The global part marking equipment market is experiencing steady growth, fueled by increasing demand for traceability, quality control, and compliance across industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and electronics. According to Grand View Research, the global product marking and coding equipment market was valued at USD 5.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.1% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is driven by stringent regulatory requirements, the rise in anti-counterfeiting measures, and the expansion of automated manufacturing processes. As industrial players prioritize permanent, precise, and high-speed marking solutions, manufacturers offering advanced technologies like laser marking, dot peen, inkjet, and electrochemical etching have gained strategic importance. In this evolving landscape, eight leading companies have emerged as innovators in part marking methods, combining technological expertise with global reach to meet the escalating demands of modern production environments.
Top 8 Part Marking Methods Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
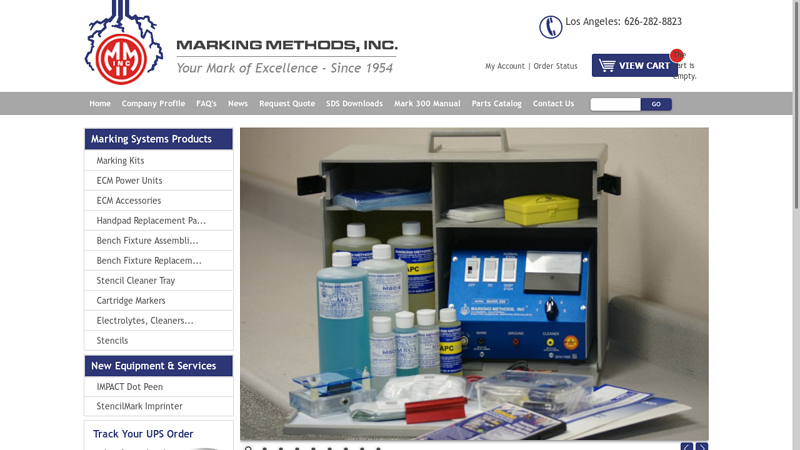
#1 MARKING METHODS, INC.®
Founded: 1954
Website: markingmethods.com
Key Highlights: Since 1954, Marking Methods has specialized in providing quality Electro-Chemical Equipment, supplies and part marking services….
#2 All about direct part marking methods
Website: gravotech.us
Key Highlights: Direct part marking is a set of techniques used in the industrial sector to identify or inscribe data on your products….
#3 Part marking methods: laser and continuous inkjet
Website: videojet.com
Key Highlights: Learn part marking methods of Direct Part Marking (DPM) for automotive and aerospace, comparing laser marking vs. inkjet part marking….
#4 Intertek
Website: intertek.com
Key Highlights: We deliver unrivalled Total Quality Assurance with precision, pace and passion, enabling our customers to make their businesses stronger….
#5 11 Top Direct Part Marking Methods
Website: keyence.com
Key Highlights: Understanding Permanent Part Marking Methods · Method 1: Laser Engraving · Method 2: Laser Etching · Method 3: Fiber Laser Marking · Method 4: UV Laser Marking….
#6 19 CFR 134.41
Website: ecfr.gov
Key Highlights: As a general rule, marking requirements are best met by marking worked into the article at the time of manufacture….
#7 UL Solutions
Website: ul.com
Key Highlights: UL Solutions is a global independent safety science company with more than a century of expertise innovating safety solutions….
#8 What is Laser Marking?
Website: telesis.com
Key Highlights: Laser marking is a versatile process that allow you to add permanent marks on almost any material. Learn all about these methods today….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Part Marking Methods

H2: Market Trends in Part Marking Methods for 2026
As we approach 2026, the part marking industry is undergoing significant transformation driven by technological advancements, increasing regulatory demands, and evolving industrial automation. Part marking methods—critical for traceability, quality control, and product authentication across sectors such as automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and electronics—are adapting to meet these challenges. Below are the key market trends shaping part marking methods in 2026:
-
Dominance of Laser Marking Technology
Laser marking continues to lead the market, with enhanced precision, speed, and compatibility with diverse materials. Fiber lasers dominate for metals, while UV and green lasers gain traction in delicate applications such as medical device marking. The integration of smart lasers with IoT-enabled systems allows real-time monitoring and adaptive marking, contributing to Industry 4.0 adoption. -
Growth in Permanent and Tamper-Proof Marking
Regulatory standards such as UDI (Unique Device Identification) in healthcare and serialization requirements in aerospace are pushing demand for permanent, high-contrast, and tamper-evident marks. Direct Part Marking (DPM) via laser and dot peen methods ensures durability under extreme conditions, making these methods essential in safety-critical industries. -
Rise of Digital Integration and Smart Marking Systems
In 2026, part marking systems are increasingly embedded within digital manufacturing ecosystems. Marking equipment is being integrated with MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) and ERP platforms, enabling automated data exchange, batch tracking, and real-time quality assurance. This trend enhances traceability across the supply chain. -
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Marking Solutions
Environmental concerns are influencing the adoption of marking methods with minimal waste and energy use. Laser systems, which require no consumables and produce negligible waste, are preferred over inkjet or chemical etching. Additionally, advancements in low-power laser technologies further reduce the environmental footprint. -
Expansion in Additive Manufacturing and Hybrid Marking
As additive manufacturing (3D printing) grows, so does the need for in-situ marking of complex components. Hybrid systems that combine printing and marking in a single workflow are emerging, enabling real-time serialization of parts during production—especially relevant for customized medical implants and aerospace components. -
Increased Adoption of Machine Vision and AI for Mark Verification
Automated optical inspection (AOI) systems using AI-powered machine vision are becoming standard for verifying mark readability, contrast, and compliance. In 2026, closed-loop systems that automatically adjust marking parameters based on feedback are improving consistency and reducing rework. -
Growth in Emerging Markets and Industrial Automation
Emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Eastern Europe are driving demand for cost-effective and reliable part marking solutions. As these regions expand their manufacturing base, especially in automotive and electronics, demand for automated marking systems is rising. -
Shift Toward Portable and Handheld Marking Devices
For field service, maintenance, and repair operations (MRO), portable laser and dot peen markers are gaining popularity. These devices enable on-site part identification and asset tracking, supporting predictive maintenance and lifecycle management strategies.
In conclusion, the 2026 landscape for part marking methods is defined by smarter, more connected, and sustainable technologies. Laser-based systems remain at the forefront, but their integration with digital infrastructure, AI, and automation is redefining capabilities. Companies investing in scalable, compliant, and future-ready marking solutions will be best positioned to capitalize on these evolving market dynamics.
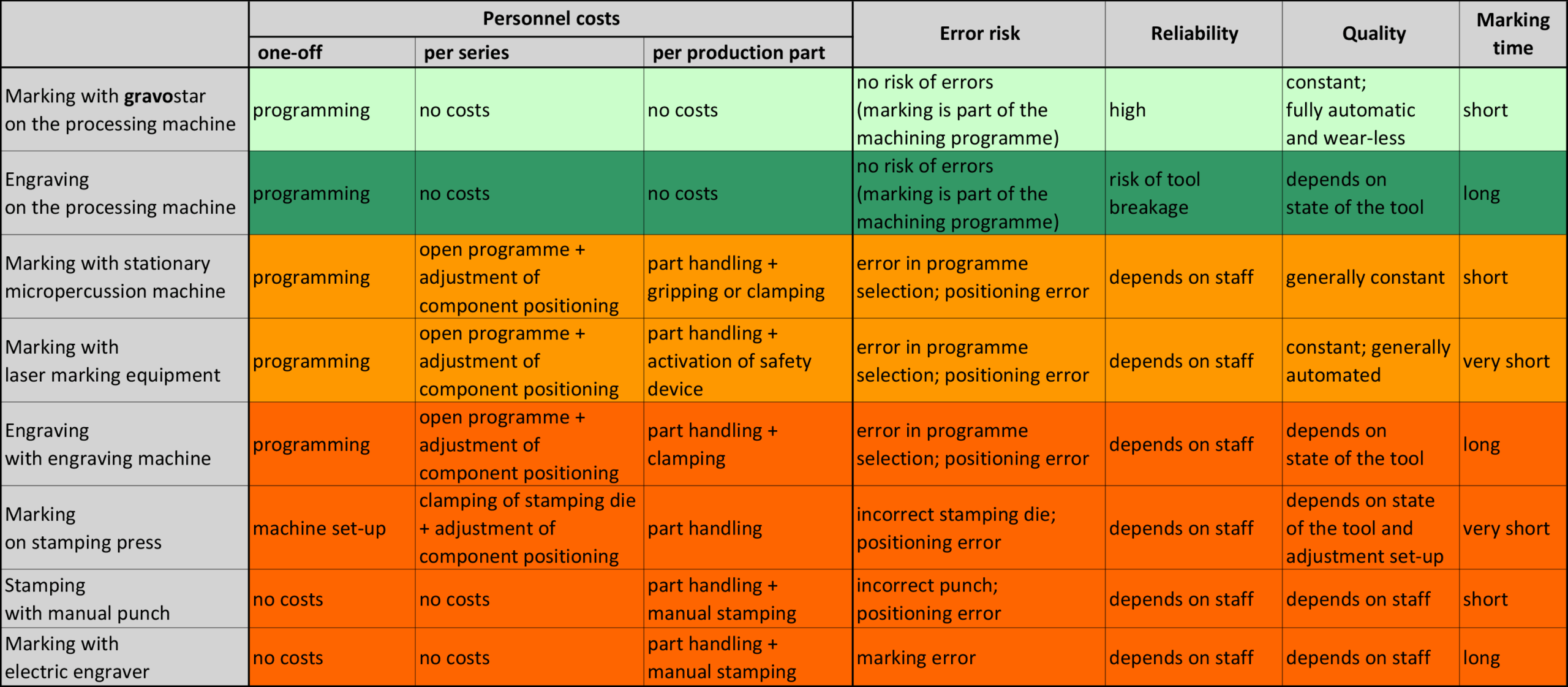
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Part Marking Methods (Quality and Intellectual Property)
When sourcing part marking methods—such as laser engraving, dot peen, inkjet, or chemical etching—companies often encounter critical challenges that can compromise product quality, regulatory compliance, and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to costly recalls, legal disputes, and reputational damage.
Inadequate Quality Control Standards
One of the most frequent issues is selecting suppliers without verifying their adherence to industry-specific quality standards (e.g., ISO 9001, AS9100, or IATF 16949). Poorly controlled marking processes can result in inconsistent depth, illegible codes, or surface damage, especially on sensitive components. Without proper validation, marks may degrade over time or fail under environmental stress, undermining traceability and product integrity.
Lack of Process Validation and Traceability
Sourced marking methods often fail under real-world conditions if not properly validated. Suppliers may not conduct durability testing (e.g., resistance to heat, chemicals, or abrasion), leading to unreadable barcodes or serial numbers in the field. Additionally, insufficient documentation or data traceability can hinder compliance with regulations like UDI (Unique Device Identification) in medical devices or FAA requirements in aerospace.
Intellectual Property Exposure
Sharing proprietary designs, logos, or sensitive product information with third-party marking vendors poses a significant IP risk. Without robust non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and clear IP ownership clauses in contracts, companies risk unauthorized use, replication, or leakage of protected information. Some suppliers may also reuse marked samples or retain digital files beyond the scope of the agreement.
Use of Non-Compliant or Unapproved Materials
Ink, dyes, or laser parameters used in marking may contain restricted substances (e.g., under RoHS, REACH, or FDA guidelines). Sourcing from vendors who do not certify material compliance can result in regulatory violations, especially in industries like medical devices, automotive, or consumer electronics.
Insufficient Supplier Qualification
Many organizations fail to thoroughly audit potential marking suppliers. This includes assessing their equipment calibration, operator training, and change control processes. Unqualified vendors may use outdated technology or lack redundancy, increasing the risk of production delays or substandard output.
Overlooking Long-Term Support and Scalability
A common oversight is selecting a vendor based solely on initial cost, without considering scalability or long-term service support. As production volumes grow or marking requirements evolve (e.g., 2D Data Matrix adoption), the supplier may lack the capacity or technical expertise to adapt, forcing costly transitions.
Failure to Define Marking Specifications Clearly
Ambiguous technical specifications—such as font size, contrast ratios, placement accuracy, or code format (e.g., Data Matrix ECC200)—can lead to inconsistent results. Without detailed work instructions and acceptance criteria, disputes over quality and rework become more likely.
Mitigating these pitfalls requires a structured sourcing strategy that includes supplier audits, rigorous contract terms, IP protections, and ongoing quality monitoring to ensure both compliance and product excellence.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Part Marking Methods
Effective part marking is essential for traceability, quality control, regulatory compliance, and efficient logistics throughout a product’s lifecycle. This guide outlines key considerations for selecting, implementing, and managing part marking methods in accordance with industry standards and logistical requirements.
Purpose of Part Marking
Part marking serves multiple critical functions across manufacturing, supply chain, and service operations. It enables identification, tracking, and authentication of components and products. Key objectives include:
- Unique identification for traceability (e.g., serial numbers, batch/lot codes)
- Compliance with regulatory requirements (e.g., FDA UDI, FAA, ISO, MIL-STD)
- Support for inventory management and logistics (e.g., barcode/RFID scanning)
- Anti-counterfeiting and brand protection
- Facilitation of maintenance, repair, and recalls
Common Part Marking Methods
Various technologies are used to mark parts, each with distinct advantages and limitations based on material, environment, and regulatory needs.
Direct Part Marking (DPM)
Direct Part Marking applies identifiers directly onto the component surface. Common DPM techniques include:
- Laser Marking: Permanent, high-precision marks on metals, plastics, and ceramics. Ideal for 2D Data Matrix codes. Compliant with AS9132 and AIAG standards.
- Dot Peen Marking: Uses a stylus to indent characters or codes. Durable in harsh environments; suitable for metal parts in automotive and aerospace.
- Inkjet Marking: Fast, non-contact method for porous and non-porous surfaces. Best for temporary or semi-permanent marks on packaging or lower-durability applications.
- Electrochemical Etching: Used primarily on conductive metals; produces high-contrast, corrosion-resistant marks.
Labels and Tags
- Pressure-Sensitive Labels: Adhesive barcodes or RFID tags; easy to apply but less durable.
- RFID Tags: Enable wireless tracking and data storage; ideal for high-value assets and complex logistics.
- Nameplates and Engraved Tags: Metal or polymer tags mechanically attached; offer long-term durability and readability.
Regulatory and Industry Standards
Compliance with applicable regulations and standards is mandatory for many industries. Key frameworks include:
- ISO 9001 / IATF 16949: Requires traceability and identification of product throughout the supply chain.
- AS9100 / AS9132: Aerospace standard mandating permanent part marking with Data Matrix codes (AIM DPM-1-2006 compliance).
- FDA UDI (Unique Device Identification): Requires medical devices to carry permanent, readable marks (e.g., 2D codes) per 21 CFR Part 801.
- REACH / RoHS: Restricts hazardous substances in markings (e.g., ink composition).
- MIL-STD-130: Specifies marking requirements for U.S. Department of Defense assets, including UID (Unique Item Identifier).
Logistics Considerations
Efficient integration of part marking into logistics operations ensures seamless tracking and reduces errors.
Mark Readability and Scanning
- Ensure marks meet minimum symbol contrast, cell modulation, and print growth specifications (per ISO/IEC 15415 or AIM DPM-1-2006).
- Validate readability using handheld or fixed-mount scanners in real-world conditions.
- Consider environmental exposure (e.g., temperature, chemicals, abrasion) when selecting marking method.
Data Structure and Encoding
- Use standardized data formats (e.g., GS1, ATA, MH10.8.7) to ensure interoperability.
- Include essential data such as serial number, batch/lot, manufacturing date, and supplier code.
- Leverage 2D codes (e.g., Data Matrix, QR) for higher data capacity in limited spaces.
Integration with ERP and MES Systems
- Synchronize marking systems with enterprise resource planning (ERP) and manufacturing execution systems (MES) for real-time data capture.
- Automate data flow to reduce manual entry errors and support audit trails.
Best Practices for Implementation
To ensure reliability and compliance, follow these guidelines:
- Material Compatibility: Test marking methods on actual production materials to ensure durability and readability.
- Verification and Validation: Implement in-process verification (e.g., camera-based inspection) to confirm mark quality before shipment.
- Documentation and Traceability: Maintain records of marking parameters, validation reports, and traceability data for audits.
- Training and Procedures: Train operators on correct marking techniques, equipment use, and compliance requirements.
- Sustainability and Safety: Use environmentally compliant inks and processes; ensure operator safety with protective equipment for laser/chemical methods.
Conclusion
A well-designed part marking strategy supports regulatory compliance, enhances supply chain visibility, and reduces operational risk. By selecting the appropriate marking method, adhering to industry standards, and integrating with logistics systems, organizations can achieve reliable, permanent identification of parts across their lifecycle. Regular audits and technology updates are recommended to maintain compliance and efficiency.
Conclusion on Sourcing Part Marking Methods
Selecting the appropriate part marking method is a critical decision in sourcing components, impacting traceability, quality control, regulatory compliance, and brand integrity. Various marking techniques—such as laser marking, inkjet printing, dot peen, engraving, and chemical etching—offer distinct advantages and limitations depending on the material, environment, durability requirements, and production volume.
When sourcing parts, it is essential to evaluate marking methods based on factors including permanence, legibility, material compatibility, production speed, and cost. Laser marking, for instance, provides high precision and durability, making it ideal for high-value or mission-critical components, while inkjet printing offers flexibility and lower initial costs for high-speed applications despite potential fading over time.
Ultimately, the choice of marking method should align with the end-use application, industry standards (e.g., automotive, aerospace, medical device regulations), and the supply chain’s need for reliable part identification throughout the product lifecycle. Collaborating with suppliers who understand these requirements and can consistently deliver marked parts of high quality ensures long-term operational efficiency and compliance. Therefore, a strategic approach to sourcing part marking methods enhances traceability, reduces risk, and supports overall supply chain resilience.