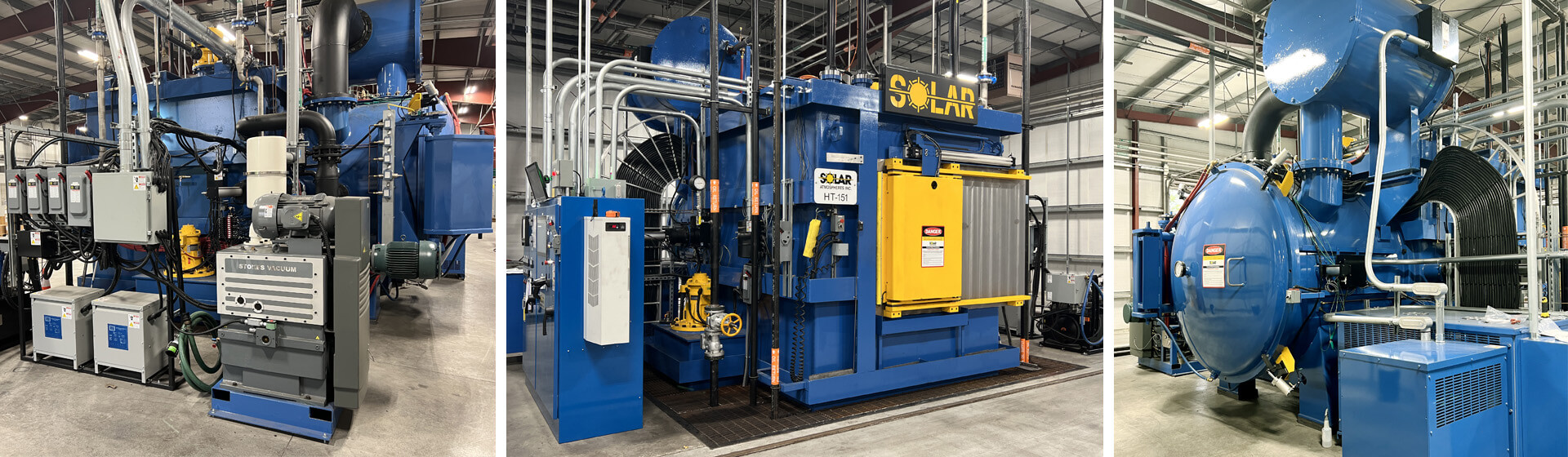
The global metal heat treatment market, a critical enabler for high-performance industrial components, continues to expand, driven by rising demand for durable materials in aerospace, automotive, and energy sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global heat treatment services market was valued at USD 104.6 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.1% from 2023 to 2030. Within this landscape, oil quenching remains a dominant process due to its superior cooling control and hardening efficiency, particularly for alloy steels and tooling applications. As industries prioritize precision and material integrity, the demand for high-quality oil quenchants has intensified. Mordor Intelligence forecasts steady growth in the industrial oils market, citing increased manufacturing activity and technological advancements in quenching media formulation. Against this backdrop, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders, leveraging innovation, global reach, and technical expertise to shape the competitive dynamics of the oil quench sector. Here are the top 9 oil quench manufacturers leading the charge in this evolving market.
Top 9 Oil Quench Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 DOW™ Quench Oil
Domain Est. 1992
Website: dow.com
Key Highlights: Fuel oil blending component products that are mixtures of (mainly unsaturated) C9 to C15 components. Produced in St. Charles, LA and is somewhat lighter….
#2 Industrial Quenching Fluids for Metal Treatment
Domain Est. 1995
Website: castrol.com
Key Highlights: Find a wide range of quenching oils and fluids for various processes used in different industries. Find the right quenching oil for your industry here….
#3 Coolants, Cutting Oils, Quenching Oils
Domain Est. 1999
Website: rockvalleyoil.com
Key Highlights: An extensive line of coolants, cutting oils, and quenching oils. Our products are designed to meet a broad range of industrial applications….
#4 CLC Quench Oils
Domain Est. 2001
Website: clclubricants.com
Key Highlights: With optimized cooling rate characteristics and state-of-the-art additive and basestock technologies, our quench oils produce unparalleled results….
#5 Heat Treatment Quenchants, Salts and Oils
Domain Est. 2017
Website: home.quakerhoughton.com
Key Highlights: Quaker Houghton is the worldwide leader in heat treatment, supplying quenching fluids and associated products, technology and application expertise….
#6 Quenching Oils
Domain Est. 1996
Website: fuchs.com
Key Highlights: The FUCHS range of THERMISOL and MARTEMP products effectively help heat treaters meet precision metallurgical specifications….
#7 Quenchants
Domain Est. 1997
Website: duboischemicals.com
Key Highlights: Oil-based and water-based quenchants for metal heat treatment processes. Providing easy cleaning, oxidation resistance, & thermal stability,…
#8 Quenching Oil
Domain Est. 2000
Website: sst.net
Key Highlights: Turn to Specialty Steel Treating for high-quality oil quenching. We specialize in batch, plug, roll, and press quenching. Call today to request a quote!…
#9 Heat Treatment
Domain Est. 2017
Website: idemitsulubricants.com
Key Highlights: Specialized quench oil solutions that provide excellent quench rates, thermal stability, distortion control, and low volatility….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Oil Quench

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Oil Quenching
As we approach 2026, the oil quenching segment within the industrial heat treatment market is undergoing significant transformation, driven by technological advancements, evolving material demands, and increasing sustainability pressures. Here is an analysis of key market trends shaping the oil quenching industry in the second half of 2026 (H2 2026):
1. Rising Demand in Automotive and Aerospace Sectors
The continued push for high-performance, lightweight, and durable components in electric vehicles (EVs) and next-generation aircraft is fueling demand for precise heat treatment processes. Oil quenching remains a preferred method for achieving optimal hardness and mechanical properties in critical components such as gears, shafts, and landing gear. In H2 2026, OEMs are increasingly specifying oil-quenched parts due to their superior consistency and fatigue resistance compared to alternative quenching media.
2. Shift Toward High-Performance Quenching Oils
In response to tighter metallurgical tolerances, manufacturers are adopting advanced quench oils with improved thermal stability, oxidation resistance, and controlled cooling rates. Synthetic and high-speed quench oils are gaining traction, particularly in precision engineering applications. These formulations reduce distortion and improve part reproducibility, aligning with Industry 4.0 standards for process control and traceability.
3. Environmental Regulations and Sustainability Pressures
Environmental concerns are accelerating the phase-out of traditional mineral-based quench oils in several regions, particularly in Europe and North America. By H2 2026, stricter emissions standards and waste disposal regulations are pushing companies to adopt biodegradable, low-smoke, and low-toxicity quenching solutions. Investment in closed-loop oil recycling systems and vapor recovery units is rising to meet ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals.
4. Integration with Digital Monitoring and AI
Smart manufacturing is transforming oil quench operations. In 2026, AI-driven process monitoring systems are being widely deployed to analyze oil condition, cooling curve performance, and part quality in real time. Predictive maintenance algorithms help optimize oil life and reduce unplanned downtime. Digital twins of quenching lines enable virtual process validation, reducing trial-and-error in new material treatments.
5. Competition from Alternative Quenching Methods
While oil quenching remains dominant for many applications, alternative technologies such as high-pressure gas quenching (HPGQ) and polymer quenchants are capturing market share—especially in vacuum heat treatment systems. However, oil quenching maintains a cost and performance advantage in high-volume, large-part processing, ensuring continued relevance through 2026.
6. Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, is emerging as the fastest-growing market for oil quenching due to expanding automotive and industrial manufacturing. In contrast, North America and Europe are focusing on retrofitting legacy systems with energy-efficient and eco-friendly oil quench technologies. Localized supply chains for quench oil formulations are developing to reduce lead times and logistical emissions.
Conclusion
In H2 2026, the oil quenching market is characterized by innovation, regulation, and digital integration. While facing competitive and environmental challenges, oil quenching remains a critical process in high-integrity metal treatment. Companies that invest in sustainable oils, digital monitoring, and process optimization are best positioned to thrive in the evolving industrial landscape.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Oil Quench (Quality & IP)
Sourcing oil quench for industrial heat treatment processes involves critical considerations beyond price and availability. Overlooking quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to significant operational, legal, and reputational risks. Here are the common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Compromising on Oil Quench Quality Specifications
One of the most frequent and damaging pitfalls is prioritizing cost over consistent quality. Low-cost suppliers may offer formulations that deviate from required technical standards, leading to:
- Inconsistent Cooling Rates: Poorly controlled viscosity or thermal stability results in variable quenching performance, increasing the risk of part distortion, cracking, or insufficient hardness.
- Shorter Oil Life and Higher Maintenance: Inferior base oils and additive packages degrade faster, leading to sludge formation, increased acid number, and more frequent oil changes—raising total cost of ownership.
- Contamination Risks: Substandard refining or handling practices may introduce water, particulates, or volatile contaminants, compromising quench performance and safety.
Best Practice: Require detailed technical data sheets (TDS), certificates of analysis (CoA), and conduct regular in-house or third-party testing to verify viscosity, flash point, thermal stability, and cooling characteristics (via IVF or similar testing).
2. Overlooking Intellectual Property (IP) Protection
Oil quench formulations are often proprietary, with specific additive packages protected by patents or trade secrets. Sourcing from unauthorized or counterfeit suppliers poses serious IP risks:
- Use of Counterfeit or Imitation Products: Unauthorized manufacturers may replicate branded formulations without proper licensing, violating IP rights and potentially delivering unsafe or ineffective products.
- Reverse Engineering & Data Misuse: Sharing detailed specifications with untrusted suppliers may expose proprietary process parameters or formulation knowledge.
- Legal Liability: Using infringing products—even unknowingly—can expose your organization to legal action from original developers or patent holders.
Best Practice: Source only from authorized distributors or OEMs. Include IP clauses in supplier contracts affirming the legitimacy of the product and indemnifying your company against IP infringement claims. Conduct due diligence on supplier credentials.
3. Inadequate Supplier Qualification and Traceability
Many companies fail to properly vet suppliers, especially when sourcing from new or low-cost regions:
- Lack of Traceability: Without batch-level traceability, it becomes impossible to investigate quality issues or perform recalls if a batch causes part failures.
- Unverified Manufacturing Practices: Suppliers without ISO or other quality certifications may lack consistent production controls, increasing variability.
Best Practice: Implement a formal supplier qualification program requiring audits, quality certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), and full traceability documentation.
4. Ignoring Compatibility and Long-Term Support
Switching quench oils without proper validation can disrupt operations:
- Incompatibility with Existing Systems: New oils may not be compatible with seals, filters, or existing residual oil, leading to system damage.
- Lack of Technical Support: Low-cost suppliers often provide minimal technical assistance, making troubleshooting difficult during process upsets.
Best Practice: Conduct compatibility testing and pilot trials before full-scale adoption. Ensure the supplier offers robust technical service and troubleshooting support.
By prioritizing quality assurance, protecting intellectual property, and conducting thorough supplier due diligence, organizations can mitigate risks and ensure reliable, compliant, and high-performance quenching operations.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Oil Quench
1. Overview
Oil quenching is a critical heat treatment process used in metallurgy to rapidly cool metals—typically steel—by immersing them in oil. This process enhances hardness, strength, and wear resistance. However, due to the use of flammable materials, high temperatures, and potential environmental hazards, strict logistics and compliance measures must be followed to ensure safety, regulatory adherence, and operational efficiency.
This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for oil quench operations across procurement, handling, storage, transportation, disposal, and regulatory standards.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Oil quench operations are subject to multiple national and international regulations. Compliance is mandatory to avoid penalties, ensure worker safety, and minimize environmental impact.
2.1 Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) – USA
– 29 CFR 1910.106: Standards for flammable liquids.
– Oil quench tanks must be located in well-ventilated, fire-resistant areas.
– Fire suppression systems (e.g., CO₂ or foam) must be installed.
– 29 CFR 1910.132: Personal Protective Equipment (PPE).
– Heat-resistant gloves, face shields, flame-resistant clothing, and aprons are required.
– Hazard Communication (HazCom) Standard (29 CFR 1910.1200):
– Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for quenching oils must be accessible.
– Employees must be trained on chemical hazards and emergency procedures.
2.2 Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) – USA
– Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA):
– Spent quenching oil may be classified as hazardous waste depending on contaminants (e.g., heavy metals).
– Proper storage, labeling, and disposal through licensed waste handlers are required.
– Spill Prevention, Control, and Countermeasure (SPCC) Rule (40 CFR 112):
– Facilities storing >1,320 gallons of oil must have an SPCC plan.
– Secondary containment (e.g., dikes, sumps) for oil storage tanks is required.
2.3 National Fire Protection Association (NFPA)
– NFPA 30: Flammable and Combustible Liquids Code
– Specifies safe distances between oil quench equipment and other structures.
– Requires automatic fire detection and suppression systems.
– NFPA 86: Standard for Ovens and Furnaces
– Governs safe operation of heat treatment equipment used in oil quenching.
2.4 International Standards (ISO & REACH)
– ISO 14001: Environmental Management Systems.
– Encourages waste minimization, emissions control, and lifecycle analysis of quenching oils.
– REACH (EU): Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals.
– Quenching oils containing SVHCs (Substances of Very High Concern) must be reported.
– Requires communication of safe use conditions in the supply chain.
3. Logistics Management
3.1 Procurement & Supply Chain
– Source quenching oils from certified suppliers adhering to ASTM D975 or ISO 6743-6 standards.
– Verify SDS and technical specifications (flash point, viscosity, thermal stability).
– Ensure supplier compliance with REACH, RoHS, or other applicable chemical regulations.
3.2 Storage
– Store quenching oils in UL-approved, grounded containers.
– Use dedicated, well-ventilated storage areas with fire-rated construction.
– Implement secondary containment systems (e.g., spill pallets) with capacity for 110% of largest container.
– Clearly label all containers with contents, hazards, and date of receipt.
3.3 Handling & Usage
– Train personnel in safe handling procedures and emergency response.
– Use closed systems or drip trays to minimize oil spills during transfer.
– Monitor oil condition (viscosity, contamination, water content) regularly to ensure performance and safety.
– Maintain quench tanks with proper agitation and cooling to reduce fire risk.
3.4 Transportation
– Transport quenching oils in DOT-compliant containers (49 CFR).
– Classify oil as flammable liquid (UN 1263, PG II or III) if applicable.
– Use vehicles equipped with grounding straps and spill kits.
– Provide shipping documents, including Safety Data Sheet and emergency contact information.
3.5 Waste Management & Disposal
– Segregate used quenching oil from other waste streams.
– Test spent oil for hazardous characteristics (e.g., TCLP for metals).
– Contract disposal through licensed hazardous waste handlers.
– Maintain records of waste manifests and disposal certificates for at least 3 years.
4. Emergency Preparedness
- Spill Response:
- Equip work areas with oil-absorbent materials, spill kits, and containment booms.
- Train staff in spill containment and reporting procedures.
- Fire Response:
- Install heat and smoke detectors near quench tanks.
- Provide Class B fire extinguishers and automatic suppression systems.
- Conduct regular fire drills and equipment inspections.
- Emergency Contacts:
- Post emergency numbers (fire department, spill response, medical) in visible locations.
5. Documentation & Auditing
- Maintain records of:
- Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
- Employee training logs
- Oil usage, maintenance, and disposal logs
- SPCC plan and environmental permits
- Incident reports and corrective actions
- Conduct internal audits semi-annually to verify compliance with OSHA, EPA, and NFPA standards.
6. Best Practices
- Use synthetic or low-odor quenching oils to reduce VOC emissions and improve workplace air quality.
- Implement oil reclamation or filtration systems to extend oil life and reduce waste.
- Automate oil handling where possible to reduce human exposure.
- Engage third-party consultants for compliance audits and risk assessments.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance in oil quench operations are essential to protect personnel, ensure regulatory adherence, and maintain environmental responsibility. By following this guide, organizations can mitigate risks, enhance operational efficiency, and demonstrate commitment to safety and sustainability.
Conclusion for Sourcing Oil Quench:
Sourcing oil quench requires a strategic approach that balances performance, safety, cost, and environmental considerations. After evaluating various suppliers, oil types (such as fast-quench, hot, and martempering oils), and technical specifications—including cooling rates, thermal stability, flash point, and oxidation resistance—the optimal choice should align with the specific metallurgical requirements of the heat treatment process. Partnering with reputable suppliers who provide consistent quality, technical support, and compliance with environmental and safety regulations is essential. Additionally, considering lifecycle costs, disposal methods, and potential for oil reconditioning can enhance operational efficiency and sustainability. In conclusion, effective sourcing of oil quench involves a holistic assessment to ensure reliability, part quality, and long-term cost-effectiveness in industrial heat treatment applications.