The global hand tools market, driven by steady demand from construction, automotive, and manufacturing sectors, is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 4.5% from 2023 to 2028, according to Mordor Intelligence. Within this expanding landscape, screwdrivers—particularly Phillips and flathead variants—remain foundational tools, accounting for a significant share of hand tool sales. As industries and DIY consumers alike prioritize durability, ergonomics, and precision, the demand for high-quality screwdriver manufacturing has intensified. This increasing need has elevated the prominence of leading global manufacturers who combine innovation, material excellence, and scalable production. Based on market presence, product range, and technological advancement, the following nine companies stand out as the top Phillips and flathead screwdriver manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 9 Phillips And Flathead Screwdriver Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Speciality Screwdriver Sets Made in the USA by Chapman …
Domain Est. 1998
Website: chapmanmfg.com
Key Highlights: Made in the USA for over 85 years, Chapman provides a variety of screwdriver sets for industrial assembly, maintenance, home repairs, and more….
#2 Screwdrivers individually or as a set
Domain Est. 2000
Website: wiha.com
Key Highlights: VDE + mechanics + with torque + bit screwdriver + ESD: Buy all screwdrivers online direct from the manufacturer + detailed guide….
#3 Screwdrivers
Domain Est. 1996
#4 Phillips screw and driver
Domain Est. 2006
Website: oregonencyclopedia.org
Key Highlights: The Phillips screw and driver, originally invented by Portlander John P. Thompson, dramatically increased the speed of manufacturing and made the Phillips ……
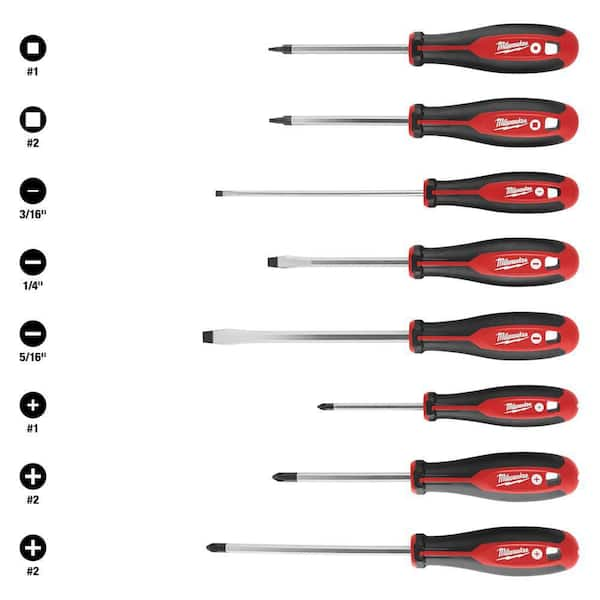
#5 Phillips and Flat Head Blade Through Type Screwdriver Set, PH1
Domain Est. 2010
#6 Screwdrivers
Domain Est. 2011
Website: protoindustrial.com
Key Highlights: Ratchet Stubby Screwdriver Set (17 pc.) PROTO® DURATEK™ #2 x 12 in. Phillips Round Bar Screwdriver….
#7 Screwdriver
Website: wera.de
Key Highlights: Professional filter · With flexible shaft · Ball tip · Torsion zone · Hollow shaft · Reduced blade and handle diameter · Halfmoon and HIOS · Suitable for Wera 2go….
#8 The Complete Guide to Screwdrivers
Domain Est. 2001
Website: uk.rs-online.com
Key Highlights: These tools are designed to fit screws with Phillips heads, which have a cross-shaped recess – hence the alternative name of cross screwdriver….
#9 Screwdriver Types and Uses
Domain Est. 2006
Website: redboxtools.com
Key Highlights: Also known as a slotted head screwdriver, flathead screwdrivers have a distinctive wedged-shaped tip that’s designed to fit slotted screws….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Phillips And Flathead Screwdriver
2026 Market Trends for Phillips and Flathead Screwdrivers
The market for traditional hand tools such as Phillips and flathead screwdrivers is expected to undergo subtle yet significant shifts by 2026, shaped by evolving consumer demands, technological integration, and sustainability considerations. While these tools remain fundamental in both professional and DIY settings, several key trends are likely to influence their production, distribution, and usage.
1. Steady Demand with Niche Growth
Despite the rise of powered tools and automated equipment, Phillips and flathead screwdrivers continue to maintain a stable market presence due to their reliability, affordability, and universal applicability. By 2026, demand is projected to remain consistent across construction, electronics repair, automotive maintenance, and home improvement sectors. The DIY (Do-It-Yourself) movement—fueled by online tutorials and home renovation trends—will sustain consumer-level demand, particularly in emerging markets where manual tools are more accessible than electric alternatives.
2. Innovation in Ergonomic and Multi-Functional Designs
Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on ergonomics, durability, and versatility. By 2026, expect widespread adoption of screwdrivers with enhanced grips, magnetic tips, and modular designs (e.g., interchangeable bits). Hybrid models combining Phillips, flathead, and other tip types in one handle will gain traction, especially in compact toolkits targeted at urban dwellers and tech repair specialists. These innovations aim to improve user comfort and efficiency without sacrificing the simplicity of traditional manual tools.
3. Premiumization and Brand Differentiation
The market is seeing a split between budget and premium screwdriver lines. High-end brands such as Wera, Wiha, and Klein Tools are investing in precision engineering, anti-slip coatings, and lifetime warranties to appeal to professional tradespeople. These premium tools are expected to command higher margins and grow in popularity as awareness of tool longevity and safety increases.
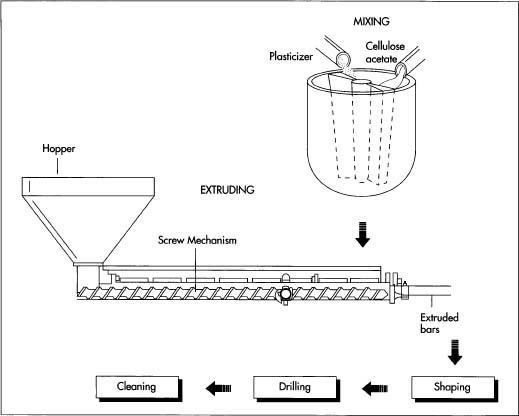
4. Sustainability and Material Innovation
Environmental concerns are influencing material choices. By 2026, manufacturers are likely to adopt more sustainable practices, such as using recycled steel for blades and bioplastics or responsibly sourced wood for handles. Packaging will shift toward minimal, recyclable materials, aligning with broader ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals in the hardware industry.
5. E-Commerce and Direct-to-Consumer Sales Growth
Online retail will continue to dominate screwdriver sales, with platforms like Amazon, Home Depot, and specialized tool websites offering detailed product comparisons, customer reviews, and bundled kits. Direct-to-consumer (DTC) models will allow niche brands to reach global audiences, bypassing traditional retail channels and enabling faster feedback loops for product development.
6. Impact of Automation and Smart Tools
While fully automated screwdriving systems are prevalent in manufacturing, the role of manual screwdrivers remains irreplaceable in precision tasks and small-scale repairs. However, by 2026, we may see the rise of “smart” manual tools—screwdrivers with torque sensors or Bluetooth connectivity for data logging—particularly in professional electronics and aerospace fields. These will complement rather than replace standard Phillips and flathead models.
7. Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, especially China and India, will drive volume growth due to urbanization and expanding middle classes investing in home tools. Meanwhile, North America and Europe will focus on quality, innovation, and after-sales service. Regulatory standards (e.g., ISO, ANSI) will continue to shape product design and safety compliance across regions.
Conclusion
By 2026, Phillips and flathead screwdrivers will remain essential tools in both industrial and household contexts. While the core functionality will stay unchanged, market evolution will center on design improvements, sustainability, and digital integration. Companies that adapt to these trends—balancing tradition with innovation—will be best positioned to thrive in the evolving hand tool landscape.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Phillips and Flathead Screwdrivers (Quality, IP)
Sourcing Phillips and flathead screwdrivers may seem straightforward, but several common pitfalls can compromise tool performance, safety, and longevity—especially when quality and Intellectual Property (IP) concerns are overlooked. Being aware of these issues ensures you procure reliable, authentic, and compliant tools.
Poor Material Quality and Durability
One of the most frequent issues is receiving screwdrivers made from substandard materials. Low-grade chrome vanadium steel or poorly heat-treated tips wear quickly, strip screw heads, or break under pressure. Inferior handles may crack or become slippery, increasing the risk of injury. Always verify material specifications and insist on third-party testing reports when sourcing in bulk.
Inaccurate Tip Dimensions and Fit
Many counterfeit or low-cost screwdrivers feature tips that don’t conform to ISO or ANSI standards. Misshapen or oversized Phillips (e.g., PH1, PH2) tips can cam out easily, damaging both the screw and the tool. Flathead tips may be too wide, too narrow, or improperly beveled. This lack of precision reduces efficiency and increases workplace frustration.
Lack of IP Compliance and Risk of Counterfeiting
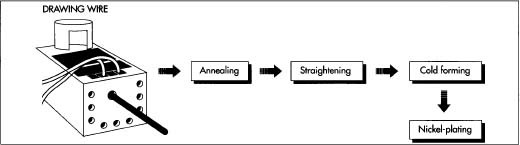
Reputable brands such as Wiha, Wera, and Klein invest heavily in patented tip designs, ergonomic handles, and anti-slip technologies. Sourcing unbranded or suspiciously cheap alternatives often means purchasing counterfeit tools that infringe on intellectual property rights. This exposes your company to legal liability, reputational damage, and unreliable tool performance.
Inadequate Insulation for Electrical Safety
If sourcing screwdrivers for electrical work, a major pitfall is selecting tools without proper VDE insulation certification. Non-compliant screwdrivers may look insulated but fail safety tests, putting users at risk of electric shock. Always confirm that insulated models are tested to IEC 60900 standards and bear clear certification markings.
Inconsistent Manufacturing and Batch Variability
Suppliers—especially those in unverified supply chains—may lack consistent quality control. This results in batch-to-batch variations in tip hardness, handle durability, or magnetic strength. Without reliable quality assurance processes, your team may receive tools that perform inconsistently across projects.
Misrepresentation of Features and Specifications
Some suppliers exaggerate features such as “drop-forged,” “anti-slip grip,” or “precision-machined tips” without providing evidence. Always request product samples, technical datasheets, and independent lab reports to verify claims before large-scale procurement.
Overlooking Ergonomic Design
Poorly designed handles can lead to hand fatigue, reduced torque, and long-term musculoskeletal issues. Tools that lack ergonomic certification (e.g., GS mark) may not support extended use. Assess handle shape, weight distribution, and slip resistance to ensure user comfort and safety.
By addressing these pitfalls during the sourcing process—through due diligence, supplier vetting, and sample testing—you can ensure the procurement of high-quality, IP-compliant Phillips and flathead screwdrivers that meet both performance and safety standards.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Phillips and Flathead Screwdrivers
Product Classification and Harmonized System (HS) Codes
Phillips and flathead screwdrivers are typically classified under the following HS codes for international trade:
– 8205.40: Hand tools (including non-powered tools) of a kind used in agriculture, horticulture, or the like; parts thereof.
– 8205.59: Other hand tools (e.g., screwdrivers, pliers, wrenches), not elsewhere specified.
Specific country variations may apply; always verify with local customs authorities.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
- Primary Packaging: Screwdrivers should be individually wrapped or clipped to a blister card to prevent damage and tampering.
- Secondary Packaging: Group units in corrugated cardboard boxes with dividers to avoid movement during transit.
- Labeling: Include product type (e.g., “Phillips #2 6-inch”), material (e.g., “Chrome Vanadium Steel”), country of origin, manufacturer details, and safety warnings (e.g., “Use with appropriate eye protection”).
- Barcodes: Apply UPC/EAN codes for retail distribution and inventory tracking.
Shipping and Transportation
- Mode of Transport: Suitable for air, sea, and ground freight. Air freight is recommended for urgent deliveries; sea freight for bulk shipments.
- Palletization: Use standard 48” x 40” pallets. Stack boxes securely and wrap with stretch film. Max pallet height: 72 inches.
- Weight Limits: Adhere to carrier-specific weight limits (e.g., 50 lbs per box for parcel services).
- Hazardous Materials: Screwdrivers are non-hazardous and do not require special handling under IATA, IMDG, or ADR regulations.
Import/Export Documentation
Required documents include:
– Commercial Invoice (with full product description, value, and HS code)
– Packing List (itemizing contents per package)
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin (if required by trade agreements)
– Import Declaration (completed by importer of record)
Regulatory Compliance
- RoHS (EU): Ensure compliance with Restriction of Hazardous Substances. Most screwdrivers meet RoHS as they contain no restricted electronics.
- REACH (EU): Confirm no SVHCs (Substances of Very High Concern) in materials used.
- Proposition 65 (California, USA): Provide warning labels if tools contain detectable lead in plating or handles.
- CPSC (USA): While not typically regulated as consumer products, ensure tools meet general safety standards for consumer use.
Storage Conditions
- Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment (10°C to 30°C).
- Avoid exposure to moisture to prevent rusting of metal components.
- Keep away from corrosive chemicals or solvents.
- Rotate stock using FIFO (First In, First Out) to maintain inventory freshness.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
- Use recyclable packaging materials (e.g., FSC-certified cardboard, biodegradable plastic blisters).
- Offer take-back or recycling programs for damaged tools where feasible.
- Source materials from suppliers with verified environmental management systems (e.g., ISO 14001).
Quality Assurance and Product Standards
- Comply with ISO 2380-1:2015 (Screwdrivers for slotted head screws) and ISO 8764 (Cross-recessed head screws).
- Conduct periodic quality checks for tip hardness, torque performance, and handle durability.
- Maintain documentation for traceability (batch numbers, production dates).
Returns and Reverse Logistics
- Accept returns only for defective or damaged items within 30 days of delivery.
- Issue return authorization (RMA) numbers and provide return shipping labels if applicable.
- Inspect returned items for eligibility; refurbish or recycle non-salvageable units responsibly.
Summary
Proper logistics and compliance management for Phillips and flathead screwdrivers ensure seamless international trade, regulatory adherence, and product integrity. Partner with certified suppliers and logistics providers, maintain accurate documentation, and stay updated on regional regulatory changes to minimize delays and avoid penalties.
Conclusion: Sourcing Phillips and Flathead Screwdrivers
In conclusion, sourcing Phillips and flathead screwdrivers requires careful consideration of quality, durability, intended application, and cost-effectiveness. Both types of screwdrivers are essential tools in various industries—including electronics, construction, manufacturing, and DIY home repairs—making it crucial to select reliable suppliers that offer consistent product standards. When sourcing, prioritize vendors that provide ergonomically designed tools made from high-grade steel to ensure longevity and user safety. Additionally, evaluating bulk pricing, supplier reputation, and compliance with international standards (such as ISO or ANSI) can help secure a sustainable and efficient supply chain. Ultimately, investing in high-quality Phillips and flathead screwdrivers from trusted sources enhances operational efficiency, reduces tool failure, and supports long-term project success.