The global material handling equipment market, driven by rising demand for efficient logistics and warehouse operations, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% from 2023 to 2028, according to Mordor Intelligence. Within this expanding sector, pallet pry bars—essential tools for breaking down, moving, and repairing wooden pallets—have seen increased demand across industries such as warehousing, construction, and manufacturing. With the global pallet market itself expected to exceed $64 billion by 2030 (Grand View Research, 2023), the need for durable, high-performance pry bars has intensified. This growth is further fueled by the surge in e-commerce, supply chain optimization initiatives, and the ongoing reuse and recycling of wooden pallets in sustainable logistics practices. As a result, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders in innovation, durability, and market reach. Below, we examine the top 8 pallet pry bar manufacturers shaping the industry through product quality, customer feedback, and global distribution strength.
Top 8 Pallet Pry Bar Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
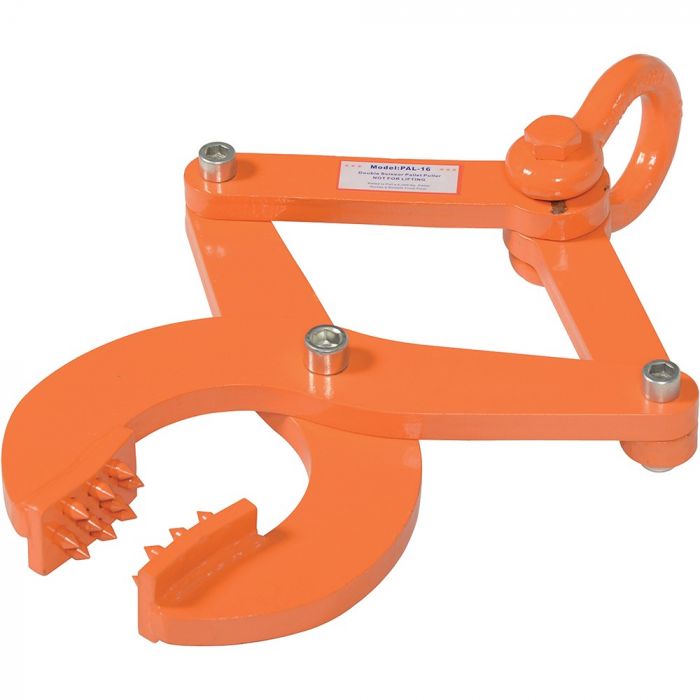
#1 5000 Lb Pallet Pullers & Pallet Pry Bars
Domain Est. 1996
Website: med.hantover.com
Key Highlights: 3-day delivery Free 30-day returnsPallet Pullers & Pallet Pry Bars. We offer a robust range of pallet pullers and pallet pry bars crafted for heavy-duty material handling tasks….
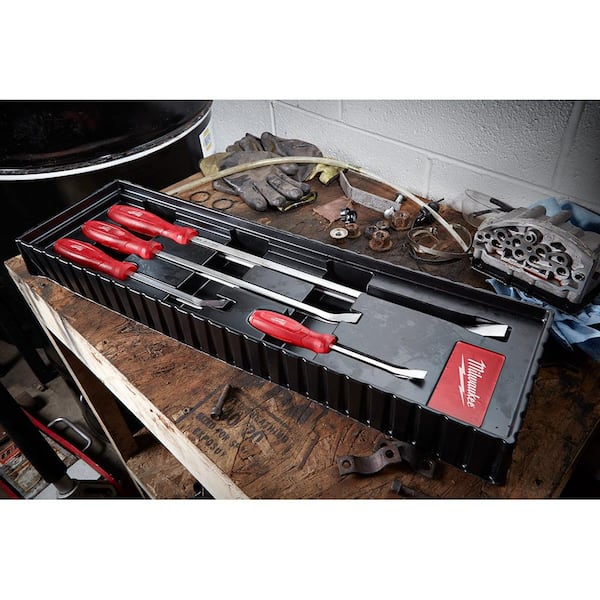
#2 Milwaukee® Tool
Domain Est. 2000
Website: milwaukeetool.com
Key Highlights: Milwaukee Tool is the most respected manufacturer of heavy-duty power tools … Picks and Pry Bars · Bending & Pulling. Layout. View All — Layout · Lasers….
#3 Pry Tools Archives
Domain Est. 1996
Website: estwing.com
Key Highlights: Forged in one piece of solid American steel, Estwing pry tools give you the strength and can-do confidence to stiff-arm your toughest challenges….
#4 Pry-Lever Bars (PLB)
Domain Est. 1998
Website: vestil.com
Key Highlights: Pry lever bar design provides personnel with the needed leverage · Thick steel nose plate with beveled edge allows user to easily get under loads · Poly-on-steel ……
#5 Pallet Pry Bars & Pullers
Domain Est. 1998
Website: jmesales.com
Key Highlights: 1–2 day delivery 30-day returnsPallet Pry Bars & Pullers ; Vestil Pallet Puller – L.P. Double Scissor. $106.64 ; Vestil Pallet Puller – Double Scissor. $99.64 ; Vestil Pallet Pulle…
#6 Starrett Products
Domain Est. 1998
Website: starrett.com
Key Highlights: Discover premium precision measuring tools and cutting solutions including micrometers, calipers, band saw blades and much more. Many American-made since ……
#7 Bars
Domain Est. 2006
Website: roughneck-tools.com
Key Highlights: ROUGHNECK are the UK brand leader in wrecking and demolition bars. Offering the most comprehensive range including the world famous Gorilla Bar….
#8 VEVOR Pallet Buster, 60
Domain Est. 2009
Expert Sourcing Insights for Pallet Pry Bar

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Pallet Pry Bars
The global market for pallet pry bars in 2026 is poised for steady growth, driven by enduring logistical demands, evolving workplace safety standards, and incremental innovation. While not a high-tech sector, the pallet pry bar market reflects broader industrial and supply chain trends, positioning itself as an essential, low-cost tool in material handling ecosystems.
1. Sustained Demand from Logistics and Warehousing Expansion:
The primary driver remains the relentless growth of e-commerce, third-party logistics (3PL), and global supply chains. The proliferation of automated and high-density warehouses still requires manual intervention for pallet breakdown, repair, and handling at loading docks. As warehouse footprints expand—particularly in emerging markets and near urban fulfillment centers—the need for durable, efficient hand tools like pry bars persists. The sheer volume of wooden pallets in circulation (estimated in the billions globally) ensures continuous demand for maintenance and disassembly tools.
2. Heightened Focus on Ergonomics and Worker Safety:
Regulatory pressures (OSHA in the US, EU directives) and corporate wellness initiatives are pushing demand toward ergonomic designs. In 2026, expect wider adoption of pry bars featuring:
* Ergonomic Handles: Molded rubber or thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) grips to reduce vibration and hand fatigue.
* Optimized Leverage: Designs that minimize required force, reducing strain on wrists, shoulders, and backs.
* Reduced Slippage Risk: Improved tip geometry and textured surfaces for better control, mitigating injury risks during use.
Brands emphasizing safety certifications and ergonomic testing will gain a competitive edge, especially in regulated industries and large corporate fleets.
3. Material Innovation and Durability Focus:
While high-carbon steel remains dominant, advancements in heat treatment processes will enhance durability and resistance to chipping or bending. Some niche players may explore lightweight, high-strength alloys or composite-reinforced designs, though cost sensitivity limits widespread adoption. The trend favors “long-life” tools, reducing replacement frequency and total cost of ownership for industrial users.
4. Sustainability and Circular Economy Influence:
The push for sustainable packaging and waste reduction indirectly benefits the pallet pry bar market. As companies prioritize pallet reuse, repair, and recycling over disposal, the need for efficient disassembly tools increases. Pry bars are key enablers in the pallet repair loop. Suppliers may leverage this narrative in marketing, positioning their tools as essential for circular supply chain operations.
5. Competitive Landscape and Distribution Channels:
The market remains fragmented, with established industrial tool brands (e.g., Stanley, DeWalt, GearWrench) competing against specialized material handling suppliers and low-cost manufacturers (primarily from Asia). Key trends include:
* B2B Dominance: Sales through industrial supply distributors (e.g., Grainger, Fastenal), safety equipment suppliers, and direct OEM channels will remain primary.
* E-commerce Growth: Online platforms (Amazon Business, specialized B2B marketplaces) are increasingly important for procurement, especially for SMEs.
* Private Labeling: Large logistics companies may increasingly source customized or private-label pry bars for fleet standardization.
6. Modest Technological Integration:
Unlike larger machinery, pallet pry bars see minimal high-tech integration. The 2026 outlook doesn’t foresee smart sensors or connectivity. However, digital tools may influence the market indirectly through:
* Enhanced Design: CAD and simulation software optimizing leverage and stress points.
* Supply Chain Tracking: RFID or QR codes on high-end models for inventory management within large tool cribs.
Conclusion:
The 2026 pallet pry bar market is characterized by resilient, low-growth demand anchored in the fundamentals of physical logistics. Success will favor manufacturers who prioritize ergonomic safety, material durability, and supply chain reliability, while effectively serving B2B distribution channels. While innovation is incremental, the tool’s critical role in pallet maintenance and the ongoing expansion of global warehousing ensure its continued relevance as an indispensable, if unglamorous, component of industrial operations.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Pallet Pry Bars (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing pallet pry bars may seem straightforward, but buyers often encounter significant challenges related to quality inconsistencies and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these pitfalls can help avoid costly mistakes, product failures, or legal complications.
Poor Material Quality and Durability
One of the most frequent issues is receiving pry bars made from substandard steel. Low-quality materials can lead to rapid wear, bending, or even breakage during use. Suppliers may use lower-grade carbon steel or fail to apply proper heat treatment, compromising strength and longevity. Always verify material specifications (e.g., hardened steel) and request test reports or samples before large orders.
Inconsistent Manufacturing Tolerances
Inconsistent forging, grinding, or finishing processes can result in variations in shape, weight, and balance. These inconsistencies affect ergonomics and functionality, reducing tool efficiency and increasing user fatigue. Without strict quality control, units in the same batch may perform differently, undermining reliability.
Lack of Proper Heat Treatment
Heat treatment is critical for achieving the right balance of hardness and toughness. Poorly heat-treated pry bars are either too brittle (prone to chipping or snapping) or too soft (bend easily). Confirm that the supplier follows standardized heat-treatment procedures and can provide documentation or certifications.
Inadequate Surface Finish and Corrosion Resistance
A poorly finished pry bar may have sharp edges, burrs, or inadequate coating, leading to rust and premature degradation—especially in warehouse or outdoor environments. Ensure the product includes protective finishes like powder coating, enamel, or zinc plating to enhance durability and user safety.
Misrepresentation of Product Origin or Branding
Some suppliers falsely claim their products are made in certain countries (e.g., “Made in USA” or “German Steel”) to justify higher prices or perceived quality. This misrepresentation can mislead buyers about actual manufacturing standards. Always verify certifications and conduct factory audits if possible.
Intellectual Property Infringement
Many established pry bar designs are protected by trademarks, design patents, or utility patents. Sourcing generic versions that closely mimic branded tools (e.g., resembling products from Estwing or Stanley) can expose buyers to IP litigation. Ensure designs are original or properly licensed to avoid legal risks, especially when selling under your own brand.
No Compliance with Safety or Industry Standards
Pallet pry bars used in professional settings should meet relevant safety standards. Lack of compliance with standards such as ANSI or OSHA guidelines—even if not mandatory—can pose liability issues and indicate poor design. Ask suppliers about adherence to recognized safety and performance benchmarks.
Inadequate Packaging and Labeling
Poor packaging can result in damage during shipping, while missing or incorrect labeling may violate import regulations or confuse end-users. Ensure packaging protects the product and includes necessary safety warnings, material info, and traceability data.
Overlooking Supplier Reliability and Traceability
Choosing suppliers based solely on price can lead to unreliable delivery, poor communication, and lack of traceability. Without a dependable supply chain, quality control becomes harder to enforce. Prioritize suppliers with proven track records, clear documentation, and willingness to provide audit trails.
By addressing these common pitfalls proactively—through due diligence, sample testing, and legal review—buyers can source high-quality, compliant pallet pry bars while minimizing IP and operational risks.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Pallet Pry Bar
Product Classification and HS Code
Identify the Harmonized System (HS) code for the pallet pry bar to ensure correct customs classification. Typically, hand tools like pry bars fall under HS Code 8205.40 (Other hand tools). Confirm with local customs authorities or a licensed customs broker, as classifications may vary by country and specific product design.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Package the pallet pry bar securely to prevent damage during transport. Use durable materials such as corrugated cardboard or wooden crates based on shipment volume. Clearly label each package with:
– Product name (“Pallet Pry Bar”)
– Quantity per unit
– Weight and dimensions
– Manufacturer or supplier information
– Barcodes or SKUs, if applicable
Ensure labels comply with destination country requirements, including language and safety warnings, if necessary.
Shipping and Transportation
Pallet pry bars are generally non-restricted goods and can be shipped via standard freight methods (air, sea, or ground). For international shipments:
– Use freight forwarders experienced in handling industrial tools
– Prepare a commercial invoice, packing list, and bill of lading/air waybill
– Declare accurate product value and origin
– Consider insurance for high-value shipments
Import/Export Documentation
Ensure all required documentation is complete and accurate:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Certificate of Origin (if claiming preferential tariffs under trade agreements)
– Bill of Lading (for sea freight) or Air Waybill (for air freight)
Some countries may require additional declarations or product conformity certificates.
Regulatory and Safety Compliance
Verify that the pallet pry bar meets safety and material standards in the destination market. While typically exempt from stringent regulations due to simplicity, consider:
– REACH and RoHS compliance (if shipping to the EU) for restricted substances in metals
– OSHA or ANSI standards (in the U.S.) if marketed for industrial safety use
Ensure no sharp edges or hazards violate packaging or consumer safety rules.
Customs Duties and Taxes
Research applicable import duties, VAT, or GST based on the destination country’s tariff schedule. Duties on hand tools vary; some countries apply low rates or duty-free entry under specific trade agreements. Accurate HS coding is essential to avoid overpayment or delays.
Storage and Handling
Store pallet pry bars in a dry, secure environment to prevent rust or corrosion. Stack packaged units properly to avoid crushing. Use standard material handling equipment (e.g., forklifts) when moving full pallets to maintain workplace safety.
Environmental and Disposal Considerations
The product is typically made of durable steel and is fully recyclable. Communicate end-of-life recycling options to commercial customers. No special disposal regulations apply under normal use.
Compliance Audits and Recordkeeping
Maintain records of shipping documents, compliance certifications, and supplier specifications for at least 5–7 years, depending on jurisdiction. Conduct periodic internal audits to ensure ongoing compliance with trade regulations.
Contact Information and Support
Designate a compliance officer or logistics coordinator to handle inquiries related to shipping, customs, or regulatory issues. Provide customer support for documentation requests or import assistance.
In conclusion, sourcing a pallet pry bar requires careful consideration of material quality, durability, ergonomic design, and intended application. Whether for industrial, warehouse, or personal use, selecting a sturdy, well-constructed pry bar made from high-grade steel ensures longevity and efficient performance. Evaluating suppliers based on reputation, pricing, lead times, and compliance with safety standards is essential to securing a reliable product. Additionally, considering customization options and bulk purchasing can offer cost savings and improved functionality. Ultimately, a well-sourced pallet pry bar enhances operational efficiency, reduces physical strain, and supports safe material handling practices.