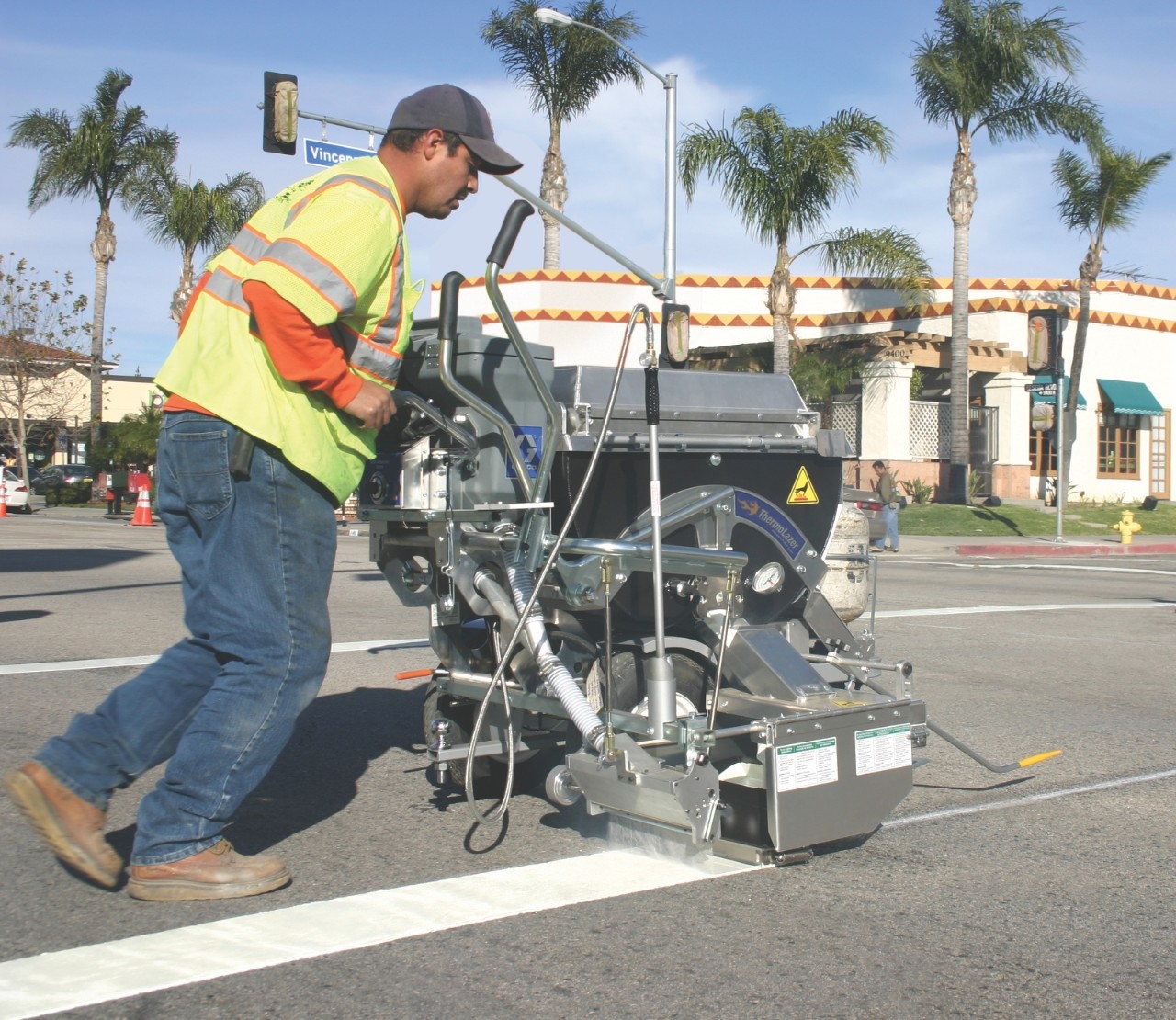
The global road marking materials market, driven by increasing infrastructure investments and stringent road safety regulations, is projected to expand at a CAGR of 5.8% from 2023 to 2028, according to Mordor Intelligence. With thermoplastic paints accounting for a significant share due to their durability, quick drying time, and high visibility, demand for high-performance road markings continues to surge—particularly in emerging economies undergoing rapid urbanization and highway development. As governments worldwide prioritize smart and sustainable transportation systems, thermoplastic coatings have emerged as the preferred solution, outpacing alternatives like water-based or solvent-based paints in lifecycle cost and performance efficiency. This growing momentum has catalyzed intense competition and innovation among manufacturers, setting the stage for the following list of the top 10 thermoplastic paint producers shaping the industry landscape.
Top 10 Painting Thermoplastic Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 World Leader in Specialty Coatings
Domain Est. 1996
Website: rpminc.com
Key Highlights: RPM International Inc. owns subsidiaries that are world leaders in specialty coatings, sealants, building materials and related services….
#2 Americhem
Domain Est. 1997
Website: americhem.com
Key Highlights: Thermoplastic Compounds & Masterbatch for Every Application. Americhem’s product families are built to meet the highest demands for performance, appearance ……
#3 Boltaron® Thermoplastics
Domain Est. 1999
Website: boltaron.com
Key Highlights: SIMONA Boltaron is one of the leading thermoform plastic sheets manufacturers, providing high-performance thermoformable plastic solutions to meet design…
#4 Crown USA, Inc.
Domain Est. 2001
Website: crownusa.com
Key Highlights: Crown USA is your trusted source for innovative pavement marking solutions. Our expanding portfolio includes advanced retroreflective materials, durable ……
#5 Specialty Polymer & Thermoplastic Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2003
Website: avient.com
Key Highlights: Global manufacturer of advanced composites, specialty polymers, color and additive systems, and thermoplastic and polymer compounds that enhance performance ……
#6 Paint
Domain Est. 2012
Website: wilbertplastics.com
Key Highlights: Wilbert Plastic Services blends industry-leading mold and paint technologies for brilliant results. From robotic lines capable of multicolor, metallics, prime ……
#7 ENNIS
Domain Est. 1990
Website: ppg.com
Key Highlights: ENNIS-FLINT® by PPG preformed thermoplastic pavement markings are a 100% solid compound that are pre-cut and ready to use out of the box….
#8 Worbla Thermoplastics
Domain Est. 2012
Website: worbla.com
Key Highlights: Worbla is a brand of innovative, non-toxic (conforms to ASTM D-4236*) thermoplastics designed to give artists a product that allows endless creativity ……
#9 Thermoplastic paint
Domain Est. 2016
Website: dynakrom.com
Key Highlights: Thermoplastic paint. We manufacture an easy-to-apply paint that offers a higher yield per linear meter, giving you the best cost-benefit ratio….
#10 Page
Domain Est. 2019
Website: rae-products.com
Key Highlights: Thermoplastic Markings. A selection of durable, high visibility, heat-applied markings. Offering long-lasting performanec. Explore ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Painting Thermoplastic

H2: Market Trends for Painting Thermoplastic in 2026
As we approach 2026, the global market for painting thermoplastic materials is poised for significant transformation driven by technological innovation, sustainability demands, and evolving industrial needs. Thermoplastic coatings—known for their durability, flexibility, and resistance to environmental stress—are gaining traction across multiple sectors, including automotive, construction, aerospace, and consumer goods. Below are the key market trends shaping the painting thermoplastic industry in 2026:
1. Rising Demand in the Automotive Sector
The automotive industry remains a dominant driver for thermoplastic coatings. With the global push toward lightweight vehicles to improve fuel efficiency and meet emissions standards, manufacturers are increasingly adopting thermoplastic materials for exterior and interior components. In 2026, painting thermoplastics are expected to see increased use in body panels, bumpers, and under-hood applications due to their excellent adhesion, scratch resistance, and ability to be recycled.
2. Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Coatings
Environmental regulations and consumer preference for green products are pushing manufacturers to develop low-VOC (volatile organic compound) and water-based thermoplastic paint systems. In 2026, the market will witness a surge in bio-based thermoplastics and recyclable coating solutions. Companies are investing in closed-loop production systems and exploring circular economy models, where painted thermoplastic parts can be reprocessed without significant quality loss.
3. Advancements in Application Technologies
Innovations in application methods—such as electrostatic spray, powder coating, and in-mold painting—are enhancing the efficiency and finish quality of thermoplastic painting. By 2026, smart coating systems integrated with IoT and AI-driven process controls are expected to become mainstream, enabling real-time monitoring of coating thickness, curing conditions, and defect detection, thereby reducing waste and improving consistency.
4. Growth in Construction and Infrastructure
The construction industry is increasingly using thermoplastic-coated materials for roofing, cladding, and structural components due to their corrosion resistance and long service life. With urbanization and infrastructure development accelerating in Asia-Pacific, the Middle East, and Africa, demand for durable, low-maintenance painted thermoplastics is set to rise significantly by 2026.
5. Expansion of the E-Mobility Market
The booming electric vehicle (EV) market is creating new opportunities for thermoplastic coatings. Battery enclosures, charging stations, and lightweight EV components require coatings that offer thermal stability, electrical insulation, and protection against moisture and chemicals. Painted thermoplastics meet these needs and are expected to be integral to EV manufacturing in 2026.
6. Regional Market Shifts
Asia-Pacific is anticipated to lead the global painting thermoplastic market in 2026, fueled by rapid industrialization, government infrastructure projects, and strong automotive production in countries like China, India, and South Korea. Meanwhile, North America and Europe will focus on high-performance and sustainable coating solutions, supported by stringent environmental policies and advanced R&D ecosystems.
7. Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships
The competitive landscape is seeing increased mergers, acquisitions, and collaborations among coating manufacturers, material suppliers, and end-users. In 2026, such partnerships will accelerate innovation and help companies scale sustainable thermoplastic painting solutions to meet diverse market demands.
In conclusion, the 2026 painting thermoplastic market will be defined by a convergence of performance, sustainability, and digitalization. As industries seek durable, eco-conscious, and cost-effective finishing solutions, thermoplastic coatings will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of surface protection and aesthetics.
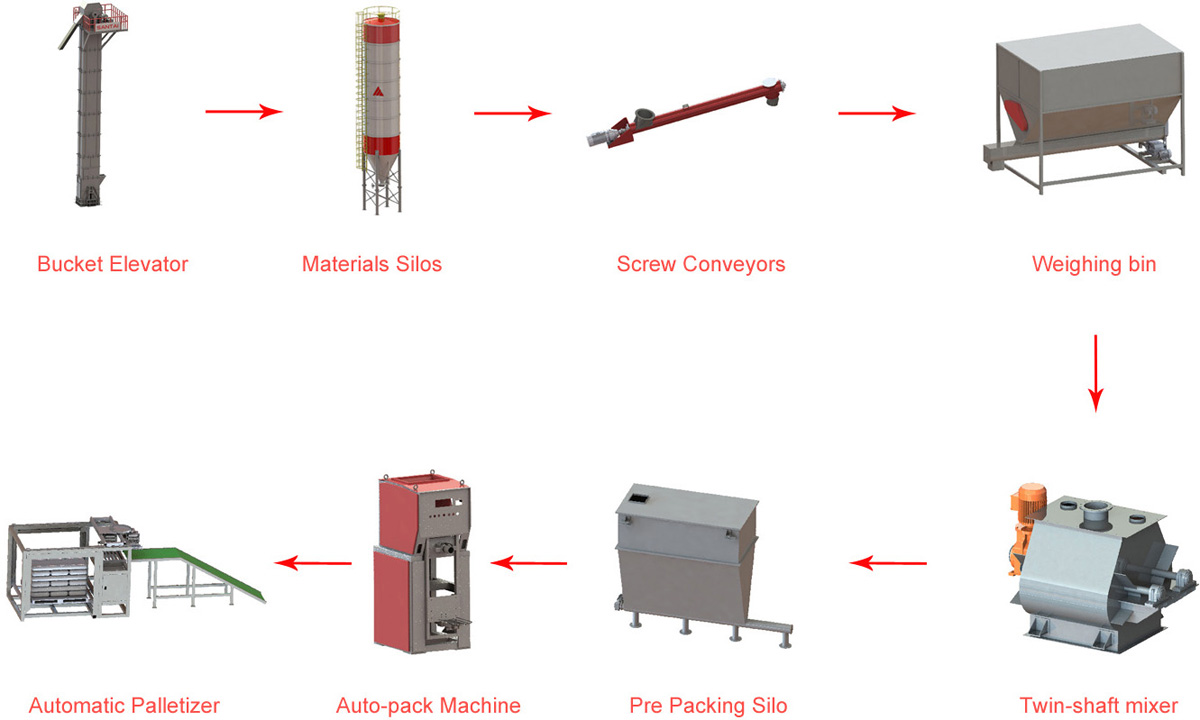
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Painting Thermoplastic: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing painting thermoplastic materials—commonly used in road markings, industrial coatings, and decorative finishes—presents several challenges, particularly concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to product failures, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Inconsistent Material Quality
One of the most frequent issues in sourcing thermoplastic coatings is variability in raw material quality. Suppliers may use substandard resins, pigments, or fillers to reduce costs, leading to poor adhesion, fading, brittleness, or reduced durability. Without strict quality control and standardized testing protocols (e.g., ASTM or ISO specifications), buyers risk receiving batches that fail in real-world applications, especially under extreme weather or heavy traffic conditions.
Lack of Certification and Traceability
Many suppliers, particularly in emerging markets, may lack proper certifications such as ISO 9001, REACH compliance, or environmental safety data sheets (SDS). Without traceability in the supply chain, it becomes difficult to verify the origin of raw materials, confirm batch consistency, or ensure compliance with regulatory standards—exposing buyers to safety and legal risks.
Unclear or Infringing Intellectual Property Rights
Thermoplastic formulations often involve proprietary blends protected by patents, trade secrets, or formulation know-how. Sourcing from suppliers who do not clearly disclose IP ownership—or who use copied or reverse-engineered formulas—can expose the buyer to IP infringement claims. This is particularly risky when sourcing from regions with weak IP enforcement, where “knock-off” products are common.
Insufficient Technical Support and Documentation
Reliable suppliers should provide comprehensive technical data sheets (TDS), safety data sheets (SDS), and application guidelines. A lack of detailed documentation may indicate limited R&D investment or poor manufacturing practices. Buyers may face challenges in application, troubleshooting, or achieving consistent results without proper support.
Hidden Costs from Poor Performance
Low initial pricing can be misleading if the thermoplastic underperforms. Frequent reapplications, premature degradation, or failure to meet durability standards increase total cost of ownership. Buyers must evaluate total lifecycle cost, not just unit price.
Failure to Audit Suppliers
Relying solely on samples or supplier claims without on-site audits or third-party lab testing increases the risk of receiving non-conforming products. Regular audits help verify production capabilities, quality systems, and adherence to agreed specifications.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence: vetting suppliers thoroughly, specifying clear quality and IP requirements in contracts, conducting independent testing, and ensuring transparency throughout the supply chain.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Painting Thermoplastic
Overview of Thermoplastic Paint
Thermoplastic paint is widely used in road marking, industrial coatings, and decorative applications due to its durability, fast drying time, and resistance to wear. Composed of polymers, resins, pigments, and fillers, thermoplastic materials transition from solid to molten state when heated and solidify upon cooling—without undergoing chemical changes. Understanding the logistics and regulatory compliance associated with its handling, storage, transportation, and application is essential for safety, environmental protection, and legal adherence.
Classification and Regulatory Status
Hazard Classification
Thermoplastic paint in solid form (pellets, powder, or preformed sheets) is typically classified as non-hazardous under international transport regulations such as the UN Model Regulations (UN TDG), ADR (Europe), IMDG (maritime), and IATA (air). However, classification depends on specific formulations:
– May contain flammable solvents or additives (rare in 100% solid thermoplastics).
– Dust from powder forms may be irritant or combustible.
– Manufacturer’s Safety Data Sheet (SDS) must be consulted for hazard determination.
Safety Data Sheet (SDS) Compliance
- Maintain up-to-date SDS for each product in accordance with GHS (Globally Harmonized System).
- SDS must include handling, storage, PPE recommendations, and emergency measures.
- Required under OSHA (U.S.), CLP Regulation (EU), WHMIS (Canada), and similar frameworks globally.
Storage Requirements
Environmental Conditions
- Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight and heat sources (>40°C may cause premature softening).
- Avoid exposure to moisture, especially for powder-based formulations.
- Keep containers sealed to prevent contamination and caking.
Storage Compatibility
- Do not store near strong oxidizers, acids, or flammable materials.
- Use non-combustible pallets and maintain at least 0.5 meters clearance from walls and sprinklers.
Shelf Life
- Typical shelf life: 12–24 months when stored properly.
- Rotate stock using FIFO (First In, First Out) to avoid degradation.
Transportation Guidelines
Packaging
- Supplied in moisture-resistant bags (e.g., polyethylene-lined woven PP) or sealed containers.
- Bulk transport in FIBCs (Flexible Intermediate Bulk Containers) must be secured against tearing and moisture.
Mode-Specific Transport Rules
- Road (ADR): No special labeling required for non-hazardous thermoplastic pellets; use standard cargo securing methods.
- Air (IATA): Declare as “Not Restricted” or “Consumer Commodity” if applicable; provide SDS.
- Sea (IMDG): Classify correctly; if non-hazardous, no UN number required.
- Always verify with carrier policies and country-specific regulations.
Temperature Control
- Avoid prolonged exposure to high ambient temperatures during transit (e.g., closed trailers in summer).
- Insulated or climate-controlled transport recommended in extreme conditions.
Handling and Worker Safety
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Gloves (nitrile or chemical-resistant)
- Safety goggles or face shield
- Dust mask (N95 or equivalent) when handling powders
- Heat-resistant gloves and protective clothing during melting/application
Dust Control
- Use local exhaust ventilation when transferring powders.
- Avoid creating airborne dust; sweep or use vacuum (ATEX-rated if explosive dust risks exist).
Melting and Application Safety
- Use calibrated thermoplastic kettles with temperature controls (typically 180–220°C).
- Ensure proper ventilation in application areas to avoid fumes (especially if overheated).
- Follow lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures during equipment maintenance.
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
Spill Management
- Solid spills: Sweep up and place in sealed container for recycling or disposal.
- Molten spills: Allow to cool, then remove mechanically; do not use water (risk of steam or splatter).
Waste Disposal
- Waste thermoplastic is typically non-hazardous and can be disposed of in licensed landfills.
- Recycling is encouraged—some suppliers offer take-back programs.
- Comply with local regulations (e.g., EPA in the U.S., Environment Agency in the UK).
Emissions and Air Quality
- Melting operations may release minor VOCs or fumes—ensure adequate ventilation.
- Use fume extraction systems in enclosed spaces.
- Monitor for compliance with local air quality regulations (e.g., EPA NESHAP, EU Industrial Emissions Directive).
Regulatory Compliance by Region
United States
- OSHA: Hazard Communication Standard (HCS) compliance required.
- EPA: Follow RCRA guidelines for waste; air emissions may require permitting.
- DOT: Proper classification under 49 CFR for transport.
European Union
- REACH: Ensure registration of substances if importing >1 ton/year.
- CLP Regulation: Correct labeling and classification.
- ADR: Adhere to road transport rules.
Other Regions
- Canada: Comply with WHMIS 2015 and TDG regulations.
- Australia: Follow NOHSC and ADG Code requirements.
- Always check local environmental and workplace safety legislation.
Training and Documentation
Employee Training
- Conduct regular training on:
- Safe handling and storage
- Emergency response
- PPE use
- Equipment operation
- Maintain training records.
Recordkeeping
- Retain SDS for minimum 10–15 years depending on jurisdiction.
- Document inspections, maintenance, spills, and disposal activities.
- Keep transport manifests and compliance certificates.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management for thermoplastic paint ensures operational efficiency, worker safety, and legal adherence. By following industry standards and regulatory requirements across storage, transportation, handling, and disposal, organizations can minimize risks and maintain environmental responsibility. Always consult product-specific documentation and stay updated on evolving regulations in your operating regions.
Conclusion for Sourcing Thermoplastic Paint
In conclusion, sourcing thermoplastic paint requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, reliability, and compliance with industry standards. Thermoplastic paint is a high-performance material essential for durable road markings and industrial applications, offering advantages such as excellent reflectivity, quick drying, and long-term resistance to weather and traffic wear.
Successful sourcing involves selecting suppliers with proven technical expertise, consistent product quality, and the capacity to meet volume and delivery requirements. It is crucial to evaluate factors such as raw material sourcing, manufacturing processes, certifications (e.g., ISO, local road authority approvals), and environmental sustainability practices.
Additionally, building strong supplier relationships, conducting regular performance evaluations, and staying informed about technological advancements will ensure a resilient supply chain. By prioritizing these elements, organizations can ensure a reliable supply of high-quality thermoplastic paint, ultimately supporting safety, efficiency, and value in their infrastructure and industrial projects.