The global food packaging market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising demand for convenient, sustainable, and tamper-evident packaging solutions—particularly in the takeaway and food delivery sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global food packaging market size was valued at USD 357.6 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing urbanization, busy lifestyles, and the surge in online food delivery services, all of which have renewed demand for durable, leak-resistant containers like oyster pails. Once primarily associated with Chinese takeout, oyster pails—folded paperboard containers with wire handles—are now gaining traction across diverse cuisines and eco-conscious brands seeking recyclable and compostable packaging. As sustainability regulations tighten and consumer preferences shift toward environmentally responsible materials, manufacturers are innovating with plant-based coatings and FSC-certified board stocks. In this evolving landscape, a select group of manufacturers are leading the charge in quality, scalability, and sustainable design. Here are the top seven oyster pail manufacturers shaping the future of foodservice packaging.
Top 7 Oyster Pail Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
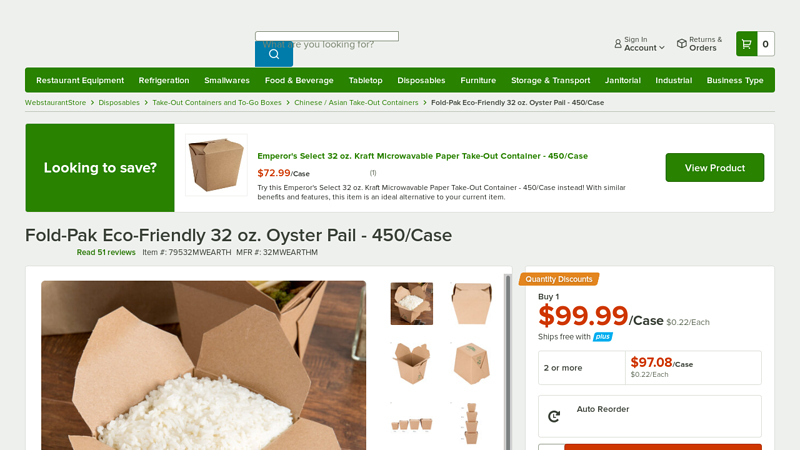
#1 Paper Food Buckets
Domain Est. 1997
Website: graphicpkg.com
Key Highlights: Ideal for large meals or quantities of food, our paper food buckets come in short and standard sizes and are ideal for all your on-the-go meals….
#2 Fold
Domain Est. 2003
#3 Custom Printed Oyster Pail Packaging Boxes At Wholesale Price …
Domain Est. 2017
Website: ybyboxes.com
Key Highlights: Get Low Minimum Custom Printed Boxes With Unique Style And Shapes To Protect The Quality Of Your Oysters. Free Designing And Free Shipping To USA And ……
#4 Custom Oyster Pail Boxes
Domain Est. 2019
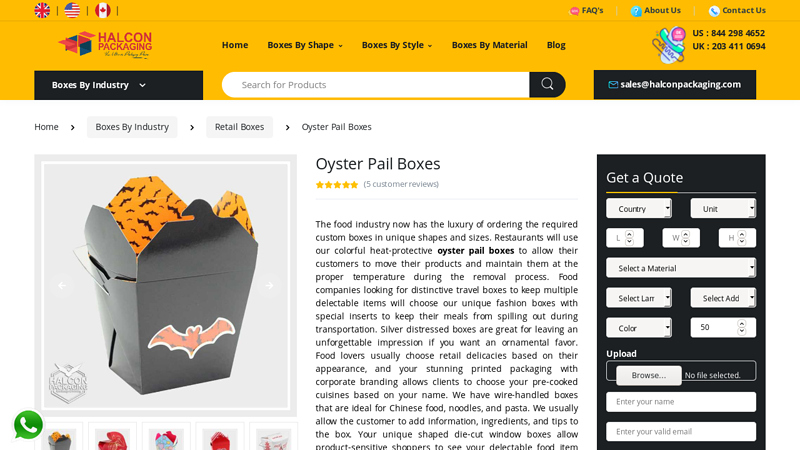
Website: halconpackaging.com
Key Highlights: Rating 4.9 (179) Oyster pail boxes can be customized in a variety of ways by Halcon Packaging. They can be made in a variety of forms and sizes….
#5 To
Website: smurfitwestrock.com
Key Highlights: The original and popular Chinese takeout box, also known as an oyster pail is made with high-quality solid bleached sulfate (SBS) paperboard with an interior ……
#6 Oyster Pail & Chinese Takeout Box California, US
Website: customboxusa.com
Key Highlights: Rating 4.7 (20) Chinese takeout box – Looking for the perfect way to serve your Chinese cuisine? Look no further than our durable and stylish Chinese takeout boxes!…
#7 Custom Logo Printed Oyster Pail Packaging Boxes at Wholesale Price
Website: emenacpackaging.com.au
Key Highlights: Rating 4.8 (106) We use superior quality material and our unmatched expertise of creating custom printed paper Oyster Pail Boxes that keep the products safe from falling down….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Oyster Pail

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Oyster Pails
As we approach 2026, the market for oyster pails—commonly known as paper soup containers or Chinese food boxes—is undergoing significant transformation driven by sustainability mandates, evolving consumer preferences, and innovations in packaging technology. Traditionally associated with takeout food service, oyster pails are adapting to a rapidly changing landscape shaped by environmental regulations, e-commerce growth, and circular economy principles.
1. Surge in Sustainable and Compostable Materials
By 2026, the oyster pail market is expected to pivot heavily toward sustainable materials. Regulatory pressures in North America and the European Union, including bans on single-use plastics and expanded producer responsibility (EPR) laws, are pushing manufacturers to replace petroleum-based coatings with plant-based alternatives. Compostable oyster pails made from molded fiber, bamboo, or sugarcane (bagasse) are gaining traction. Major foodservice providers and restaurant chains are increasingly sourcing FSC-certified, recyclable, and commercially compostable oyster pails to align with corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals.
2. Growth in Online Food Delivery Driving Demand
The continued expansion of food delivery platforms such as Uber Eats, DoorDash, and regional competitors is fueling demand for functional and leak-resistant oyster pails. In 2026, the design of oyster pails is expected to prioritize performance—featuring improved sealing mechanisms, moisture barriers, and stackable configurations that reduce transportation damage. The rise of ghost kitchens and virtual restaurant brands further amplifies the need for cost-effective, brandable, and efficient packaging, positioning oyster pails as a staple in delivery-centric operations.
3. Innovation in Design and Functionality
In response to consumer expectations, oyster pails are evolving beyond their traditional folded paper design. Anticipated 2026 trends include smart packaging integrations (e.g., QR codes for recycling instructions or brand storytelling), dual-compartment pails for mixed entrees, and enhanced thermal retention properties. Some manufacturers are experimenting with water-based barrier coatings that maintain grease resistance while improving recyclability—addressing a long-standing industry challenge.
4. Regional Market Diversification
While North America remains the largest market for oyster pails due to the popularity of Asian-inspired takeout, growth in Asia-Pacific and Latin America is accelerating. Urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and the globalization of food culture are expanding the use of oyster pails beyond Chinese cuisine to include salads, grain bowls, and desserts. Localized manufacturing hubs in Southeast Asia and Mexico are reducing supply chain dependencies and enabling faster response to regional demand fluctuations.
5. Price Volatility and Supply Chain Resilience
The oyster pail market in 2026 will continue to face cost pressures stemming from fluctuating raw material prices (particularly virgin paper pulp and bio-coatings) and energy costs. Companies are investing in supply chain resilience by securing long-term contracts with sustainable fiber suppliers and adopting nearshoring strategies. Additionally, industry consolidation is expected as smaller producers struggle to meet compliance and innovation benchmarks.
Conclusion
By 2026, the oyster pail market will be defined by sustainability, functionality, and adaptability. No longer seen as a simple takeaway container, the oyster pail is transforming into a strategic component of brand identity and environmental stewardship. Companies that prioritize eco-innovation, digital integration, and supply chain agility will lead the market, turning regulatory and consumer challenges into competitive advantages.
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Oyster Pails (Quality, IP)
When sourcing oyster pails—commonly known as paper takeout containers—businesses often encounter challenges related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) concerns. Being aware of these pitfalls can help ensure reliable supply, customer satisfaction, and legal compliance.
Poor Material Quality and Construction
Many low-cost oyster pails are made from substandard paperboard, leading to issues like leakage, sogginess, or structural failure when holding hot or greasy foods. Thin coatings or inadequate wax/plastic lining compromise moisture resistance, resulting in customer complaints and potential brand damage. Additionally, weak seams or poorly sealed folds can cause spills during transport.
Inconsistent Sizing and Fit
Oyster pails from different suppliers may vary slightly in dimensions, making it difficult to maintain consistency in packaging lines or retail displays. Inconsistent sizing can also affect lid compatibility, especially if sourcing from multiple vendors, leading to operational inefficiencies and customer dissatisfaction.
Misleading Sustainability Claims
Suppliers may advertise oyster pails as “eco-friendly,” “compostable,” or “biodegradable” without proper certifications. Some containers still contain PFAS (“forever chemicals”) or non-recyclable plastic linings, undermining environmental commitments and exposing brands to greenwashing accusations.
Lack of Food Safety Compliance
Not all oyster pails are manufactured using food-grade materials or in facilities compliant with FDA or equivalent food safety standards. Sourcing from non-compliant suppliers risks contamination and regulatory violations, especially for businesses in highly regulated markets.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Custom-designed oyster pails—especially those with logos, unique patterns, or patented structural features—can pose IP risks if sourced from unauthorized manufacturers. Some suppliers may replicate patented designs (e.g., specific folding mechanisms or locking tabs) without licensing, exposing the buyer to legal liability. Additionally, using branded designs without proper rights can lead to trademark infringement claims.
Supplier Transparency and Traceability Gaps
Many oyster pails are sourced from overseas manufacturers with limited supply chain visibility. This lack of transparency makes it difficult to verify ethical labor practices, environmental standards, or material origins—increasing reputational and compliance risks.
Failure to Protect Custom Designs
Businesses that develop proprietary oyster pail designs may fail to secure trademarks, design patents, or copyrights. Without IP protection, competitors or unscrupulous suppliers can copy the design, diluting brand uniqueness and losing competitive advantage.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough due diligence, clear specifications, supplier audits, and proactive IP management when sourcing oyster pails.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Oyster Pail
Overview
The oyster pail, commonly known as a paper soup container or Chinese food takeout box, is widely used in the foodservice industry for packaging hot and cold food items. Ensuring proper logistics and compliance throughout its lifecycle—from manufacturing to disposal—is essential for food safety, environmental responsibility, and regulatory adherence.
Material Specifications & Food Contact Compliance
Oyster pails are typically made from paperboard coated with a food-grade polyethylene (PE) or wax lining to provide moisture resistance. To comply with food safety regulations:
– The materials must meet FDA 21 CFR standards for food contact surfaces in the United States.
– In the EU, compliance with Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 and specific measures such as Commission Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 for plastic materials is required if plastic linings are used.
– Manufacturers must provide documentation confirming compliance, including letters of guarantee or food contact declarations.
Sustainable Sourcing & Environmental Compliance
- Paper used in oyster pails should be sourced from sustainably managed forests, preferably certified by FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) or PEFC (Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification).
- Wax-lined pails are not recyclable in most municipal programs due to contamination concerns. PE-lined versions may be recyclable in facilities equipped to process contaminated paper.
- Increasingly, compostable oyster pails made from uncoated paper with PLA (polylactic acid) lining are available and certified to standards such as ASTM D6400 or EN 13432 for industrial compostability.
Packaging & Storage Logistics
- Store oyster pails in a dry, temperature-controlled environment to prevent warping, mold, or contamination.
- Stack pallets securely with appropriate load limits to avoid crushing lower layers.
- Use protective shrink wrap or stretch film to prevent moisture ingress during transit.
Transportation & Distribution
- Ship in sealed, pest-proof containers to maintain hygiene.
- Follow Good Distribution Practices (GDP) for food contact materials, ensuring traceability and protection from contamination during transport.
- Maintain separation from hazardous or non-food-grade materials in shared transport vehicles.
End-of-Life Management & Labeling
- Clearly label oyster pails with disposal instructions (e.g., “Compostable in Industrial Facilities” or “Not Recyclable”).
- Provide consumer education on proper disposal to support waste reduction goals.
- Monitor evolving local regulations regarding single-use food packaging and compostable materials.
Regulatory Monitoring & Documentation
- Regularly review updates from regulatory bodies (e.g., FDA, EPA, EU Commission, local environmental agencies).
- Maintain records of supplier compliance, material safety data sheets (MSDS), and certifications.
- Conduct periodic audits of supply chain partners to ensure ongoing compliance.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management for oyster pails ensures food safety, environmental sustainability, and adherence to global regulatory standards. By selecting compliant materials, optimizing distribution, and supporting responsible end-of-life practices, businesses can reduce risk and enhance their sustainability profile.
In conclusion, sourcing oyster pail containers requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, sustainability, and supplier reliability. These versatile paperboard containers are widely used in the foodservice industry, particularly for takeout and delivery, due to their durability, leak resistance, and iconic design. When sourcing oyster pails, businesses should consider factors such as material quality (food-safe, grease-resistant coatings), environmental impact (preferably recyclable or compostable options), customization needs (branding, size variations), and compliance with food safety regulations.
Establishing partnerships with reputable suppliers—whether domestic or international—can ensure consistent supply and product consistency. Additionally, evaluating minimum order quantities, lead times, and shipping costs is essential for cost-efficiency, especially for small to medium-sized operations. With growing consumer demand for sustainable packaging, prioritizing eco-friendly materials and transparent sourcing practices not only supports environmental goals but also enhances brand reputation.
Ultimately, a well-considered sourcing strategy for oyster pails contributes to operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and long-term sustainability in the competitive food packaging market.