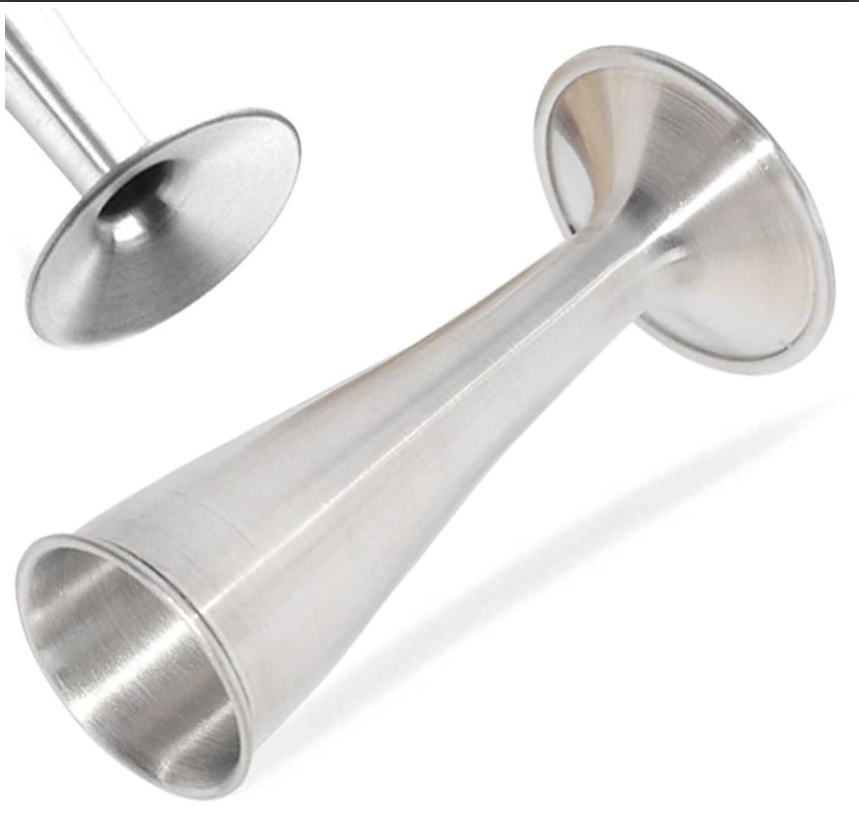
The global stethoscope market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for diagnostic tools in healthcare settings and rising awareness around cardiovascular and respiratory health. According to Grand View Research, the global stethoscope market size was valued at USD 560.7 million in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is further supported by advancements in acoustic technology, the expansion of healthcare infrastructure in emerging economies, and the continued reliance on auscultation as a fundamental diagnostic practice. Amid this expanding market, Pinard stethoscopes—simple, durable fetal stethoscopes used to monitor fetal heart rates during pregnancy—remain a critical tool in prenatal care, especially in low-resource and rural settings. As demand for reliable, cost-effective obstetric tools persists, a select group of manufacturers has emerged at the forefront of producing high-quality Pinard stethoscopes, combining traditional design with modern manufacturing precision. Here are the top six Pinard stethoscope manufacturers leading the way in innovation, accessibility, and clinical trust.
Top 6 Pinard Stethoscope Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 IndoSurgicals Aluminium Pinard Foetal Stethoscope
Domain Est. 2014
Website: indosurgicals.com
Key Highlights: Introducing the Aluminium Pinard Foetal Stethoscope by IndoSurgicals, a top brand and the largest manufacturer of Pinard Foetal Stethoscopes in the world….
#2 PINARD STETHOSCOPE
Domain Est. 1997
Website: fazzini.it
Key Highlights: The international leading supplier of hospital furniture and medical equipment, producing and distributing all over the world more than 3.000 medical and ……
#3 Pinard stethoscopes
Domain Est. 2000
Website: kawemed.com
Key Highlights: Pinard stethoscope, large. Produkt merken. Pinard stethoscope, small. Produkt merken. Product category….
#4 Pinard Pediatric Stethoscope
Domain Est. 2004
#5 PINARD STETHOSCOPE
Website: fazzini.eu
Key Highlights: the international leading supplier of hospital furniture and medical equipment, producing and distributing all over the world more than 3.000 medical and ……
#6 PINARD STETHOSCOPE
Website: gimaitaly.com
Key Highlights: LONG OBSTETRIC STETHOSCOPE – wood · PINARD STETHOSCOPE – aluminium · SHORT OBSTETRIC STETHOSCOPE – wood. Nuova ricerca. Gima S.p.A. Via Marconi, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Pinard Stethoscope

2026 Market Trends for Pinard Stethoscope: A Focused Outlook
Despite the dominance of electronic fetal monitoring and advanced Doppler technology in modern obstetrics, the Pinard stethoscope— a simple, trumpet-shaped acoustic device for auscultating fetal heartbeats—continues to hold a niche in global maternal care. As we approach 2026, several key trends are shaping its market presence and relevance:
Resurgence in Midwifery-Led and Low-Intervention Birth Models
The growing demand for natural, low-intervention childbirth, particularly in high-income countries, is driving renewed interest in traditional tools like the Pinard. Midwives and birthing centers promoting physiological birth are increasingly incorporating the Pinard into practice, valuing its non-invasive, hands-on approach. This trend is bolstered by consumer preference for minimizing medical technology during labor, positioning the Pinard as a symbol of human-centered care.
Expansion in Low- and Middle-Income Countries (LMICs)
In regions with limited healthcare infrastructure and budget constraints, the Pinard remains a vital tool due to its affordability, durability, and lack of dependency on electricity or batteries. Global maternal health initiatives and NGO programs are integrating Pinard training into community health worker curricula, reinforcing its role in early detection of fetal distress where advanced equipment is unavailable. This sustained demand in LMICs will continue to anchor the Pinard’s global market.
Integration with Training and Education
Medical and midwifery schools are emphasizing foundational clinical skills, leading to a revival of Pinard instruction as part of antenatal assessment training. The device serves as an effective educational tool for teaching fetal heart rate recognition and position assessment, fostering a deeper understanding of fetal well-being without technological mediation. By 2026, expect increased curriculum adoption and simulation-based training incorporating the Pinard.
Challenges from Technological Advancements
The rise of portable, smartphone-connected Doppler devices offering real-time data and recording capabilities presents ongoing competition. These digital tools appeal to tech-savvy practitioners and patients seeking documentation and remote monitoring. While the Pinard cannot match these features, its simplicity and reliability ensure it remains a fallback option during equipment failure or power outages.
Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing
As healthcare consumers and institutions prioritize sustainability, the Pinard’s long lifespan and minimal environmental footprint become competitive advantages. Manufacturers emphasizing ethical production, recyclable materials (e.g., medical-grade wood or bioplastics), and fair labor practices may differentiate their offerings in socially conscious markets.
Conclusion
The Pinard stethoscope market in 2026 will remain modest in volume but resilient in purpose. Driven by maternal care philosophies favoring minimal intervention, persistent utility in resource-limited settings, and educational value, the Pinard is unlikely to disappear. Instead, it will occupy a complementary role alongside modern technologies—valued not for innovation, but for its enduring simplicity, accessibility, and connection to the human aspect of obstetric care.
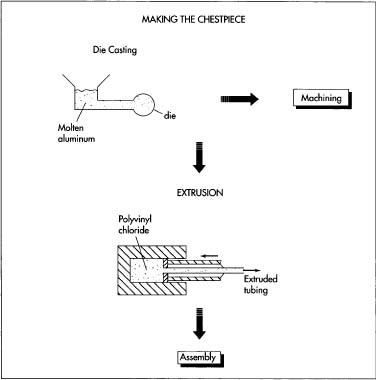
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Pinard Stethoscopes: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing Pinard stethoscopes—especially from low-cost manufacturing regions—can be fraught with challenges related to product quality and intellectual property (IP). Being aware of these pitfalls is essential to ensure you receive a reliable medical device that complies with legal and safety standards.
Poor Material Quality and Construction
One of the most common issues is receiving Pinard stethoscopes made from substandard materials. Inferior metals (such as low-grade aluminum or zinc alloys) can corrode, dent easily, or produce muffled sound, compromising acoustic performance. Poor craftsmanship may result in rough edges, misaligned horns, or weak structural integrity, which affects both usability and safety.
Inaccurate Acoustic Performance
A genuine Pinard stethoscope must deliver clear fetal heart tones. Many counterfeit or low-quality versions fail here due to improper internal bore design or flawed horn geometry. Without proper acoustic testing, sourced units may be clinically ineffective, leading to misdiagnosis or loss of trust from healthcare providers.
Lack of Regulatory Compliance
Many suppliers, particularly on open marketplaces, offer Pinard stethoscopes without regulatory certifications (e.g., CE, FDA, ISO 13485). Sourcing non-compliant devices can expose your business to legal liability, import restrictions, or product recalls. Always verify that the manufacturer adheres to medical device standards.
Counterfeit or Branded Imitations
Some suppliers falsely market their products as “original” or “medical-grade” Pinard stethoscopes, mimicking well-known brands. These counterfeit versions often infringe on trademarks and may mislead end users. Using or distributing such products can lead to IP infringement claims, especially if branded logos or patented designs are copied.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
The design of certain Pinard stethoscopes—especially those with unique ergonomic or acoustic features—may be protected by design patents or trademarks. Sourcing from manufacturers who replicate these protected designs without authorization exposes your company to IP litigation, shipment seizures, or forced product withdrawal.
Inadequate Supplier Verification
Failing to conduct due diligence on suppliers increases the risk of partnering with unauthorized or unethical manufacturers. Without site audits, quality control checks, or legal agreements, you may unknowingly source from facilities with poor labor practices or IP violations.
No Traceability or Quality Assurance Documentation
Reliable medical devices require documentation for materials, manufacturing processes, and quality testing. Many low-cost suppliers cannot provide certificates of conformance, material safety data sheets (MSDS), or batch testing results, making it difficult to verify quality or respond to regulatory inquiries.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, conduct thorough supplier vetting, request product samples for acoustic and durability testing, verify regulatory certifications, and ensure intellectual property rights are respected. Partnering with reputable manufacturers and using legal contracts can mitigate both quality and IP risks when sourcing Pinard stethoscopes.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Pinard Stethoscope
Product Overview and Classification
The Pinard stethoscope, also known as a fetoscope, is a simple acoustic device used primarily in obstetrics to monitor fetal heart rate. It is a passive, non-electronic instrument typically made of wood or metal. Under international medical device regulations, the Pinard stethoscope is generally classified as a Class I medical device due to its low risk and non-invasive nature.
Regulatory Compliance
Medical Device Registration
Depending on the destination market, the Pinard stethoscope may require registration with the relevant regulatory authority. Examples include:
– USA: FDA 510(k) exemption for Class I devices; general controls apply.
– European Union: CE marking under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) 2017/745 as a Class I device.
– Canada: Medical Device License (MDL) Class I through Health Canada.
– Australia: Inclusion in the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG).
Ensure all applicable technical documentation, including risk analysis and declarations of conformity, is maintained.
Labeling and Packaging Requirements
Labels must comply with local regulations and include:
– Product name and model
– Manufacturer name and address
– CE mark (if applicable)
– Lot or serial number
– “For medical use” or similar designation
– Language requirements for destination country (e.g., French in Canada, bilingual labels in EU countries)
Import and Export Regulations
Harmonized System (HS) Code
The recommended HS code for the Pinard stethoscope is 9018.90, which covers medical, surgical, or veterinary instruments and appliances. Confirm with local customs authorities, as classifications may vary by country.
Import Duties and Tariffs
Most countries impose low or zero import duties on Class I medical devices. However, verify tariff rates using the destination country’s customs database. Free trade agreements may also reduce or eliminate duties.
Export Controls
The Pinard stethoscope is not typically subject to export controls or sanctions. However, exporters must ensure compliance with general export regulations, including:
– No inclusion on denied persons lists
– Compliance with anti-bribery laws (e.g., FCPA, UK Bribery Act)
– Accurate end-use declarations
Shipping and Logistics
Packaging and Handling
- Use protective packaging to prevent damage during transit.
- Include user instructions (if applicable) in the local language.
- Avoid moisture-sensitive materials; consider anti-corrosion packaging for metal models.
Temperature and Storage
The Pinard stethoscope has no special temperature or humidity requirements. Store in a dry, clean environment away from direct sunlight and contaminants.
Shipping Methods
Suitable for standard air and sea freight. No special handling or hazardous material classification is required. Ensure proper insurance coverage based on shipment value.
Quality Assurance and Post-Market Surveillance
Quality Management System
Manufacturers and distributors should comply with ISO 13485:2016 for quality management systems specific to medical devices. Maintain records of design, production, and distribution.
Post-Market Surveillance
Even for low-risk devices, manufacturers must:
– Monitor and report adverse events (if any) to regulatory bodies.
– Track customer complaints and perform root cause analysis.
– Update risk assessments and technical documentation as needed.
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
- The Pinard stethoscope contains no hazardous materials under RoHS or REACH (if made of wood or untreated metal).
- Confirm material compliance for painted or treated models.
- End-of-life disposal should follow local waste management guidelines for medical instruments.
Conclusion
The Pinard stethoscope is a low-risk medical device with straightforward logistics and compliance requirements. Adherence to medical device regulations, accurate classification, proper labeling, and quality documentation are essential for smooth international trade. Regular monitoring of regulatory updates in target markets is recommended to maintain compliance.
Conclusion: Sourcing the Pinard Stethoscope
In conclusion, sourcing a Pinard stethoscope presents a valuable opportunity to support low-resource maternal healthcare settings through an affordable, durable, and highly effective tool for fetal heart rate monitoring. Its simplicity, ease of use, and lack of reliance on technology or power sources make it particularly suitable for community health workers, midwives, and prenatal care providers in remote or underserved areas.
Sourcing decisions should prioritize quality craftsmanship—typically found in models made from sustainably sourced wood or high-grade metal—and ethical manufacturing practices. Establishing relationships with reputable suppliers, traditional artisans, or certified medical equipment distributors ensures authenticity and supports fair trade principles. Additionally, consideration should be given to bulk procurement, training integration, and long-term maintenance to maximize impact.
Overall, incorporating the Pinard stethoscope into maternal health programs not only enhances prenatal assessment capabilities but also honors traditional birthing practices while promoting equitable access to essential care. Thoughtful sourcing strengthens global maternal health efforts and reaffirms the importance of low-tech, high-impact solutions in modern healthcare delivery.