Est. 2022
Website: nidec-dtc.com
Key Highlights: Nidec DTC offers Legendary Innovation, Legendary Quality and Legendary Reliability with all our precision gear reduction technologies……
#8 Planetary Gearheads for Maximum Torque
Domain Est. 1997
Website: faulhaber.com
Key Highlights: Efficient. Precise. Compact. Planetary gearheads from FAULHABER for maximum performance in minimum space. ➤ Discover & calculate now….
#9 Reggiana Riduttori
Domain Est. 2000
Website: reggianariduttori.com
Key Highlights: Worldwide customer service · Customized gearboxes · The guarantee of Made in Italy · Configure your products · A tailor-made gearbox for every area of application….
#10 GearKo Reducers
Domain Est. 2018
Website: gearkoreducer.com
Key Highlights: GearKo design and production of planetary gear reducers. Our facility is over thirty thousand square feet and over 100 staff….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Planetary Gear Reducer

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Planetary Gear Reducers
The global planetary gear reducer market is expected to undergo significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in automation, rising demand for energy-efficient systems, and the expansion of robotics and electric mobility. As industries continue to prioritize precision, compactness, and high torque transmission, planetary gear reducers are becoming increasingly integral components across various sectors. Below are key market trends anticipated to shape the planetary gear reducer landscape in 2026:
-
Growth in Industrial Automation and Robotics
The surge in industrial automation, particularly in manufacturing, logistics, and material handling, is a primary driver for planetary gear reducer demand. Collaborative robots (cobots), automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and CNC machinery require high-precision motion control—capabilities that planetary gear systems excel at. By 2026, the integration of smart factories and Industry 4.0 practices will further increase the need for compact, reliable gear reducers with low backlash and high efficiency. -
Expansion in Electric Vehicles (EVs) and E-Mobility
The automotive sector, especially electric vehicles, is emerging as a major application area for planetary gear reducers. Used in EV transmissions and electric drivetrains, these gear systems offer superior power density and smooth torque delivery. With global EV production projected to rise sharply by 2026 due to environmental policies and technological advancements, demand for high-performance planetary reducers in automotive applications will grow significantly. -
Renewable Energy Sector Adoption
Wind turbines and solar tracking systems increasingly rely on planetary gearboxes for their ability to handle high torque and variable loads in harsh environments. As renewable energy infrastructure expands globally, particularly in offshore wind farms, the demand for durable and maintenance-efficient planetary gear solutions will climb. Innovations in hybrid and direct-drive systems incorporating planetary stages are expected to gain traction by 2026. -
Technological Advancements and Material Innovation
Manufacturers are investing in advanced materials (e.g., high-strength alloys, composites) and precision manufacturing techniques (e.g., additive manufacturing, CNC grinding) to improve gear efficiency, reduce noise, and extend service life. Integration with sensors and IoT-enabled monitoring systems is also emerging, enabling predictive maintenance and real-time performance tracking—key selling points for industrial buyers. -
Regional Market Shifts
Asia-Pacific, led by China, Japan, and South Korea, is projected to dominate the planetary gear reducer market by 2026 due to strong industrial growth, government support for automation, and a burgeoning EV industry. However, North America and Europe are also expected to see steady growth, driven by automation in aerospace, medical devices, and high-tech manufacturing. -
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Regulations
Stricter global energy efficiency standards are pushing industries to adopt components that minimize energy loss. Planetary gear reducers, known for their high efficiency (often exceeding 95% per stage), align well with these sustainability goals. By 2026, regulatory pressures and corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) commitments will favor energy-optimized transmission solutions. -
Increased Competition and Strategic Consolidation
The market is witnessing rising competition among key players such as Sumitomo Drive Technologies, SEW-Eurodrive, Nabtesco, and Apex Dynamics. This is leading to strategic partnerships, mergers, and R&D investments to differentiate products through customization, miniaturization, and improved thermal management.
In conclusion, the planetary gear reducer market in 2026 will be shaped by the convergence of digitalization, electrification, and sustainability. Companies that innovate in design, embrace smart technologies, and cater to evolving sector-specific needs will be best positioned to capitalize on these trends.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Planetary Gear Reducers (Quality and IP)
Sourcing planetary gear reducers involves navigating several potential challenges that can impact performance, longevity, and legal compliance. Below are key pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP) to watch for:
Poor Manufacturing Quality and Material Standards
Low-cost suppliers may use substandard materials or imprecise manufacturing processes, leading to premature wear, increased backlash, or gear failure. Inadequate heat treatment, poor gear tooth finishing, or inconsistent tolerances can compromise efficiency and reliability, especially under high torque or continuous operation.
Inaccurate or Inflated Performance Specifications
Some suppliers exaggerate torque capacity, efficiency, or service life in their datasheets. Without independent testing or certifications, it’s difficult to verify these claims, potentially resulting in underperforming components that fail in real-world applications.
Lack of IP Protection and Risk of Counterfeit Products
Sourcing from regions with weak intellectual property enforcement increases the risk of purchasing counterfeit or cloned gear reducers. These products may mimic reputable brands but lack the original design integrity, quality control, and performance characteristics, exposing buyers to reliability issues and potential legal liability.
Insufficient Documentation and Traceability
Reputable manufacturers provide full technical documentation, test reports, and traceable batch information. Suppliers that lack these may be cutting corners, making it difficult to validate quality or support warranty claims. Missing or falsified documentation can also complicate compliance with industry standards.
Hidden IP Infringement in Design or Components
Even if a planetary reducer appears functional, its internal design may infringe on patented technologies (e.g., unique gear geometries, bearing arrangements, or sealing systems). Using such components can expose the end-user or integrator to infringement lawsuits, especially in regulated or export-sensitive markets.
Limited After-Sales Support and Warranty Enforcement
Low-cost suppliers often offer weak or unenforceable warranties. If quality issues arise, lack of local support, spare parts availability, or responsiveness can lead to costly downtime and replacement expenses, negating initial cost savings.
Non-Compliance with International Standards
Some reducers may not meet recognized standards (e.g., ISO, DIN, or NEMA), affecting interchangeability, safety, and integration. Non-compliant products may also fail audits or certifications required in industries like robotics, aerospace, or medical devices.
By carefully vetting suppliers, demanding proof of quality and IP legitimacy, and prioritizing certified manufacturers, businesses can avoid these common pitfalls and ensure reliable, legally sound sourcing of planetary gear reducers.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Planetary Gear Reducer
Overview
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the transportation, handling, import/export, and regulatory adherence of planetary gear reducers. These precision mechanical components are widely used in industrial automation, robotics, and power transmission systems, and require careful management throughout the supply chain to ensure safety, performance, and legal compliance.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Planetary gear reducers are sensitive to shock, moisture, and contamination. Proper packaging and handling are critical to prevent damage during transit:
– Use original manufacturer packaging or equivalent protective materials (foam inserts, corrugated cardboard, wooden crates for heavy units).
– Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “Do Not Invert,” and “Protect from Moisture” indicators.
– Secure internal components to prevent movement during transport.
– Avoid stacking heavy items atop gear reducer packages.
– Handle with care using appropriate lifting equipment for units exceeding 20 kg.
Transportation Considerations
- Mode of Transport: Suitable for road, air, and sea freight. Air freight is preferred for urgent or high-value shipments due to faster delivery and reduced handling.
- Temperature & Humidity Control: Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures (below -20°C or above 60°C) and humidity above 90% to prevent condensation and lubricant degradation.
- Shock and Vibration Mitigation: Use cushioned pallets and vibration-dampening materials, especially for long-distance or rough-terrain transport.
- Documentation: Include packing lists, commercial invoices, and technical specifications with each shipment.
Import/Export Regulations
Planetary gear reducers may be subject to international trade regulations depending on destination and technical specifications:
– HS Code Classification: Typically classified under HS 8483.40 (gear boxes and other speed changers). Confirm local tariff codes for accurate customs declaration.
– Export Controls: Check if the product contains controlled technologies (e.g., high-precision components subject to ITAR or dual-use regulations under EAR). Most standard gear reducers are not controlled, but verify based on specs.
– Certificates of Origin: Required for preferential tariff treatment under trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, RCEP).
– Customs Valuation: Ensure declared value includes cost, insurance, and freight (CIF) to avoid delays or penalties.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure planetary gear reducers meet relevant regional and international standards:
– CE Marking (EU): Comply with Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive if integrated with motors.
– UKCA Marking (UK): Required for sale in Great Britain; aligns with CE standards post-Brexit.
– UL/CSA (North America): Required if the reducer is part of a larger assembly subject to safety certification.
– RoHS and REACH (EU): Confirm compliance with restrictions on hazardous substances and chemical registration.
– Energy Efficiency Standards: Some regions may require efficiency labeling if part of a drive system.
Documentation and Traceability
Maintain complete records for compliance and warranty purposes:
– Product datasheets and technical manuals
– Certificate of Conformity (CoC)
– Material Declarations (RoHS, REACH)
– Batch/serial numbers for traceability
– Test reports (e.g., load testing, noise levels)
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
- Follow WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives in the EU for end-of-life management if the reducer is part of an electric drive system.
- Lubricants must be disposed of in accordance with local environmental regulations (e.g., EPA guidelines in the U.S.).
- Encourage recycling of metal components (aluminum, steel) through certified facilities.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management ensure planetary gear reducers reach customers in optimal condition and meet legal requirements across global markets. Partner with certified freight forwarders, maintain up-to-date documentation, and stay informed on evolving regulatory standards to minimize risks and ensure smooth operations.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Planetary Gear Reducer
In conclusion, sourcing a planetary gear reducer requires a comprehensive evaluation of technical specifications, application requirements, quality standards, and supplier reliability. Planetary gear reducers offer significant advantages, including high torque density, compact design, efficiency, and durability, making them ideal for demanding industrial, automation, robotics, and renewable energy applications. When selecting a supplier, it is crucial to consider factors such as precision engineering, material quality, customization capabilities, post-sales support, and cost-effectiveness.
Prioritizing reputable manufacturers with proven industry experience and certification ensures long-term performance and minimizes downtime. Additionally, engaging in early collaboration with suppliers can facilitate better integration into existing systems and support innovation in design and functionality. Ultimately, a well-informed sourcing strategy for planetary gear reducers not only enhances operational efficiency but also contributes to the overall reliability and competitiveness of the end application.