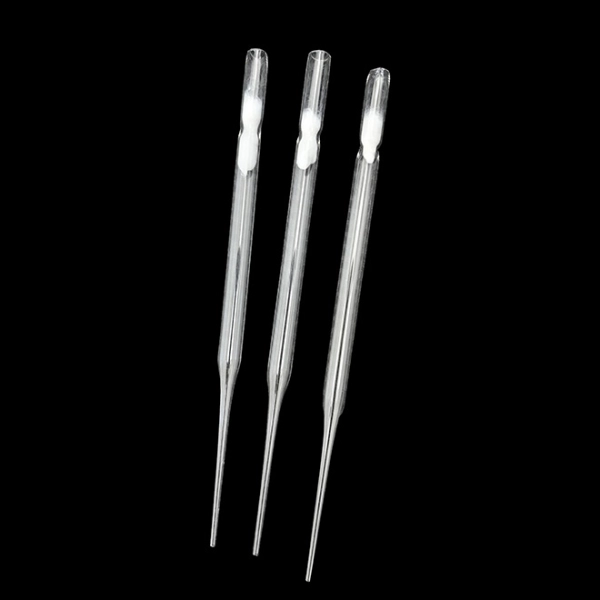
The global laboratory consumables market, which includes essential tools such as Pasteur pipette droppers, is experiencing steady expansion driven by increasing R&D investments in pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and academic research. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the laboratory consumables market was valued at USD 37.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% through 2029. This growth is underpinned by rising demand for precision instruments in diagnostic and research laboratories, coupled with advancements in microfluidics and miniaturized lab processes. Pasteur pipettes, widely used for transferring small volumes of liquids with accuracy, remain a staple across clinical, educational, and industrial labs. As demand increases, manufacturers are scaling production, enhancing material quality (notably moving toward sterile, disposable polyethylene and glass variants), and improving packaging automation to meet global regulatory standards. In this evolving landscape, nine key manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining innovation, scalability, and global distribution networks to capture significant market share and support advancing laboratory workflows.
Top 9 Pasteur Pipette Dropper Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Pasteur Pipette Factory Manufacturers in China
Domain Est. 2022
Website: bkmbio.com
Key Highlights: BKMAM is one of the most professional pasteur pipette manufacturers in China, specialized in providing high quality products and service….
#2 Pasteur Pipette
Domain Est. 2003
Website: glasscolabs.com
Key Highlights: 2-day returnsBest Manufacturer, Suppliers & Exporters of High Quality Laboratory Pasteur Pipette – Made of Glass and Plastic, Easy and safe to use, Economical….
#3 Pasteur Pipets
Domain Est. 1995
Website: fishersci.com
Key Highlights: Browse a full range of Pasteur Pipets products from leading suppliers. Shop now at Fisher Scientific for all of your scientific needs….
#4 Pasteur Pipettes
Domain Est. 1996
Website: dwk.com
Key Highlights: Explore DWK’s range of pasteur pipettes, designed for accurate and safe fluid handling in laboratories. Available in non-sterile and sterile!…
#5 Pastette Pasteur and Transfer Pipette
Domain Est. 1998
Website: alphalabs.co.uk
Key Highlights: Available in over 50 designs, Pastettes are flexible, unbreakable, transfer or Pasteur pipettes and are ideal for a multitude of tasks….
#6 Transfer and Pasteur Pipettes
Domain Est. 2000
Website: pipette.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 10-day returnsHeathrow Scientific. 2mL latex dropper. These natural latex rubber droppers are designed for use with Pasteur pipets, small pipets, and medicine dropper…
#7 Boenmed® Glass Pasteur Pipette, Plain/Plugged
Domain Est. 2006
Website: boenmedical.com
Key Highlights: BOENMED manufactures GLASS PASTEUR PIPETTES. The Glass Pasteur Pipettes, also known as droppers, are made of soda lime glass, borosilicate glass….
#8 Lab Medical 3ml Graduated Transfer Dropper Pasteur Pipettes
Domain Est. 2008
Website: cnwtc.com
Key Highlights: This plastic pipette dropper is made from eco-friendly polyethylene materials, durable, unbreakable, chemically inert and non-toxic….
#9 5ml Pipette Dropper Disposable Pasteur Pipette
Domain Est. 2021
Website: nest-biotech.com
Key Highlights: Rating 5.0 (38) Application: It is suitable for drawing, transferring and blending a certain volume of liquid. Both sterile and non-sterile Pasteur pipettes are available….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Pasteur Pipette Dropper

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Pasteur Pipette Droppers
The global market for Pasteur pipette droppers is poised for steady growth and transformation by 2026, driven by evolving demands in healthcare, biotechnology, academic research, and consumer industries. Several key trends are expected to shape the landscape of this seemingly simple yet essential laboratory and industrial tool.
1. Rising Demand in Life Sciences and Diagnostics
The expansion of biotechnological research, pharmaceutical development, and point-of-care testing is a primary driver for Pasteur pipette droppers. With increasing investments in genomics, proteomics, and personalized medicine, laboratories require reliable, low-cost liquid handling tools. Pasteur pipettes—especially sterile, disposable variants—remain vital in sample transfer, reagent preparation, and microbiological assays. The proliferation of decentralized diagnostic kits, particularly in emerging markets, will further boost demand for dropper-based delivery systems.
2. Shift Toward Single-Use and Sterile Disposable Products
Driven by stringent contamination control protocols, the trend toward single-use laboratory consumables will continue to influence the Pasteur pipette market. Manufacturers are focusing on sterile, pre-packaged droppers made from medical-grade plastics or biodegradable materials to meet regulatory standards in clinical and pharmaceutical settings. This shift reduces cross-contamination risks and supports automation compatibility in high-throughput environments.
3. Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Material Innovation
Environmental concerns are prompting a reevaluation of traditional plastic pipettes. By 2026, market leaders are expected to expand offerings of biodegradable or compostable Pasteur pipettes made from plant-based polymers (e.g., polylactic acid). Regulatory pressures and corporate sustainability goals are accelerating R&D in eco-conscious alternatives, particularly in Europe and North America where green procurement policies are tightening.
4. Expansion in Non-Traditional Sectors
Beyond laboratories, Pasteur pipette droppers are gaining traction in cosmetics, essential oils, food testing, and at-home science kits. The precision and ease of use make them ideal for small-volume dispensing in consumer products. The growing DIY biology movement and STEM education initiatives are also fueling demand for affordable, user-friendly droppers in hobbyist and educational markets.
5. Regional Market Growth and Localization
Asia-Pacific is projected to be the fastest-growing region due to expanding R&D infrastructure in China, India, and South Korea. Local manufacturing hubs are reducing dependence on Western suppliers, leading to cost-competitive products tailored to regional needs. Meanwhile, North America and Europe maintain high per-capita consumption, supported by advanced healthcare systems and strong academic research funding.
6. Integration with Automation and Digital Workflows
Although Pasteur pipettes are typically manual tools, there is a growing trend to standardize their design for compatibility with semi-automated systems. Some manufacturers are developing droppers with uniform tip geometry and barcoding to integrate with lab inventory and digital tracking systems, improving traceability and reproducibility.
Conclusion
By 2026, the Pasteur pipette dropper market will be characterized by innovation in materials, increased demand across diverse sectors, and a strong emphasis on sustainability and precision. While the core function remains unchanged, advancements in production, sterility, and environmental impact will redefine value propositions for end users. Companies that adapt to these trends—particularly in eco-design and application diversification—are likely to capture significant market share in the evolving global landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Pasteur Pipette Droppers (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing Pasteur pipette droppers—especially for regulated industries like pharmaceuticals, diagnostics, or research—can involve several critical pitfalls related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these can lead to supply chain disruptions, non-compliance, or legal risks. Below are the most common issues to watch for:
1. Inconsistent Material Quality and Purity
Many suppliers use substandard or contaminated plastics (e.g., polystyrene or polyethylene) that may leach chemicals or interfere with sensitive assays. Poor-quality rubber bulbs can degrade, leading to particulate contamination or inconsistent droplet delivery. Always verify material certifications (e.g., USP Class VI, FDA-compliant, DNase/RNase-free) and request lot-specific test reports.
2. Lack of Standardization and Dimensional Variability
Pasteur pipettes are not always manufactured to precise tolerances. Variability in tip diameter, bulb compression, and overall length can affect droplet size and dispensing accuracy—critical in quantitative applications. Sourcing from manufacturers without strict process controls increases the risk of batch-to-batch inconsistency.
3. Inadequate Sterility Assurance
For sterile applications, it’s essential to confirm the sterilization method (e.g., gamma irradiation or ethylene oxide) and sterility validation (e.g., SAL 10⁻⁶). Some suppliers claim “sterile” without proper validation or packaging integrity testing, risking contamination in cleanroom or clinical environments.
4. Poor Packaging and Contamination Risks
Inadequate packaging (e.g., non-individually wrapped units or non-protective bulk containers) can expose pipettes to dust, moisture, or airborne contaminants. This is especially problematic for molecular biology or cell culture applications where even trace contaminants can ruin experiments.
5. Misrepresentation of Intellectual Property (IP) and Branding
Some suppliers falsely claim compatibility with or endorsement by major brands (e.g., “compatible with Brand X” or using misleading logos). This can violate trademark laws and expose buyers to IP litigation. Always verify branding claims and ensure supplier authorization if reselling under a private label.
6. Infringement on Patented Designs
Certain dropper designs (e.g., specialized tip geometries or integrated filters) may be protected by patents. Sourcing generic versions that mimic patented features can lead to infringement—even if unintentional. Conduct due diligence on product design origins, especially when sourcing from low-cost manufacturers in regions with weak IP enforcement.
7. Unreliable Supply Chain Transparency
Suppliers may outsource production without disclosing subcontractors, making it difficult to audit quality systems or ensure ethical manufacturing. Lack of traceability also complicates root cause analysis in case of product failure or regulatory inspection.
8. Insufficient Regulatory Documentation
For use in regulated environments, suppliers must provide full documentation: Certificates of Analysis (CoA), Certificates of Conformance (CoC), and regulatory compliance statements (e.g., REACH, RoHS, ISO 13485). Missing or generic documentation is a red flag for non-compliant sourcing.
Best Practices to Avoid Pitfalls
- Audit suppliers (on-site or via third party) for quality management systems.
- Require material and product specifications in writing.
- Test samples rigorously before scaling procurement.
- Clarify IP ownership and branding rights in contracts.
- Prioritize suppliers with transparent manufacturing and regulatory compliance histories.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, organizations can ensure reliable, compliant, and legally sound sourcing of Pasteur pipette droppers.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Pasteur Pipette Droppers
Product Overview
Pasteur pipette droppers, also known as transfer pipettes or teat pipettes, are single-use laboratory tools typically made from polyethylene or glass with a rubber or latex bulb. They are used for transferring small volumes of liquid in scientific, educational, and medical settings. This guide outlines key logistics, handling, storage, and regulatory compliance considerations for these devices.
Packaging & Labeling Requirements
Ensure all Pasteur pipette droppers are packaged in sealed, sterile containers suitable for laboratory use. Packaging must include:
– Product name and description (e.g., “Sterile Pasteur Pipette Droppers”)
– Quantity per unit (e.g., 100/pk)
– Material composition (e.g., LDPE tip, latex bulb)
– Sterility status and sterilization method (if applicable)
– Lot number and expiration date (where applicable)
– Manufacturer or distributor name and contact information
– Regulatory markings (e.g., CE for EU, if medical device classification applies)
Labels must be durable, legible, and resistant to moisture and common lab solvents.
Storage Conditions
Store in a clean, dry, temperature-controlled environment (15–25°C recommended). Avoid direct sunlight and exposure to UV radiation. Keep away from volatile chemicals, strong oxidizers, and flammable materials. Do not store near heat sources or in high-humidity areas to prevent degradation of plastic components and microbial contamination. Maintain original packaging until point of use.
Transportation & Handling
Transport in closed, protected vehicles to prevent physical damage, moisture, or contamination. Use secondary containment if shipping sterile or medical-grade pipettes. Handle with clean gloves to avoid contamination. Avoid dropping or crushing packages. For international shipments, comply with IATA/IMDG regulations if classified as diagnostic or medical devices. Most plastic pipettes are non-hazardous and not subject to dangerous goods regulations.
Regulatory Compliance
- United States (FDA): If intended for diagnostic or medical use, may be classified as a Class I medical device under 21 CFR 864.3900. General lab-use pipettes typically do not require FDA clearance.
- European Union (EU): Falls under IVDR (In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation) if used for diagnostic purposes. Otherwise, general lab supply under REACH and RoHS compliance. Ensure CE marking if applicable.
- REACH & RoHS: Confirm that materials (plastics, dyes, latex) comply with REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directives.
- Latex Allergens: If bulbs contain natural rubber latex, include allergen warnings per FDA and EU guidelines. Consider latex-free alternatives (e.g., nitrile) to meet safety standards.
- Sterility Claims: If marketed as sterile, validate sterilization process (e.g., gamma irradiation or ethylene oxide) and follow ISO 11135 or ISO 11137 standards.
Import/Export Considerations
Verify destination country regulations. Some countries require:
– Certificate of Conformity (CoC)
– Certificate of Analysis (CoA)
– Free Sale Certificate (FSC)
– Import permits for medical devices
Ensure Harmonized System (HS) Code accuracy (e.g., 9017.80 or 3926.30 depending on material and use). Consult local customs authorities for specific requirements.
Waste Disposal & Environmental Compliance
Dispose of used pipettes according to local biohazard, chemical, or sharps waste regulations. Contaminated pipettes must be treated as biohazardous waste if exposed to biological materials. Intact plastic pipettes from non-hazardous use may be recyclable under local plastic recycling programs (check resin identification code). Follow OSHA and EPA guidelines in the U.S., or equivalent national regulations.
Quality Assurance & Documentation
Maintain records of:
– Supplier certifications (ISO 13485, if applicable)
– Batch testing and sterility reports
– Material declarations (REACH, RoHS)
– Shipping and storage logs
Conduct regular audits to ensure continued compliance with regulatory and quality standards.
Training & Safety
Train personnel on proper handling, storage, and disposal. Emphasize latex allergy risks if applicable. Provide safety data sheets (SDS) for pipette materials upon request. Encourage use of personal protective equipment (PPE) when handling used or contaminated pipettes.
Conclusion for Sourcing Pasteur Pipette Droppers
In conclusion, sourcing Pasteur pipette droppers requires careful consideration of material quality, supplier reliability, cost-effectiveness, and compliance with industry standards. Whether opting for glass or disposable plastic variants, it is essential to partner with reputable suppliers who provide consistent quality, proper sterilization (if needed), and timely delivery. Evaluating factors such as volume accuracy, packaging (individually wrapped or bulk), and compatibility with laboratory applications ensures the pipettes meet operational requirements. By conducting thorough supplier assessments and considering total cost of ownership—including shipping, storage, and potential waste—organizations can secure a reliable supply of Pasteur pipettes that support efficient and accurate liquid handling in laboratory environments.