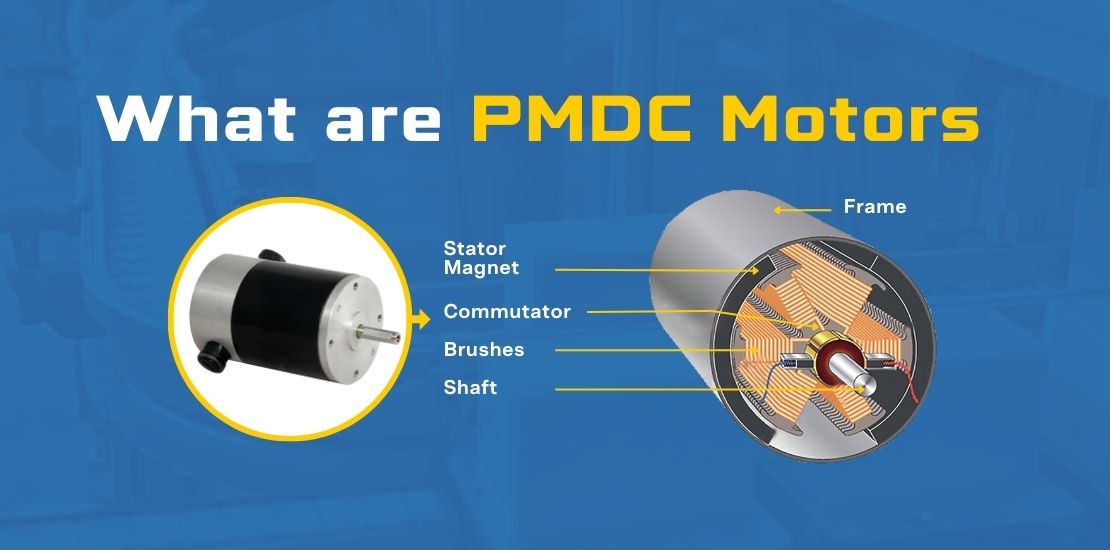
The global permanent magnet DC (PMDC) machine market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for energy-efficient motors across automotive, industrial, and consumer electronics sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global DC motor market size was valued at USD 11.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. Permanent magnet DC machines, in particular, are gaining traction due to their higher efficiency, compact design, and superior performance in variable-speed applications. Mordor Intelligence further highlights that advancements in Rare Earth magnets and the increasing adoption of PMDC motors in electric vehicles (EVs), medical devices, and robotics are key growth catalysts. With North America, Europe, and Asia Pacific leading in both production and demand, the competitive landscape is evolving rapidly. In this dynamic environment, a select group of manufacturers are emerging as leaders through innovation, scale, and global reach. Here’s a data-driven look at the top 10 permanent magnet DC machine manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 10 Permanent Magnet Dc Machine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 DC Motors with innovative winding technology
Domain Est. 1997
Website: faulhaber.com
Key Highlights: How do brushed DC motors work? The stator of a DC motor is a permanent magnet. Direct current is conducted into the rotor. This creates magnetic fields that are ……
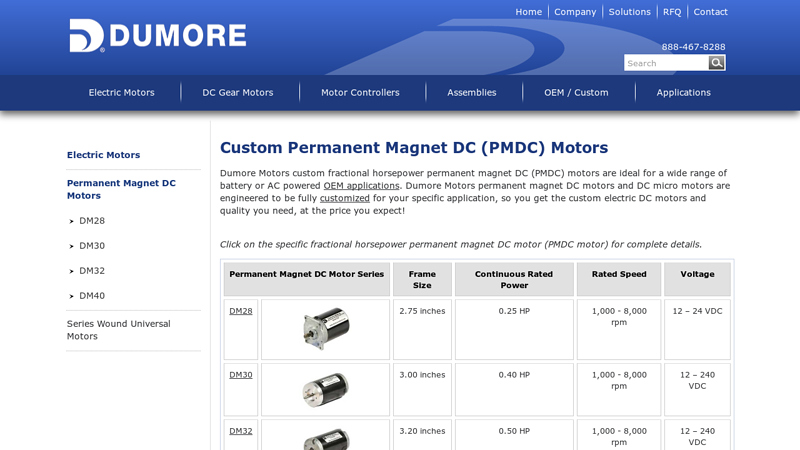
#2 Custom Permanent Magnet DC (PMDC) Motors
Domain Est. 2000
Website: dumoremotors.com
Key Highlights: Dumore Motors custom fractional horsepower permanent magnet DC (PMDC) motors are ideal for a wide range of battery or AC powered OEM applications….
#3 PMDC Permanent Magnet DC Motors
Domain Est. 1995
Website: kollmorgen.com
Key Highlights: Kollmorgen offers high performance PMDC motors which are designed for durability, quality construction and dependable operation….
#4 Fractional and Permanent Magnet
Domain Est. 1995
Website: baldor.com
Key Highlights: Our versatile permanent magnet (PM) DC motors. These range in output from 1/8 Hp to the industry’s only 5 Hp. Ruggedness, dependability and ease of use….
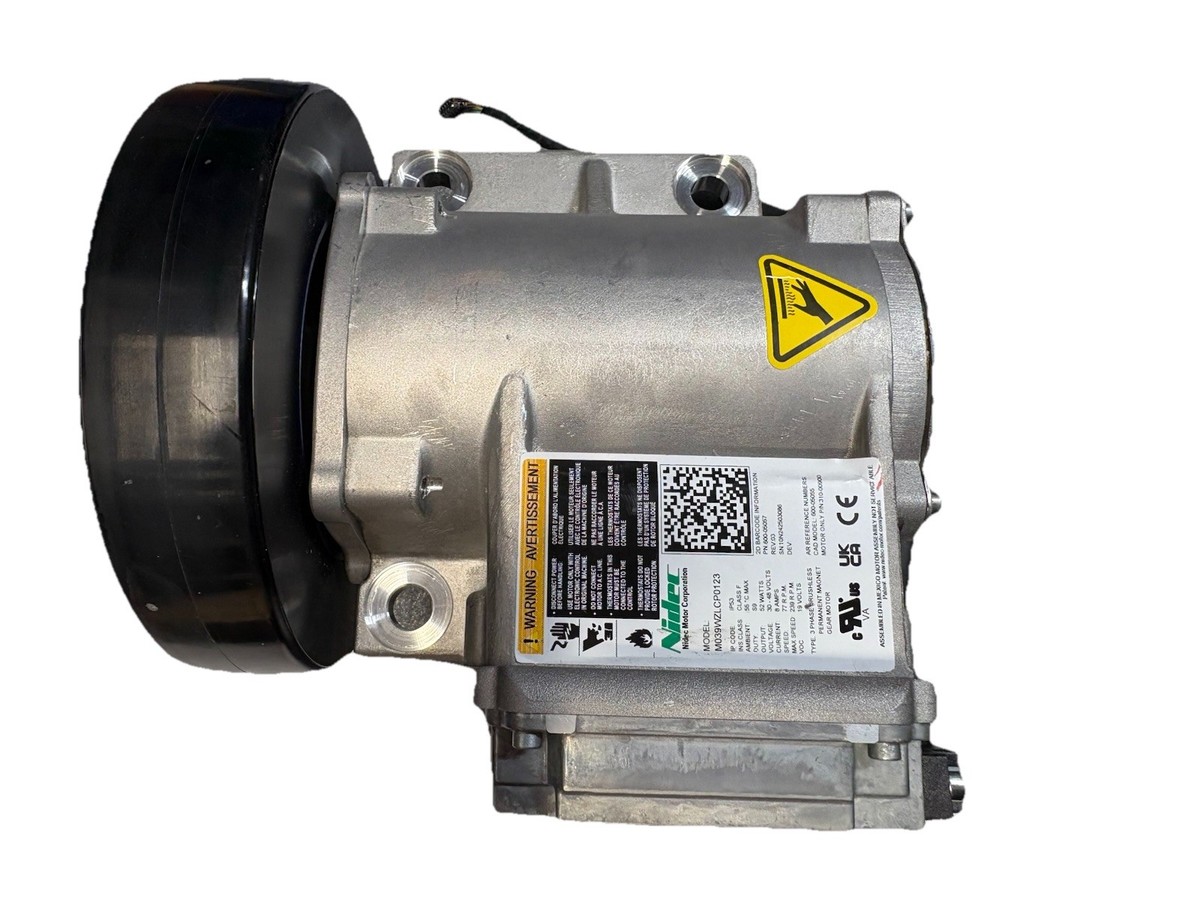
#5 Nidec Motors
Domain Est. 1997
Website: acim.nidec.com
Key Highlights: Permanent magnet motors under the Nidec Motor Corporation umbrella supply both the high power & reliable longevity that you need. Click here for more info….
#6 DC Motors
Domain Est. 1997
Website: bodine-electric.com
Key Highlights: 3-day deliveryShop our line of permanent magnet DC motors available in 24A, 33A and 42A frames. These cost-competitive gearmotors are ideal for adjustable speed ……
#7 Permanent Magnet DC Motors
Domain Est. 2001
Website: metmotors.com
Key Highlights: Met Motors provides three major classes of Permanent Magnet DC Motors in Wisconsin & Minnesota e.g. Brush DC, Brush less DC, Stepper Motors….
#8 Electric Motors
Domain Est. 2001
Website: arnoldmagnetics.com
Key Highlights: Arnold’s Ramco Electric Motors division manufactures a variety of AC Induction Rotors, DC Permanent Magnet Rotors, and Switched Reluctance Rotors. Learn ……
#9 Custom Permanent Magnet DC Motors
Domain Est. 2003
Website: ohioelectricmotors.com
Key Highlights: Ohio Electric Motors manufactures high-quality, custom-designed Permanent Magnet DC (PMDC) motors that provide superior performance and high-power density….
#10 Permanent
Domain Est. 2017
Website: luyangmotor.com
Key Highlights: Permanent-magnet DC motor can be directly connected to a DC power supply, or an AC power supply operated through a rectifier….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Permanent Magnet Dc Machine
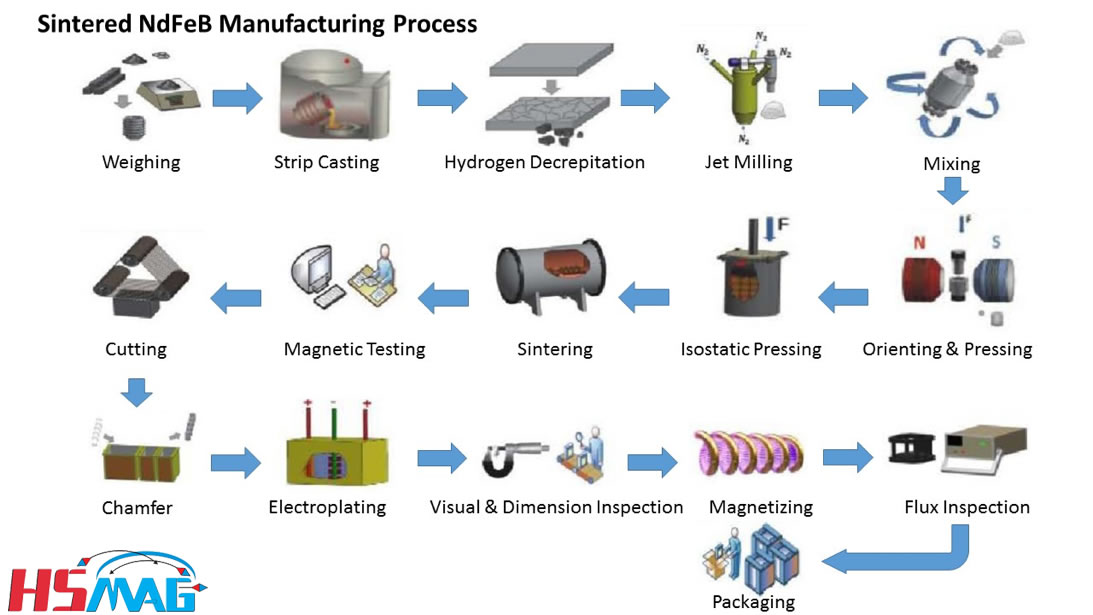
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Permanent Magnet DC Machines
As the global industrial and technological landscape evolves, the market for Permanent Magnet DC (PMDC) machines is undergoing significant transformation. By 2026, several key trends are expected to shape the demand, innovation, and competitive dynamics in this sector.
1. Steady Demand in Niche Applications
While brushless DC (BLDC) and AC motors continue to dominate due to higher efficiency and lower maintenance, PMDC machines retain relevance in specific niche applications. These include automotive subsystems (e.g., windshield wipers, power windows, seat adjusters), medical devices (e.g., portable infusion pumps, dental tools), and small household appliances. The simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and reliable performance of PMDC motors in low-to-medium power applications sustain their demand, particularly in cost-sensitive markets.
2. Impact of Rare Earth Material Volatility
The performance of PMDC machines heavily relies on rare earth permanent magnets, particularly neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB). Fluctuations in the supply and pricing of rare earth elements—driven by geopolitical tensions, export restrictions (especially from China), and increased competition from green technologies (e.g., EVs, wind turbines)—are expected to influence manufacturing costs. By 2026, manufacturers are likely to adopt strategies such as material substitution, magnet recycling, and localized supply chains to mitigate these risks.
3. Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, led by China, India, and Southeast Asia, will remain the largest market for PMDC machines due to expanding manufacturing bases, rising automotive production, and growing consumer electronics demand. Meanwhile, North America and Europe will see modest growth, driven by industrial automation and medical device innovation. However, stringent energy efficiency regulations in these regions may limit the expansion of traditional PMDC motors unless efficiency improvements are made.
4. Technological Enhancements and Hybrid Solutions
In response to efficiency standards, manufacturers are investing in improved magnet materials, optimized magnetic circuit design, and better thermal management. Some companies are exploring hybrid configurations that integrate PMDC principles with electronic controls to extend operational life and reduce brush wear. While these innovations may not displace BLDC motors in high-end applications, they extend the viability of PMDC machines in legacy and cost-driven systems.
5. Competitive Pressure from Brushless Alternatives
The ongoing shift toward brushless technologies remains a challenge. BLDC motors offer longer life, higher efficiency, and reduced maintenance—advantages that are increasingly prioritized in smart and connected devices. By 2026, PMDC machines are expected to occupy a shrinking but stable segment of the market, primarily in applications where initial cost and simplicity outweigh long-term efficiency considerations.
6. Sustainability and Regulatory Influence
Environmental regulations, such as the EU’s Ecodesign Directive and similar initiatives, are pushing for higher motor efficiency. While PMDC motors generally fall short of the efficiency levels of BLDC motors, they may benefit from exemptions in low-power categories. However, increasing emphasis on sustainability could accelerate the development of recyclable magnet systems and eco-friendly manufacturing processes within the PMDC segment.
Conclusion
By 2026, the Permanent Magnet DC machine market will likely experience moderate growth, supported by entrenched applications and regional industrial demand. While technological and regulatory headwinds favor more advanced motor types, PMDC machines will maintain a foothold through continuous innovation, cost leadership, and adaptation to specialized use cases. Companies that focus on supply chain resilience, material efficiency, and targeted application development will be best positioned to capitalize on this evolving market.
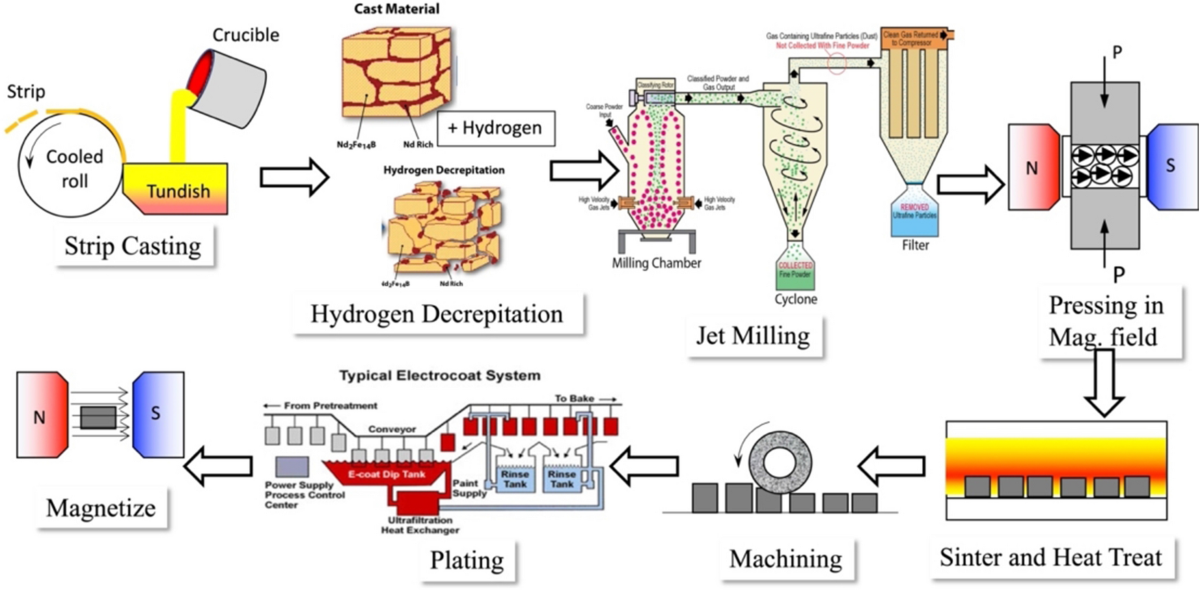
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Permanent Magnet DC Machines (Quality, IP)
Sourcing Permanent Magnet DC (PMDC) machines involves several critical considerations, particularly regarding quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to performance issues, supply chain disruptions, and legal risks.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Supplier Qualification
Failing to thoroughly vet suppliers is a leading cause of quality issues. Many low-cost manufacturers use substandard materials—such as lower-grade neodymium magnets or undersized copper windings—to cut costs, resulting in reduced efficiency, overheating, or premature failure. Without on-site audits or third-party testing, these inconsistencies often go undetected until after integration.
Inconsistent Manufacturing Processes
PMDC motors require precise assembly to maintain consistent magnetic alignment and air gap tolerances. Suppliers with poor process control may produce units with varying torque, speed, or lifespan. Lack of statistical process control (SPC) and inconsistent quality management systems (e.g., absence of ISO 9001 certification) increases the risk of batch-to-batch variability.
Insufficient Testing and Certification
Some suppliers provide only basic functional tests rather than comprehensive performance validation under real-world conditions. Missing critical tests—such as thermal endurance, vibration resistance, or life cycle testing—can result in field failures. Additionally, absence of compliance with international standards (e.g., IEC 60034) undermines reliability claims.
Poor Environmental and Mechanical Sealing (IP Rating Misrepresentation)
IP (Ingress Protection) ratings are often inaccurately claimed. A supplier may state an IP65 rating, but without proper testing documentation (e.g., from accredited labs), the motor may not actually resist dust or water jets. This is especially critical in industrial or outdoor applications where environmental resilience is essential.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Design Replication and Counterfeiting
Custom-designed PMDC motors are vulnerable to unauthorized replication. If contracts lack robust IP clauses or if manufacturing occurs in jurisdictions with weak IP enforcement, suppliers may reverse-engineer and sell identical designs to competitors.
Lack of Clear IP Ownership Agreements
Ambiguity in contracts about who owns the design, tooling, and specifications can lead to disputes. Without explicit transfer of IP rights or confidentiality agreements, buyers may lose control over their innovations, especially in collaborative development scenarios.
Insufficient Protection in Global Supply Chains
Sourcing from regions with lax IP regulations increases exposure to theft and unauthorized production. Even with NDAs, enforcing IP rights internationally can be costly and time-consuming. Failure to register designs or patents in key markets further weakens legal recourse.
Tooling and Fixture Misuse
Custom tooling used to manufacture specific motor components can be duplicated or reused without permission. Suppliers may use the same molds or jigs to produce parts for other clients, compromising design uniqueness and potentially violating IP agreements.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Conduct rigorous supplier audits and demand full traceability of materials.
– Require certified test reports and independent verification of IP ratings.
– Include strong IP clauses in contracts, specifying ownership, confidentiality, and usage rights.
– Limit production to trusted facilities and consider geographic risk in sourcing decisions.
– Use progressive tooling release and monitor production closely in custom projects.
Proactive due diligence in both quality and IP management is essential to ensure reliable, legally protected PMDC motor supply.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Permanent Magnet DC Machines
Product Classification and Regulatory Overview
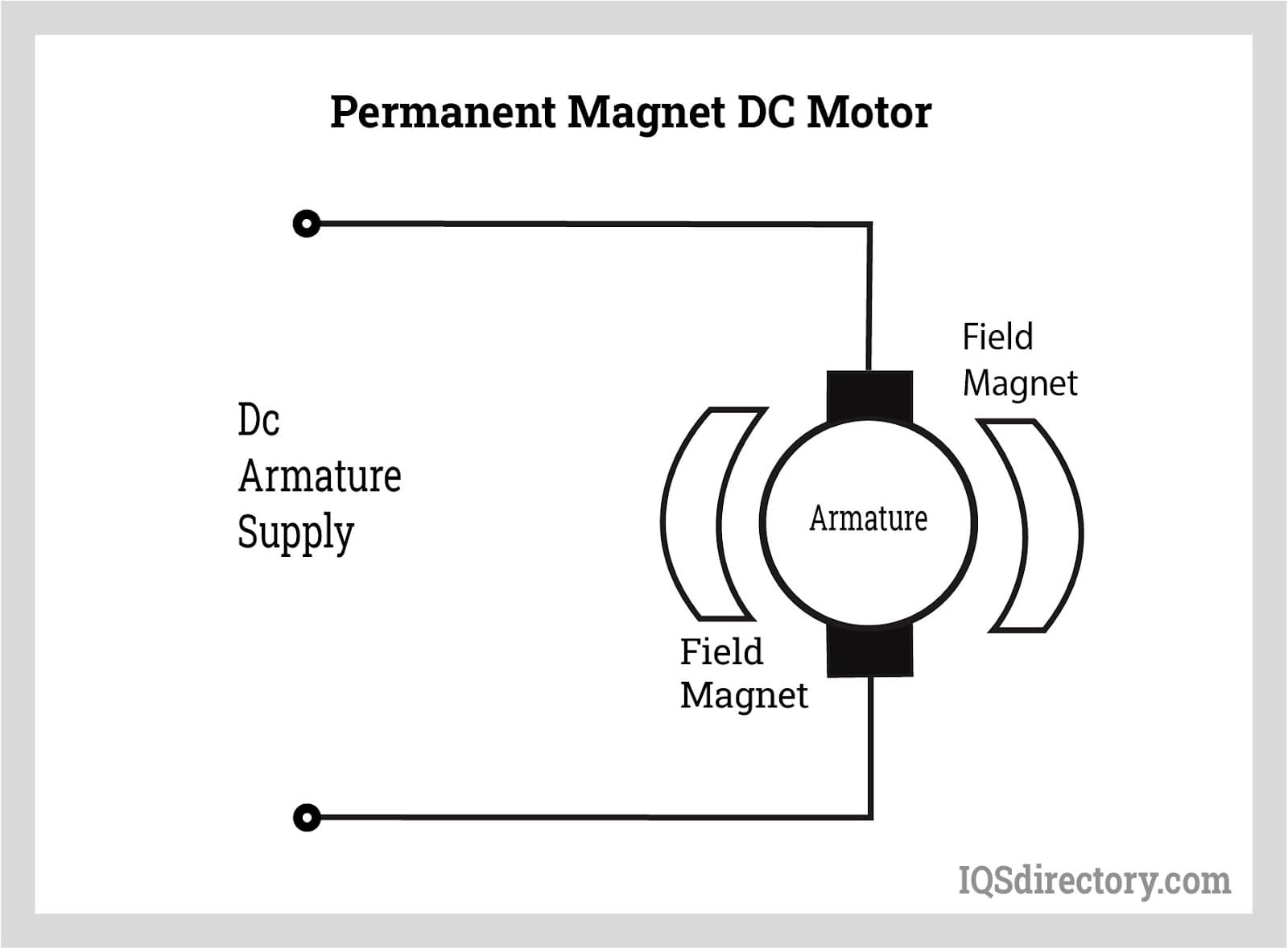
Permanent Magnet DC (PMDC) machines are electric motors that utilize permanent magnets in the stator to generate the magnetic field, eliminating the need for field windings. These devices are subject to various international and regional regulations based on their application, power rating, and destination market. Proper classification under the Harmonized System (HS) code is essential for customs clearance. Common HS codes include 8501.31 (DC motors and generators of an output not exceeding 750 W) or 8501.32 (exceeding 750 W), depending on specifications. Accurate classification ensures correct duty assessment and compliance with import/export controls.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging is critical to prevent mechanical and environmental damage during transit. PMDC machines should be packed in rigid, shock-absorbent materials such as double-walled cardboard boxes or wooden crates, especially for larger units. Internal components must be secured to prevent movement, and terminals should be protected with insulating caps or tape to avoid short circuits. Anti-corrosion measures such as VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) paper or desiccants should be used in humid environments. Labels must include handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”), product identification, and electrostatic-sensitive device (ESD) warnings if applicable.
Transportation and Shipping Considerations
PMDC machines are generally non-hazardous and can be shipped via air, sea, or land freight. However, motors containing rare-earth magnets (e.g., neodymium) may be subject to magnetic field restrictions during air transport under IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR), specifically Section II, if the magnetic field strength exceeds 0.00525 gauss at 4.6 meters (15 feet) from the package. Packages must be tested and labeled accordingly if they meet magnetic criteria. For sea freight, ensure compliance with IMDG Code guidelines when applicable. Use of temperature-controlled containers is recommended if the motor contains sensitive electronic components or lubricants.
Import/Export Documentation
Accurate and complete documentation is required for international shipments. Standard documents include:
– Commercial Invoice (declaring value, quantity, HS code, and country of origin)
– Packing List (detailing dimensions, weight, and contents per package)
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin (may be required for preferential tariff treatment)
– Export Declaration (required in the exporting country, such as the AES filing in the U.S.)
Additional certifications may be needed depending on the destination, including CE marking for the European Union, UKCA for the United Kingdom, or EAC for Eurasian Economic Union countries.
Regulatory Compliance and Certifications
PMDC machines must comply with electrical safety and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards in the target market:
– EU/UK: Must meet the Low Voltage Directive (LVD 2014/35/EU) and EMC Directive (2014/30/EU), typically demonstrated via CE/UKCA marking.
– North America: UL 1004 or CSA C22.2 No. 100 standards may apply for safety; FCC Part 15 Subpart B for EMC.
– Other Regions: Check local requirements (e.g., CCC in China, PSE in Japan, BIS in India).
Environmental compliance includes adherence to RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH (chemical safety) in the EU. Motors containing substances of very high concern (SVHCs) must be declared.
Customs Clearance and Tariff Management
To expedite customs clearance, ensure all documentation matches exactly. Provide technical specifications (voltage, power rating, RPM) to support HS code classification. Be aware of tariff rate quotas, anti-dumping duties, or trade restrictions that may apply to motors from certain countries. Use Authorized Economic Operator (AEO) programs where available to benefit from simplified customs procedures. Maintain records of compliance documentation for audit purposes, particularly for RoHS, REACH, and conflict minerals reporting if applicable.
End-of-Life and Environmental Responsibility
PMDC machines, especially those with rare-earth magnets, may be subject to WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) regulations in the EU and similar recycling laws elsewhere. Producers may be required to register with national WEEE schemes and contribute to take-back and recycling programs. Design for disassembly and include product marking (e.g., crossed-out wheeled bin symbol) where mandated. Provide information on proper disposal and recycling options to end-users.
Risk Mitigation and Audit Preparedness
Maintain a compliance management system that includes supplier declarations of conformity, test reports from accredited laboratories, and internal audits. Train logistics personnel on handling requirements and export controls. Regularly review regulatory updates in target markets. Keep records for a minimum of five years to support customs audits and product liability inquiries. Engage with customs brokers or compliance consultants for complex shipments or new market entries.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Permanent Magnet DC (PMDC) Machine
Sourcing a Permanent Magnet DC (PMDC) machine requires a careful evaluation of several key factors including performance requirements, application environment, efficiency, size, cost, and supplier reliability. PMDC machines are favored for their simplicity, high starting torque, compact size, and reliable operation in applications such as automotive systems, robotics, medical devices, and industrial automation.
When selecting a supplier, it is essential to prioritize manufacturers or distributors with proven quality standards, technical expertise, and consistent product availability. Consideration should be given to customization capabilities, lead times, after-sales support, and compliance with international standards (such as ISO, CE, or RoHS). Additionally, emerging trends such as energy efficiency regulations and the shift toward sustainable materials may influence long-term sourcing strategies.
In conclusion, a successful sourcing strategy for PMDC machines involves balancing technical specifications with supply chain stability and total cost of ownership. By partnering with reputable suppliers and conducting thorough due diligence, organizations can ensure reliable, efficient, and cost-effective integration of PMDC machines into their systems or products.