The global packaged food and beverage industry continues to expand, driven by rising consumer demand for convenience and on-the-go products—trends that directly benefit specialized packaging segments like those serving citrus and orange-based beverages and products. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global packaging market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% from 2023 to 2028, with regional demand in emerging markets and innovations in sustainable materials acting as key growth catalysts. As orange juice and citrus-infused products maintain strong sales in both retail and foodservice channels, the need for durable, visually appealing, and eco-conscious packaging has never been greater. This growth has elevated the importance of specialized orange packaging manufacturers who balance functionality, branding, and environmental responsibility. Drawing from industry performance metrics and technological advancements, here are the top five manufacturers leading innovation and market share in orange packaging.
Top 5 Orange Packaging Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Pharmaceutical Packaging -Allentown, PA
Domain Est. 1998
Website: orangeproducts.com
Key Highlights: Orange Products, Inc. of Allentown, PA Serving the Global Vitamin & Pharmaceutical Industry; Precision Roll-On Applicators, Bottles & Caps. (610) 791-9711….
#2 Orange Packaging
Domain Est. 2001
Website: orangepkg.com
Key Highlights: Orange Packaging is a leading thermoformed packaging and POP display manufacturer offering a variety of acrylic, corrugated, and plastic packaging ……
#3 Orange Printers
Domain Est. 2011
Website: orangexpress.com
Key Highlights: We are a multi-award-winning specialty packaging company, commercial printer, label manufacturer, creative design agency, and pre-media solutions provider…
#4 Tetra Pak processing and packaging solutions for food and …
Domain Est. 1993
Website: tetrapak.com
Key Highlights: Tetra Pak is the world’s leading food processing and packaging solutions company working closely with our customers and suppliers to provide safe food….
#5 Orange Packaging UK
Domain Est. 2021
Website: orangepackaging.co.uk
Key Highlights: We offer personalized packaging solutions for your brand when the minimum order quantity is met. Our design team will collaborate with you to create unique ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Orange Packaging

H2: Market Trends Shaping Orange Packaging in 2026
As we approach 2026, the orange packaging sector is undergoing significant transformation driven by evolving consumer preferences, regulatory shifts, technological innovation, and heightened sustainability demands. This analysis explores the key market trends expected to shape the orange packaging industry in 2026, focusing on material innovation, sustainability, smart packaging, supply chain dynamics, and regional market developments.
1. Accelerated Shift Toward Sustainable and Compostable Materials
By 2026, sustainability remains the dominant driver in orange packaging innovation. Consumers and regulators are demanding reduced plastic usage and increased use of compostable or recyclable materials. Orange juice and fresh citrus packaging are increasingly adopting fiber-based solutions derived from post-consumer recycled (PCR) content or rapidly renewable resources like sugarcane and bamboo. Bioplastics such as polylactic acid (PLA) are gaining traction, particularly in flexible packaging formats. Brands are responding by redesigning packaging to be lightweight, recyclable, and plastic-free—aligning with extended producer responsibility (EPR) laws now enforced across the EU, Canada, and parts of the U.S.
2. Growth of Plant-Based and Edible Coatings for Fresh Oranges
A major innovation in fresh citrus packaging is the rise of edible and biodegradable coatings to replace traditional plastic wraps and clamshells. Companies are investing in water-based, plant-derived coatings that extend shelf life while eliminating the need for secondary packaging. These coatings, often made from citrus peel extracts or algae, reduce food waste and align with circular economy principles—a key priority for retailers and consumers alike in 2026.
3. Smart and Active Packaging Integration
Smart packaging technologies are being adopted to enhance traceability, freshness, and consumer engagement. By 2026, orange packaging increasingly features QR codes, NFC tags, and time-temperature indicators that allow consumers to verify product origin, freshness, and carbon footprint. Active packaging solutions—such as oxygen scavengers and antimicrobial liners—are being used in juice cartons to prolong shelf life without preservatives, supporting clean-label trends.
4. Regulatory Pressure Driving Standardization
Global regulatory frameworks are converging on stricter packaging standards. By 2026, the EU’s Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR), U.S. state-level plastic bans, and similar initiatives in Asia-Pacific are pushing brands to standardize packaging formats for recyclability. This is leading to consolidation in packaging design, with emphasis on mono-materials and simplified labeling to improve sorting efficiency. Compliance costs are rising, but they are also incentivizing innovation and partnerships across the value chain.
5. E-Commerce Optimization and Consumer-Centric Design
With sustained growth in online grocery sales, orange packaging in 2026 is being engineered for e-commerce resilience. Packaging must now withstand longer distribution cycles while minimizing material use. Brands are adopting right-sized, stackable, and crush-resistant designs. Additionally, packaging serves as a key marketing tool, with bold colors, storytelling labels, and nutritional transparency becoming essential for shelf (and screen) appeal.
6. Regional Market Diversification and Local Sourcing
In response to supply chain volatility and carbon reduction goals, major orange-producing regions—such as Florida, California, Brazil, and South Africa—are localizing packaging production. This trend reduces transportation emissions and supports regional economies. Emerging markets in Southeast Asia and Africa are also adopting improved packaging solutions to reduce post-harvest losses and access export markets.
7. Circular Economy Models and Reuse Pilots
By 2026, pilot programs for reusable orange juice containers are expanding in Europe and North America, particularly in urban areas with high return rates. Deposit-return schemes and refill stations in grocery stores are gaining consumer acceptance, supported by digital platforms that track container returns. While still niche, these models signal a long-term shift toward circular packaging systems.
Conclusion
The orange packaging market in 2026 is characterized by a convergence of environmental responsibility, technological sophistication, and consumer empowerment. Companies that prioritize sustainable materials, embrace digital integration, and align with regulatory and societal expectations will lead the market. Success will depend on agility, collaboration across the supply chain, and a deep commitment to reducing environmental impact while maintaining product quality and safety.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Orange Packaging (Quality, IP)
Sourcing orange packaging—whether for branded consumer goods, agricultural products, or promotional materials—comes with unique challenges, particularly concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to address these pitfalls can result in product recalls, legal disputes, or reputational damage.
Inconsistent Color Quality and Brand Misalignment
One of the most critical issues when sourcing orange packaging is maintaining consistent color accuracy. Orange is a vibrant, attention-grabbing hue, but slight variations in shade (e.g., neon, burnt, tangerine) can significantly affect brand perception. Suppliers may use different dyes, inks, or substrates, leading to batch-to-batch inconsistencies. Without strict Pantone or CMYK specifications and proper color management protocols, the final packaging may not align with brand guidelines, undermining marketing efforts.
Substandard Material Quality and Durability
Orange packaging is often used for perishable goods (like citrus fruits or juices), requiring materials that offer moisture resistance, strength, and shelf-life protection. Sourcing from low-cost suppliers may result in flimsy cardboard, non-food-safe inks, or inadequate barrier properties. Poor quality can lead to damaged products in transit, contamination risks, or failure to meet regulatory standards—especially in food and pharmaceutical sectors.
Lack of IP Protection and Design Infringement
Using distinctive orange packaging—such as a specific shade or design layout—can raise intellectual property concerns. For example, companies like Fanta or certain cleaning product brands have trademarked their signature orange hues or packaging designs. Sourcing custom packaging without proper IP clearance risks infringing on existing trademarks or design patents. Additionally, suppliers in certain regions may replicate protected designs without authorization, exposing the buyer to legal liability.
Unlicensed Use of Branded Elements
When sourcing packaging that includes logos, patterns, or graphics, there’s a risk that suppliers use copyrighted artwork without proper licensing. This is especially common in regions with lax IP enforcement. Even if unintentional, using unlicensed visuals or fonts can result in cease-and-desist letters, fines, or shipment seizures at customs.
Inadequate Supplier Verification and Transparency
Many sourcing pitfalls stem from working with suppliers who lack transparency about their production processes. Without on-site audits or third-party certifications, it’s difficult to verify whether the orange packaging is made using approved materials, sustainable practices, or compliant with safety regulations. This opacity increases the risk of counterfeit components or unethical manufacturing practices.
Failure to Secure Design Rights in Contracts
When commissioning custom orange packaging, businesses often assume they own the design outright. However, without clear contractual terms, the supplier may retain rights to the artwork or mold designs. This can prevent the company from sourcing the same packaging from another vendor or scaling production, creating dependency and limiting IP control.
To mitigate these risks, businesses should conduct thorough due diligence, specify technical and legal requirements in procurement contracts, perform regular quality checks, and consult legal experts to ensure IP compliance when sourcing orange packaging.
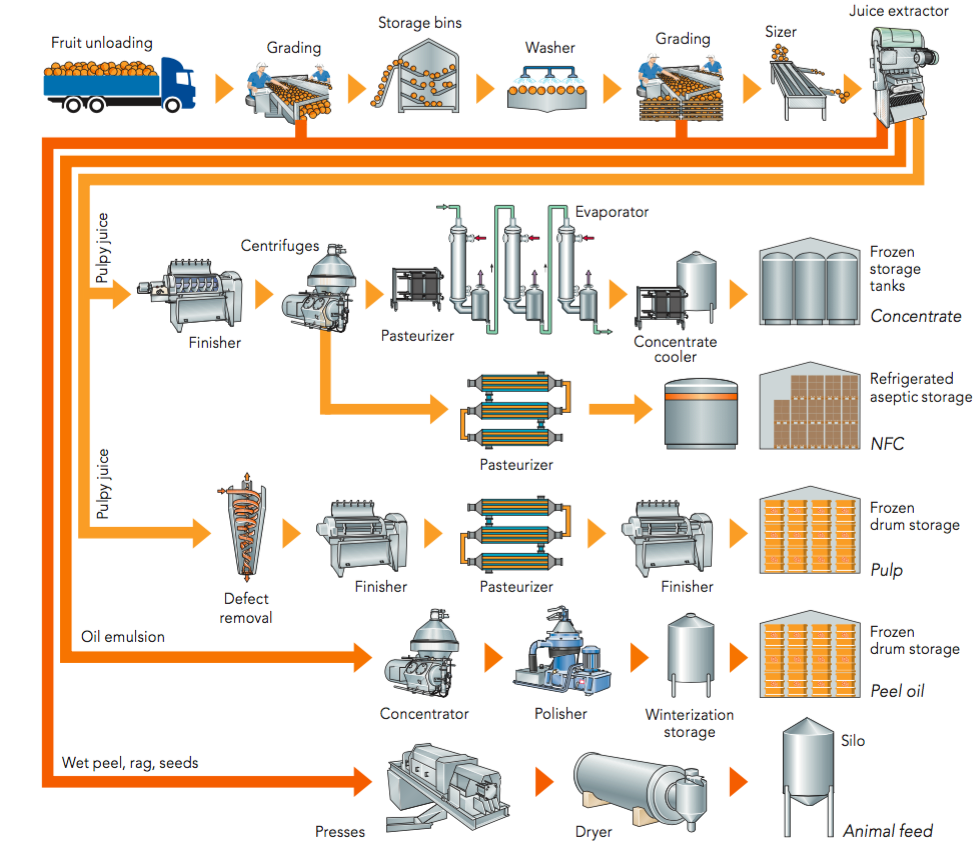
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Orange Packaging
This guide outlines essential logistics and compliance considerations for handling, transporting, and managing orange packaging materials throughout the supply chain. Adherence to these guidelines ensures product safety, regulatory compliance, sustainability, and efficient operations.
Packaging Specifications and Standards
All orange packaging must meet predefined specifications aligned with industry standards and regulatory requirements. Packaging materials should be food-grade where applicable, especially for agricultural or consumer goods. Ensure compliance with ISO 22000 (food safety), ISO 14001 (environmental management), and relevant regional regulations (e.g., FDA in the U.S., EU Framework Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 for food contact materials). Clearly label packaging with batch numbers, production dates, and handling instructions.
Material Sourcing and Sustainability Compliance
Source packaging materials from certified sustainable suppliers. Prioritize recyclable, compostable, or biodegradable materials where possible. Comply with Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) regulations in target markets. Document supplier certifications (e.g., FSC for paper-based packaging) and conduct periodic audits to ensure adherence to environmental and ethical sourcing policies.
Transportation and Handling Procedures
Use appropriate transport methods to prevent damage to orange packaging during transit. Palletize loads securely and use stretch wrap or straps to stabilize. Protect packaging from moisture, direct sunlight, and extreme temperatures. Follow OSHA and local safety standards for manual handling to reduce workplace injuries. Utilize automated handling systems when feasible to improve efficiency and reduce human error.
Regulatory Labeling and Documentation
Ensure all packaging is correctly labeled in compliance with destination country regulations. Labels must include product identification, net weight, handling symbols (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Way Up”), and any required hazard warnings. Maintain accurate shipping documentation, including commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of compliance. For international shipments, comply with customs requirements such as HS codes and import/export declarations.
Cold Chain and Perishable Goods Considerations
If orange packaging is used for perishable goods (e.g., fresh citrus), integrate with cold chain logistics. Monitor and document temperature throughout the supply chain using data loggers. Packaging must maintain thermal integrity and be compatible with refrigerated transport and storage facilities. Validate packaging performance under real-world conditions to ensure product freshness and safety.
Waste Management and End-of-Life Compliance
Implement a waste management plan for used orange packaging. Segregate recyclable materials and partner with certified recycling facilities. Comply with local waste disposal regulations and report packaging waste data where required (e.g., under the UK Packaging Waste Regulations or EU Directive 94/62/EC). Promote reuse programs or take-back schemes to enhance circularity.
Quality Assurance and Audits
Conduct regular internal and third-party audits of packaging processes to verify compliance with logistics and regulatory standards. Maintain traceability records from raw material sourcing to final delivery. Address non-conformances promptly through corrective and preventive actions (CAPA). Train staff annually on updated compliance requirements and handling procedures.
Incident Reporting and Corrective Actions
Establish a clear protocol for reporting and managing incidents involving packaging damage, contamination, or regulatory violations. Document all incidents, perform root cause analysis, and implement corrective actions to prevent recurrence. Communicate relevant issues to stakeholders, including suppliers, carriers, and regulatory bodies, as required.
By following this guide, organizations can ensure that orange packaging is managed safely, sustainably, and in full compliance with applicable laws and industry best practices.
Conclusion for Sourcing Orange Packaging:
Sourcing effective and sustainable orange packaging requires a balanced approach that considers product protection, cost-efficiency, environmental impact, and brand alignment. After evaluating various materials, suppliers, and design options, it is evident that choosing packaging made from recyclable or biodegradable materials—such as molded pulp, recycled cardboard, or compostable films—not only supports sustainability goals but also meets increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly solutions. Additionally, partnering with reliable suppliers who offer scalability, quality assurance, and innovation ensures consistent packaging performance and supply chain resilience.
Customization options such as branding, ventilation, and ergonomic design further enhance both functionality and market appeal. Ultimately, investing in well-sourced orange packaging contributes to reduced waste, improved shelf life, and a stronger brand image. By prioritizing sustainability, cost, and quality, businesses can achieve a packaging solution that protects the product, satisfies customers, and aligns with long-term environmental and commercial objectives.







