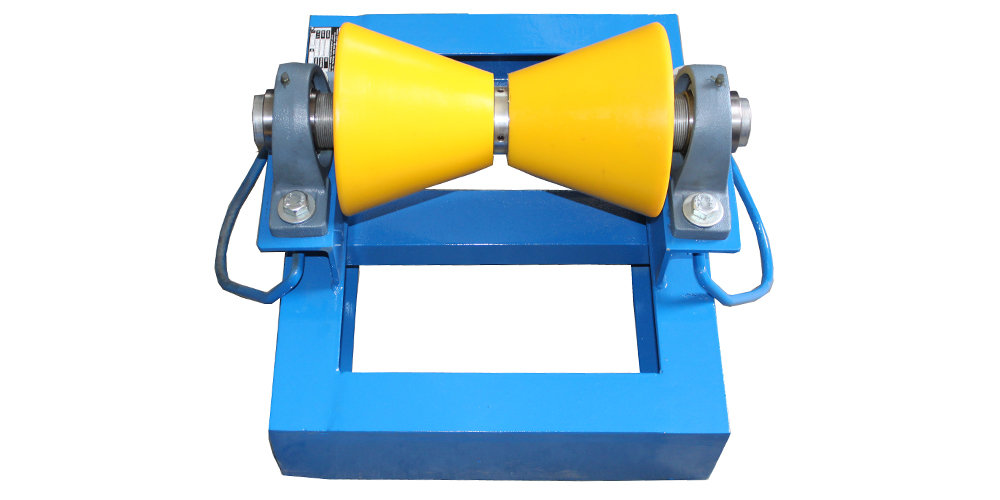
The global pipe roller market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand in oil & gas, construction, and industrial manufacturing sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the pipe handling equipment market—which includes pipe rollers—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% from 2024 to 2029, fueled by expanding pipeline infrastructure projects and increased investments in energy transportation systems. Additionally, Grand View Research reports that the global industrial roller market, a broader segment encompassing pipe rollers, was valued at USD 4.2 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 5.1% through 2030, supported by automation trends and the need for efficient material handling solutions. As demand for durable, high-performance pipe rollers rises, manufacturers are focusing on innovation, load capacity, and resistance to harsh environments. In this competitive landscape, seven manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining engineering excellence, global reach, and a strong track record of reliability—making them the top choices for industries that depend on seamless pipe handling operations.
Top 7 Pipe Roller Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
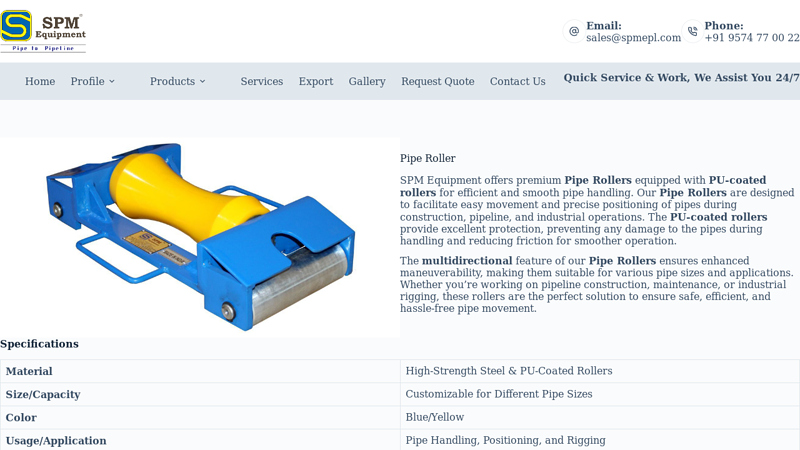
#1 Pipe Roller Manufacturer & Exporter
Domain Est. 2017
Website: spmepl.com
Key Highlights: Our Pipe Rollers are designed to facilitate easy movement and precise positioning of pipes during construction, pipeline, and industrial operations….
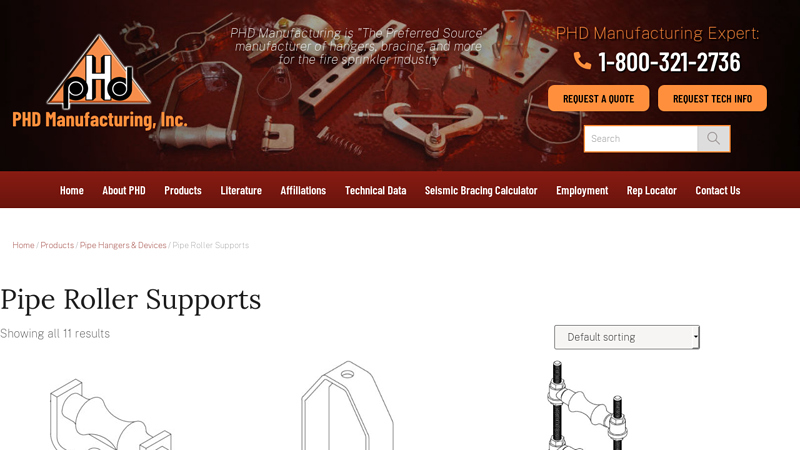
#2 Pipe Roller Supports Archives
Domain Est. 1998
Website: phd-mfg.com
Key Highlights: PHD Manufacturing is “The Preferred Source” manufacturer of hangers, bracing, and more for the fire sprinkler industry….
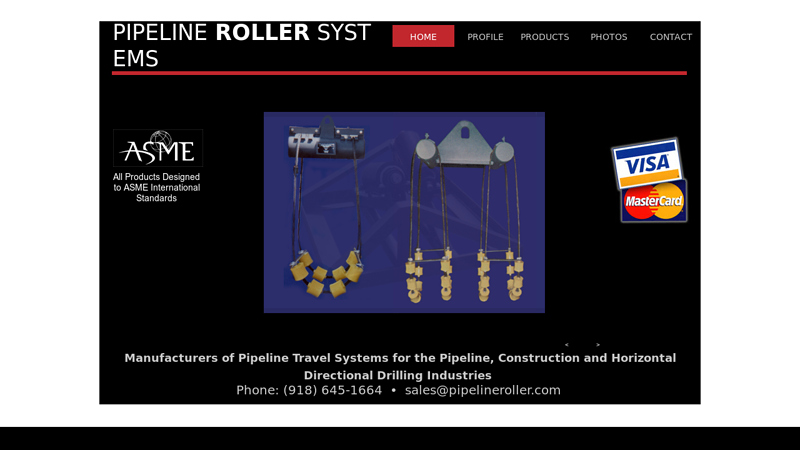
#3 pipeline
Domain Est. 1999
Website: pipelineroller.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturers of Pipeline Travel Systems for the Pipeline, Construction and Horizontal Directional Drilling Industries….
#4 PIPE ROLLER MANUFACTURER
Domain Est. 2016
Website: spmequipment.com
Key Highlights: SPM EQUIPMENT engages in manufacturing and supplying a wide range of Pipe Roller Cone Type PU Coated. Our pipe rollers have been extremely sturdy and ……
#5 Pipe Roller Manufacturer & Supplier
Domain Est. 2021
Website: spmequipments.com
Key Highlights: SPM Equipment is a reliable Pipe Roller Manufacturer & Supplier, offering high-quality oil and gas pipeline equipment for efficient pipe handling worldwide….
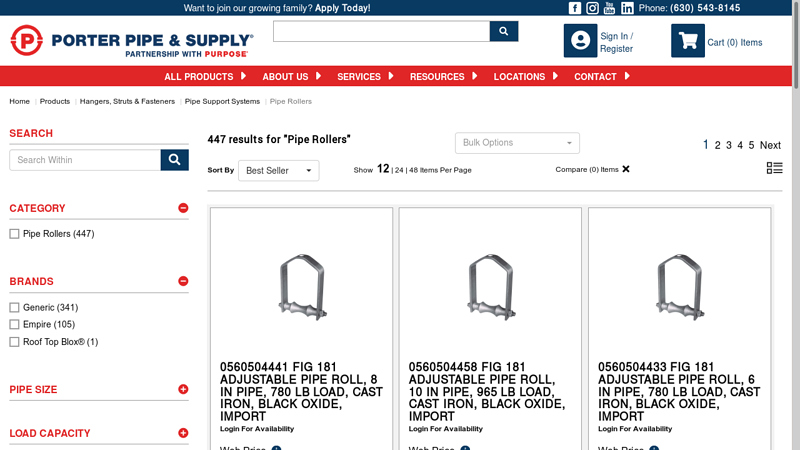
#6 Pipe Rollers
Domain Est. 1996
#7 Pipe Roller
Domain Est. 2016
Website: ptenergy.com
Key Highlights: The Pipe Roller was developed to enhance safety in tubular handling, addressing the risks associated with conventional pipe rolling methods….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Pipe Roller
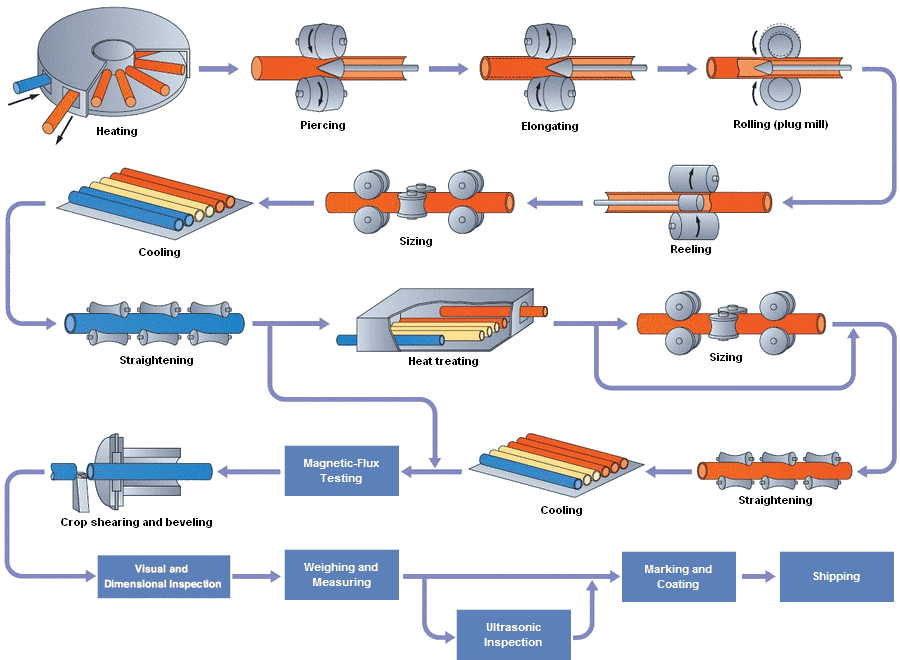
H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Pipe Rollers
The global pipe roller market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by industrial growth, technological advancements, and shifting market demands. Here’s a detailed analysis of key trends expected to shape the landscape:
1. Steady Market Growth Driven by Infrastructure & Energy Investments:
* Sustained Demand: The market is forecast to experience steady growth (estimated CAGR of 4-6% through 2026), primarily fueled by massive global investments in infrastructure (water supply, sewage, gas distribution) and energy sectors (oil & gas pipelines, renewables like geothermal).
* Regional Hotspots: Growth will be particularly strong in Asia-Pacific (driven by China, India, and Southeast Asia’s rapid urbanization), the Middle East (major pipeline projects), and North America (pipeline maintenance, replacement, and energy security initiatives).
2. Technological Advancements Enhancing Efficiency & Safety:
* Hybrid & Automated Rollers: Increased adoption of hybrid (e.g., manual-electric assist) and semi-automated pipe rollers featuring motorized rotation, remote control operation, and programmable settings for consistent rolling. This boosts productivity and reduces operator fatigue.
* Smart Integration: Integration of sensors and IoT capabilities for real-time monitoring of load, speed, and alignment is emerging. This data aids in predictive maintenance, quality control, and optimizing rolling parameters.
* Ergonomic & Lightweight Designs: Continued focus on improving ergonomics (adjustable heights, better grips) and developing lightweight yet durable models (using advanced composites or high-strength alloys) to enhance portability and reduce workplace strain.
3. Heightened Focus on Safety and Operator Well-being:
* Regulatory Drivers: Stricter global occupational health and safety regulations will continue to push demand for rollers with enhanced safety features (better guarding, anti-tip mechanisms, emergency stops, non-slip surfaces).
* Reducing Manual Handling Injuries: The core value proposition of pipe rollers – minimizing the risk of musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) associated with manual pipe handling – remains a primary driver for adoption, especially with increasing focus on worker safety.
4. Material & Application Diversification:
* Beyond Steel: While steel pipes dominate, demand for rollers capable of handling diverse materials (stainless steel, PVC, HDPE, composite pipes) will grow, requiring rollers with adjustable rollers or specialized padding to prevent damage.
* Specialized Rollers: Increased demand for specialized rollers: heavy-duty models for large-diameter/thick-walled pipes (common in energy), compact rollers for confined spaces (tunnels, shipyards), and rollers designed for specific tasks like pre-welding alignment.
5. Supply Chain Optimization & Sustainability Pressures:
* Resilience & Localization: Ongoing supply chain scrutiny may lead to increased regional manufacturing or nearshoring, impacting sourcing strategies for both manufacturers and buyers.
* Durability & Longevity: Focus on product longevity and ease of maintenance will grow, aligning with sustainability goals and reducing total cost of ownership. Use of recyclable materials in construction may become a minor differentiator.
6. Competitive Landscape Evolution:
* Consolidation & Innovation: The market may see further consolidation among mid-tier players, while competition will intensify around technological innovation (automation, smart features) and value-added services (training, customization).
* Digital Sales & Support: Expansion of e-commerce platforms for B2B equipment and enhanced digital customer support (AR/VR for training, online configurators) will become more prevalent.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the pipe roller market will be characterized by steady growth driven by global infrastructure needs, significant technological advancements focusing on automation and data, and an unwavering emphasis on safety and ergonomics. Success will depend on manufacturers’ ability to innovate with smarter, safer, and more adaptable solutions while navigating supply chain dynamics and evolving customer expectations for efficiency and sustainability.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Pipe Rollers (Quality, IP)
Sourcing pipe rollers—critical components in pipeline construction and maintenance—can be fraught with challenges, especially when balancing quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can result in equipment failure, project delays, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to avoid.
Poor Quality Control and Substandard Materials
One of the most frequent issues is receiving pipe rollers that do not meet required mechanical or durability standards. Suppliers, particularly low-cost offshore manufacturers, may use inferior steel, inadequate welding practices, or imprecise machining. This leads to premature wear, roller misalignment, or catastrophic failure under load. Buyers often fail to implement rigorous incoming inspection protocols or third-party quality audits, assuming certifications alone are sufficient.
Lack of Compliance with Industry Standards
Many sourced pipe rollers do not conform to recognized standards such as API, ASME, or ISO. Without clear specifications during procurement, suppliers may deliver products that appear functional but lack the necessary load ratings, safety factors, or dimensional tolerances. This mismatch can compromise operational safety and void insurance or warranty coverage.
Inadequate Documentation and Traceability
Reliable sourcing requires full traceability of materials and manufacturing processes. Poor documentation—missing mill test reports, welder certifications, or non-destructive testing (NDT) records—raises red flags about quality and compliance. Without proper traceability, it becomes difficult to validate performance claims or respond to field failures.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Sourcing from manufacturers who replicate proprietary designs without authorization exposes buyers to IP litigation. Some suppliers reverse-engineer patented roller configurations, bearings, or mounting systems. Purchasing such products—even unknowingly—can implicate the buyer in infringement claims, especially if the rollers are used in high-profile or regulated projects.
Insufficient Vendor Vetting and Due Diligence
Relying solely on price or convenience when selecting suppliers increases exposure to unqualified vendors. Many fail to conduct site audits, review manufacturing capabilities, or verify past performance. This oversight can result in unreliable delivery schedules, inconsistent quality, and limited after-sales support.
Ambiguous Contracts and IP Clauses
Procurement agreements that lack clear IP ownership terms or usage rights create legal vulnerabilities. For custom-designed rollers, the absence of clauses assigning IP to the buyer or restricting supplier reuse can lead to design theft or competitive disadvantages.
Overlooking After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
High-quality pipe rollers require maintenance and occasional replacement parts. Sourcing from suppliers with poor logistical support or limited spare parts inventory can lead to extended downtime. Buyers often neglect to evaluate service capabilities during the procurement process, focusing only on upfront cost.
Failure to Protect Custom Designs
When sourcing custom-engineered rollers, companies may share detailed drawings and specifications without non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) or design protection measures. This exposes proprietary innovations to misuse or replication by the supplier for other clients.
By addressing these pitfalls through thorough supplier qualification, robust contracts, and proactive IP safeguards, organizations can ensure reliable, compliant, and legally secure sourcing of pipe roller systems.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Pipe Roller
Overview
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the transportation, handling, storage, and regulatory adherence of pipe rollers—specialized equipment used in pipeline construction and maintenance to support and guide pipes during installation.
Packaging and Handling
Proper packaging and handling are critical to prevent damage during transit.
– Secure Crating: Pipe rollers should be shipped in robust wooden or metal crates with internal bracing to prevent movement.
– Lifting Points: Use only designated lifting points; never lift by chains, rollers, or support brackets unless approved by the manufacturer.
– Weather Protection: Cover units with waterproof tarpaulins if stored or transported outdoors to prevent rust and corrosion.
Transportation Requirements
Ensure safe and compliant transportation across different modes.
– Weight and Dimensions: Verify the gross weight and external dimensions to comply with road, rail, or air freight regulations. Oversized loads may require special permits.
– Load Securing: Fasten pipe rollers to transport vehicles using rated tie-down straps or chains. Comply with FMCSA (U.S.) or ADR (Europe) load securement standards.
– Documentation: Include a detailed packing list, bill of lading, and equipment specifications with each shipment.
Import/Export Compliance
Adhere to international trade regulations when shipping across borders.
– HS Code Classification: Classify pipe rollers under the appropriate Harmonized System (HS) code—typically 8431.39 (parts for machinery for making or assembling metal products). Confirm with local customs authorities.
– Export Controls: Check if the equipment contains materials or technologies subject to export control regimes (e.g., ITAR, EAR). Most standard pipe rollers are not controlled, but verify based on design and destination.
– Certificates of Origin: Provide a Certificate of Origin where required to qualify for preferential tariffs under trade agreements.
Regulatory and Safety Standards
Comply with regional safety and quality standards.
– CE Marking (EU): If sold in the European Economic Area, ensure conformity with Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and affix CE marking.
– OSHA (U.S.): Adhere to OSHA 29 CFR 1910 for workplace safety, particularly in handling and operation.
– ISO Standards: Follow ISO 12100 (safety of machinery) and ISO 9001 (quality management) for design and manufacturing consistency.
Storage Guidelines
Proper storage preserves equipment integrity.
– Indoor Storage Preferred: Store in a dry, ventilated warehouse to prevent moisture accumulation.
– Elevation: Keep units on wooden pallets or racks to avoid ground moisture contact.
– Inspection Before Use: Check for corrosion, deformation, or missing components after prolonged storage.
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
Manage end-of-life responsibly.
– Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE): If the pipe roller includes electrical components, dispose of per WEEE Directive in the EU.
– Recycling: Metal components (steel, aluminum) should be recycled through certified facilities in accordance with local environmental regulations.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain accurate records for audit and traceability.
– Technical Files: Retain design schematics, test reports, and compliance certificates for at least 10 years.
– Shipping Logs: Record shipment dates, carriers, destinations, and condition upon delivery.
– Compliance Registers: Track certifications, renewals, and regulatory changes affecting product compliance.
Conclusion
Proper logistics planning and compliance adherence minimize risks, avoid delays, and ensure the safe and legal movement of pipe rollers globally. Always consult local regulations and involve qualified logistics and compliance professionals when expanding into new markets.
Conclusion for Sourcing Pipe Rollers
In conclusion, sourcing pipe rollers requires a comprehensive evaluation of quality, cost, durability, supplier reliability, and compliance with industry standards. Selecting the right pipe rollers is essential for ensuring efficient material handling, minimizing downtime, and maintaining workplace safety in industries such as oil and gas, construction, and manufacturing. After assessing various suppliers, comparing technical specifications, and considering long-term operational needs, it is recommended to partner with a reputable supplier that offers high-quality, custom-fit pipe rollers backed by strong after-sales support and timely delivery. A strategic sourcing approach not only optimizes performance but also contributes to cost savings and project success over the equipment’s lifecycle.