The global outboard motor market continues to gain momentum, fueled by rising recreational boating activities, advancements in fuel-efficient and electric propulsion technologies, and growing marine tourism. According to a 2023 report by Grand View Research, the global outboard motors market was valued at approximately USD 6.5 billion and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects steady growth, citing increased demand in emerging economies and a shift toward eco-friendly outboard systems as key drivers. With major players investing in lightweight designs, digital integration, and hybrid powertrains, competition among manufacturers has intensified. As the industry navigates technological transformation and regulatory shifts, nine manufacturers have emerged as leaders—shaping innovation, capturing significant market share, and setting the standard for performance, reliability, and sustainability in marine propulsion.
Top 9 Outboard Motor Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Mercury Marine
Domain Est. 1995
Website: mercurymarine.com
Key Highlights: Mercury Marine is the world’s leading manufacturer of recreational marine propulsion engines. Get sales, service and parts info, and find a local dealer ……
#2 Outboards
Domain Est. 1997
Website: global.yamaha-motor.com
Key Highlights: Information about Products, Yamaha Outboard Stories, Overseas Sales Network, etc. All Products · Accessories · Four Stroke Functions and features….
#3 OUTBOARD MOTORS
Domain Est. 1997
Website: tohatsu.com
Key Highlights: Official web site for Tohatsu Outboard Motors. View all the information about Tohatsu, Japan’s oldest outboards manufacturer….
#4 Suzuki Marine
Domain Est. 1997
#5 Evinrude
Domain Est. 1997
Website: evinrude.com
Key Highlights: Find the engine your boat deserves with Evinrude’s unparalleled line of outboard motors, parts, and accessories, available at dealers nationwide….
#6
Domain Est. 1998
Website: mercuryracing.com
Key Highlights: Mercury Racing builds the best marine & automotive propulsion systems, accessories, and parts on the market. Learn the value of raw performance and power….
#7 Yamaha Outboards
Domain Est. 2002
Website: yamahaoutboards.com
Key Highlights: Yamaha Outboards provides industry-leading innovation, outstanding performance, incredible power, unequalled customer satisfaction and legendary ……
#8 Cox Marine Diesel Outboards
Domain Est. 2014
Website: coxmarine.com
Key Highlights: Cox Marine’s powerful diesel outboard engines. Engineered for durability, fuel savings, and reduced emissions. Power your fleet with next-gen marine ……
#9 Outboard Global Store
Domain Est. 2023
Website: outboardglobalstore.com
Key Highlights: We are large distributor for outboard engine,inboard engine,marine accessories , diesel engine,marine electronic Etc. We sell the latest and used products….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Outboard Motor

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for the Outboard Motor Industry
The outboard motor market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, evolving consumer preferences, and increasing environmental regulations. Key trends shaping the industry include:
1. Accelerated Electrification and Hybrid Adoption:
Electric outboard motors will move beyond niche applications into the mainstream. Driven by advancements in battery technology (higher energy density, faster charging) and falling costs, electric motors will gain significant market share, particularly in the sub-60 HP segment for recreational and commercial applications in environmentally sensitive areas. Hybrid systems, combining internal combustion engines with electric propulsion, will bridge the gap for larger vessels requiring extended range. Major manufacturers like Torqeedo, Yamaha, and Mercury are expected to expand their electric and hybrid portfolios significantly by 2026.
2. Stringent Emission Regulations Driving Innovation:
Global environmental standards, particularly in North America and Europe, will continue to tighten. Regulations such as the U.S. EPA Tier 3 and potential future Euro VII standards will push manufacturers to invest heavily in cleaner-burning four-stroke engines, direct fuel injection, and exhaust after-treatment technologies. This regulatory pressure will accelerate the phase-out of older two-stroke models and favor manufacturers with strong R&D capabilities in emissions reduction.
3. Integration of Smart Technologies and Connectivity:
Outboard motors will become increasingly “smart,” featuring advanced digital integration. By 2026, expect widespread adoption of:
* Digital Command Center (DCC) integration with multifunction displays (MFDs) for real-time engine diagnostics, fuel monitoring, and performance optimization.
* Autonomous navigation features like joystick docking, autopilot integration, and dynamic positioning systems enhancing safety and ease of use.
* IoT-enabled remote monitoring allowing owners and service providers to track engine health, schedule maintenance, and receive over-the-air updates.
4. Growth in Recreational Boating and Premium Segments:
Continued growth in leisure boating, especially in North America and parts of Asia-Pacific, will fuel demand for higher-horsepower outboards (150 HP and above). Consumers are increasingly seeking premium features, performance, and reliability, driving demand for advanced propulsion systems with enhanced user experience and aesthetics.
5. Expansion in Emerging Markets and Commercial Applications:
Markets in Southeast Asia, Latin America, and Africa present growth opportunities due to rising disposable incomes and tourism development. Additionally, the commercial sector—including aquaculture, ferry services, and eco-tourism—will increasingly adopt electric and hybrid outboards to meet sustainability goals and reduce operating costs.
6. Supply Chain Resilience and Sustainability Focus:
Manufacturers will prioritize supply chain diversification and localized production to mitigate disruptions. Concurrently, there will be a growing emphasis on sustainable manufacturing practices, recyclable materials, and end-of-life product management, aligning with broader ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) trends.
In summary, the 2026 outboard motor market will be defined by a shift toward electrification, smarter propulsion systems, and compliance with environmental standards. Companies that innovate in clean technology, digital integration, and sustainable operations will be best positioned to lead in this evolving landscape.
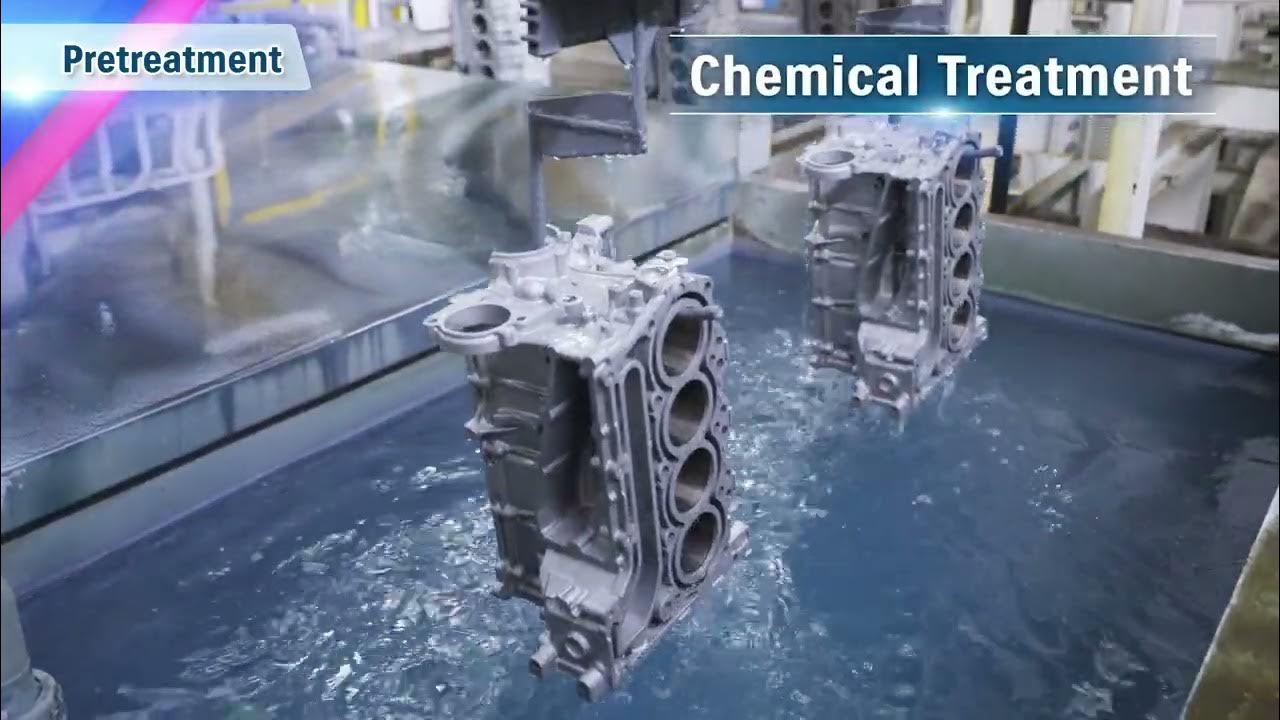

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Outboard Motors (Quality, IP)
Sourcing outboard motors, especially from international suppliers or lower-cost regions, presents several critical risks related to product quality and intellectual property (IP). Failing to address these pitfalls can lead to safety hazards, regulatory non-compliance, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are the most common challenges to watch for:
Poor Build Quality and Material Deficiencies
Many low-cost outboard motors suffer from substandard construction, including the use of inferior metals, plastics, and seals. This can result in premature corrosion, engine failure, or safety risks when operating in harsh marine environments. Components like gears, crankshafts, and fuel systems may not meet required tolerances or durability standards, leading to frequent breakdowns and high warranty costs.
Inadequate or Missing Certification and Compliance
Reputable outboard motors must comply with international standards such as EPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency), EU Directive 2003/44/EC (marine equipment), and ISO standards for safety and emissions. Sourcing from non-compliant suppliers may result in motors that fail environmental regulations or lack essential safety certifications, making them illegal to sell or operate in key markets.
Counterfeit or Clone Motors Infringing IP Rights
A major concern is the proliferation of counterfeit or cloned outboard motors that copy well-known brands (e.g., Yamaha, Mercury, Evinrude) in design, branding, and performance specifications. These products often violate trademarks, design patents, and technical patents. Purchasing or distributing such motors exposes the buyer to legal liability, seizure of goods by customs, and damage to brand reputation.
Lack of Technical Documentation and IP Verification
Suppliers may fail to provide complete technical documentation, such as engineering drawings, test reports, or proof of IP ownership. Without these, it’s difficult to verify whether the design is original or infringes on existing patents. This opacity increases the risk of unintentional IP infringement and complicates efforts to obtain regulatory approvals.
Inconsistent Quality Control and Testing Procedures
Many manufacturers, particularly smaller or less established ones, lack rigorous quality assurance processes. Motors may not undergo standardized performance, durability, or safety testing (e.g., salt spray testing, vibration testing, or load testing). This inconsistency leads to variable product quality across batches and increases the likelihood of field failures.
Hidden Design Flaws and Safety Risks
Cloned or reverse-engineered motors might replicate the appearance of genuine products but lack critical engineering refinements. This can result in unsafe operating conditions—such as overheating, fuel leaks, or electrical hazards—that are not immediately apparent during initial inspection or testing.
Supply Chain and After-Sales Support Gaps
Even if the initial product appears acceptable, poor sourcing decisions can lead to long-term operational issues. Suppliers may not offer spare parts, technical support, or warranty services, leaving end-users without maintenance options. This undermines customer trust and increases total cost of ownership.
Failure to Conduct Proper Due Diligence
Buyers often skip essential verification steps—such as factory audits, third-party lab testing, or IP clearance searches—due to time or cost pressures. This oversight increases exposure to both quality defects and legal risks associated with IP infringement.
To mitigate these pitfalls, buyers should conduct thorough supplier vetting, insist on compliance certifications, perform independent quality inspections, and engage legal experts to review IP rights before finalizing procurement.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Outboard Motors
Overview
Outboard motors, as marine propulsion devices, require careful handling throughout the logistics chain to ensure product integrity, regulatory compliance, and timely delivery. This guide outlines key considerations for shipping, storage, customs, and environmental compliance when transporting outboard motors globally.
Classification & Harmonized System (HS) Codes
Proper classification is essential for international shipping and customs clearance. Outboard motors are typically classified under the following HS codes:
– 8407.21: Outboard motors, two-stroke, of a cylinder capacity not exceeding 50cc
– 8407.29: Other outboard motors (four-stroke, higher capacity, etc.)
Accurate classification ensures correct duty rates, eligibility for trade agreements, and compliance with import regulations.
Packaging & Handling Requirements
To prevent damage during transit:
– Use manufacturer-approved packaging with protective foam or padding
– Secure motors in upright position to prevent oil leakage
– Seal all openings (air intakes, exhaust) to prevent contamination
– Label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Tip” markings
– Avoid stacking heavy items on top of packaged motors
Storage Conditions
Store outboard motors in a:
– Dry, climate-controlled environment (avoid humidity to prevent corrosion)
– Well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight
– Upright position to maintain internal lubrication
– Secure location away from flammable materials (due to fuel system components)
Transportation Modes
Choose the appropriate transport method based on volume, destination, and urgency:
– Ocean Freight: Ideal for bulk shipments; use FCL (Full Container Load) for better control
– Air Freight: Suitable for urgent or low-volume deliveries
– Overland Trucking: Common for regional distribution; ensure proper securing and temperature control
Ensure transport vehicles are clean and free from contaminants.
Customs Documentation
Essential documents for international shipments:
– Commercial Invoice (with accurate value, HS code, and origin)
– Packing List (detailing quantity, weight, and dimensions per package)
– Bill of Lading (for ocean freight) or Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin (may be required for tariff preferences)
– Import License (if required by destination country)
Verify country-specific requirements in advance.
Regulatory & Environmental Compliance
Outboard motors are subject to various environmental and safety regulations:
– EPA Certification (USA): All outboard motors sold in the U.S. must meet EPA emission standards
– EU Type Approval (EU): Comply with Directive 2003/44/EC for recreational craft
– CARB Compliance (California): Stricter emissions standards; required for sale in California
– Noise Regulations: Some regions regulate sound levels (e.g., ISO 9001 or national standards)
Ensure motors are labeled with required certification marks.
Import Restrictions & Duties
Check for:
– Import tariffs based on HS code and trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, ASEAN)
– Anti-dumping or countervailing duties on motors from certain countries
– Prohibited components (e.g., lead-based paints in some regions)
– Labeling requirements in local language (e.g., Spanish in Mexico, French in Canada)
Battery & Fuel System Considerations
- Fuel Tanks: Must be completely drained before shipping (hazardous material regulations)
- Batteries: If shipped separately, comply with IATA/IMDG regulations for lithium or lead-acid batteries
- Declare any residual fuel as “empty, drained, and purged” to avoid hazardous classification
End-of-Life & Recycling Compliance
Be aware of extended producer responsibility (EPR) laws in destination markets:
– WEEE Directive (EU): May require registration and take-back programs for electronic components
– Producer Responsibility Organizations (PROs): Register with local entities if selling directly to consumers
Best Practices for Supply Chain Management
- Partner with experienced freight forwarders familiar with marine equipment
- Conduct pre-shipment inspections to verify packaging and labeling
- Use track-and-trace systems for real-time shipment visibility
- Maintain records of compliance certifications for audits
Conclusion
Successful logistics and compliance for outboard motors depend on accurate classification, proper handling, and adherence to international and regional regulations. Proactive planning and documentation minimize delays, reduce costs, and ensure market access across global regions.
Conclusion:
Sourcing outboard motor suppliers requires a strategic approach that balances cost-efficiency, product quality, reliability, and long-term partnership potential. After evaluating various suppliers based on criteria such as manufacturing capabilities, certification standards (e.g., ISO, EPA, or CE compliance), pricing, lead times, customer support, and reputation in the marine industry, it is evident that selecting the right supplier significantly impacts product performance and customer satisfaction.
Prioritizing suppliers with proven experience, strong R&D capabilities, and adherence to international environmental and safety regulations ensures not only compliance but also enhances brand credibility. Additionally, establishing clear communication channels and considering factors such as after-sales service, warranty provisions, and logistical support helps mitigate risks and improves supply chain resilience.
In conclusion, a thorough vetting process combined with ongoing performance monitoring will enable the selection of dependable outboard motor suppliers capable of supporting business growth, innovation, and customer demand in a competitive maritime market. Building strategic partnerships with these suppliers lays the foundation for sustainable success in the marine propulsion sector.