The global laboratory fume hood market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for safety infrastructure in research laboratories, pharmaceutical facilities, and academic institutions. According to Mordor Intelligence, the fume hood market was valued at USD 789.2 million in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% from 2023 to 2028. A key contributor to this expansion is the rising emphasis on chemical safety, particularly when handling hazardous substances like perchloric acid—used in digesting organic materials in analytical chemistry. Perchloric fume hoods, specifically designed to manage the corrosive fumes and explosive perchlorate salts generated during such processes, represent a critical niche within the broader fume hood sector. With stringent regulatory standards from OSHA and NFPA mandating the use of specialized ventilation systems for perchloric acid applications, demand for high-performance, code-compliant perchloric fume hoods continues to rise. This growing imperative has positioned several manufacturers as industry leaders, combining engineering precision, safety certification, and advanced airflow technology to serve sectors where contamination control and user protection are non-negotiable. Below are the top six perchloric fume hood manufacturers leading innovation and market share in this specialized domain.
Top 6 Perchloric Fume Hood Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
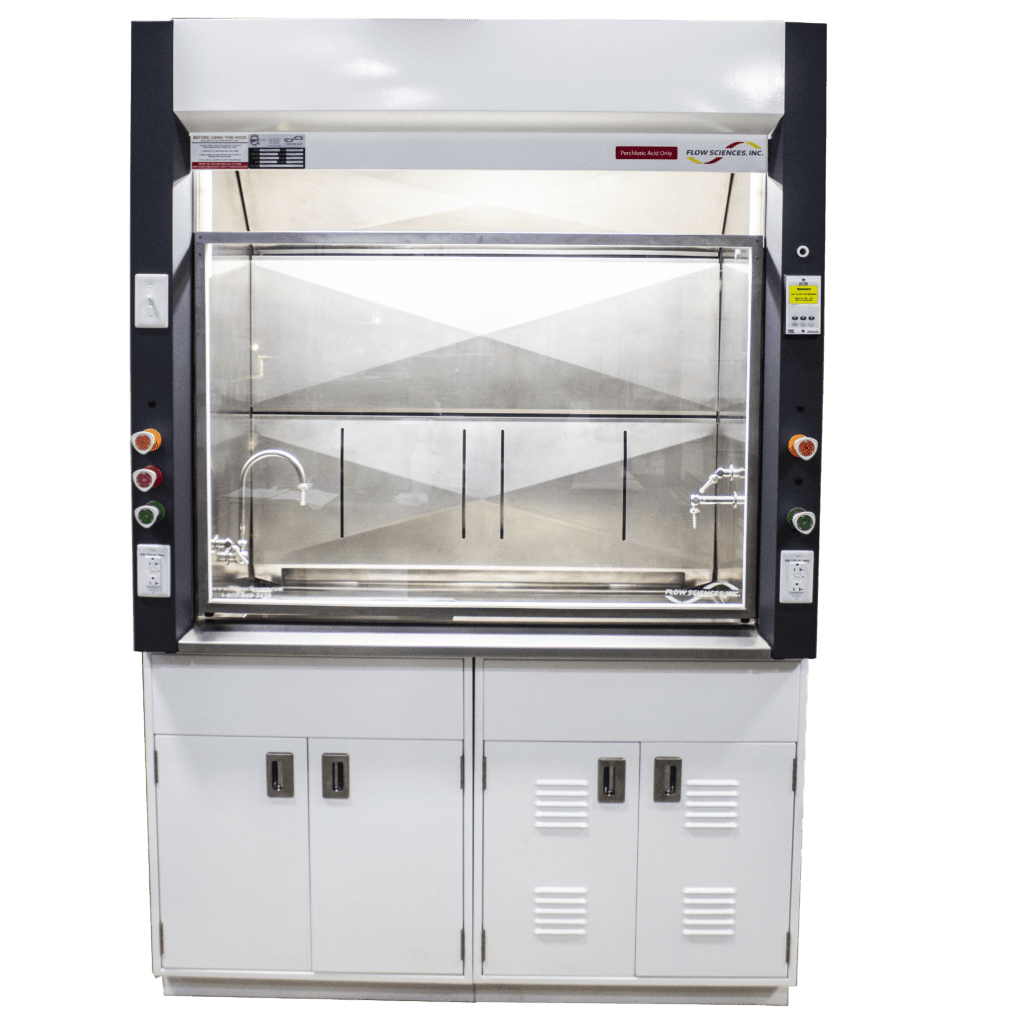
#1 Perchloric Acid Fumehood
Domain Est. 1998
Website: locscientific.com
Key Highlights: LOC’s Perchloric Acid Fume Hoods are expertly engineered for the safe handling of perchloric acid. These hoods feature a coved stainless steel liner….
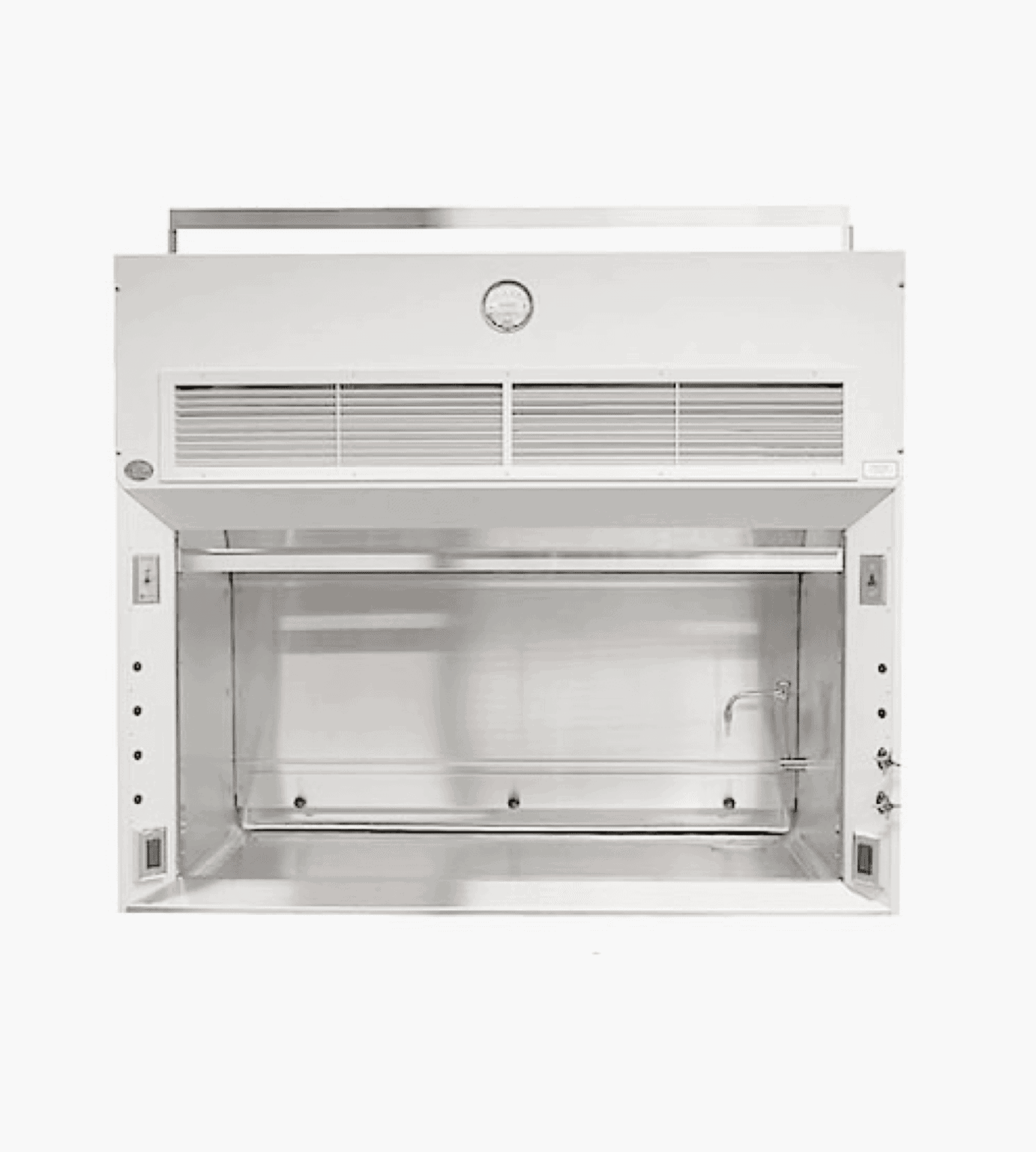
#2 UniFlow Perchloric Acid Fume Hoods
Domain Est. 1999
Website: hemcocorp.com
Key Highlights: Perchloric Acid hoods are offered in sizes 48”, 60”, & 72” widths and include a dedicated wash down and exhaust system. It is recommended to thoroughly wash ……
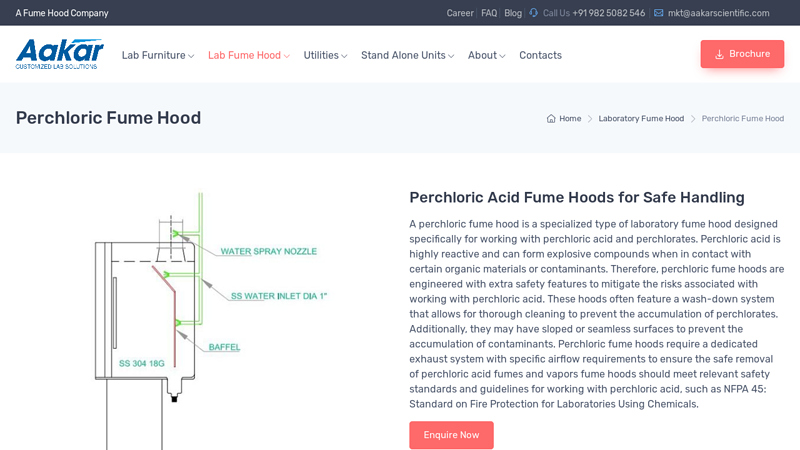
#3 Perchloric Fume Hood
Domain Est. 2001
Website: aakarscientific.com
Key Highlights: Buy high-quality Perchloric Fume Hoods from Aakar Scientific. Safe, durable, and compliant with NFPA 45 standards for handling perchloric acid in labs….
#4 Frontier® Perchloric Ducted Fume Hood
Domain Est. 2013
Website: escolifesciences.com
Key Highlights: Esco Frontier Perchloric Fume Hood (EFP) is a ducted fume hood designed for routine handling of hot perchloric acid and hot nitric acid….
#5 Perchloric Acid Fume Hoods
Domain Est. 2019
Website: h2igroup.com
Key Highlights: H2I Group offers perchloric acid fume hoods specifically designed for this extremely dangerous chemical to ensure safety and compliance within ……
#6 Why Buy a Perchloric Acid Fume Hood from iQ Labs?
Domain Est. 2020
Website: iq-laboratory.com
Key Highlights: With a full line of custom perchloric acid fume hoods to choose from, iQ Labs is your one-stop shop for custom stainless-steel fume hood design and ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Perchloric Fume Hood

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Perchloric Acid Fume Hoods
The market for Perchloric Acid Fume Hoods in 2026 is expected to be shaped by a confluence of regulatory, technological, and industrial forces, moving towards increased safety, integration, and specialized performance. Key trends include:
-
Heightened Regulatory Scrutiny & Standardization: Global safety standards (OSHA, ANSI/ASHRAE 110, EN 14175) will likely become even more stringent, particularly concerning trace perchlorate detection and worker exposure limits. This will drive demand for hoods with superior containment performance, mandatory wash-down systems meeting specific efficiency thresholds, and comprehensive validation protocols. Compliance will be non-negotiable, pushing adoption in both established and emerging markets.
-
Advanced Wash-Down System Integration & Automation: The defining feature of perchloric hoods – the integrated water wash-down system – will see significant innovation. Expect wider adoption of:
- Automated, Programmable Cycles: Timed, sensor-triggered wash-downs ensuring consistent and documented decontamination without relying on user diligence.
- Optimized Nozzle Design & Water Distribution: Enhanced coverage and efficiency to minimize water usage while maximizing salt dissolution and removal from difficult areas (baffles, ducts).
- Smart Monitoring: Integration with building management systems (BMS) to log wash-down cycles, water pressure, and system status for audit trails and predictive maintenance.
-
Material Science Advancements for Durability: Perchloric acid’s corrosive nature, especially when hot and concentrated, demands robust materials. The market will favor hoods constructed with:
- Enhanced 316L Stainless Steel: Improved passivation techniques and higher purity grades for superior resistance.
- Advanced Coatings & Liners: Exploration of specialized polymer linings or ceramic coatings within the plenum and ductwork for extreme environments, though stainless steel will remain the primary standard.
- Focus on Weld Integrity: Improved welding and finishing techniques to eliminate crevices where salts can accumulate.
-
Increased Focus on Energy Efficiency & Sustainability: While safety is paramount, pressure to reduce energy consumption will grow. Trends include:
- Variable Air Volume (VAV) Systems: Wider adoption of VAV controls that modulate exhaust volume based on sash position, maintaining safe face velocity while significantly reducing energy use compared to constant volume hoods.
- Low-Flow & High-Performance Designs: Development of hoods achieving required containment at lower minimum face velocities (e.g., 60 fpm instead of 100 fpm) through superior aerodynamics, further cutting energy costs.
- Energy Recovery Integration: Exploration of heat recovery systems on exhaust streams, though complexity and contamination risk remain challenges.
-
Growth in Demand from Specific High-Risk Sectors: Primary drivers will be industries heavily reliant on perchloric acid:
- Advanced Materials & Nanotechnology: Increased use in etching, digestion, and synthesis processes for novel materials.
- Pharmaceuticals & Biotechnology: Stringent purity requirements in analytical labs (e.g., ICP-MS sample prep) using perchloric acid.
- Defense & Aerospace: Continued need for materials testing and analysis involving perchlorate compounds.
- Environmental Testing: Monitoring for perchlorate contamination in water and soil will sustain demand in analytical labs.
-
Rise of Smart Hoods & IoT Integration: Perchloric hoods will become “smarter”:
- Real-time Containment Monitoring: Potential integration of trace gas sensors (though challenging) or advanced airflow sensors to provide immediate alerts on performance degradation.
- Predictive Maintenance: Sensors monitoring exhaust fan performance, filter status (if applicable), and wash-down system function to anticipate failures.
- User Interfaces & Data Logging: Digital displays showing sash position, face velocity, wash-down status, and connected to lab information management systems (LIMS) for compliance reporting.
-
Supply Chain Resilience & Sourcing Challenges: Geopolitical factors and material costs (especially high-grade stainless steel) may impact pricing and lead times. Manufacturers will focus on securing reliable supply chains and potentially regional manufacturing to mitigate risks.
Conclusion for 2026: The Perchloric Acid Fume Hood market in 2026 will be characterized by uncompromising safety standards, technological sophistication centered on automated wash-down and monitoring, a strong push for energy efficiency, and growth driven by high-tech industries. Success will belong to manufacturers offering robust, compliant, smart, and energy-conscious solutions backed by strong validation data and service support. The focus will shift from basic containment to intelligent, sustainable, and verifiably safe performance.

H2: Common Pitfalls in Sourcing a Perchloric Acid Fume Hood – Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing a perchloric acid fume hood requires careful attention due to the highly corrosive and potentially explosive nature of perchloric acid fumes. Improper selection or procurement can lead to safety hazards, regulatory non-compliance, and operational inefficiencies. Below are common pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP) when sourcing these specialized fume hoods, with mitigation strategies.
1. Compromised Build Quality and Material Selection
Pitfall:
Many suppliers offer fume hoods marketed as “perchloric acid compatible,” but use substandard materials (e.g., improper stainless steel grades, inadequate sealing, or non-compliant coatings), leading to corrosion, leakage, or crystalline perchlorate buildup—posing explosion risks.
IP and Quality Link:
Reputable manufacturers often hold proprietary designs and material specifications (e.g., ASTM-certified 316L stainless steel with electropolished surfaces). Counterfeit or imitation products may copy appearances but not critical internal engineering.
Mitigation (H2 Strategy):
– Verify compliance with ANSI/ASHRAE 114.5 and NFPA 45 standards.
– Require third-party certification (e.g., SEFA, UL) and material traceability reports.
– Avoid vendors unwilling to disclose material specs or fabrication processes.
2. Lack of Wash-Down System Integrity
Pitfall:
An effective perchloric fume hood requires a built-in automated wash-down system to dissolve and flush accumulated perchlorate crystals. Poorly designed or non-functional systems compromise safety.
IP Consideration:
Advanced wash-down mechanisms (e.g., rotating spray nozzles, programmable timers, drainage interlocks) may be protected by patents. Cloned versions often lack precision engineering, leading to dead zones or incomplete cleaning.
Mitigation (H2 Strategy):
– Request design schematics and operating manuals to assess system sophistication.
– Confirm IP-backed innovation (e.g., patent numbers) to ensure authenticity.
– Conduct on-site or video validation of wash-down cycle performance.
3. Counterfeit or Unlicensed Replicas
Pitfall:
Some suppliers offer “equivalent” fume hoods that mimic leading brands but infringe on patented designs. These may lack rigorous testing and fail under real-world conditions.
IP Risk:
Purchasing counterfeit or IP-infringing equipment exposes the buyer to legal liability and invalidates insurance or compliance certifications.
Mitigation (H2 Strategy):
– Source directly from OEMs or authorized distributors.
– Verify IP ownership (via patent databases like USPTO or WIPO).
– Include IP indemnification clauses in procurement contracts.
4. Inadequate Documentation and Design Transparency
Pitfall:
Suppliers may withhold critical documentation (e.g., CAD drawings, airflow validation data, corrosion resistance test results), making quality assessment impossible.
IP Justification Misuse:
Vendors may hide behind “proprietary design” claims to avoid sharing safety-critical data—an abuse of IP protection.
Mitigation (H2 Strategy):
– Require full technical disclosure as part of the procurement process.
– Use contractual terms that balance IP protection with safety transparency.
– Engage third-party engineers for independent design review.
5. Poor After-Sales Support and Design Lock-In
Pitfall:
Some suppliers use proprietary components (e.g., filters, controls) protected by IP, making maintenance costly or restricted to a single vendor.
Quality Impact:
This can lead to downtime or forced use of overpriced parts, affecting long-term operational quality.
Mitigation (H2 Strategy):
– Negotiate for open standards or modular designs.
– Secure licensing rights or spare parts agreements upfront.
– Evaluate total cost of ownership, not just purchase price.
Conclusion (H2 Summary):
Sourcing a perchloric acid fume hood demands due diligence in both quality assurance and IP legitimacy. Prioritize vendors with certified designs, transparent engineering, and verifiable IP rights. Avoid cost-driven decisions that compromise safety or expose your institution to legal risk. Always validate claims with documentation, standards compliance, and independent verification.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Perchloric Acid Fume Hoods
Perchloric acid fume hoods are specialized ventilation systems designed to safely handle perchloric acid, a strong oxidizer that can form explosive perchlorate salts when concentrated or in contact with organic materials. Proper logistics, handling, and compliance are essential to ensure safety, regulatory adherence, and operational efficiency.
H2.1 Regulatory Compliance
Perchloric acid fume hoods must comply with multiple national and international standards and regulations:
-
OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration)
OSHA 29 CFR 1910.1450 (Laboratory Standard) requires that fume hoods used for hazardous chemicals, including perchloric acid, provide adequate ventilation and containment. Specific guidance is provided for handling oxidizers. -
NFPA 45: Standard on Fire Protection for Laboratories Using Chemicals
NFPA 45 mandates that fume hoods used with perchloric acid must be: - Constructed of noncombustible, corrosion-resistant materials (e.g., stainless steel).
- Equipped with a wash-down system to prevent crystallization of perchlorate residues.
-
Clearly labeled as “PERCHLORIC ACID – WASH DOWN REQUIRED.”
-
ASHRAE Standard 110: Method of Testing Performance of Laboratory Fume Hoods
Performance testing (face velocity, tracer gas containment) must be conducted annually or after modifications. Perchloric hoods must pass ASHRAE testing under operational conditions. -
EPA & DOT Regulations
- The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates waste disposal of perchloric acid and its residues.
- The Department of Transportation (DOT) governs the transportation of perchloric acid (classified as a Class 5.1 oxidizer; UN1874 or UN2032 depending on concentration).
H2.2 Installation & Design Requirements
- Material Specifications: Hood interior, ductwork, and plenum must be made of 316L stainless steel to resist corrosion.
- Duct System: Dedicated, continuously welded stainless steel ducting with minimal horizontal runs to prevent residue accumulation.
- Wash-Down System: Must include:
- Automatic or manual internal spray nozzles.
- Capability to rinse interior surfaces, baffles, and ductwork.
- Weekly wash-down recommended; documented in lab safety protocols.
- Exhaust System: Direct to an external scrubber or treated exhaust system capable of neutralizing perchloric acid vapors.
- Location: Installed away from combustible storage and traffic areas. Clear signage required.
H2.3 Operational Logistics
- User Training: Personnel must be trained in:
- Safe handling of perchloric acid.
- Proper use of the fume hood.
- Wash-down procedures.
- Emergency response (spills, fire).
- Usage Logs: Maintain logs for:
- Date and time of perchloric acid use.
- Wash-down records.
- Maintenance and testing.
H2.4 Maintenance & Inspection
- Routine Inspections:
- Monthly visual checks for corrosion or residue buildup.
- Annual ASHRAE 110 performance testing.
- Wash-Down Maintenance: After each use involving heated perchloric acid, conduct a wash-down. Weekly wash-downs are required even if not used.
- Filter & Duct Inspection: Inspect ductwork and exhaust filters for perchlorate accumulation; clean/replace as needed.
- Certification: Documented certification by a qualified technician is required annually.
H2.5 Decommissioning & Disposal
- Decontamination: Before service or removal, fully decontaminate the hood and duct system using approved wash-down procedures.
- Waste Disposal: Perchloric acid waste must be:
- Collected in compatible, labeled containers.
- Neutralized or disposed of via licensed hazardous waste handlers.
- System Decommissioning: If removing the hood, inspect and clean the entire duct run to prevent explosive residue.
H2.6 Emergency Preparedness
- Spill Response: Use non-combustible absorbents (e.g., vermiculite). Never use paper or cellulose.
- Fire Response: Use water spray to cool containers; do not use dry chemical extinguishers unless directed.
- Evacuation Plan: Include perchloric acid incidents in lab emergency plans. Notify fire department of perchloric acid use.
H2.7 Documentation & Recordkeeping
Maintain records for:
– Installation specifications and certifications.
– Wash-down logs.
– Training records.
– Inspection and maintenance reports.
– Incident reports involving perchloric acid.
Adhering to this logistics and compliance guide ensures safe operation, regulatory compliance, and protection of personnel and facilities when using perchloric acid fume hoods.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Perchloric Acid Fume Hood:
Sourcing a perchloric acid fume hood is a critical step in ensuring laboratory safety, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency when handling perchloric acid—a highly reactive and potentially hazardous chemical. After evaluating various suppliers, design features, material compatibility, and compliance standards (such as NFPA 45 and OSHA guidelines), it is evident that selecting a properly certified perchloric acid fume hood with a wash-down system, seamless stainless steel construction, and UL-listed components is essential.
The ideal solution combines robust engineering, long-term durability, and adherence to safety protocols to mitigate risks such as explosion, corrosion, and exposure to toxic fumes. Additionally, considering lifecycle costs, service support, and ease of maintenance will enhance sustainability and operational continuity.
In conclusion, investing in a high-quality, purpose-built perchloric acid fume hood from a reputable manufacturer, coupled with proper installation, training, and regular maintenance, ensures a safe working environment and protects both personnel and infrastructure from the unique hazards associated with perchloric acid use. This strategic sourcing decision underscores a commitment to safety, compliance, and scientific integrity in the laboratory.