The global pipe extrusion machine market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising infrastructure development, increasing demand for plastic and composite piping in construction, agriculture, and water management, and advancements in extrusion technology. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the pipe extrusion machine market was valued at USD 2.85 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% from 2024 to 2029. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the broader plastic extrusion machinery market—which includes pipe extrusion—is expected to expand at a CAGR of 5.4% from 2023 to 2030, fueled by urbanization and industrialization across emerging economies. With North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific leading in both production and adoption, manufacturers are increasingly focusing on energy-efficient, automated, and customizable extrusion solutions. As demand surges, identifying leading players that combine innovation, reliability, and global reach becomes critical for stakeholders in the plastics and pipeline industries. Here’s a data-backed look at the top 10 pipe extrusion machine manufacturers shaping the future of the sector.
Top 10 Pipe Extrusion Machine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Guill Tool & Engineering Co. Inc.
Domain Est. 1998
Website: guill.com
Key Highlights: Guill is the leading Extrusion Tooling Designer & Manufacturer with nearly 60 years of experience. Our engineers specialize in plastic extrusion tooling design….
#2 DRTS
Domain Est. 1997
Website: drts.com
Key Highlights: DRTS builds pipe extrusion and drip irrigation production machinery, turnkey systems, helping manufacturers scale fast and cut waste….
#3 Rollepaal
Domain Est. 1998
Website: rollepaal.com
Key Highlights: Rollepaal is a global supplier of plastic pipe extrusion technology. With 60 years of process knowledge, we build high-quality and cost-effective solutions….
#4 LIANSU MACHINERY
Domain Est. 2002
Website: ls-extrusion.com
Key Highlights: LIANSU is dedicated in plastic pipe extrusion equipment manufacturing over 30 years. We have been committed to providing plastic pipe manufacturers with the ……
#5 PPR Pipe Extrusion Line
Domain Est. 2018
Website: twinscrew.net
Key Highlights: PPR pipes are widely used in Europe and America for water supply, heating, and industrial pipelines, known for their high temperature resistance, ……
#6 Extrusion Equipment
Domain Est. 1996
Website: conairgroup.com
Key Highlights: Discover Conair’s full line of extrusion equipment—cutters, pullers, vacuum sizing, and cooling solutions—engineered for precision and reliability….
#7 Pexco
Domain Est. 1997
Website: pexco.com
Key Highlights: The North American leader in custom plastic extrusion, injection molding, and high-performance polymers. We are where ideas take shape….
#8 Bausano
Domain Est. 2000
Website: bausano.com
Key Highlights: Bausano designs and manufactures customized plastic extrusion lines & machinery completely made in italy and perfectly suiting your needs. Find out more!…
#9 Plastics Extrusion Machinery
Domain Est. 2000
Website: pemusa.com
Key Highlights: Plastics Extrusion Machinery LLC (PEM) is an industry-leading provider of quality downstream equipment in the PVC pipe and custom profile industries….
#10 Extrusionsanlagen und Extruder von Battenfeld Cincinnati
Domain Est. 2010
Website: battenfeld-cincinnati.com
Key Highlights: battenfeld-cincinnati offers complete extrusion lines and customized solutions made to measure for pipe extrusion applications. Whether made of PO, PVC or ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Pipe Extrusion Machine
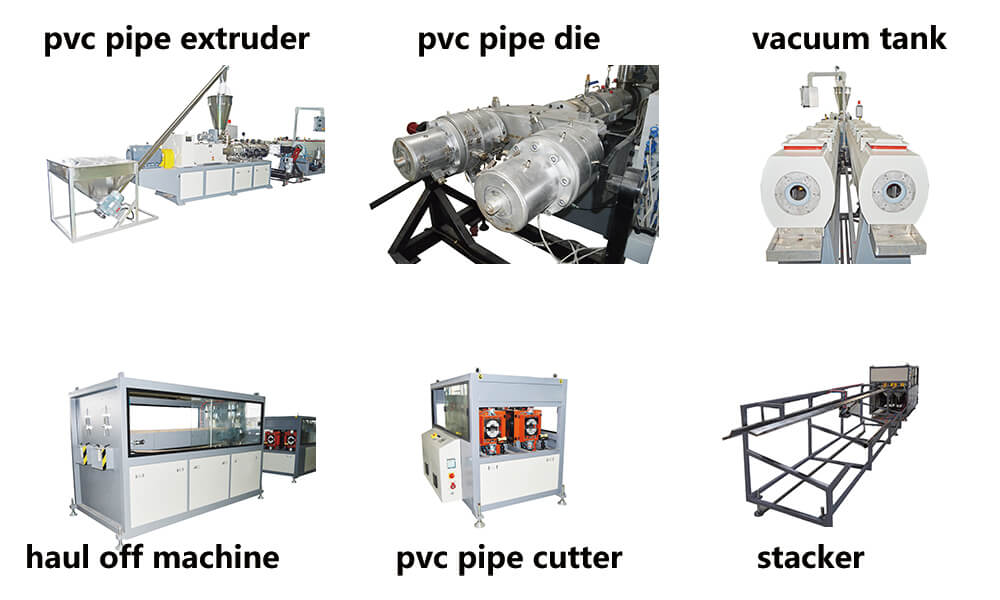
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Pipe Extrusion Machines
The global pipe extrusion machine market in 2026 is expected to be shaped by a confluence of technological advancements, sustainability imperatives, evolving material demands, and shifting regional dynamics. Driven by infrastructure development, environmental regulations, and industrial modernization, the market will likely exhibit several key trends:
1. Accelerated Adoption of Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0 Integration:
By 2026, connectivity and automation will be central to competitive pipe extrusion. Machines will increasingly feature integrated IoT sensors, real-time data analytics, predictive maintenance systems, and cloud-based monitoring. This enables higher precision, reduced downtime, improved energy efficiency, and remote operation capabilities. Digital twins for process simulation and optimization will become more common, allowing manufacturers to fine-tune parameters before physical production, enhancing product consistency and reducing waste.
2. Strong Emphasis on Sustainability and Energy Efficiency:
Environmental regulations and corporate ESG goals will push demand for energy-optimized extrusion lines. Machines featuring high-efficiency motors, advanced heating/cooling systems (like induction heating), and heat recovery technologies will gain market share. Additionally, the ability to process recycled plastics (PCR) efficiently and maintain product quality will be a critical differentiator. Equipment designed for lower energy consumption per meter of pipe produced will be highly sought after.
3. Growth in Multi-Layer and Co-Extrusion Technologies:
Demand for high-performance pipes—especially in construction, water management, and industrial applications—will drive adoption of co-extrusion systems. These allow the production of multi-layer pipes combining different materials (e.g., barrier layers, recycled cores, and virgin outer layers) to enhance durability, chemical resistance, insulation, and sustainability. Machines capable of precise control over multiple extruders and layer distribution will see increased demand.
4. Regional Infrastructure Development Driving Demand:
Asia-Pacific, particularly India and Southeast Asia, will remain a high-growth region due to extensive urbanization, water supply and sanitation projects, and industrial expansion. Similarly, infrastructure renewal programs in North America and Europe—especially for water, gas, and telecom conduits—will sustain demand for modern extrusion equipment. Africa and Latin America will also present emerging opportunities linked to development initiatives and resource extraction.
5. Material Innovation and Versatility:
While polyethylene (PE) and PVC remain dominant, extrusion machines will need greater flexibility to process advanced polymers such as cross-linked polyethylene (PEX), polypropylene (PP-R), and composite materials. Machines with modular screw and die designs, adaptable temperature control, and material handling systems will be favored, enabling quick changeovers and broader application coverage.
6. Automation and Labor Optimization:
As labor costs rise and skilled labor shortages persist, fully automated extrusion lines—from raw material feeding to pipe cutting, marking, and bundling—will become standard in new installations. Robotics for handling and packaging will be increasingly integrated, improving throughput and reducing human error.
In conclusion, the 2026 pipe extrusion machine market will be characterized by smarter, greener, and more flexible systems designed to meet the demands of high-efficiency production, sustainability compliance, and diverse application needs. Manufacturers investing in digitalization, energy efficiency, and multi-material processing capabilities will be best positioned to capture growth in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Pipe Extrusion Machine (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing a pipe extrusion machine involves critical decisions that can significantly impact production efficiency, product quality, and long-term business sustainability. Buyers often encounter challenges related to machine quality and intellectual property (IP) concerns, especially when dealing with international suppliers. Below are common pitfalls to avoid in these areas.
Poor Quality Control and Substandard Components
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing pipe extrusion machines—particularly from low-cost manufacturers—is receiving equipment built with inferior materials and inconsistent quality control. Machines may use low-grade steel, outdated gearboxes, or poorly calibrated temperature controls, leading to frequent breakdowns, inconsistent pipe dimensions, and increased maintenance costs. Buyers should verify supplier certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), request third-party inspections, and, if possible, conduct on-site factory audits before purchase.
Lack of After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even if the initial machine quality is acceptable, many suppliers—especially smaller or offshore manufacturers—fail to provide reliable after-sales service. This includes delays in technical support, unavailability of spare parts, and lack of trained technicians. Without prompt support, production downtime can severely impact operations. Ensure the supplier has a clear service agreement, an established support network, and readily available spare parts before finalizing the deal.
Inadequate Customization and Technical Specifications
Some suppliers offer “standard” models that may not meet specific production requirements, such as pipe diameter range, material compatibility (e.g., PVC, HDPE, PP), or output capacity. Buyers may discover post-purchase that the machine cannot handle required materials or production volumes. Clearly define technical specifications in the contract and confirm customization capabilities with documented proof of past projects.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Sourcing from regions with weak IP enforcement can expose buyers to legal and reputational risks. Some manufacturers produce machines that replicate patented technologies or designs from established brands without authorization. Purchasing such equipment could lead to legal liability, especially if used in markets with strict IP laws. Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s design origins, request proof of IP ownership or licensing, and avoid suppliers offering well-known branded machines at suspiciously low prices.
Hidden Technology Transfer and Reverse Engineering
When working with certain suppliers—especially during customization or co-development—there is a risk of unintentional technology transfer. Suppliers may reverse engineer proprietary features or process parameters, later using them to build competitive machines. To mitigate this, use non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), limit the sharing of sensitive information, and consider patenting unique machine configurations or processes.
Misrepresentation of Machine Origin and Branding
Some suppliers mislabel machines as being manufactured in technologically advanced countries (e.g., Germany, Italy) when they are actually rebranded or assembled using imported components. This misrepresentation can affect performance expectations and resale value. Always verify the actual country of manufacture, inspect build quality firsthand, and validate claims with independent references or industry experts.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence, engage third-party inspectors, and prioritize transparency and contractual clarity with suppliers. Investing time in evaluating both quality and IP aspects upfront can prevent costly disruptions and legal complications down the line.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Pipe Extrusion Machine
Overview
Transporting and installing a pipe extrusion machine involves complex logistics and strict compliance requirements due to the machine’s size, weight, and technical specifications. This guide outlines key considerations for safe, efficient, and legally compliant handling from origin to final destination.
Pre-Shipment Planning
- Machine Assessment: Confirm dimensions, weight, and fragility of components (extruder, die head, haul-off unit, cutter, control panel).
- Route Survey: Evaluate transport routes for bridge weight limits, road width, overhead clearance, and turning radius.
- Packaging Requirements: Use weatherproof, reinforced wooden crates with internal bracing; label with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and handling instructions.
- Export Documentation: Prepare commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, certificate of origin, and export license (if applicable).
Transportation Methods
- Sea Freight (FCL/LCL): Recommended for international shipments. Secure machine on flat rack or in open-top container if oversized.
- Air Freight: Only for urgent, smaller components due to high cost and size limitations.
- Land Transport: Use low-bed trailers or extendable flatbed trucks with proper permits for overweight/overdimensional loads.
Customs & Import Compliance
- HS Code Classification: Typically under 8477.20 (Machinery for working rubber or plastic). Confirm with local customs authority.
- Duties & Taxes: Research import tariffs, VAT, and potential exemptions based on trade agreements.
- Regulatory Approvals: Ensure compliance with destination country’s machinery safety standards (e.g., CE for EU, UL for USA, CCC for China).
- Inspection Requirements: Prepare for potential customs inspections; provide technical manuals and conformity certificates.
Installation & Site Readiness
- Foundation Requirements: Verify floor load capacity, vibration isolation, and alignment specifications.
- Utilities: Ensure availability of correct power supply (voltage, phase, frequency), compressed air, and cooling water.
- Clearance Space: Maintain minimum clearance around machine for operation, maintenance, and safety access.
- Crane & Rigging: Use certified equipment and personnel for offloading and positioning; follow OEM rigging points.
Safety & Regulatory Compliance
- CE Marking / UL Certification: Confirm machine meets regional safety directives (e.g., EU Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC).
- Electrical Compliance: Adhere to local electrical codes (e.g., NEC in USA, IEC standards internationally).
- Operator Training: Provide certified training on safe operation, lockout/tagout (LOTO), and emergency procedures.
- Environmental Regulations: Comply with noise emissions, waste handling (e.g., trim recycling), and energy efficiency standards.
Post-Installation Compliance
- Commissioning & Testing: Conduct performance and safety tests per OEM guidelines; document results.
- Registration & Inspection: Register machine with local industrial safety authority if required; schedule periodic inspections.
- Maintenance Records: Maintain logs for compliance audits and warranty validity.
Risk Mitigation & Contingency
- Insurance: Secure all-risk cargo insurance covering transit, handling, and installation.
- Spare Parts Shipment: Ship critical spares separately to avoid downtime.
- Contingency Planning: Identify alternate routes, backup freight forwarders, and emergency contacts.
Conclusion
Proper logistics planning and regulatory compliance are essential to ensure the safe, timely, and legal delivery and operation of a pipe extrusion machine. Partner with experienced freight forwarders, comply with all regional regulations, and follow OEM guidelines to minimize risks and ensure operational readiness.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Pipe Extrusion Machine
After conducting a detailed evaluation of technical requirements, production capacity, budget constraints, and supplier reliability, sourcing a pipe extrusion machine is a critical investment that significantly impacts product quality, operational efficiency, and long-term profitability. It is essential to prioritize machines that offer robust construction, energy efficiency, precise process control, and compatibility with the required materials and pipe specifications.
Careful consideration should be given to both domestic and international suppliers, weighing factors such as after-sales support, warranty terms, spare parts availability, and technical training. Partnering with reputable manufacturers who provide proven performance and responsive customer service ensures minimal downtime and smooth integration into existing production lines.
Additionally, conducting factory inspections, reviewing client references, and comparing quotations from multiple vendors will help in making an informed and cost-effective decision. Ultimately, the right pipe extrusion machine should align with current production needs while allowing room for future scalability and technological upgrades.
In conclusion, a strategic approach to sourcing—balancing quality, cost, and support—will result in a reliable, high-performing extrusion system that enhances manufacturing capabilities and supports sustainable business growth.