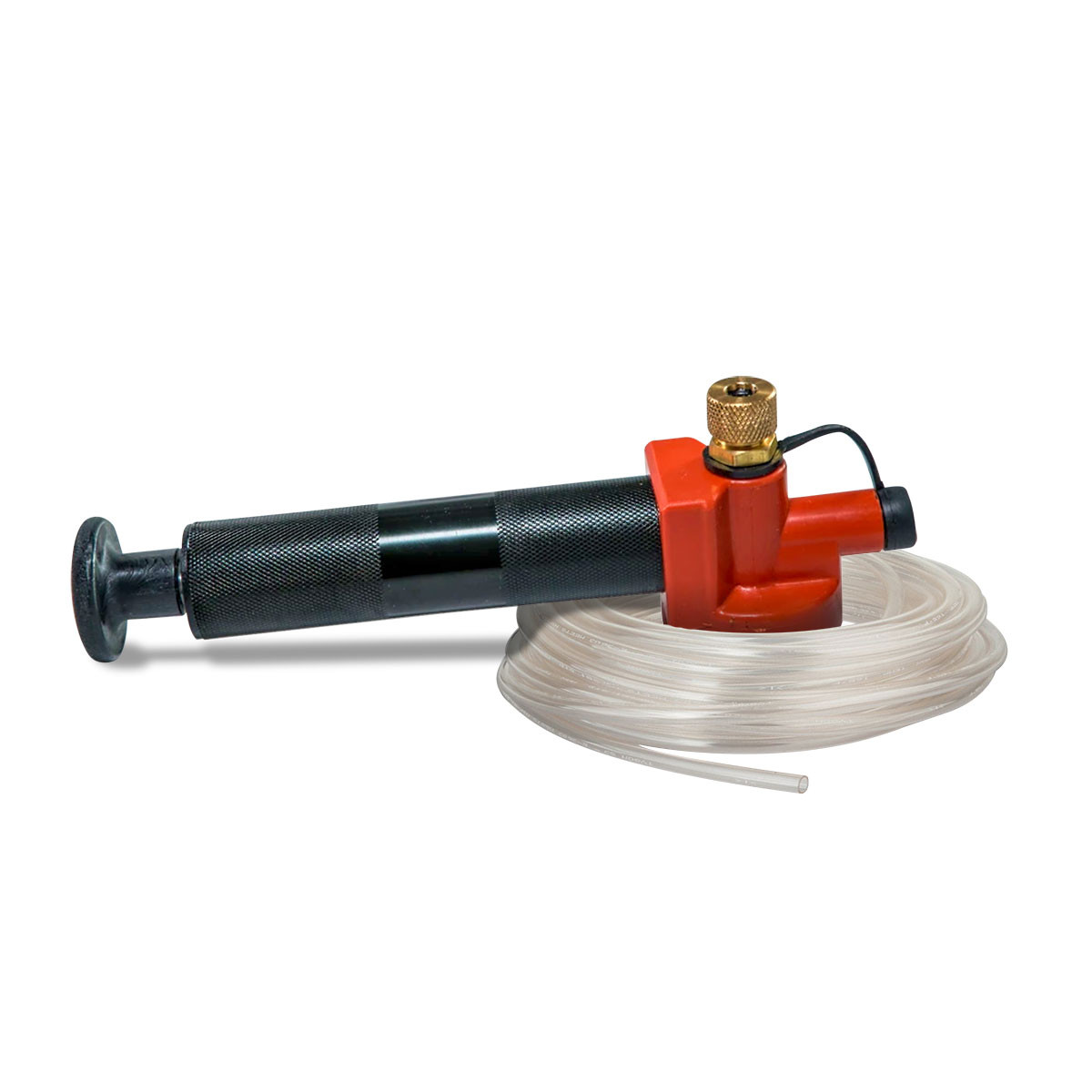
The global oil syphon pump market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand across automotive, industrial maintenance, and marine sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global fuel transfer pump market—closely aligned with oil syphon applications—was valued at USD 2.1 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% from 2023 to 2030. Rising vehicle ownership, coupled with the need for efficient fluid transfer solutions in equipment maintenance, continues to fuel innovation and competition in the space. As reliability, suction efficiency, and material durability become critical purchasing factors, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders in performance and market reach. Based on product reviews, distribution footprint, and technical specifications, the following nine companies represent the top oil syphon manufacturers shaping the industry today.
Top 9 Oil Syphon Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 PIUSI
Domain Est. 2000
Website: piusi.com
Key Highlights: PIUSI is a leading Fluid management company specialised in fluid handling technology and fuel management systems. Optimise your fuel operations with our ……
#2 Oil Extractor Pumps & Evacuation Equipment
Domain Est. 1994
Website: graco.com
Key Highlights: Our oil evacuation systems are designed to drain, evacuate and transfer used oil efficiently and quickly in a smooth process. These ……
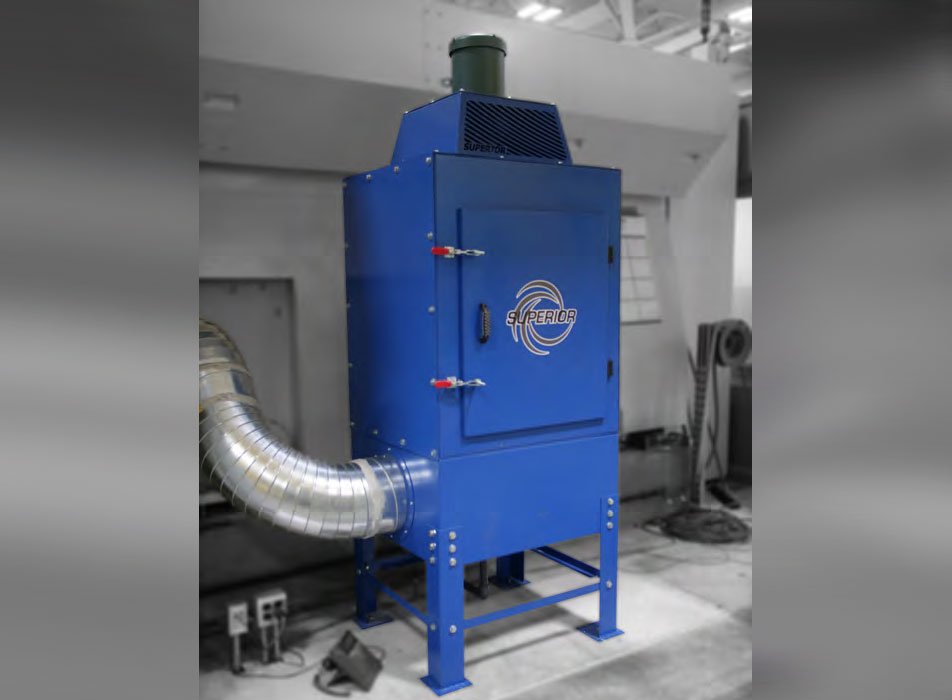
#3 Superior Filtration, Industrial Dust and Mist Collector
Domain Est. 1995
Website: parker.com
Key Highlights: We offer a range of efficient and cost-effective air pollution control solutions, including industrial DustHog dust and Smoghog mist collectors….
#4 Oil Extractors
Domain Est. 1998
Website: northerntool.com
Key Highlights: Shop 21 Oil Extractors at Northern Tool + Equipment. Browse a variety of top brands in Oil Extractors such as JohnDow Industries, …Missing: syphon manufacturer…
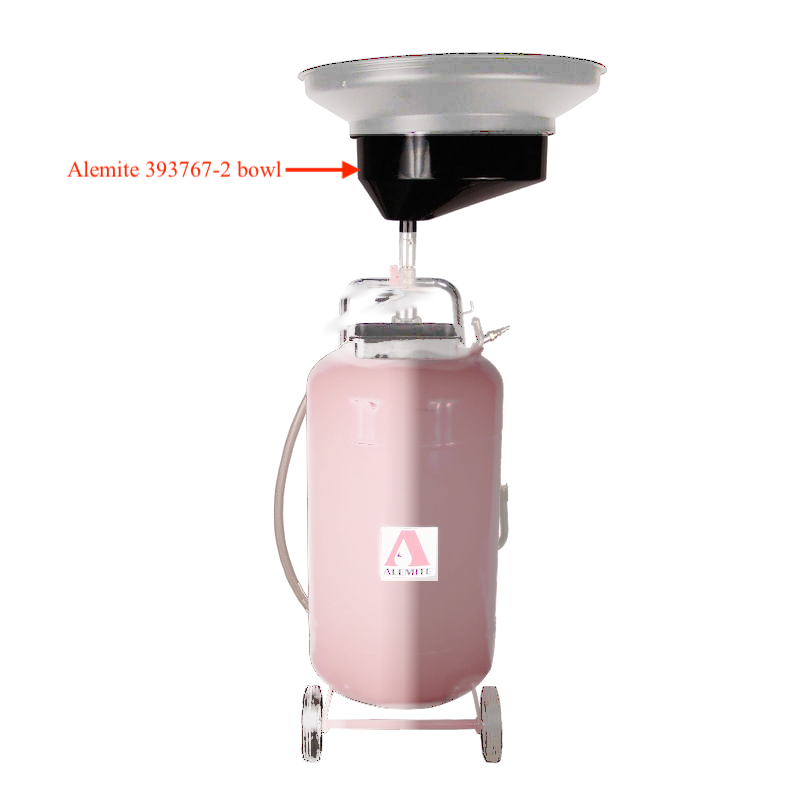
#5 to Alemite
Domain Est. 1996
Website: skf.com
Key Highlights: Portable Oil Extractor 8588 · Pressurized Oil Dispenser 8589 and 8589-A · Fluid Management Systems · AFCS Enterprise · Fluid Guard 2 · RFC · RFC Plus · Grease ……
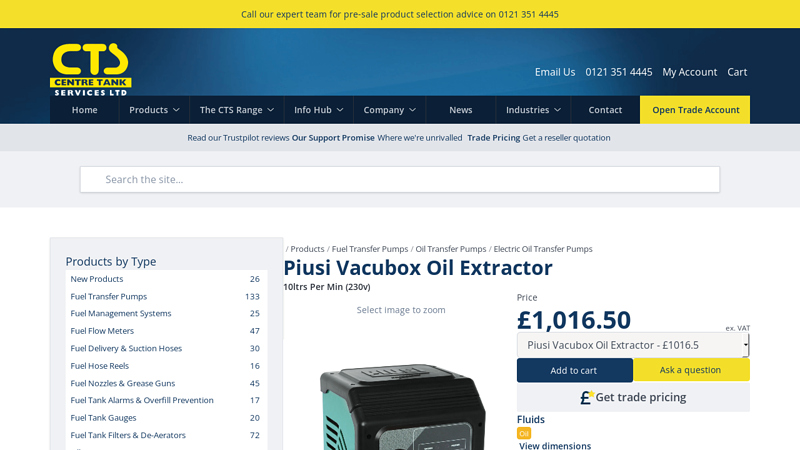
#6 Piusi Vacubox Oil Extractor
Domain Est. 1999
Website: centretank.com
Key Highlights: A powerful, wall mounted oil extraction unit, designed for small to medium workshops where clean, spill-free oil removal from vehicles is required….
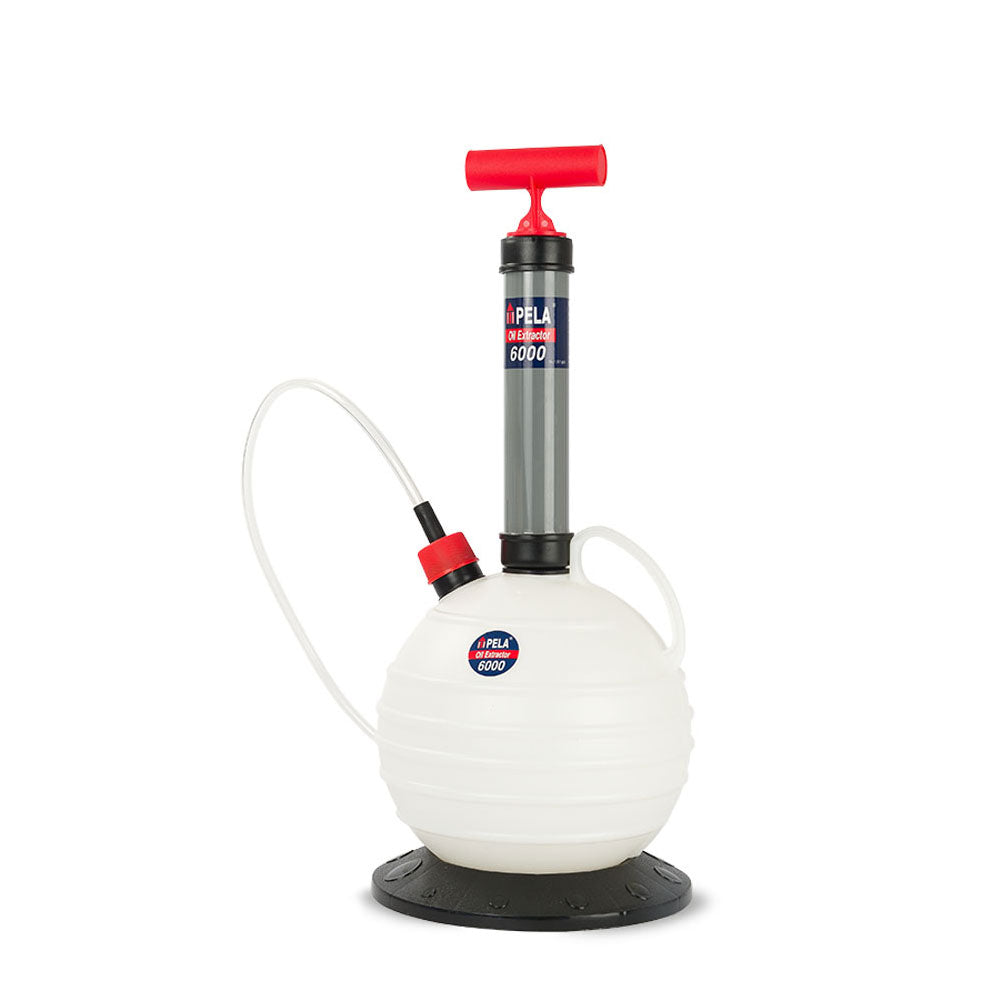
#7 Quick, Easy & Clean Oil Changes with PELA Products
Domain Est. 2000
Website: pelaproducts.com
Key Highlights: We specialize in manually operated vacuum pumps for fluid removal. The most common application is oil changing. All you need to do is pump the unit 10 to 20 ……
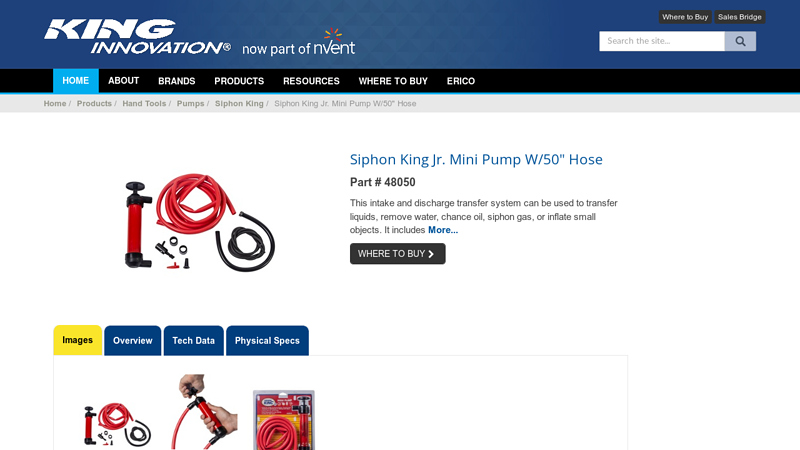
#8 Siphon King Jr. Mini Pump W/50″ Hose
Domain Est. 2002
Website: kinginnovation.com
Key Highlights: This intake and discharge transfer system can be used to transfer liquids, remove water, chance oil, siphon gas, or inflate small objects….
#9 Merchant Automotive Oil Syphon Pump with Tubing
Domain Est. 2006
Expert Sourcing Insights for Oil Syphon
H2: 2026 Market Trends Forecast for Oil Syphon
As we approach 2026, the market dynamics for oil syphons—devices used primarily for transferring oil from engines, storage tanks, or industrial systems—are undergoing transformation due to technological advancements, environmental regulations, and shifting industry demands. Here is a comprehensive analysis of key trends expected to shape the oil syphon market in 2026:
-
Increased Demand in Automotive and Industrial Maintenance
The continued growth of the global automotive sector, especially in emerging markets, supports sustained demand for maintenance tools such as oil syphons. With a rising number of internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles still on the road and industrial machinery requiring routine lubrication maintenance, oil syphons remain essential. Additionally, the aftermarket automotive repair segment is expanding, driving the need for efficient, user-friendly syphon tools. -
Shift Toward Electric Vehicles (EVs) – A Dual Impact
While the long-term rise of EVs may reduce demand for traditional engine oil change tools, EVs still require fluid maintenance for gearboxes, cooling systems, and brake fluids. This creates new niches for oil syphon applications. Manufacturers are adapting by developing multi-purpose syphoning tools capable of handling various fluids used in hybrid and electric vehicles. -
Technological Innovation and Product Differentiation
By 2026, oil syphon manufacturers are expected to emphasize smart features, such as integrated sensors, flow control mechanisms, and ergonomic designs. Battery-powered and vacuum-assisted syphons are gaining traction for their efficiency and ease of use, particularly in professional garages and industrial settings. These innovations enhance precision, reduce spillage, and improve user safety—key selling points in competitive markets. -
Environmental and Regulatory Pressure
Stricter environmental regulations around oil disposal and spill prevention are pushing businesses and consumers toward cleaner, more controlled oil transfer methods. Syphoning is increasingly favored over traditional draining methods due to its reduced risk of contamination and efficient fluid recovery. In regions with strong environmental compliance standards (e.g., EU, North America), demand for eco-friendly syphon systems is expected to rise. -
Growth in DIY and Home Mechanic Segments
The do-it-yourself (DIY) automotive maintenance trend continues to expand, supported by online tutorials and accessible tools. Compact, affordable, and easy-to-use oil syphons are becoming popular among home users. E-commerce platforms are facilitating wider distribution, with product designs focusing on portability, durability, and compatibility with multiple oil types and container sizes. -
Sustainability and Material Innovation
By 2026, manufacturers are expected to adopt more sustainable materials in oil syphon production, such as recyclable plastics and non-toxic components. This aligns with broader industry ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) goals and appeals to environmentally conscious consumers and B2B clients. -
Regional Market Variations
- Asia-Pacific: Fastest-growing market due to rising vehicle ownership, industrialization, and expanding aftermarket services.
- North America and Europe: Mature markets with steady demand, driven by professional workshops and regulatory compliance needs.
-
Latin America and Africa: Growing adoption due to increasing automotive penetration and investment in maintenance infrastructure.
-
Integration with Digital Platforms and IoT
While still in early stages, some high-end syphon systems may begin incorporating IoT connectivity by 2026—enabling usage tracking, maintenance alerts, and inventory management for industrial clients. This trend is more likely in fleet management and large-scale operations.
Conclusion
The oil syphon market in 2026 will be characterized by innovation, regulatory influence, and adaptation to evolving vehicle technologies. While challenges from EV adoption persist, opportunities in multi-fluid applications, sustainability, and smart tool development are expected to sustain market growth. Companies that invest in user-centric design, environmental compliance, and digital integration will be best positioned to lead in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Oil Siphons: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing oil siphons—particularly for industrial, automotive, or marine applications—can expose buyers to significant risks if quality standards and intellectual property (IP) rights are not carefully evaluated. Overlooking these aspects can lead to product failures, safety hazards, legal liabilities, and reputational damage. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid.
Poor Material Quality and Construction
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing oil siphons is substandard material quality. Low-cost suppliers may use inferior plastics, subpar seals, or weak tubing that degrades when exposed to petroleum-based fluids, heat, or pressure. This can lead to leaks, ruptures, or contamination of the oil being transferred. Always verify that materials are chemically resistant (e.g., nitrile rubber, fluorocarbon, or polyethylene) and meet industry standards (such as ISO or ASTM). Request material certifications and conduct sample testing before bulk procurement.
Inaccurate or Inconsistent Performance Specifications
Some suppliers exaggerate performance metrics such as flow rate, suction strength, or maximum lift height. Without independent verification, buyers may receive siphons that fail to perform under real-world conditions. Ensure technical specifications are backed by test data and request third-party validation or performance reports. Pilot testing in your specific operating environment is highly recommended.
Lack of Compliance with Safety and Environmental Standards
Oil siphons used in regulated industries must comply with safety and environmental standards (e.g., EPA, OSHA, or ATEX in explosive environments). Sourcing non-compliant products can lead to fines, operational shutdowns, or liability in case of accidents. Always confirm that the product meets relevant regional and industry-specific regulations, and request compliance documentation such as Declarations of Conformity or test certificates.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Sourcing from manufacturers that copy patented designs or trade-dress elements of leading brands can expose your business to IP litigation. Common issues include replicating proprietary pump mechanisms, hose configurations, or branding elements. To mitigate risk:
– Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s design origin and manufacturing rights.
– Avoid suppliers offering “compatible with” or “identical to” branded models unless they are licensed.
– Include IP indemnification clauses in procurement contracts.
– Consider working with original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) or authorized partners.
Inadequate Quality Control and Traceability
Suppliers with weak quality management systems may deliver inconsistent batches, missing critical components, or incorrect labeling. Without traceability (e.g., lot numbers, production dates), identifying and addressing defects becomes difficult. Insist on suppliers with certified quality systems (e.g., ISO 9001) and request batch test reports or inspection records. On-site audits or third-party inspections (e.g., SGS, TÜV) can provide additional assurance.
Hidden Costs from Short Product Lifespan
While low initial pricing may seem attractive, poor-quality siphons often require frequent replacement, increasing total cost of ownership. Factor in durability, maintenance needs, and warranty terms when evaluating suppliers. A higher upfront cost for a robust, long-lasting product typically delivers better value over time.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, organizations can ensure reliable performance, regulatory compliance, and legal protection when sourcing oil siphons.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Oil Syphon
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for the safe and legal handling, transportation, storage, and disposal of Oil Syphon products and related materials.
Regulatory Compliance Overview
Oil Syphon operations must adhere to federal, state, and local regulations governing hazardous materials, environmental protection, workplace safety, and transportation. Key regulatory bodies include the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT), Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), and relevant state environmental and transportation agencies.
Hazardous Materials Classification
Oil Syphon products, particularly used oil and certain cleaning solvents, may be classified as hazardous materials under DOT and EPA regulations. Determine the specific classification (e.g., UN1202, UN1268) based on composition, flash point, and toxicity. Always consult Safety Data Sheets (SDS) to confirm hazard class and proper shipping name.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
All shipments must use UN-rated, leak-proof containers compatible with the contents. Containers must be securely closed and labeled with:
– Proper shipping name
– UN number
– Hazard class label (e.g., Class 3 Flammable Liquid)
– Orientation arrows
– Accumulator or generator information (if applicable)
Labels must be durable and clearly visible.
Transportation Regulations
Transportation of Oil Syphon materials must comply with 49 CFR (DOT Hazardous Materials Regulations):
– Drivers must have appropriate training and, if required, a Hazardous Materials Endorsement (HME)
– Vehicles must display proper placards based on material type and quantity
– Shipping papers must accompany all loads and include emergency response information
– Manifests must be completed and retained as per regulatory requirements
Storage Guidelines
Store Oil Syphon products and waste materials in designated areas that are:
– Well-ventilated and away from ignition sources
– Equipped with secondary containment (e.g., spill pallets, berms) capable of holding 110% of the largest container
– Labeled clearly with contents and hazard warnings
– Inspected regularly for leaks, corrosion, or damage
Spill Prevention and Response
Implement a Spill Prevention, Control, and Countermeasure (SPCC) plan if storing 1,320 gallons or more of oil aboveground. All personnel must be trained in:
– Immediate spill response procedures
– Use of spill kits (absorbents, booms, PPE)
– Reporting requirements to local and federal authorities (e.g., National Response Center)
– Proper cleanup and disposal of contaminated materials
Waste Disposal and Recycling
Used oil and contaminated materials must be managed as hazardous or universal waste per EPA regulations (40 CFR 279). Use only licensed waste transporters and treatment, storage, and disposal facilities (TSDFs). Document all waste shipments using manifests and retain records for a minimum of three years.
Personnel Training and Documentation
All employees involved in handling, storing, or transporting Oil Syphon products must receive initial and recurrent training in:
– Hazard communication (HazCom)
– DOT HAZMAT handling
– Spill response and emergency procedures
– Site-specific safety protocols
Maintain training records and SDS files accessible to all personnel.
Environmental Compliance
Ensure operations comply with Clean Water Act (CWA) and Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) standards:
– Prevent discharges to storm drains or waterways
– Implement best management practices (BMPs) for pollution prevention
– Conduct regular environmental audits and maintain compliance documentation
Recordkeeping and Audits
Maintain detailed records including:
– Shipping and disposal manifests
– Training logs
– Inspection reports (containers, storage areas)
– Spill incident reports
– Regulatory permits and certifications
Conduct internal audits annually to verify compliance and identify areas for improvement.
By adhering to this guide, Oil Syphon operations can ensure regulatory compliance, protect personnel and the environment, and maintain efficient logistics processes.
Conclusion for Sourcing Oil Syphon:
In conclusion, sourcing an oil syphon requires careful consideration of quality, functionality, compatibility, and cost-effectiveness. Whether intended for automotive maintenance, industrial use, or marine applications, selecting a reliable oil syphon ensures efficient, clean, and safe oil removal. Key factors such as suction power, hose length and material, ease of use, and durability should guide the procurement decision. Additionally, evaluating suppliers based on reputation, certifications, and after-sales support contributes to long-term reliability. By prioritizing these elements, organizations and individuals can secure a high-performing oil syphon that meets operational needs, enhances maintenance efficiency, and reduces environmental and safety risks. Ultimately, investing in a well-sourced oil syphon leads to improved equipment longevity and reduced downtime.