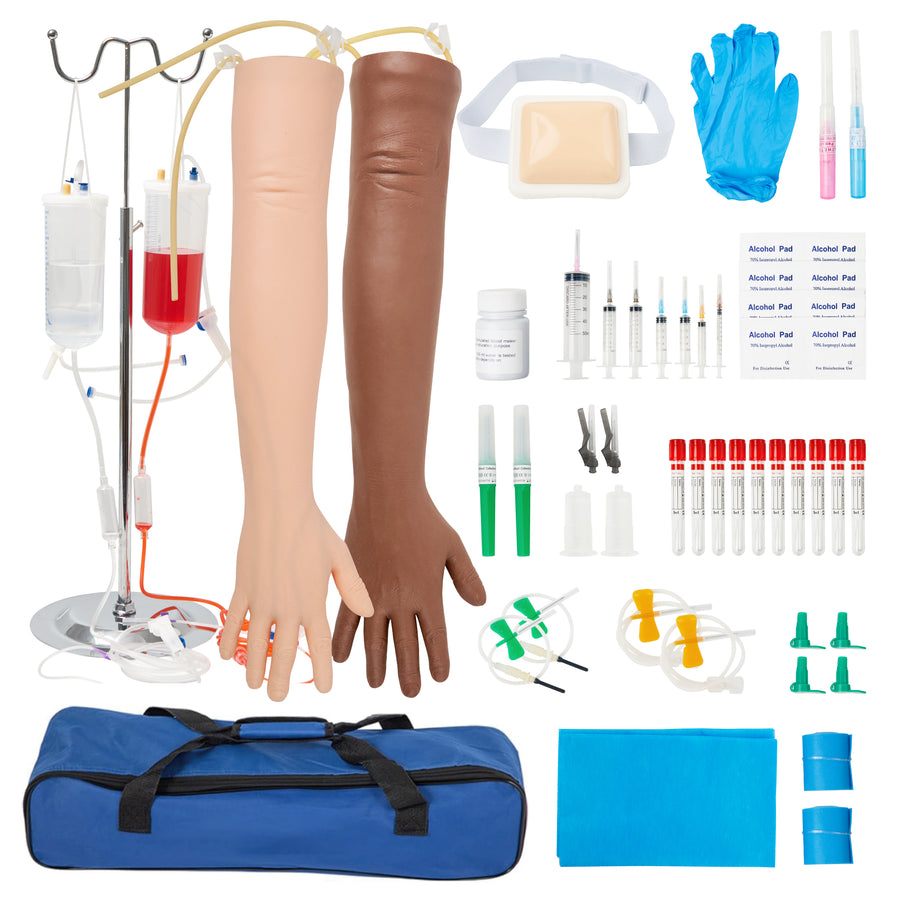
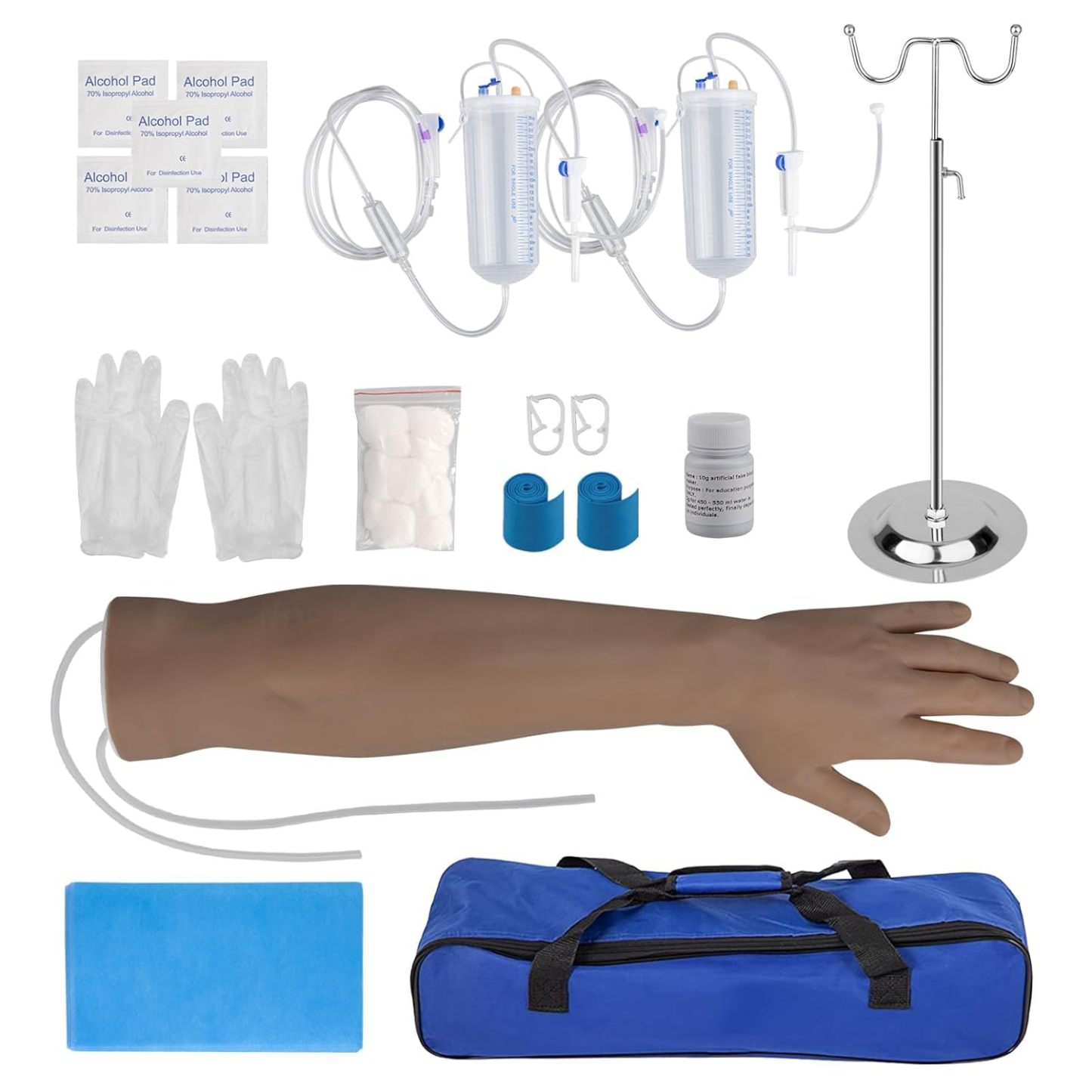
The global phlebotomy training equipment market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for skilled medical professionals and expanded investment in healthcare education. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global medical simulation market—encompassing training tools such as phlebotomist practice arms—is projected to grow at a CAGR of 9.8% from 2023 to 2028. This growth is fueled by the rising emphasis on patient safety, advancements in simulation technology, and expanding nursing and lab technician training programs worldwide. As institutions and training centers seek realistic, durable, and cost-effective solutions for venipuncture practice, the demand for high-quality phlebotomist practice arms has intensified. With an increasing number of manufacturers entering the space, selecting the right training model requires careful evaluation of anatomical accuracy, material durability, and educational effectiveness. Based on market presence, product innovation, and user feedback, here are the top 6 phlebotomist practice arm manufacturers leading the industry today.
Top 6 Phlebotomist Practice Arm Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 IV & Phlebotomy Practice Kit with Full
Domain Est. 1995
Website: carolina.com
Key Highlights: In stock 7–14 day deliveryThis IV and phlebotomy practice kit includes 1-year access to the Apprentice Academy’s online venipuncture training course with step-by-step video tutoria…
#2 VEVOR Phlebotomy Practice Kit, IV Venipuncture Intravenous …
Domain Est. 2009
#3 Adult Complete Phlebotomy Practice Arm Kit, Metal Stand
Domain Est. 2012
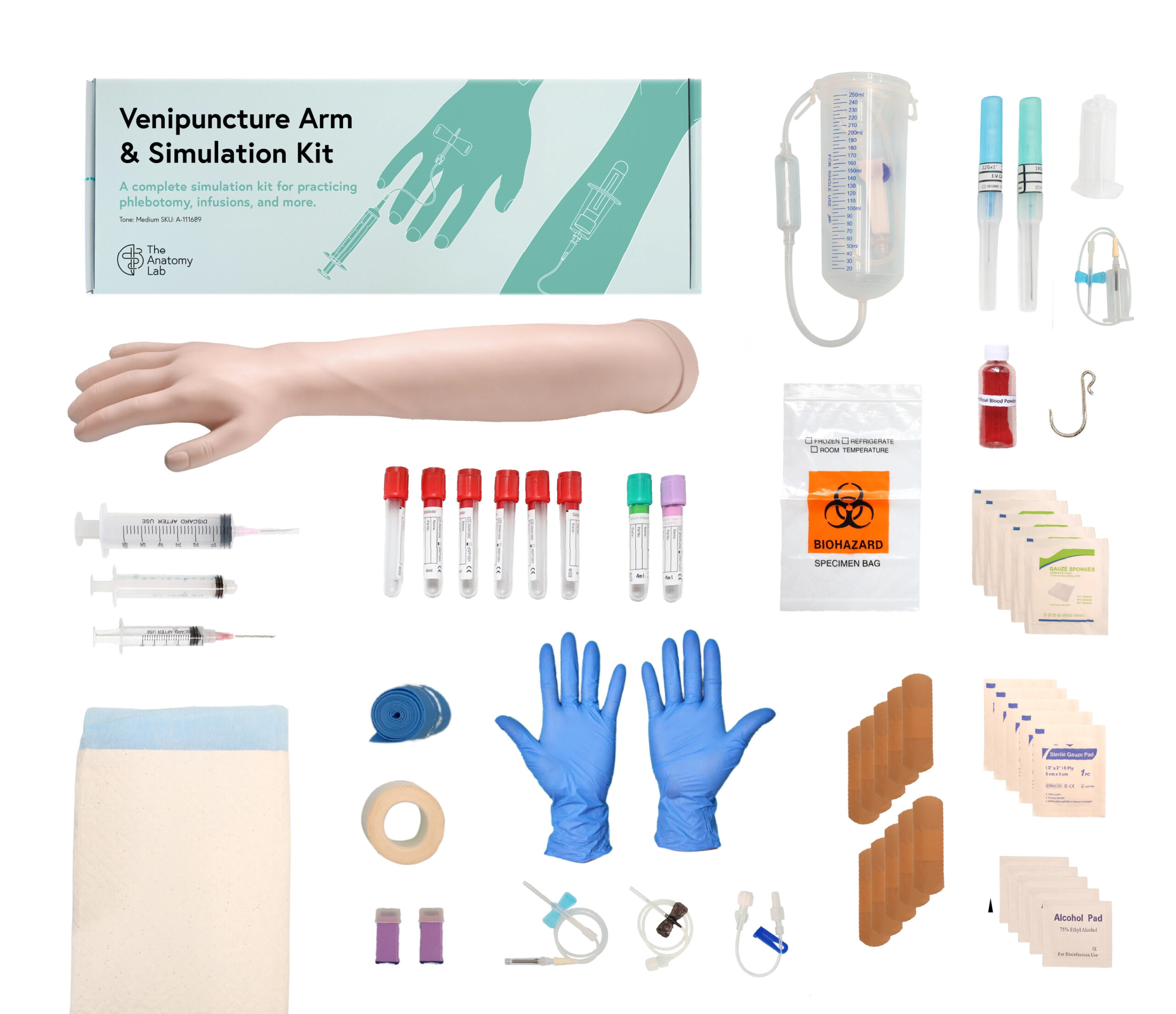
#4 Anatomy Lab Venipuncture and IV Practice Arm Kit and Simulation …
Domain Est. 2013
Website: pristine-medical.com
Key Highlights: In stock 4–10 day deliveryPhlebotomy trainer with a realistic IV practice arm featuring lifelike veins. Includes syringes, needles, and catheters for hands-on venipuncture training…
#5 Alcedo IV & Phlebotomy Simulation Practice Arm
Domain Est. 2018
Website: alcedohealth.com
Key Highlights: Engineered to replicate the look and feel of real human anatomy, this kit enables hands-on practice in blood collection, IV insertion, and medication ……
#6 SimCoach Phlebotomy Practice Arm Kit
Domain Est. 2023
Website: simcoach.net
Key Highlights: The SimCoach Phlebotomy Practice Arm Kit is designed for realistic training in phlebotomy, venipuncture, vein palpation, and other blood collection skills….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Phlebotomist Practice Arm
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Phlebotomist Practice Arms
The global market for phlebotomist practice arms is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in medical training technologies, rising demand for skilled healthcare professionals, and increasing emphasis on simulation-based education. Key trends shaping the market include:
-
Growth in Healthcare Training Programs: With the expanding global healthcare workforce, particularly in emerging economies, there is heightened demand for effective phlebotomy training tools. Phlebotomist practice arms—realistic simulation devices used to teach venipuncture techniques—are becoming essential in nursing and medical schools. The proliferation of accredited training programs is expected to boost market demand through 2026.
-
Adoption of High-Fidelity Simulation: There is a clear shift toward high-fidelity, anatomically accurate practice arms that mimic human tissue response, vein visibility, and blood flashback mechanisms. Manufacturers are incorporating advanced materials such as silicone and synthetic skin to enhance realism, improving learning outcomes and user confidence.
-
Integration with Digital and Augmented Technologies: By 2026, integration with digital platforms—such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and performance-tracking software—is anticipated to become standard. These smart practice arms can provide real-time feedback, assess technique accuracy, and track student progress, aligning with modern competency-based education models.
-
Focus on Infection Control and Reusability: Post-pandemic hygiene standards have elevated the importance of easy-to-clean, durable, and reusable training equipment. Companies are developing antimicrobial surfaces and modular designs that allow for quick replacement of consumable parts (e.g., synthetic veins), reducing long-term costs and waste.
-
Increased Demand in Emerging Markets: Regions such as Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa are witnessing rapid expansion in medical education infrastructure. Governments and private institutions are investing in simulation labs, creating new market opportunities for affordable and scalable phlebotomy training solutions.
-
Rise of E-Learning and Hybrid Training Models: The persistence of online and hybrid learning formats in healthcare education is fueling demand for at-home or portable practice arms. Compact, cost-effective models suitable for remote learners are expected to gain traction by 2026.
-
Regulatory and Standardization Pressures: As simulation becomes critical in certification processes, regulatory bodies may introduce standards for training device quality. This could lead to market consolidation and favor established manufacturers with compliant, validated products.
In summary, the phlebotomist practice arm market in 2026 will be characterized by technological innovation, expanded access to training tools, and growing integration with digital education ecosystems. Stakeholders who prioritize realism, data integration, and scalability will be best positioned to capture market share in this evolving landscape.
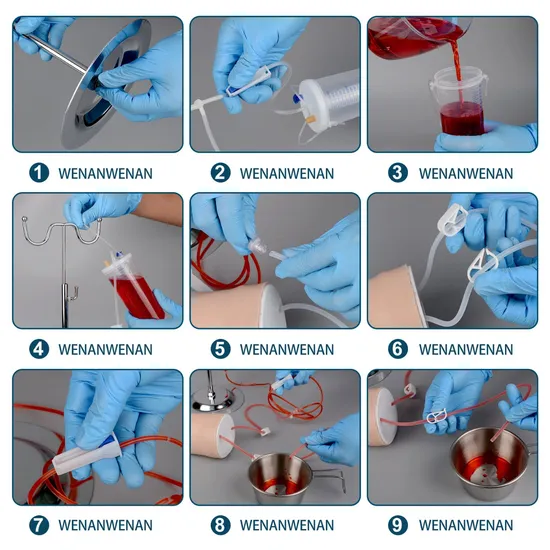
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Phlebotomist Practice Arms: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
When sourcing phlebotomist practice arms—training tools used to simulate venipuncture—organizations and educators must navigate several challenges. Two critical areas where issues often arise are product quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Avoiding these pitfalls ensures effective training, legal compliance, and long-term cost savings.
1. Compromised Quality Due to Low-Cost Suppliers
One of the most common pitfalls is selecting practice arms based solely on price, particularly from overseas or uncertified manufacturers. Low-cost options may use inferior materials that don’t accurately mimic human tissue, leading to:
– Poor realism in needle insertion and blood flashback simulation
– Short product lifespan due to rapid wear and tear
– Inconsistent performance across training sessions
These shortcomings can negatively impact student learning and skill retention. Always verify material specifications (e.g., silicone quality), durability testing, and compliance with educational standards before purchase.
2. Lack of Regulatory and Safety Compliance
Although practice arms are training devices and not medical devices per se, they should still meet safety and biocompatibility standards—especially if used in accredited programs. Sourcing products that lack certifications (e.g., ISO 13485, RoHS, or REACH compliance) can expose institutions to liability and hinder accreditation efforts.
3. Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Many high-quality phlebotomy training models are protected by patents, trademarks, or design copyrights. A major pitfall arises when sourcing from third-party manufacturers who produce “compatible” or “generic” versions that closely imitate branded designs (e.g., replicas of leading brands like Simulaids or Laerdal). This can lead to:
– Legal action for patent or trademark infringement
– Seizure of goods by customs authorities
– Damage to institutional reputation
Always ensure that suppliers can provide proof of IP rights or licensing for their designs. Conduct due diligence by reviewing patent databases or consulting legal advisors when uncertain.
4. Inadequate Technical Support and Replacement Parts
Low-quality or IP-infringing models often lack available replacement veins, skins, or technical documentation. This can disrupt training programs and result in higher total costs over time. Reputable suppliers typically offer warranties, repair services, and consumable restock options.
5. Misleading Product Descriptions and Counterfeit Goods
Online marketplaces may list counterfeit or misrepresented practice arms that appear identical to premium models but perform poorly. Be cautious of vague descriptions, stock photos, or unusually low prices. Request product samples, user manuals, and direct communication with the manufacturer to validate authenticity.
Best Practices to Avoid Pitfalls
– Source from reputable, transparent suppliers with verifiable credentials
– Request product samples and conduct performance testing
– Verify IP ownership or licensing documentation
– Prioritize long-term value over initial cost
– Partner with suppliers who offer training support and warranties
By addressing quality and intellectual property concerns proactively, institutions can ensure they procure effective, compliant, and legally sound phlebotomy training tools.
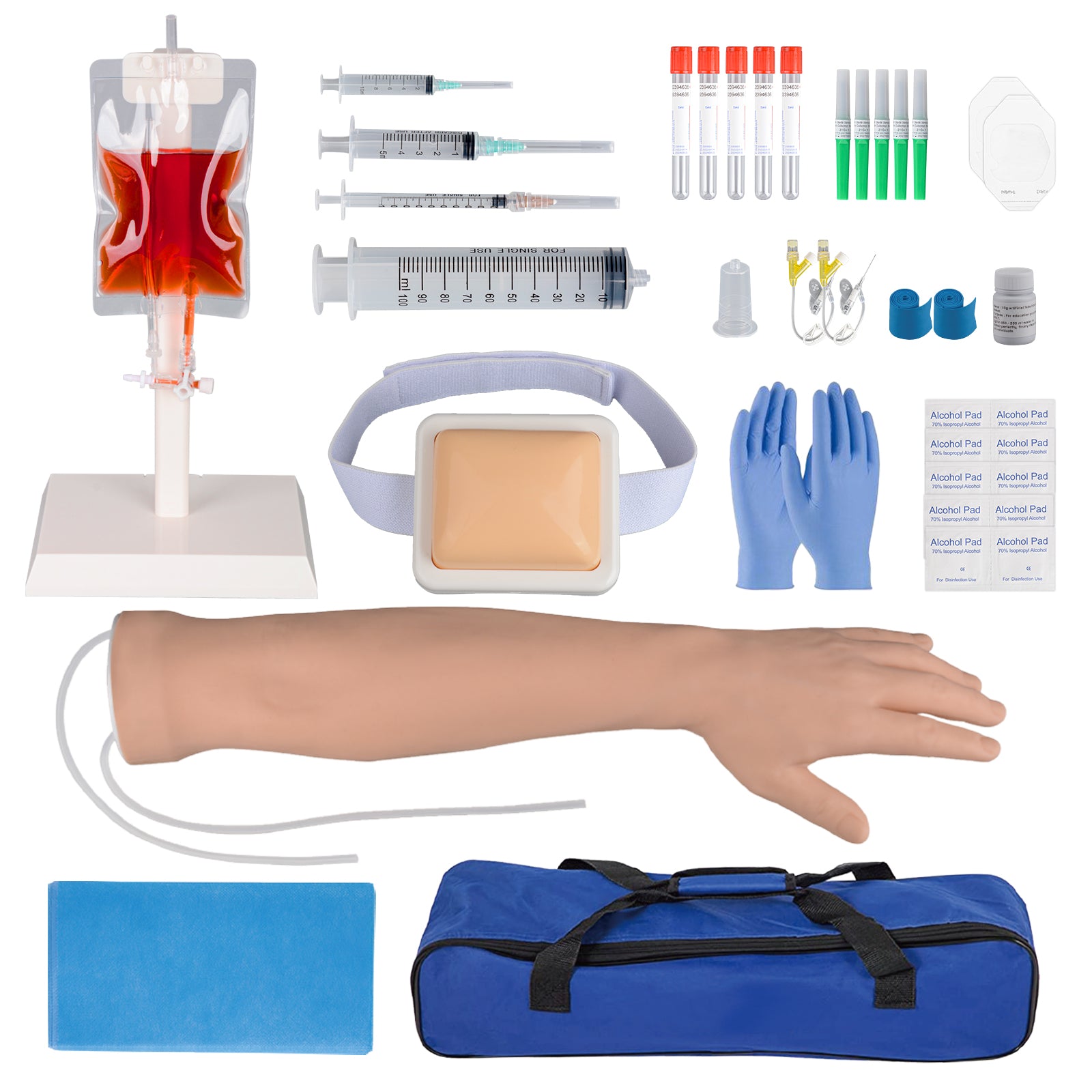
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Phlebotomist Practice Arm
This guide outlines the essential logistical considerations and compliance requirements for the operation of a phlebotomist practice arm within a healthcare facility, clinic, or laboratory setting. Adherence to these standards ensures patient safety, specimen integrity, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency.
Facility Layout and Equipment
Ensure the phlebotomy area is designed to promote patient comfort, workflow efficiency, and infection control. Designate clearly marked zones for patient check-in, waiting, specimen collection, and post-procedure observation. The space should include adjustable phlebotomy chairs or reclining seats, hand hygiene stations (soap, water, and alcohol-based hand sanitizer), sharps containers, biohazard waste bins, and a clean workspace for supplies. All equipment must be maintained according to manufacturer guidelines and undergo regular inspection.
Supply Management and Inventory Control
Maintain an organized, well-stocked inventory of phlebotomy supplies, including evacuated blood collection tubes, needles (various gauges), tourniquets, alcohol prep pads, gauze, bandages, gloves, and patient identification materials. Implement a first-expired, first-out (FEFO) system to prevent expired product usage. Conduct regular audits and document inventory levels to ensure continuity and prevent shortages. Store supplies according to manufacturer recommendations—typically in a clean, dry, temperature-controlled environment.
Specimen Collection Procedures
Standardize phlebotomy techniques across all practitioners to minimize errors and ensure patient safety. All phlebotomists must verify patient identity using two unique identifiers (e.g., full name and date of birth) prior to collection. Follow the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines for proper order of draw, venipuncture technique, and tube labeling at the bedside. Label tubes immediately after collection with patient name, ID, date, time, and collector initials. Avoid collection errors such as hemolysis, underfilling, or mislabeling through consistent training and adherence to protocols.
Infection Prevention and Control
Strict infection control practices are mandatory. All phlebotomists must perform hand hygiene before and after each patient encounter and wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, and potentially gowns or face protection depending on risk assessment. Use single-use, sterile needles and dispose of all sharps immediately into puncture-resistant containers. Disinfect collection chairs and surfaces between patients using EPA-registered disinfectants. Follow OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Standard (29 CFR 1910.1030) for exposure control, including post-exposure evaluation and follow-up.
Patient Safety and Comfort
Prioritize patient well-being throughout the phlebotomy process. Screen patients for risk factors such as fainting history, anticoagulant use, or difficult venous access. Use proper positioning and tourniquet application techniques to minimize discomfort. Observe patients post-draw for signs of adverse reactions (e.g., vasovagal response). Provide clear aftercare instructions, including pressure application and signs of complications. Offer support and reassurance, particularly to pediatric, geriatric, or anxious patients.
Documentation and Traceability
Accurate documentation is critical for compliance and patient care. Maintain a log of all specimen collections, including patient identifiers, test orders, time of draw, collector name, and any relevant observations (e.g., difficult draw, patient reaction). Integrate phlebotomy records with the facility’s electronic health record (EHR) or laboratory information system (LIS) to ensure traceability. Any specimen rejection or incident must be documented with root cause and corrective action.
Regulatory Compliance and Certification
Ensure all phlebotomists hold current certification from an accredited body (e.g., ASCP, NHA, or AMT) and maintain required continuing education. The practice arm must comply with federal, state, and local regulations, including CLIA (Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments), HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), OSHA, and CAP (College of American Pathologists) if applicable. Conduct regular internal audits and participate in proficiency testing programs to validate performance.
Training and Competency Assessment
Provide initial and ongoing training for all phlebotomy staff on collection techniques, safety protocols, emergency procedures, and customer service. Conduct annual competency assessments that include observation of venipuncture, knowledge testing, and review of documentation practices. Maintain training records for each employee as part of compliance documentation.
Specimen Transport and Chain of Custody
Establish protocols for secure and timely transport of specimens to the laboratory. Use appropriate biohazard transport containers and maintain required temperature conditions (e.g., room temperature, refrigerated, or frozen). For legally sensitive specimens (e.g., drug testing, forensic cases), implement a documented chain of custody process with tamper-evident seals and dual signatures to ensure legal defensibility.
Emergency Preparedness
Prepare for potential emergencies such as patient fainting, needlestick injuries, or blood spills. Train staff in basic first aid and CPR. Maintain an accessible emergency kit with supplies for managing fainting, bleeding, and exposure incidents. Ensure all staff know the location of emergency equipment and reporting procedures for occupational exposures per the facility’s Exposure Control Plan.
Quality Assurance and Continuous Improvement
Implement a quality management system to monitor performance indicators such as specimen rejection rates, patient satisfaction, and incident reports. Use data to identify trends and initiate corrective actions. Encourage staff feedback and conduct regular team meetings to review compliance, safety, and service improvements. Stay current with industry best practices and regulatory updates to maintain a high standard of care.
Conclusion:
Sourcing a phlebotomist practice arm is a crucial step in providing effective, hands-on training for aspiring phlebotomists. These simulation tools offer a safe and hygienic environment for learners to develop essential venipuncture skills, improving confidence and competence before working with real patients. When selecting a practice arm, it is important to consider factors such as realism, durability, ease of maintenance, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with training objectives. By investing in high-quality practice arms, educational institutions, healthcare training programs, and certification centers can enhance the learning experience, ensure consistent skill development, and ultimately contribute to higher standards of patient care in clinical settings. Therefore, thorough research and careful supplier evaluation are essential to obtaining reliable, realistic, and cost-efficient training tools that meet both educational and professional needs.