The global peanut butter market has experienced steady growth, driven by rising consumer demand for protein-rich, plant-based spreads and expanding distribution channels. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at approximately USD 4.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.5% from 2024 to 2029. This growth is propelled by increasing health consciousness, product innovation (such as reduced-sugar and organic variants), and rising popularity in both developed and emerging markets. As consumer preferences shift toward natural ingredients and convenient snacking options, key manufacturers are scaling production, enhancing supply chains, and investing in sustainable sourcing. In this competitive landscape, the top 10 peanut butter manufacturers stand out through market reach, product diversification, and strategic brand positioning—shaping the future of one of the world’s most beloved pantry staples.
Top 10 Peanut Butter Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 John B. Sanfilippo & Son, Inc.
Domain Est. 1997
Website: jbssinc.com
Key Highlights: Customers and consumers across the country and around the world turn to John B. Sanfilippo & Son (JBSS) as the nut industry leader it is today….
#2 Texas Peanuts
Domain Est. 1998
Website: texaspeanuts.com
Key Highlights: We are Texas Peanut advocates. Our team works on behalf of producers, promoting Texas Peanut production and all that it entails. Contact us today for more ……
#3 Golden Peanut
Domain Est. 1998
Website: goldenpeanut.com
Key Highlights: Golden Peanut is a global company that partners with manufacturers to provide a full range of peanut ingredients….
#4 Peanut & Tree Nut Butter Manufacturing Solutions
Domain Est. 2015
Website: postconsumerbrands.com
Key Highlights: 8th Avenue is a leading nut butter manufacturer offering high-quality peanut and tree nut butters and private label solutions….
#5 American Dream Nut Butter
Domain Est. 2020
Website: americandreamnutbutter.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $75I personally source every ingredient from top-notch farms and manufacturers. Every jar is made in small batches, just for you – no sitting on store shelves….
#6 Jif® Peanut Butter
Domain Est. 1995
Website: jif.com
Key Highlights: Whether you spoon it, squeeze it or scoop it, Jif® peanut butter makes it better. Find it online or in a store near you….
#7 Peanut Butter & Co • Family Owned • USA
Domain Est. 1999
Website: ilovepeanutbutter.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $49Have you tried our 10 delicious flavors of peanut butter? Find recipes, coupons, store locations and explore our powdered peanut butter, squeeze packs, ……
#8 SKIPPY ® peanut butter
Domain Est. 1999
Website: peanutbutter.com
Key Highlights: Nothing beats the simple pleasures in life, like a clean spoon and a smooth, fresh jar of SKIPPY® Peanut Butter….
#9 Laura Scudder’s Peanut Butter
Domain Est. 2007
Website: laurascudderspeanutbutter.com
Key Highlights: Our natural peanut butter varieties are made with 99% fresh-roasted peanuts and little to no salt. The difference is delightful….
#10 Spread The Love
Domain Est. 2013
Website: spreadthelovefoods.com
Key Highlights: Spread The Love: Shop all-natural nut butters and spreads! Family-made, high-quality products with no junk. Taste the love today!…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Peanut Butter

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Peanut Butter
The global peanut butter market in 2026 is expected to reflect significant shifts driven by evolving consumer preferences, health awareness, sustainability concerns, and innovation in product offerings. As plant-based diets and clean-label foods gain momentum, peanut butter—a staple pantry item in many households—continues to adapt to meet modern demands. Here are the key trends shaping the peanut butter market in 2026:
-
Rise of Health-Conscious Formulations
Peanut butter brands are increasingly focusing on clean-label, organic, and minimally processed options. Consumers in 2026 are seeking products with no added sugar, reduced sodium, no hydrogenated oils, and non-GMO certifications. There is also growing interest in peanut butter fortified with protein, fiber, or functional ingredients like probiotics and adaptogens, catering to wellness-oriented buyers. -
Plant-Based and Allergen-Friendly Alternatives
Despite peanut butter’s popularity, the rise of nut allergies and plant-based diets has led to hybrid products and blends—such as peanut-almond or peanut-sunflower mixes—that offer diversified nutrition and appeal to a broader audience. Additionally, allergen-free facilities and transparent labeling are becoming industry standards to build consumer trust. -
Premiumization and Flavor Innovation
The market is witnessing a surge in premium peanut butter offerings with gourmet flavors such as sea salt dark chocolate, cinnamon swirl, spicy chili, and botanical-infused variants. These premium products often feature sustainable packaging and ethical sourcing, aligning with the values of affluent and environmentally conscious consumers. -
Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing
By 2026, sustainability is a decisive factor in purchasing decisions. Leading peanut butter brands are investing in regenerative farming practices, carbon-neutral production, and fair-trade sourcing of peanuts. Transparent supply chains and eco-friendly packaging, such as compostable jars or recyclable materials, are becoming competitive differentiators. -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
While North America remains the largest consumer of peanut butter, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa are showing strong growth potential. Increased urbanization, exposure to Western diets, and rising disposable incomes are driving demand. Localized flavor adaptations are helping brands penetrate these new regions effectively. -
E-Commerce and Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) Growth
Online sales channels continue to expand, with specialty and artisanal peanut butter brands leveraging e-commerce platforms and subscription models. Personalization, bundling with snacks, and educational content about peanut farming and nutrition are enhancing customer engagement. -
Private Label and Retailer Influence
Major retailers are investing in high-quality private-label peanut butter lines, often matching or exceeding national brands in quality while offering competitive pricing. This trend is increasing price competition and pushing established brands to innovate further.
In conclusion, the 2026 peanut butter market is characterized by a blend of tradition and innovation. As consumers demand more from their food—nutritionally, ethically, and experientially—manufacturers and retailers must stay agile, transparent, and responsive to maintain relevance and drive growth.
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Peanut Butter: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
Sourcing peanut butter—whether for private label branding, food manufacturing, or retail distribution—can be fraught with challenges, especially when it comes to ensuring consistent quality and protecting intellectual property. Understanding these pitfalls early can prevent costly mistakes, brand damage, and legal complications.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Raw Material Sourcing
One of the most significant quality issues arises from variability in raw peanuts. Factors such as origin, crop season, and storage conditions can impact flavor, texture, and safety. Sourcing peanuts from multiple unvetted suppliers may result in inconsistent roasting profiles, oil separation, or off-flavors.
Poor Manufacturing Practices
Suppliers with substandard hygiene or outdated processing methods may introduce contaminants such as aflatoxins (toxic molds) or allergen cross-contact. Inadequate temperature control during roasting or grinding can also compromise shelf life and sensory qualities.
Lack of Quality Control Testing
Reliable peanut butter production requires rigorous testing for microbiological safety, heavy metals, and allergen presence. Suppliers that skip batch testing or lack third-party certifications (e.g., SQF, BRCGS) pose a significant risk to brand integrity.
Additive and Ingredient Transparency
Some suppliers use low-cost additives like palm oil, sugar, or hydrogenated fats to reduce costs or improve texture. Without clear ingredient disclosure, buyers may unknowingly source products that don’t meet clean-label or nutritional claims, potentially misleading consumers.
Inadequate Packaging and Shelf Life Management
Poor packaging—such as non-barrier materials or improper sealing—can lead to rancidity or moisture ingress. Additionally, inaccurate shelf-life determination may result in product spoilage before reaching consumers.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
Private Label Formulation Theft
When working with contract manufacturers, especially overseas, there’s a risk that your proprietary peanut butter formula (including unique blends, textures, or flavor profiles) could be replicated and sold to competitors without authorization.
Branding and Trademark Infringement
Using a name, logo, or packaging design that inadvertently infringes on an existing trademark can lead to legal disputes. This is especially common when entering new markets where similar brands may already exist.
Copycat Products by Suppliers
Some manufacturers produce identical or very similar products under different brand names. If your supplier sells the same formulation to others under competing private labels, it dilutes your brand’s uniqueness and market position.
Lack of IP Agreements
Failing to establish clear contractual terms—such as work-for-hire clauses, confidentiality agreements (NDAs), and IP ownership provisions—leaves your formulations and branding vulnerable. Always ensure that legal agreements explicitly assign IP rights to your company.
Reverse Engineering Risks
Peanut butter is relatively simple to analyze chemically. Without protective measures (e.g., trade secret safeguards or patented processes), your product could be reverse-engineered, especially if it gains market traction.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct thorough supplier audits and request certifications.
- Require batch-specific quality test reports.
- Use legally binding agreements to secure IP rights.
- Register trademarks in all target markets.
- Limit access to proprietary information on a need-to-know basis.
- Consider patenting unique processing techniques or formulations if applicable.
Avoiding these common pitfalls requires due diligence, clear contracts, and ongoing quality monitoring. Proactive management of both quality and IP issues ensures a reliable, defensible, and competitive peanut butter product in the marketplace.
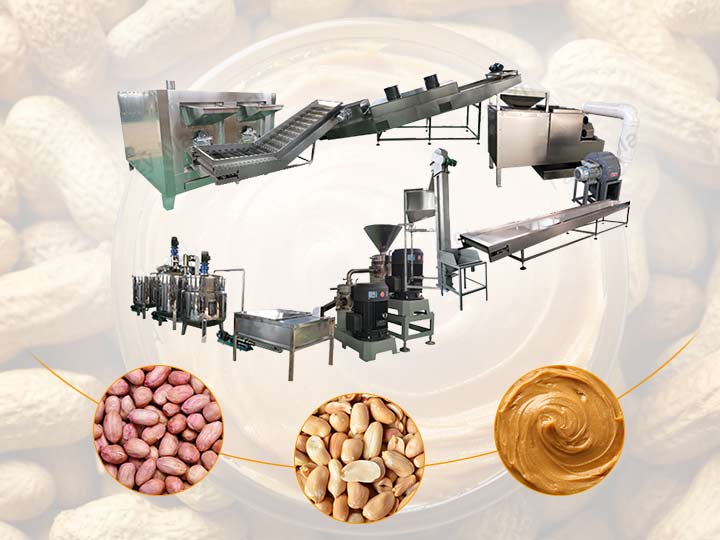

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Peanut Butter
Peanut butter is a widely traded food product, but its transportation, storage, and sale are subject to various regulatory and logistical requirements to ensure safety, quality, and compliance. This guide outlines key considerations for handling peanut butter across the supply chain.
Regulatory Compliance
Peanut butter must comply with food safety regulations in both the country of origin and the destination market. Key regulatory frameworks include:
- U.S. FDA (Food and Drug Administration): Under the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA), manufacturers and distributors must implement hazard analysis and risk-based preventive controls (HARPC). Peanut butter is considered a high-risk product due to past Salmonella outbreaks.
- USDA/FDA Jurisdiction: In the U.S., peanut butter falls under FDA regulation (not USDA), as it is a processed food product.
- Labeling Requirements: Must include ingredient list, allergen declaration (peanuts are a major allergen), nutrition facts, net quantity, and manufacturer/distributor information. Declaration of “may contain tree nuts” is required if cross-contact is possible.
- EU Regulations: Complies with EU Regulation (EC) No 178/2002 (General Food Law) and Regulation (EC) No 852/2004 on food hygiene. Allergen labeling must follow EU Directive 2000/13/EC.
- Codex Alimentarius: Provides international standards for peanut butter composition and labeling, which many countries reference.
Allergen Control and Cross-Contamination
- Allergen Management: Peanuts are a top allergen. Facilities producing peanut butter must implement strict allergen control programs to prevent cross-contact with other products.
- Dedicated Lines or Scheduling: Use dedicated production lines or clean thoroughly between runs if shared with tree nut or other allergen-containing products.
- Supplier Verification: Ensure raw peanuts and ingredients are sourced from approved, audited suppliers with allergen control protocols.
Storage and Handling
- Temperature Control: Store peanut butter at temperatures between 50°F and 70°F (10°C to 21°C) to prevent oil separation and maintain consistency. Avoid extreme heat or cold.
- Humidity: Maintain low humidity (below 65%) to prevent moisture absorption, which can promote microbial growth.
- Shelf Life: Typically 9–12 months for unopened products. Monitor expiration dates and practice FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory rotation.
- Packaging Integrity: Ensure containers (jars, pails, or totes) are sealed properly to prevent contamination and oxidation.
Transportation Requirements
- Container Conditions: Use food-grade, clean, and sanitized vehicles or containers. Avoid transporting with non-food items or allergen-containing goods unless properly segregated.
- Temperature Monitoring: While peanut butter does not require refrigeration, avoid prolonged exposure to high temperatures (>85°F / 29°C) during transit to prevent quality degradation.
- Pest Control: Ensure transport vehicles are pest-free and protected from contamination.
- Documentation: Maintain Bills of Lading, Certificates of Analysis (CoA), and Sanitation Certificates where required.
Import/Export Considerations
- Customs Documentation: Include commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, and certificate of origin.
- Food Facility Registration (U.S.): Foreign facilities exporting peanut butter to the U.S. must register with the FDA.
- Prior Notice (U.S.): Submit prior notice of food shipment to FDA before arrival.
- Import Licenses: Some countries require import permits or pre-approval for dairy or nut-based products.
- Phytosanitary Certificates: Not typically required for processed peanut butter, but may be needed for raw peanuts or certain formulations.
Quality and Testing
- Microbiological Testing: Regularly test for pathogens such as Salmonella and Listeria monocytogenes, especially in ready-to-eat products.
- Aflatoxin Testing: Raw peanuts must be tested for aflatoxin levels (regulated limit: typically 20 ppb in the U.S., 4 ppb for direct human consumption in EU).
- Certificate of Analysis (CoA): Provide CoA with each batch, including results for microbiological safety, aflatoxin, and nutritional content.
Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing
- Responsible Sourcing: Ensure peanuts are sourced from farms that follow good agricultural practices (GAP) and avoid child or forced labor.
- Packaging: Use recyclable or sustainable packaging materials where possible to meet environmental standards.
Adhering to this logistics and compliance guide ensures that peanut butter is safely produced, transported, and distributed while meeting all legal and quality requirements across global markets.
In conclusion, sourcing peanut butter manufacturers requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, scalability, and compliance. It is essential to thoroughly evaluate potential manufacturers based on their production capabilities, ingredient sourcing practices, food safety certifications (such as HACCP, GMP, or ISO), and ability to meet regulatory standards in your target market. Conducting site visits, requesting product samples, and reviewing client references can provide valuable insights into a manufacturer’s reliability and product consistency.
Additionally, clear communication regarding custom formulations, packaging preferences, labeling requirements, and minimum order quantities is crucial to ensure alignment with your brand standards. Whether sourcing locally or internationally, building strong, transparent relationships with manufacturers will support long-term success and adaptability in a competitive market.
Ultimately, selecting the right peanut butter manufacturer goes beyond price—it’s about finding a trustworthy partner committed to quality, sustainability, and shared growth.