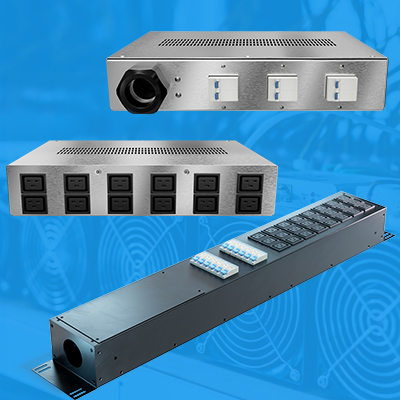
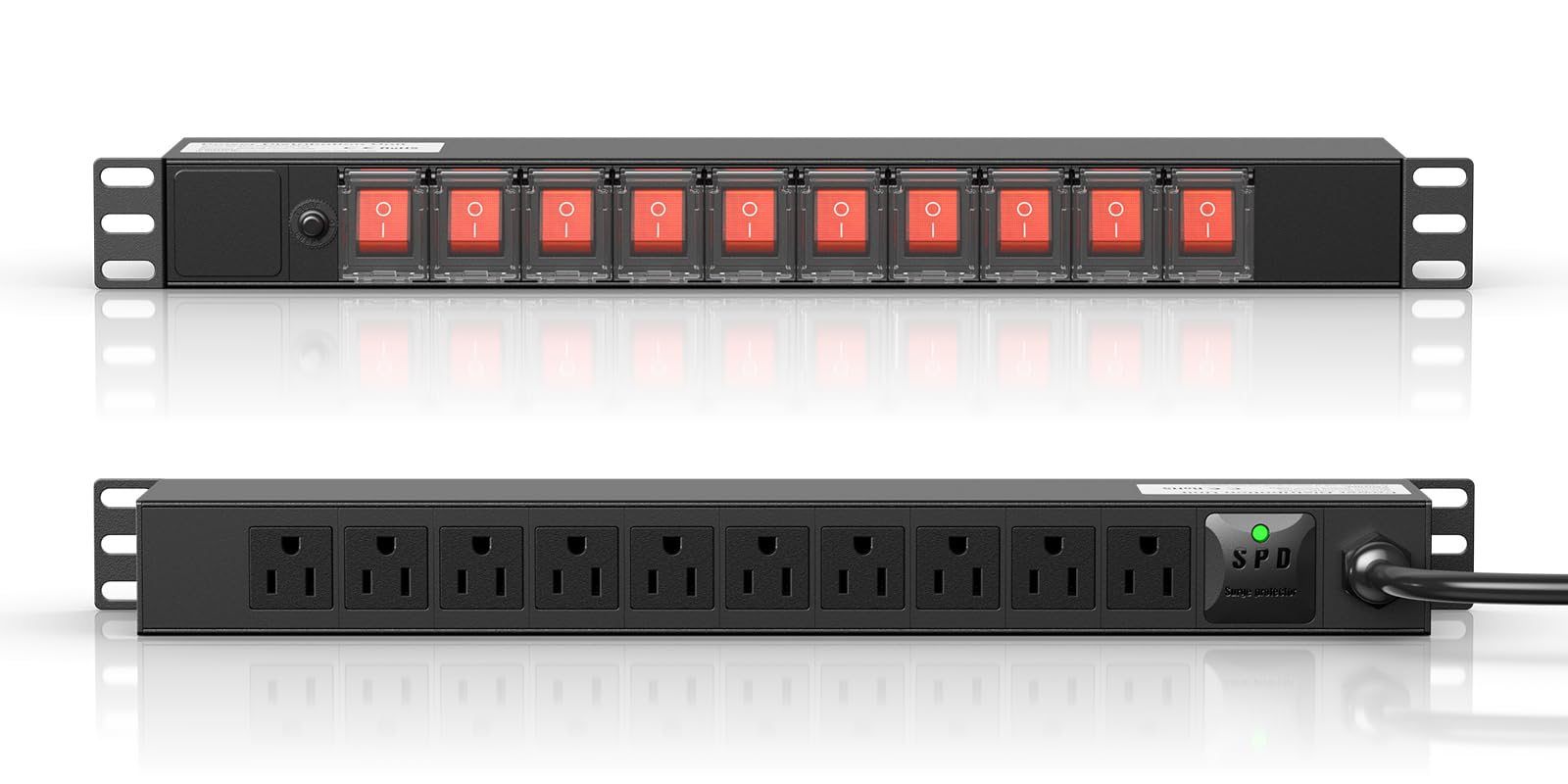
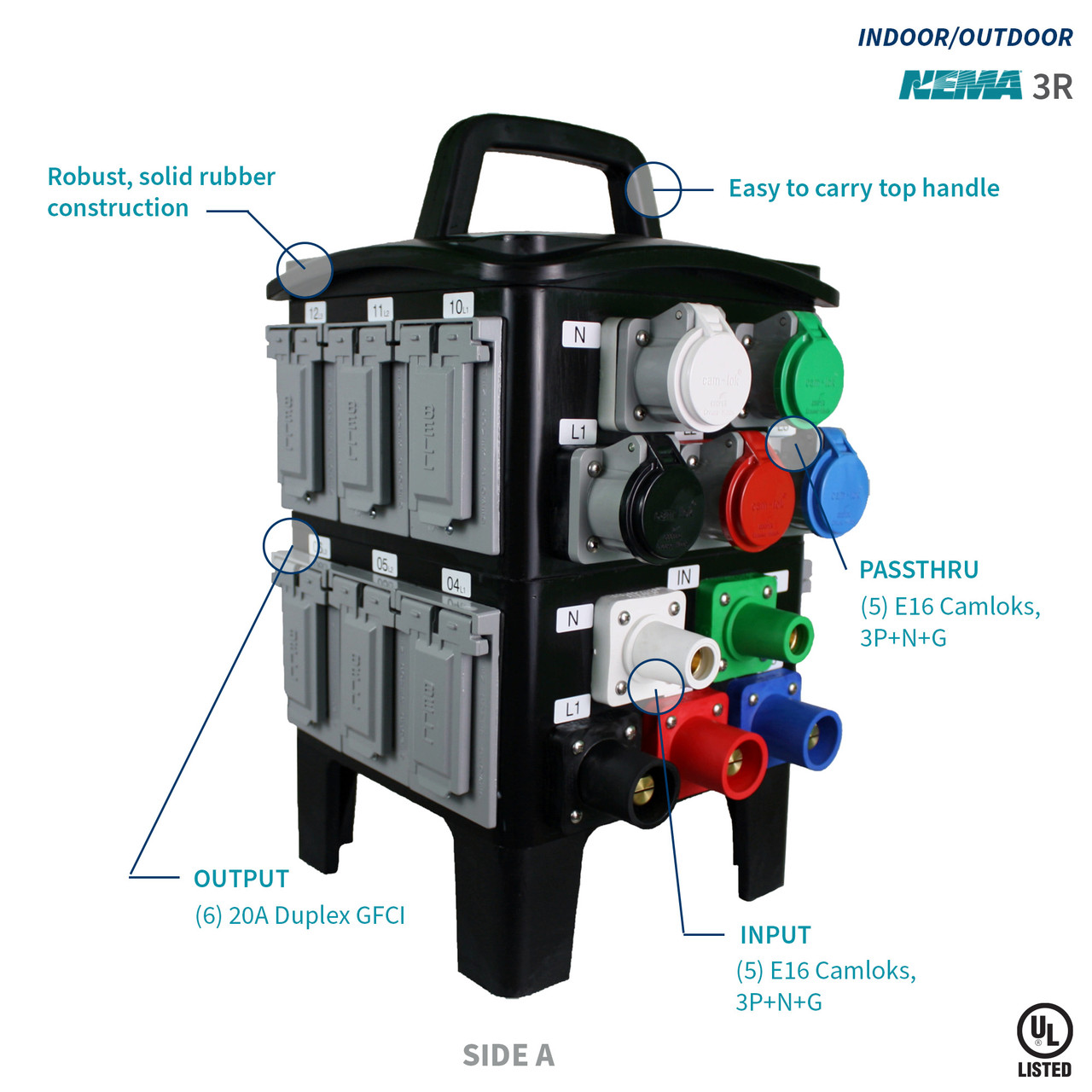
The global Power Distribution Unit (PDU) market is experiencing robust growth, driven by the rapid expansion of data centers and increasing demand for energy-efficient power management solutions. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the PDU market was valued at USD 7.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10.4% from 2023 to 2028, reaching an estimated USD 14.2 billion by the end of the forecast period. A significant contributor to this growth is the rising adoption of switched PDUs, which offer remote monitoring, individual outlet control, and real-time power data—critical features for optimizing operational efficiency and minimizing downtime in modern data infrastructure. As organizations prioritize intelligent power distribution, manufacturers are innovating to deliver scalable, secure, and network-integrated solutions. This growing demand underscores the importance of identifying the leading manufacturers that combine reliability, advanced functionality, and global support.
Top 10 Pdu With Switches Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 PDUs and UPS Manufacturer for Military, Crypto Mining, and Industrial
Domain Est. 2013
Website: raptorpowersystems.com
Key Highlights: Raptor Power Systems has stock and custom PDUs, DC to AC Inverters, DC to DC Converters, AC Frequency Converters, and UPS’s that can deliver for military, ……
#2 Server Technology: Data Center Power Distribution Units
Domain Est. 1995
Website: servertech.com
Key Highlights: Server Technology produces the highest quality Data Center rackmount power distribution units (PDUs) and monitoring solutions….
#3 Products
Domain Est. 1995
Website: raritan.com
Key Highlights: Raritan’s data center power products include rack power distribution units (rack PDUs), inline meters, transfer switches, and branch circuit monitoring systems….
#4 Rack PDU
Domain Est. 1996
Website: eaton.com
Key Highlights: From basic to advanced, switched PDUs, Eaton as rackmount PDUs for everything from small network closets to the world’s most sophisticated data centers….
#5 Switched PDUs for Data Centers
Domain Est. 1996
Website: tripplite.eaton.com
Key Highlights: Tripp Lite switched PDUs let you remotely control individual outlets and reboot equipment to minimize downtime and avoid expensive service calls….
#6 AC/DC PDUs, Battery Monitoring, & Sensor Power
Domain Est. 1996
Website: dpstele.com
Key Highlights: Remote power switches, also known as Power Distribution Units (PDUs) or “power strips” – enable you to have remote control over the power to your equipment….
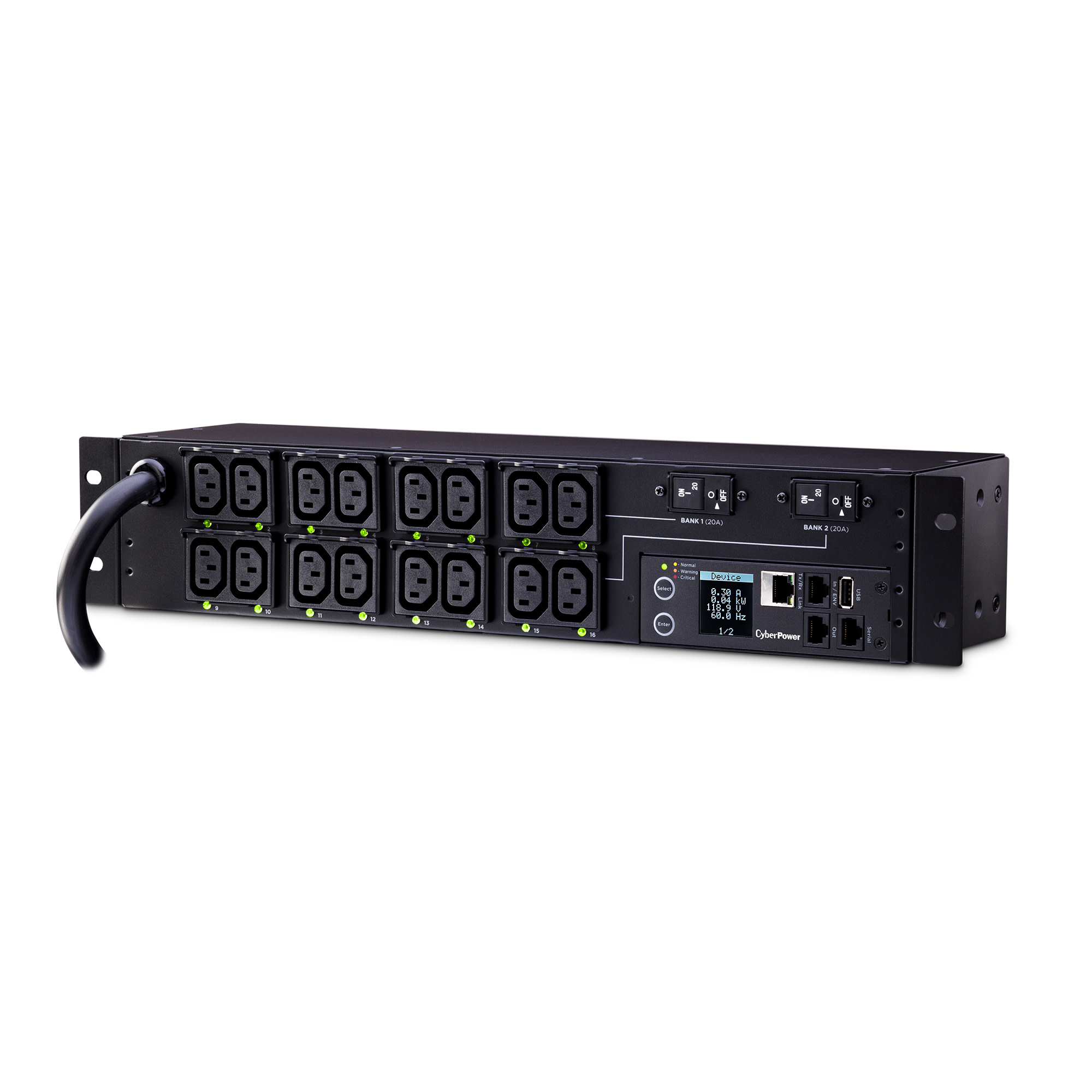
#7 PDU Power Distribution Units
Domain Est. 1997
Website: cyberpowersystems.com
Key Highlights: Features of the Switched PDU Series include upgradeable firmware, SNMP network interface, durable metal housing, and horizontal/vertical mounting. Switched PDUs ……
#8 Power Distribution Units (PDUs)
Domain Est. 1997
Website: marway.com
Key Highlights: Power distribution solutions. Custom and standard. Networked and basic. Rugged and commercial. A photo collage of custom PDUs in various configurations….
#9 PDU with switched and unswitched outlets
Domain Est. 1997
Website: lowellmfg.com
Key Highlights: PDU with switched and unswitched outlets · 15A rackmount power panel. PDU with 9 (15A) Outlets, Surge Suppression. ACR-1509-S $339.58 MSRP · Compare · Rackmount ……
#10 Power Distribution Unit (PDU) for Data Centers
Domain Est. 2011
Website: vertiv.com
Key Highlights: Looking for a reliable PDU? Vertiv’s power distribution units can remotely monitor and deliver consistent power to keep your operations running….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Pdu With Switches
2026 Market Trends for PDUs with Switches
Rising Demand for Intelligent Power Management
The market for Power Distribution Units (PDUs) with switching capabilities is expected to experience significant growth by 2026, driven by the increasing need for intelligent power management in data centers and edge computing environments. As organizations prioritize energy efficiency and real-time monitoring, switchable PDUs offer granular control over power distribution, enabling remote on/off functionality, load balancing, and outage prevention. This trend is amplified by the growing adoption of IoT devices and cloud infrastructure, which require reliable and responsive power solutions.
Expansion of Edge Computing Infrastructure
One of the most influential drivers shaping the PDU with switches market is the proliferation of edge computing. By 2026, edge data centers—smaller, decentralized facilities located closer to end-users—are projected to become increasingly common across industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, and telecommunications. These environments demand compact, scalable, and remotely manageable PDUs. Switched PDUs are well-suited for these deployments, offering secure, real-time control over connected equipment without requiring physical access, thus reducing downtime and operational costs.
Integration with Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM)
Switched PDUs are becoming integral components of comprehensive Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM) systems. By 2026, interoperability between PDUs and DCIM platforms is expected to be a standard expectation among enterprise buyers. This integration allows for centralized monitoring of power usage, environmental conditions, and equipment status across multiple locations. Vendors are increasingly embedding advanced telemetry, SNMP support, and API access into their switched PDUs to facilitate seamless integration, enhancing predictive maintenance and capacity planning capabilities.
Emphasis on Cybersecurity and Remote Access
As remote management features become standard in switched PDUs, cybersecurity is emerging as a critical concern. By 2026, market expectations will demand robust security protocols, including encrypted communications (TLS/SSL), multi-factor authentication, and firmware integrity checks. With the rise of cyber threats targeting critical infrastructure, manufacturers are responding by designing PDUs with enterprise-grade security to protect against unauthorized access and ensure compliance with regulations such as NIST and ISO 27001.
Growth in Sustainable and Energy-Efficient Solutions
Sustainability initiatives are shaping PDU design and functionality. In 2026, switched PDUs will increasingly feature energy-saving modes, automatic shutdown capabilities during low usage, and integration with renewable energy sources. Organizations are seeking tools to measure and reduce their carbon footprint, and switched PDUs contribute by providing accurate power usage data per outlet. This granularity supports energy audits and helps companies meet ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals.
Regional Market Dynamics and Competitive Landscape
North America and Europe are expected to lead the adoption of advanced switched PDUs due to mature data center ecosystems and stringent energy regulations. However, the Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to witness the highest growth rate, fueled by digital transformation initiatives in countries like India, Japan, and South Korea. Key market players such as Schneider Electric, Eaton, Vertiv, and Tripp Lite are investing heavily in R&D to offer smarter, modular, and cloud-connected PDUs, intensifying competition and driving innovation.
Conclusion
By 2026, the market for PDUs with switches will be defined by intelligence, security, and sustainability. The convergence of edge computing, DCIM integration, and energy efficiency demands will propel the evolution of switched PDUs from simple power strips to mission-critical infrastructure components. Organizations that adopt these advanced power management solutions will gain operational resilience, cost savings, and a strategic advantage in an increasingly digital world.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing PDUs with Switches (Quality, IP)
When integrating Power Distribution Units (PDUs) with built-in network switches, organizations often encounter several critical issues related to quality and Internet Protocol (IP) management. Being aware of these pitfalls can help ensure reliable, secure, and efficient deployments.
Poor Build Quality and Component Reliability
One of the most common issues is selecting PDUs with switches based on cost alone, leading to subpar build quality. Low-quality components—such as under-spec power circuits, unreliable switching chips, or flimsy connectors—can result in frequent failures, downtime, or even fire hazards. Cheaply manufactured units may not comply with safety certifications (e.g., UL, CE), increasing operational risk.
Inadequate Power and Load Management
Many integrated PDU-switch units are not designed to handle high-density power loads. Users may overlook the combined power draw from both the PDU and the switch, leading to circuit overloads. Additionally, lack of proper power metering or remote load balancing features limits visibility and control, increasing the risk of outages.
Limited or Outdated Switching Capabilities
Integrated switches in PDUs often come with basic, unmanaged switching functionality. These typically offer limited bandwidth (e.g., 10/100 Mbps instead of Gigabit), poor throughput, and no Quality of Service (QoS) or VLAN support. Such limitations can bottleneck network performance, especially in data center or high-availability environments.
Poor IP Management and Network Integration
Many PDU-switch units use proprietary firmware with limited IP configuration options. They may lack support for standard protocols like SNMP, DHCP, or secure access via SSH/TLS. This complicates integration into existing network management systems and monitoring tools, creating blind spots in infrastructure oversight.
Security Vulnerabilities
Units with outdated firmware or default credentials are prime targets for cyberattacks. Many low-cost PDU-switch combos lack regular firmware updates, have open management interfaces, or use unencrypted communication (e.g., HTTP instead of HTTPS). This exposes the network to unauthorized access, data interception, or remote hijacking.
Lack of Scalability and Future-Proofing
Integrated solutions may not scale efficiently. Adding more units often leads to IP address conflicts, management complexity, or network segmentation issues. The inability to stack switches or use LACP for link aggregation further limits scalability and redundancy.
Insufficient Remote Management and Monitoring
While marketed as “smart,” many PDU-switch units offer weak remote monitoring—lacking real-time alerts, logging, or API access. This undermines the core benefit of remote infrastructure control and increases mean time to repair (MTTR) during outages.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, prioritize PDUs with switches from reputable vendors that offer enterprise-grade hardware, robust IP management, strong security features, and comprehensive monitoring. Always verify specifications, certifications, and firmware update support before deployment.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for PDUs with Switches
Overview
Power Distribution Units (PDUs) with integrated switches provide intelligent power management in data centers, enabling remote monitoring, control, and outlet-level switching. Proper logistics handling and compliance adherence are essential to ensure product integrity, regulatory conformity, and safe deployment.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Electrical Safety Standards
PDUs with switches must comply with recognized electrical safety standards depending on the target market. Key certifications include:
– UL 60950-1 / UL 62368-1 (United States and Canada) – Covers safety of information technology equipment.
– IEC 60950-1 / IEC 62368-1 – International standard for electrical safety, widely adopted globally.
– CE Marking – Required for sale in the European Economic Area (EEA), indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
– CB Scheme – Facilitates mutual recognition of test reports among participating countries.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
Switched PDUs may generate electromagnetic interference (EMI). Compliance with EMC regulations ensures they do not disrupt other equipment:
– FCC Part 15 (Class A) – Required for commercial environments in the U.S.
– CISPR 32 – International standard for EMC emissions.
– EN 55032 & EN 61000-3-2/3-3 – European standards covering emissions and harmonic current limits.
Environmental and Material Compliance
Ensure adherence to environmental directives restricting hazardous substances:
– RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) – Limits use of lead, mercury, cadmium, and other harmful materials (EU Directive 2011/65/EU).
– REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) – Requires disclosure of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC).
– WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) – Mandates proper disposal and recycling; includes labeling and take-back requirements in the EU.
Network and Data Security
Switched PDUs with network connectivity must meet cybersecurity standards:
– NIST SP 800-53 or ISO/IEC 27001 – Recommended for secure configuration and data protection.
– FIPS 140-2 – Required for federal use in the U.S. if encryption is used.
– Ensure firmware is updatable and secure boot mechanisms are in place to prevent unauthorized access.
Logistics Handling and Transportation
Packaging and Labeling
- Use robust, ESD-safe packaging to protect sensitive electronic components.
- Clearly label packages with:
- Product name and model number
- Input voltage and electrical ratings
- Handling symbols (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”)
- Compliance marks (CE, UL, RoHS, etc.)
- Barcode/QR code for inventory tracking
Storage Conditions
- Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment (ideally 10°C to 30°C, 20–80% non-condensing humidity).
- Avoid exposure to dust, corrosive gases, or direct sunlight.
- Stack packages according to manufacturer guidelines to prevent physical damage.
Shipping and Import Considerations
- Verify destination country regulations for voltage compatibility and plug types.
- Prepare commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of conformity (e.g., DoC for CE).
- For international shipments, ensure compliance with:
- Customs-Trade Partnership Against Terrorism (C-TPAT) – For U.S. imports.
- Authorized Economic Operator (AEO) – For EU and other regions.
- Declare accurate Harmonized System (HS) codes (e.g., 8536.69 for power distribution units).
Installation and Site Compliance
Electrical Installation
- PDUs must be installed by qualified electricians in accordance with:
- National Electrical Code (NEC) – Article 645 for information technology equipment in the U.S.
- IEC 60364 – International standard for electrical installations.
- Verify grounding, overcurrent protection, and circuit compatibility before energizing.
Rack and Physical Integration
- Confirm rack compatibility (e.g., 19-inch standard, depth, mounting rails).
- Ensure adequate airflow and avoid blocking ventilation paths.
- Secure cabling to prevent strain and maintain cable management best practices.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Required Documentation
Maintain the following for compliance audits and traceability:
– Product compliance certificates (UL, CE, RoHS, etc.)
– User manuals with safety instructions and specifications
– Firmware version logs and update history
– Warranty and service records
Labeling at Point of Use
- Install permanent labels indicating:
- Maximum load capacity
- Input voltage and frequency
- Manufacturer contact information
- Asset tag or serial number
End-of-Life and Disposal
Recycling and Decommissioning
- Follow WEEE or local e-waste regulations for proper disposal.
- Partner with certified e-waste recyclers to ensure environmentally sound treatment.
- Remove network configuration data before disposal to prevent data leakage.
Summary
Compliance and logistics for switched PDUs span safety, environmental, and operational domains. Adhering to international standards, ensuring secure handling, and maintaining comprehensive documentation are critical for successful deployment and regulatory alignment. Always consult local authorities and product-specific guidelines prior to installation and operation.
Conclusion: Sourcing PDUs Alongside Network Switches
When sourcing Power Distribution Units (PDUs) in conjunction with network switches, it is essential to adopt a holistic approach that ensures compatibility, scalability, reliability, and operational efficiency. Integrating PDUs with switch deployments enhances power management, supports redundancy, and contributes to the overall stability of critical IT infrastructure.
Key considerations include matching PDU specifications—such as outlet type, power capacity, and voltage—to the power requirements of the switches and other connected equipment. Intelligent or metered PDUs provide valuable monitoring and remote management capabilities, enabling proactive maintenance, energy optimization, and improved uptime. Furthermore, aligning PDU selection with rack configuration and environmental factors (e.g., cooling, cable management) streamlines installation and improves airflow and serviceability.
Sourcing both switches and PDUs from compatible or integrated vendors can simplify procurement, reduce integration challenges, and improve support responsiveness. Ultimately, a well-planned PDU strategy complements network switch deployment by ensuring resilient, efficient, and manageable power distribution—laying a strong foundation for current operations and future scalability.