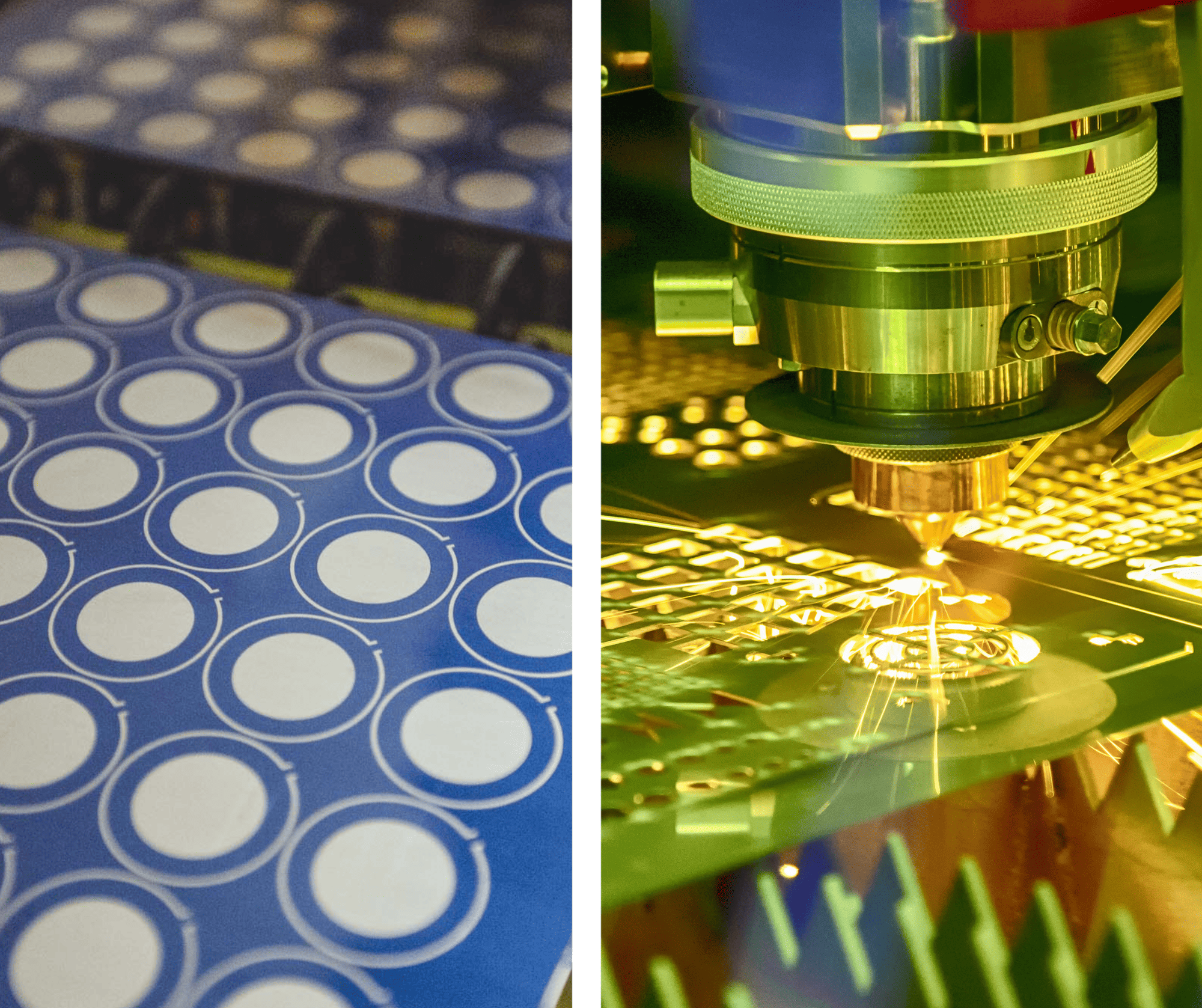
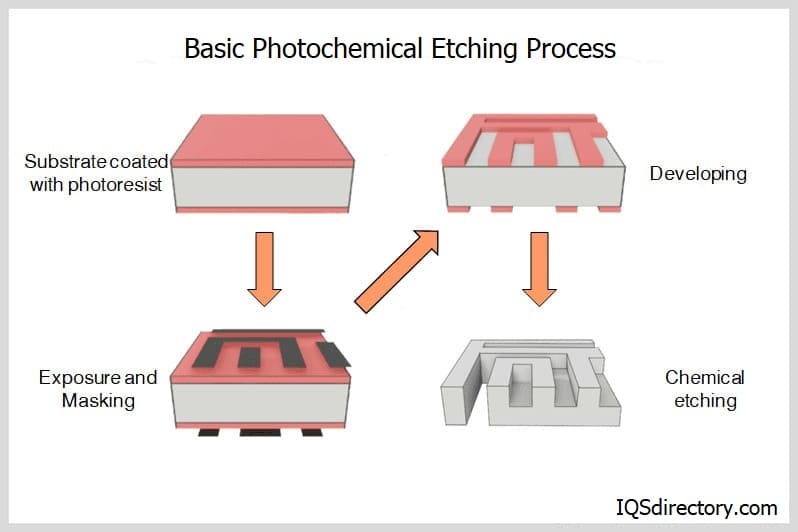
The global photochemical etching market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for precision metal components in industries such as electronics, automotive, medical devices, and aerospace. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the photochemical etching market was valued at USD 2.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.8% from 2024 to 2029. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates the market to expand at a CAGR of 7.1% during the forecast period of 2023 to 2030, fueled by the rising adoption of miniaturized components and advancements in etching technologies. As manufacturers continue to prioritize high precision, cost-efficiency, and scalability, the role of leading photochemical etching service providers becomes increasingly critical. Below are the top 10 manufacturers at the forefront of innovation, quality, and global reach in the photochemical etching space.
Top 10 Photochemical Etching Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 PCM Products, Inc.
Domain Est. 1998
Website: pcmproducts.com
Key Highlights: PCM Products can etch all metals, all alloys and even exotic metals. We provide etching of Copper, Brass, Nickel, Stainless Steel, Titanium, Niobium, Zirconium, ……
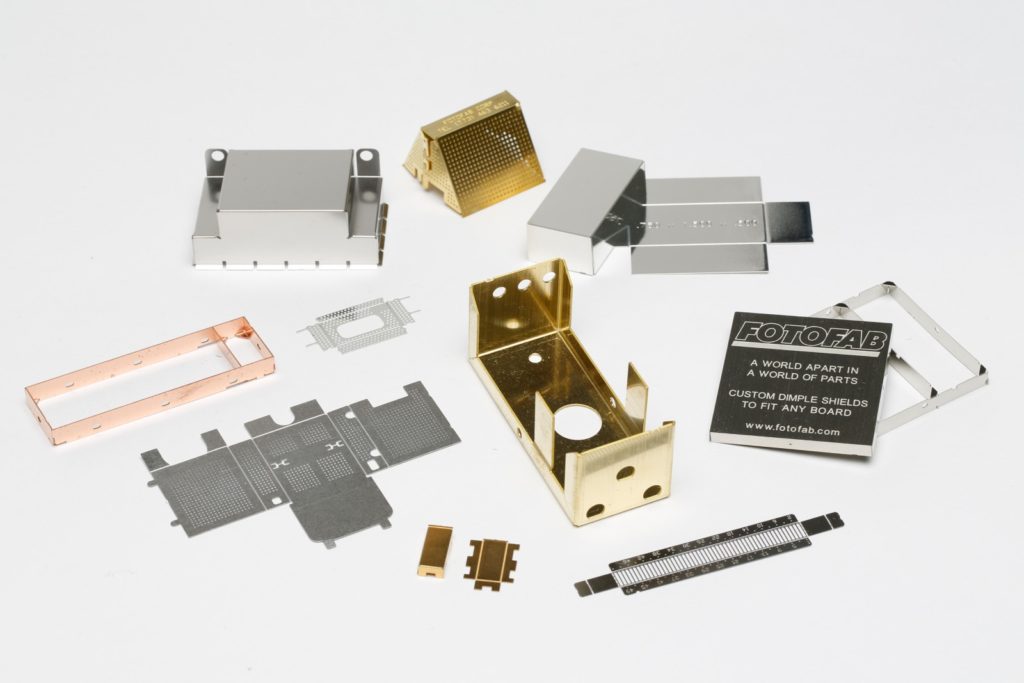
#2 Fotofab: Metal Etching Services
Domain Est. 1996
Website: fotofab.com
Key Highlights: Using the process of photochemical machining, also known as etching, Fotofab achieves quicker lead times and tighter tolerances than traditional manufacturing ……
#3 Leader in Precision Etching & Photo Etched Precision Metal Parts
Domain Est. 1997
Website: photofabrication.com
Key Highlights: PEI is the industry leader in photo etching precision metal parts. Specializing in photochemical etching and custom metal components….
#4 Vaga Industries
Domain Est. 1997
Website: vaga.com
Key Highlights: We supply precision-photochemical etching parts that meet the most exacting specifications—minus the cost limits of traditional stamping methods….
#5 Photo Etching and Photochemical Machining
Domain Est. 1997
Website: conardcorp.com
Key Highlights: Elevate precision with Conard Corporation’s expertise in photochemical machining. Discover innovative solutions for your components….
#6 Metal Etch And Laser Cutting Services
Domain Est. 1999
Website: metaletching.com
Key Highlights: Our custom metal parts manufacturing facility specializes in the photo etching and laser cutting processes. Both provide the highest quality and precision for ……
#7 Precision Micro
Domain Est. 2001
Website: precisionmicro.com
Key Highlights: Precision Micro specialises in transforming sheet metals into high-precision components with the flexibility, short lead times and full traceability….
#8 Switzer Precision Metal Manufacturing Photochemical Etching
Domain Est. 2014
Website: switzermfg.com
Key Highlights: If you need precision metal fabrication, you’ve come to the right place! Our photochemical machining (PCM) process is ideal for a wide range of applications….
#9 Photochemical Etching
Domain Est. 2019
Website: fathommfg.com
Key Highlights: Photo chemical etching produces multiple parts from a single sheet of metal. Little or no finishing is required. No Changes to the Integrity of the Metal. Many ……
#10 Photochemical Etching
Domain Est. 2020
Website: met-mfg.com
Key Highlights: Chemical etching is the optimum process for producing microelectronic components with complex patterns such as lead frames and filters. This ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Photochemical Etching
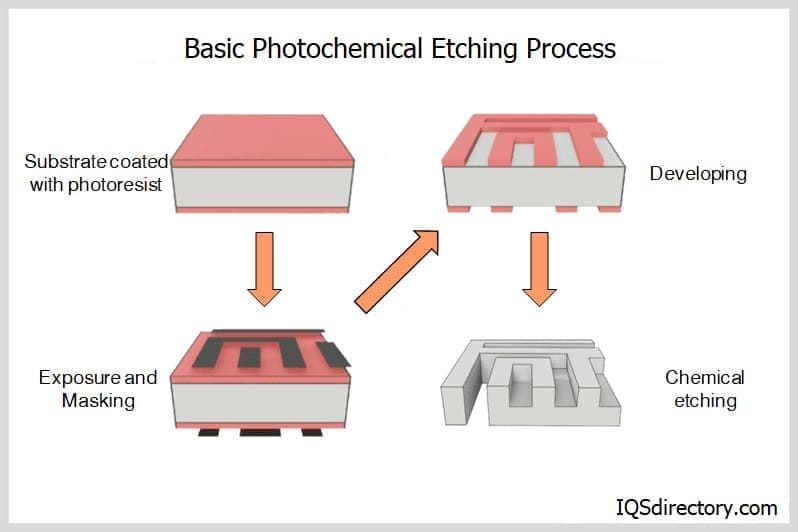
H2: Projected Market Trends in Photochemical Etching for 2026
By 2026, the photochemical etching (PCE) market is expected to experience significant growth and transformation, driven by advancements in precision manufacturing, rising demand across high-tech industries, and increased emphasis on sustainable production methods. Key trends shaping the market include:
-
Expansion in Electronics and Semiconductor Applications
The continued miniaturization of electronic components and the proliferation of wearable devices, flexible circuits, and advanced sensors are increasing demand for ultra-precise, burr-free metal parts. Photochemical etching, which enables high-resolution patterning without mechanical stress, is becoming a preferred method for producing intricate components such as lead frames, connectors, and EMI shielding. The growth of 5G infrastructure and IoT devices will further accelerate adoption in electronics supply chains. -
Growth in Medical Device Manufacturing
The medical industry is increasingly adopting PCE for producing surgical tools, implants, diagnostic equipment, and microfluidic devices. The process’s ability to etch biocompatible materials like titanium, stainless steel, and nickel alloys with high accuracy and no thermal distortion makes it ideal for critical healthcare applications. Regulatory compliance and demand for single-use, precision devices are expected to boost market penetration. -
Automotive and EV Industry Integration
With the global shift toward electric vehicles (EVs), photochemical etching is gaining traction in the production of battery components, sensor housings, and power electronics. The lightweighting trend in automotive design aligns well with PCE’s capability to produce thin, complex metal parts without compromising structural integrity. As EV manufacturing scales, especially in Asia-Pacific and North America, demand for etched components will grow. -
Advancements in Materials and Process Efficiency
Innovations in photoresist technology, etching chemistries, and automation are improving throughput and reducing waste. Manufacturers are investing in digital workflow integration, AI-driven process monitoring, and closed-loop chemical recovery systems to enhance precision and sustainability. These improvements are lowering operational costs and expanding the range of applicable materials, including advanced alloys and ultra-thin foils. -
Sustainability and Environmental Compliance
Environmental regulations are pushing manufacturers toward cleaner production processes. Unlike traditional machining or stamping, PCE generates no heat-affected zones or tool wear and allows for recyclable metal use. By 2026, eco-conscious production standards and circular economy principles will favor PCE as a low-waste alternative, particularly in regulated industries. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific will remain the dominant market due to robust electronics manufacturing in China, Japan, and South Korea. However, North America and Europe are expected to see accelerated growth due to reshoring initiatives, increased defense spending (driving demand for aerospace and RF components), and support for advanced manufacturing technologies.
In summary, the photochemical etching market in 2026 will be shaped by technological innovation, sector-specific demand from electronics, medical, and automotive industries, and a growing emphasis on precision and sustainability. Companies that invest in R&D, automation, and environmentally responsible practices are likely to lead the market.

H2: Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Photochemical Etching – Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing photochemical etching (also known as photo etching or chemical milling) offers advantages such as high precision, low tooling costs, and the ability to process complex designs in thin metal sheets. However, companies often encounter significant challenges related to quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Understanding these pitfalls is critical to mitigating risk and ensuring reliable, secure manufacturing outcomes.
H3: Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Inconsistent Etch Uniformity
A common issue in photochemical etching is uneven material removal, leading to variations in part thickness, edge definition, or feature dimensions. Poor process control—such as inconsistent chemical concentration, temperature fluctuations, or uneven spray patterns—can result in non-conforming parts.
Mitigation: Require suppliers to provide process capability data (e.g., Cpk values), perform regular audits, and use statistical process control (SPC) for critical dimensions. -
Tolerances Beyond Supplier Capability
While photochemical etching is precise, it has inherent limitations—especially for very tight tolerances (<±10% of material thickness) or ultra-fine features. Overestimating supplier capability can lead to rejected batches.
Mitigation: Validate supplier claims with sample parts and technical audits. Define tolerances based on material type, thickness, and design complexity. -
Material and Surface Defects
Incoming material defects (e.g., scratches, rolling marks, impurities) can be exacerbated during etching. Additionally, improper cleaning or handling can introduce contamination.
Mitigation: Specify stringent material sourcing standards (e.g., ASTM, AMS) and require material certifications. Implement incoming inspection protocols. -
Poor Masking and Registration
Misalignment of photoresist masks leads to feature inaccuracies. Poor edge acuity or undercutting can compromise functionality, especially in RF or medical components.
Mitigation: Confirm suppliers use high-resolution phototools and automated alignment systems. Request first-article inspections with microscopy reports.
H3: Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
-
Unprotected Design Files and Data Sharing
Sharing detailed CAD files, phototools, or process specifications with etching vendors exposes sensitive design IP. Without proper safeguards, designs can be reverse-engineered or shared with competitors.
Mitigation: Use NDAs with clear IP clauses, limit data to only what is necessary (e.g., Gerber files instead of full CAD), and watermark or encrypt deliverables. -
Lack of IP Ownership Clauses in Contracts
Some suppliers claim partial ownership of tooling or process improvements derived from customer designs. This can restrict future sourcing options or lead to legal disputes.
Mitigation: Define IP ownership explicitly in procurement agreements—ensure all custom tooling, phototools, and design adaptations remain the customer’s property. -
Subcontracting Without Consent
Etching providers may outsource work to third-party facilities without notifying the customer, increasing the risk of IP leakage or quality deviations.
Mitigation: Include subcontracting restrictions in contracts and require supplier transparency. Conduct on-site audits of secondary facilities if applicable. -
Insufficient Cybersecurity Measures
Digital workflows in photochemical etching involve file transfers, cloud storage, and CAM software—potential entry points for cyber theft.
Mitigation: Assess suppliers’ IT security policies, require secure file transfer protocols (e.g., SFTP, encrypted email), and avoid public cloud sharing for sensitive data.
H2: Conclusion
Sourcing photochemical etching requires balancing precision manufacturing needs with robust quality assurance and IP protection strategies. Organizations must proactively evaluate supplier capabilities, enforce contractual safeguards, and maintain control over sensitive design data. By addressing these common pitfalls under the H2 themes of quality and IP, companies can secure reliable, high-integrity etched components while protecting their competitive advantage.
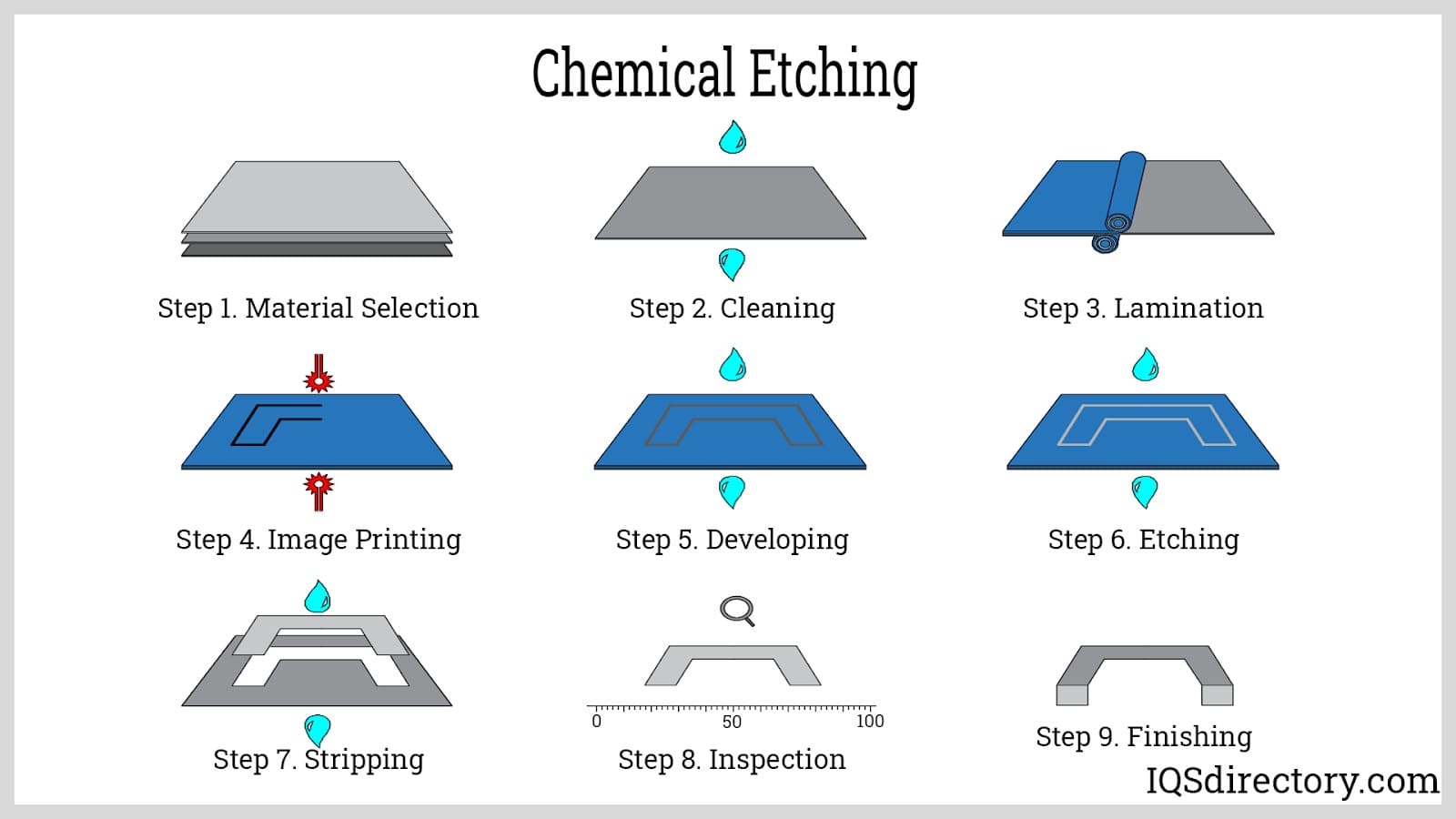
H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Photochemical Etching
Photochemical etching (also known as photo etching or chemical milling) is a precision manufacturing process used to create complex, burr-free metal components through selective chemical dissolution. While highly efficient and cost-effective for thin metal fabrication, it involves handling hazardous materials and regulated waste streams. A robust logistics and compliance strategy is essential to ensure operational safety, environmental responsibility, and adherence to legal standards.
This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for photochemical etching operations, structured under H2-level headings for clarity and actionability.
H2: Regulatory Compliance Framework
Ensure alignment with national, regional, and local regulations governing chemical use, waste disposal, and worker safety.
- OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) – Comply with HazCom (Hazard Communication Standard), PPE requirements, and permissible exposure limits (PELs) for chemicals such as ferric chloride, nitric acid, and solvents.
- EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) – Adhere to RCRA (Resource Conservation and Recovery Act) for managing hazardous waste, including spent etchants and rinse waters.
- DOT (Department of Transportation) – Follow regulations for the safe transport of hazardous chemicals to and from facilities.
- Local Environmental Agencies – Comply with discharge permits (e.g., NPDES) for wastewater effluent and air emissions (if applicable).
Maintain up-to-date Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for all chemicals and conduct regular compliance audits.
H2: Chemical Procurement and Inventory Management
Efficient logistics begins with responsible sourcing and tracking of process chemicals.
- Source certified suppliers for etchants (e.g., ferric chloride, cupric chloride), developers, strippers, and cleaning agents.
- Implement a Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory system to minimize on-site storage of hazardous materials.
- Store chemicals in approved, segregated, and labeled containers within ventilated, spill-containment areas.
- Use barcode or digital tracking systems to monitor chemical usage, expiration, and reorder points.
Regular inventory checks prevent shortages and reduce risk of accidental overstocking.
H2: Waste Handling and Disposal Logistics
Spent etchants, photoresist residues, and contaminated rinse water are classified as hazardous waste and require proper treatment and disposal.
- Segregate waste streams by chemical composition (e.g., chloride-based vs. acid-based etchants).
- Neutralize and precipitate metals from spent etchants using approved treatment systems (e.g., pH adjustment, filtration).
- Partner with licensed hazardous waste disposal vendors for off-site treatment and documentation.
- Maintain detailed waste manifests and disposal records for regulatory audits.
Consider closed-loop recycling systems to recover metal byproducts (e.g., copper recovery from cupric chloride), reducing disposal volume and costs.
H2: Wastewater Management and Treatment
Photochemical etching generates process wastewater containing dissolved metals and chemical residues.
- Install on-site wastewater treatment systems to remove heavy metals (e.g., iron, copper) and neutralize pH.
- Conduct routine water quality testing to ensure compliance with local discharge limits.
- Recycle treated water where feasible (e.g., for rinsing stages) to reduce water consumption.
- Obtain and maintain necessary discharge permits; report any non-compliance immediately.
Implement leak detection and secondary containment for all liquid-handling systems.
H2: Transportation and Material Handling
Safe and compliant movement of raw materials, work-in-process, and finished parts is critical.
- Use appropriate packaging and labeling for transporting etched components, especially if they retain chemical residues.
- Train staff in proper handling of metal sheets, photoresist films, and chemical containers to prevent injury and contamination.
- Ensure all transport vehicles (inbound and outbound) comply with DOT hazardous materials regulations when carrying chemicals.
- Coordinate with logistics providers experienced in industrial chemical transport.
H2: Worker Safety and Training Programs
Personnel are exposed to chemical, inhalation, and splash hazards during etching operations.
- Provide comprehensive training on chemical handling, emergency response, and PPE use.
- Conduct annual refresher courses on GHS labeling, spill response, and lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures.
- Supply and enforce use of appropriate PPE: chemical-resistant gloves, face shields, aprons, and respirators where needed.
- Install emergency showers and eyewash stations within 10 seconds’ travel from chemical handling zones.
Document all training and maintain records for OSHA inspections.
H2: Environmental Monitoring and Reporting
Proactive monitoring ensures early detection of non-compliance and environmental risks.
- Monitor air quality for chemical vapors (e.g., HCl, NOx) using fixed or portable sensors.
- Test wastewater effluent monthly for pH, conductivity, and metal concentrations.
- Keep logs of all monitoring activities and submit required reports to regulatory bodies on schedule.
- Implement corrective actions promptly upon detection of anomalies.
H2: Emergency Preparedness and Spill Response
Be prepared for chemical spills, leaks, or system failures.
- Develop and maintain a site-specific Spill Prevention, Control, and Countermeasure (SPCC) plan.
- Stock spill kits with absorbents, neutralizers, and containment booms near chemical storage and processing areas.
- Train designated response teams in spill containment and reporting procedures.
- Establish communication protocols with local emergency responders and environmental agencies.
Conduct biannual emergency drills to evaluate response effectiveness.
H2: Sustainability and Continuous Improvement
Integrate environmentally responsible practices into daily operations.
- Evaluate alternative, less hazardous etchants (e.g., organic-based systems) to reduce environmental impact.
- Optimize rinse cycles to minimize water and energy use.
- Pursue ISO 14001 certification to formalize environmental management systems.
- Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as chemical consumption, waste volume, and water reuse rates.
Regularly review and update logistics and compliance protocols to reflect regulatory changes and technological advancements.
By adhering to this structured logistics and compliance guide, photochemical etching operations can ensure safety, regulatory adherence, and long-term operational sustainability.
Conclusion for Sourcing Photochemical Etching
Sourcing photochemical etching offers a highly efficient, cost-effective, and precise solution for manufacturing complex metal components without the need for expensive tooling or secondary operations. This non-traditional machining process is ideal for producing intricate designs, thin materials, and stress-free parts with tight tolerances, making it particularly suitable for industries such as aerospace, medical devices, electronics, and automotive.
When sourcing photochemical etching, it is essential to partner with a reputable supplier that demonstrates technical expertise, quality certifications (such as ISO 9001 or AS9100), and consistent process control. Considerations such as material compatibility, lead times, scalability, and design support should guide the selection process to ensure alignment with project requirements.
In summary, photochemical etching provides a competitive advantage through design flexibility, reduced production costs, and rapid prototyping capabilities. By strategically sourcing this process from qualified vendors, companies can achieve high-quality metal components efficiently and reliably, supporting innovation and time-to-market objectives.