The global organic flaxseed market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising consumer awareness of plant-based nutrition and the health benefits associated with omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and lignans found in flaxseed. According to a 2023 report by Grand View Research, the global flaxseed market size was valued at USD 1.38 billion and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.6% from 2023 to 2030, with organic variants gaining significant traction due to increased demand in the health food and natural supplements sectors. This surge in demand has spurred the expansion of specialized organic flaxseed manufacturers, particularly across North America—the largest producer and exporter of flaxseed—along with growing production hubs in Europe and Australia. As retailers and food brands prioritize clean-label and sustainably sourced ingredients, identifying reliable, high-quality organic flaxseed suppliers has become critical. The following list highlights the top nine manufacturers known for their certifications, traceability, scalability, and commitment to organic integrity, reflecting the evolving landscape of this niche yet expanding segment.
Top 9 Organic Flax Seed Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
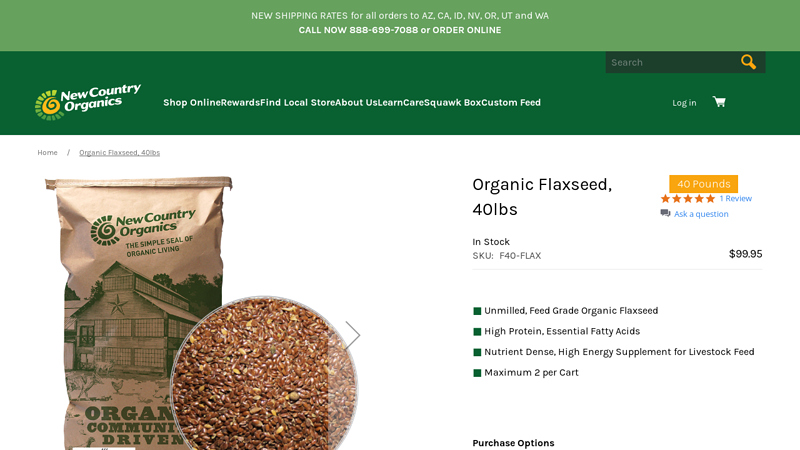
#1 Organic Flaxseed, 40lbs
Domain Est. 2015
Website: newcountryorganics.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 5.0 (1) Mar 6, 2024 · Unmilled Flaxseed is ideal for diet supplementation, diet formulation, and large scale producers. Flaxseed has a dense nutrient profile that…
#2 Flaxseed Trading S.A.
Website: flaxseed.eu
Key Highlights: Flaxseed specializes in importing and exporting linseed (linseed) for all types of applications for food, animal feed and industrial use….
#3 Flaxseed Supplier: Brown & Golden Flax
Domain Est. 1996
Website: scoular.com
Key Highlights: Scoular offers high-quality brown and golden flaxseed, whole or milled, for the food, crush, feed and pet food markets. Contact us for tailored solutions….
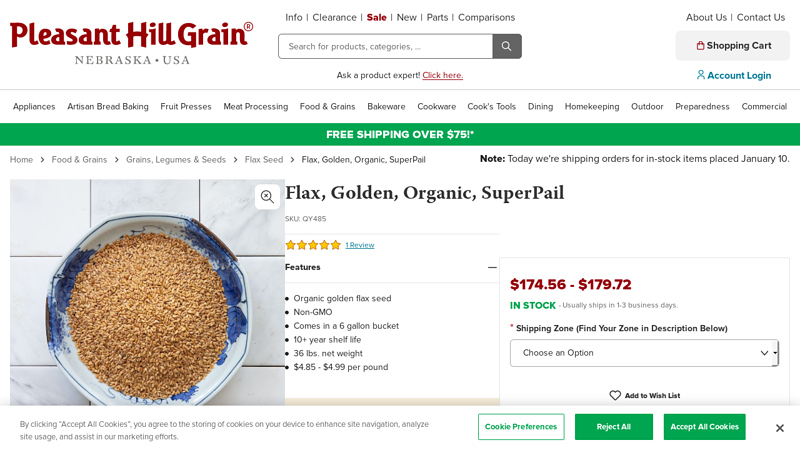
#4 Golden flax seed, flaxseed, organic, bulk 36 lb. superpail at PHG
Domain Est. 1999
Website: pleasanthillgrain.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 5.0 (1) Our golden flax seed (linum flavum) is certified organic, non-GMO and useful for all kinds of cooking purposes. Golden flax has a mild, pleasantly nutty f…
#5 AmeriFlax
Domain Est. 2001
Website: ameriflax.com
Key Highlights: The company produces organic and non-GMO flaxseed (brown and yellow), garbanzo beans (chickpeas), lentils, quinoa, chia and radish seed.The company in ……
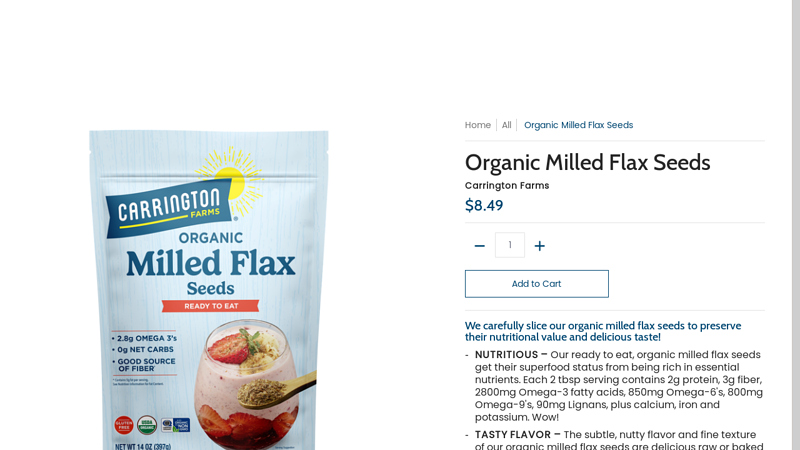
#6 Organic Milled Flax Seeds
Domain Est. 2006
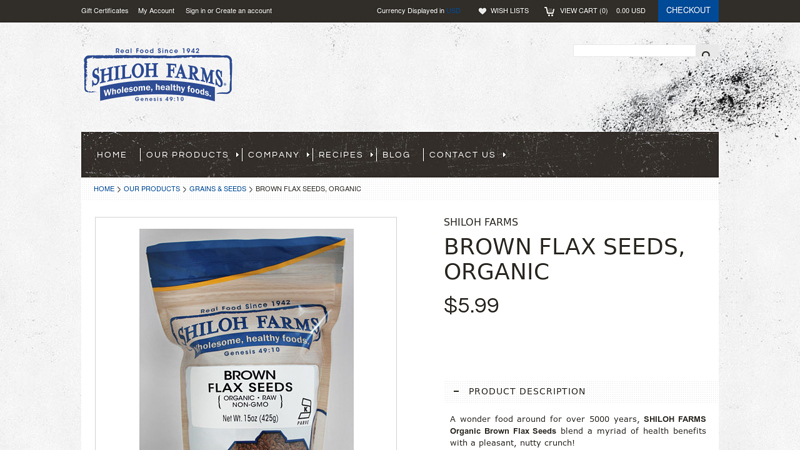
#7 Brown Flax Seeds
Domain Est. 2007
#8 Organic Flax Seeds
Domain Est. 2008
#9 Organic Ground Flax Seed – Healthy, Fiber
Domain Est. 2022
Website: quaynaturals.com
Key Highlights: Organic Ground Flax Seed is high in fiber and omega-3. Ideal for baking, smoothies and cooking helping support heart health, digestion and overall wellness….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Organic Flax Seed
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Organic Flax Seed
The global organic flax seed market is poised for robust growth in 2026, driven by converging consumer, regulatory, and environmental trends. Key dynamics shaping the market include:
1. Accelerated Demand for Plant-Based Nutrition:
Consumer focus on heart health, digestive wellness, and plant-based protein sources continues to fuel demand. Organic flax seed, rich in omega-3 fatty acids (ALA), lignans, and fiber, is increasingly positioned as a functional food ingredient. By 2026, product innovation—especially in clean-label, ready-to-eat formats like organic flax bars, plant-based dairy alternatives, and fortified cereals—will expand its presence beyond bulk sales into mainstream retail.
2. Premiumization and Transparency:
Consumers are demanding greater transparency in sourcing and certification. Organic flax seed commands a price premium, supported by verified non-GMO, pesticide-free, and sustainable farming practices. In 2026, blockchain traceability and regenerative agriculture claims are expected to become key differentiators, enhancing consumer trust and brand loyalty.
3. Expansion in Food & Beverage Applications:
The food industry is integrating organic flax seed into a wider range of products—from bakery items and pasta to meat substitutes and functional beverages. Its natural binding properties and nutritional profile make it ideal for clean-label formulations, aligning with the clean-eating trend. This application growth will drive B2B demand, particularly in North America and Europe.
4. Regional Market Growth:
North America remains the largest market, with the U.S. and Canada leading in per capita consumption. Europe follows closely, fueled by stringent organic regulations and health-conscious populations. Meanwhile, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific are expected to witness the fastest growth by 2026, as awareness of plant-based nutrition rises in countries like India and China.
5. Supply Chain Challenges and Sustainability Pressures:
Climate variability and land use constraints may impact yields, increasing pressure on supply chains. However, this also incentivizes investment in sustainable farming techniques and vertical integration. Organic flax producers who adopt climate-resilient practices and ensure ethical labor standards will gain a competitive edge.
6. Regulatory Support and Certification Harmonization:
Supportive government policies promoting organic agriculture—such as subsidies and research funding—are expected to continue in key producing regions (e.g., Canada, EU). Harmonization of organic certification standards across borders could reduce trade barriers and streamline global distribution by 2026.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the organic flax seed market will be characterized by strong demand, product diversification, and heightened emphasis on sustainability and transparency. Stakeholders who innovate in product development, ensure supply chain resilience, and communicate authentic organic values are well-positioned to capitalize on this growth trajectory.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Organic Flax Seed (Quality, IP)
Sourcing organic flax seed requires careful attention to both quality parameters and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to supply chain disruptions, regulatory non-compliance, and reputational damage.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Verification of Organic Certification
Relying solely on supplier claims without verifying up-to-date, recognized organic certifications (e.g., USDA NOP, EU Organic, Canada Organic) is a major risk. Certificates can be outdated or fraudulent. Always request current certification documents and verify them with the issuing body.
Contamination with Non-Organic or GMO Material
Flax is often grown in rotation with conventional crops and processed in shared facilities. Without stringent segregation and cleaning protocols, cross-contamination with non-organic or genetically modified (GMO) material can occur. Ensure suppliers have robust identity preservation (IP) and contamination prevention systems.
Poor Seed Storage and Handling Practices
Flax seed is prone to rancidity due to its high oil content. Exposure to heat, light, and moisture during storage or transport degrades quality and shortens shelf life. Suppliers lacking climate-controlled storage and proper handling procedures can deliver oxidized, off-smelling, or moldy seed.
Inconsistent Seed Size, Color, and Purity
Variability in seed characteristics may indicate poor sorting, blending from multiple sources, or adulteration. This affects processing efficiency and final product consistency. Require clear specifications and third-party lab testing for purity, foreign matter, and visual defects.
Insufficient Testing for Mycotoxins and Residues
Organic flax can still be exposed to environmental contaminants. Failure to test for mycotoxins (e.g., aflatoxin, ochratoxin) and prohibited pesticide residues risks regulatory rejection or health hazards. Insist on batch-specific test results from accredited laboratories.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
Unlicensed Use of Protected Flax Varieties
Many high-performing flax varieties (e.g., CDC varieties in Canada) are protected under plant breeders’ rights or patents. Sourcing seeds from unauthorized distributors or using them for propagation without a license can lead to legal action and supply termination.
Lack of Traceability in Seed Origin
Without clear documentation of seed lineage and sourcing channels, it’s difficult to verify IP compliance. Suppliers should provide pedigrees and licensing proof, especially for certified organic seed stock.
Unauthorized Propagation or Resale of Breeder Seed
Purchasing “organic flax seed” does not grant rights to replant or resell it as seed. Some buyers inadvertently breach IP agreements by saving and replanting harvested crops. Ensure contracts specify intended use (e.g., for food, not seed multiplication).
Failure to Audit IP Compliance in the Supply Chain
Relying on intermediaries without auditing their sourcing practices increases exposure to IP violations. Conduct due diligence on suppliers’ procurement methods and require warranties of IP compliance in contracts.
Mitigating these pitfalls requires rigorous supplier vetting, clear contractual terms, independent testing, and ongoing monitoring of both quality and legal compliance throughout the sourcing process.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Organic Flax Seed
This guide outlines key considerations for the logistics and regulatory compliance involved in handling, transporting, and trading organic flax seed. Adherence to these practices ensures product integrity, meets legal requirements, and maintains organic certification.
Sourcing and Certification
Ensure all organic flax seed is sourced from certified organic producers or suppliers. Verify valid certification documents from a USDA-accredited (or equivalent, such as EU, Canada Organic) certification body. Maintain records of organic transaction certificates (OTCs), certificates of analysis (COAs), and supplier affidavits to demonstrate chain of custody and compliance with organic standards.
Storage Requirements
Store organic flax seed separately from conventional or non-organic commodities to prevent commingling and contamination. Use clean, dry, pest-free storage facilities with controlled temperature and humidity (ideally below 70°F and 65% relative humidity) to preserve freshness and prevent mold. Clearly label all containers and bins as “Organic” and include lot numbers, harvest date, and certification details.
Transportation and Handling
Use dedicated or thoroughly cleaned vehicles and equipment for transporting organic flax seed. Prevent contamination from prohibited substances (e.g., synthetic pesticides, fumigants, or non-organic grains) during loading, transit, and unloading. Maintain transport documentation, including bills of lading and organic affidavits, to support organic integrity throughout the supply chain.
Regulatory Compliance
Comply with all national and international regulations, including the USDA National Organic Program (NOP), EU Organic Regulation (EC) No 834/2007, or other applicable standards. Ensure proper labeling in accordance with organic labeling rules—use of the USDA Organic seal (if applicable), ingredient lists, and certifier identification. For export, meet destination country requirements, including import permits and phytosanitary certificates.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive records for a minimum of five years, including organic certificates, purchase and sales records, shipping logs, storage logs, cleaning procedures, and audit reports. Accurate documentation is essential for traceability and successful certification audits.
Pest and Contamination Control
Implement an organic-approved pest management plan using physical, mechanical, or biological controls. Prohibited substances such as synthetic fumigants (e.g., methyl bromide) must not be used. Use only NOP-compliant pest control methods and materials, and document all interventions.
Testing and Quality Assurance
Conduct regular testing for mycotoxins, heavy metals, GMOs, and residual solvents, especially when sourcing from high-risk regions. Testing supports compliance with food safety standards (e.g., FDA, EFSA) and organic regulations that prohibit GMOs. Retain COAs and test results as part of quality assurance protocols.
Import and Export Considerations
For international trade, verify equivalency agreements between certifying countries (e.g., U.S.-EU Organic Equivalency Arrangement). Prepare necessary export documentation: commercial invoice, packing list, phytosanitary certificate, OTC, and certificate of origin. Confirm that the importing country recognizes the organic certification body and complies with its labeling laws.
Handling Non-Conformities
Establish a corrective action plan for addressing non-compliant shipments, such as accidental commingling or contamination. Segregate affected material, investigate root causes, document actions taken, and notify the certifier promptly. Implement preventive measures to avoid recurrence.
In conclusion, sourcing organic flaxseed requires careful consideration of quality, sustainability, certification, and supply chain transparency. Choosing certified organic flaxseed ensures that the product is free from synthetic pesticides, herbicides, and GMOs, supporting both consumer health and environmentally responsible farming practices. It is essential to partner with reputable suppliers who adhere to rigorous organic standards and provide traceability from farm to final product. Additionally, evaluating factors such as origin, growing conditions, and processing methods contributes to consistent quality and nutritional integrity. By prioritizing ethical sourcing and building strong relationships with trusted producers, businesses can deliver a premium organic flaxseed product that meets consumer demand for purity, sustainability, and nutritional benefits.