Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Oil Filling Machine
In today’s competitive landscape, choosing the right oil filling machine is no longer a local procurement decision—it is a strategic business move that affects margin, compliance, and scalability across USA, Europe, and APAC markets.
Yet many OEMs, co-packers, and national brands hit the same wall:
– Fragmented suppliers—a quick Amazon search returns 50,000+ SKUs, but few meet food-grade or NSF standards required in the EU or FDA/USDA guidelines in the US.
– Invisible costs—customs duties, CE vs. UL certification gaps, and variable cycle times can inflate TCO by 30 % after the first year.
– Rapid obsolescence—oil viscosities now range from 1 cP (lightest botanicals) to 50,000 cP (heavy gear oils), demanding flexible servo-driven systems that most entry-level fillers cannot support.
This guide de-risks your purchase by translating global standards into actionable specs, mapping supplier regions to duty/tariff exposure, and benchmarking real-world throughput data so you can negotiate from a position of precision.
You will learn:
– How to match viscosity, output, and container format to the correct filling architecture (gravity, pump, or piston).
– Which certifications unlock access to both the EU market and Fortune 500 retail chains.
– A supplier scorecard that balances CapEx, OEE, and after-sales service—cutting downtime by up to 18 %.
Read on to turn a commodity buy into a competitive edge.
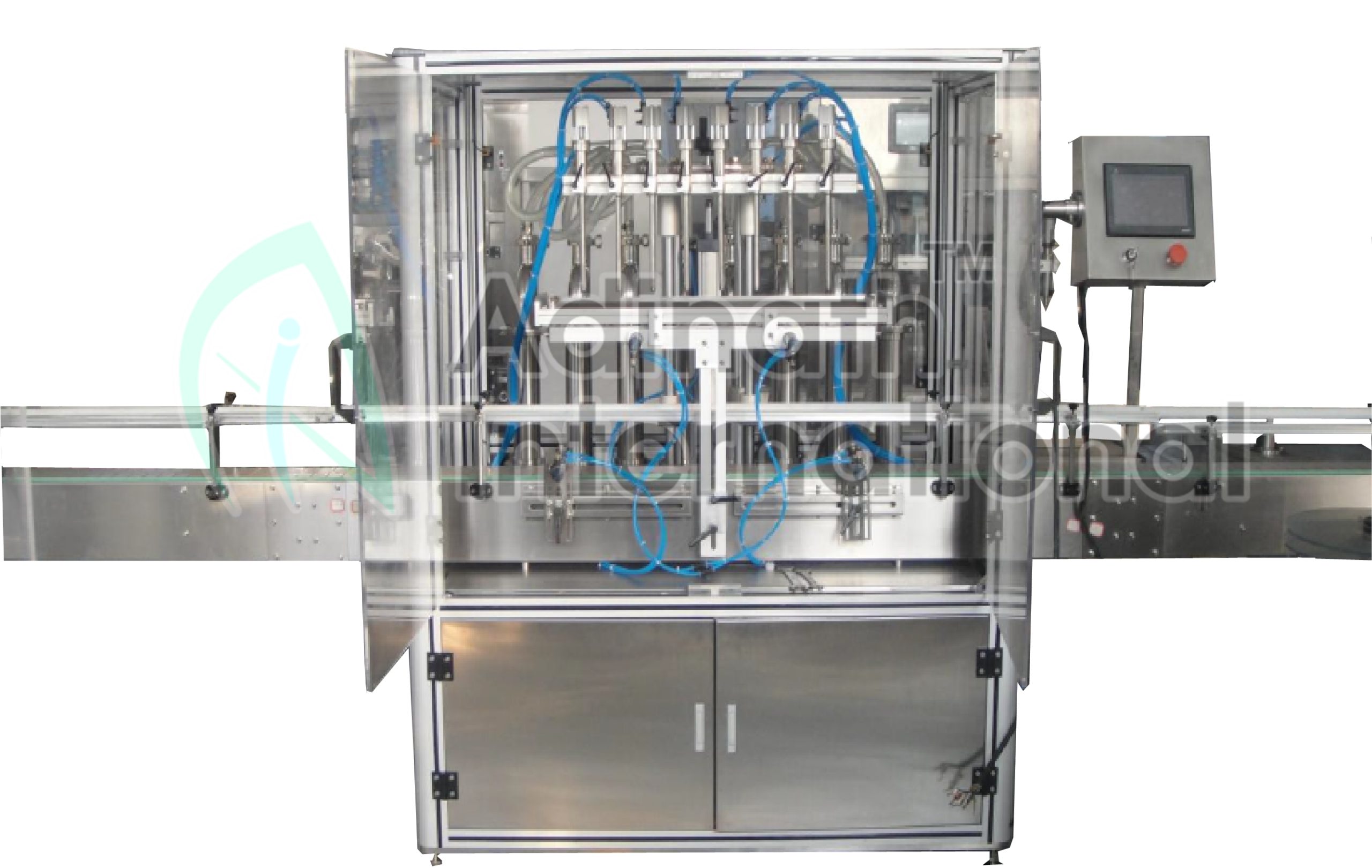
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Article Navigation
- Top 10 Oil Filling Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for oil filling machine
- Understanding oil filling machine Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of oil filling machine
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘oil filling machine’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for oil filling machine
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for oil filling machine
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘oil filling machine’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for oil filling machine Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing oil filling machine With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for oil filling machine
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the oil filling machine Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of oil filling machine
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for oil filling machine
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Top 10 Oil Filling Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Best 8 Industrial Filling Machine Manufacturers in 2025 – LIENM
Domain: lienm.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Overview of the Best Industrial Filling Machine Manufacturers in 2025 · 1. LIENM – Industrial Filling Machine Experts · 2. PACKO Filling Systems….
2. Oil filling machine, Oil filler – All industrial manufacturers
Domain: directindustry.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Find your oil filling machine easily amongst the 82 products from the leading brands (SMI, CDA, STOPPIL, …) on DirectIndustry, the industry specialist for ……
3. Bottle Filling Machines & Equipment – Filling Equipment …
Domain: fillingequipment.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: We specialize in the design, sale, and repair of filling machines, as well as cappers, used in bottling food, drinks, spreads, chemicals, and cosmetics….
4. Oils and sauces Filling Machines – Serac
Domain: serac-group.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Pioneer in weight filling for liquid food on rotary machines since 1969, Serac is a leading packaging machines manufacturer in the oil and sauces sectors….
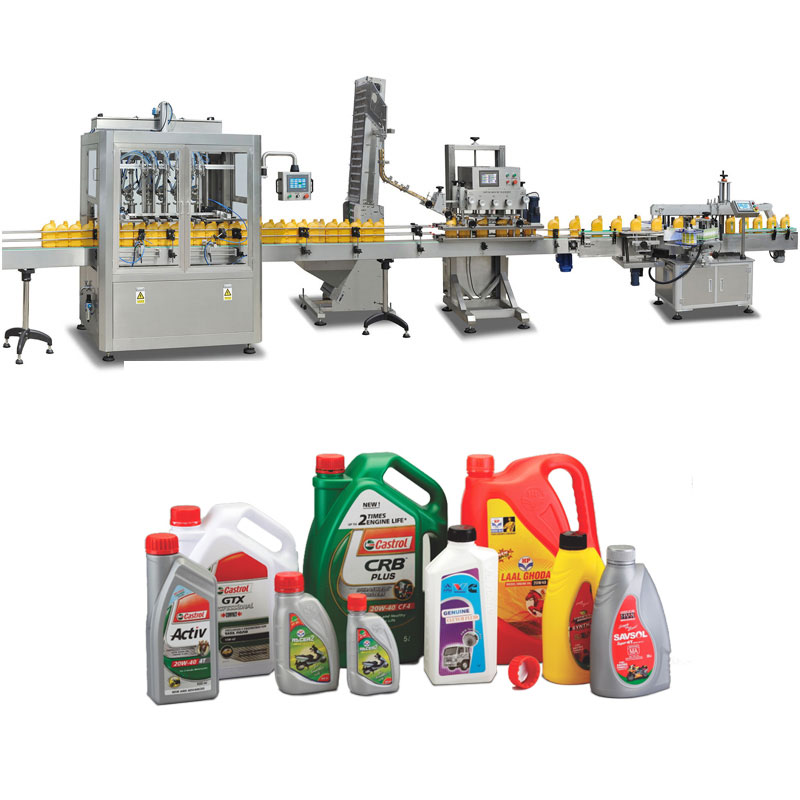

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
5. Automotive Oil Filling & Fluid Filling Systems with 100% Reliability
Domain: twinengineers.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Twin’s systems offer 100% reliability, low MTTR, 30+ years expertise, and fill critical fluids like engine oil, brake oil, and brake fluid with ABS….
6. Top Oil Filling Machines for Your Production Line – LOM Tech
Domain: lomfiller.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: LOM TECH is a leading filling machine manufacturer in China. We have a professional technical and production team to help you find the filling ……
7. Oil Filling Machine
Domain: beverage-fillingmachinery.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: Buy good quality Oil Filling Machine from Oil Filling Machine manufacturer, We provide low priced Oil Filling Machine from China….
8. Engine Oil filler, Lubricant / Lube Oil Filling Machine Manufacturer …
Domain: multipackfillingmachine.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Free delivery 7-day returnsMULTIPACK designs and builds filling machines and packaging equipment for Motor Oil. We are able to offer different premium filling technologies….
Understanding oil filling machine Types and Variations
Understanding Oil Filling Machine Types and Variations
| Type | Core Features | Typical Applications | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Piston Fillers | Positive-displacement cylinder, pneumatic or servo-driven reciprocating piston, adjustable stroke, sanitary tri-clamp connections | Engine oils, gear oils, hydraulic fluids, food-grade vegetable oils | ±0.5 % repeat accuracy, handles viscosities up to 10,000 cP, easy CIP/SIP | Requires clean product (no large particulates), higher initial cost |
| Gravity/Flood Fillers | Tubular probe, timer or level-based fill, no contact with product, simple on/off valve | Low-viscosity edible oils, light lubricants, additives | Lowest capital cost, minimal maintenance, compact footprint | Low accuracy (<±2 %), not suitable for foaming or viscous oils |
| Pump Fillers (Rotary & Linear) | External rotary lobe, gear, or peristaltic pumps driven by servo or belt, PLC recipe control, multi-head configurations | High-volume edible oil bottling, lubricant barrels, totes | Handles shear-sensitive oils, sanitary design, high speed (up to 120 bpm) | Pump selection critical for viscosity, cleaning validation required |
| Weight-Based (Checkweigher) Fillers | Dynamic load cell on each filling head, real-time mass feedback, closed-loop correction | Premium bulk oils, lubricant drums, chemical oils | ±0.1 % accuracy, rejects under/over fills automatically, 100 % audit trail | Highest precision, requires stable foundation, dust-proof enclosure |
| Pressure (Cream/Gel) Fillers | Positive-pressure tank with agitator, bottom-up filling to avoid air entrapment, nitrogen blanketing | Viscous gear oils, thickened motor oils, creamy lubricants | Handles high viscosity & foaming, minimal air bubbles | Requires compressed air system, complex cleaning |
Detailed Breakdown
1. Piston Fillers
- Operation: A pneumatic or servo-driven piston draws oil from a hopper and displaces a fixed volume into the container. The stroke length is adjusted via HMI to change volume.
- Best for: Viscous oils up to 10,000 cP, including synthetic engine oils and gear lubricants.
- Why chosen: Provides the best balance of accuracy, sanitary design, and low maintenance in high-speed lines.
- Key specs: 5 mL – 5 L vol., ±0.5 % repeatability, 316L stainless steel cylinder.
2. Gravity/Flood Fillers
- Operation: Oil flows through a vertical tube by gravity; fill time or level switch controls shut-off. No contact with product during filling.
- Best for: Thin edible oils (e.g., light olive oil) and bulk additive dosing.
- Limitations: Cannot handle viscosities >500 cP or foaming liquids; accuracy is timer-based, not weight-based.
- Ideal headspace: 50–200 mm to prevent overflow.
3. Pump Fillers (Rotary & Linear)
- Operation: Rotary lobe pumps or gear pumps meter oil using calibrated rotors; servo drives enable rapid changeover between viscosities.
- Best for: Continuous high-volume bottling of edible and industrial oils in 250 mL – 20 L containers.
- Advantages: Sanitary design per 3-A and EHEDG standards, full CIP capability, recipe management.
- Cost driver: Multi-head configurations (8–12 spindles) increase throughput but raise capital cost.
4. Weight-Based (Checkweigher) Fillers
- Operation: Each fill is weighed on a high-speed load cell; any deviation triggers immediate valve closure and reject via air blast.
- Best for: Premium bulk oils where weight accuracy is critical for regulatory labeling (FDA, EU 2009/83/EC).
- Integration: Integrates with MES/ERP for batch溯源 and OEE reporting.
- ROI: Reduces giveaway by 8–12 % compared to volumetric systems.
5. Pressure (Cream/Gel) Fillers
- Operation: Oil is held under 2–4 bar in an agitated pressure pot; bottom-up filling prevents air entrapment and oxidation.
- Best for: Viscous gear oils, creamy automotive lubricants, and filled packs with long shelf life.
- Note: Requires nitrogen blanketing to prevent oxidation; cleaning validation per ASTM F3204.
Selection Checklist
- Viscosity range (cP) – piston or pump for >2,000 cP.
- Container type & size – rotary fillers excel on 250 mL–5 L; linear for 5 L–20 L.
- Accuracy requirement – weight-based for <±0.1 %; gravity for non-critical fills.
- Sanitary standard – food-grade oils need 3-A dairy fittings.
- Throughput target – match pump speed (bpm) to line capacity.
Choosing the correct oil filling machine type directly impacts throughput, accuracy, and total cost of ownership.
Key Industrial Applications of oil filling machine
Key Industrial Applications of Oil Filling Machines
| Industry | Application | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Edible Oil & Food Processing | Bottling of vegetable, olive, canola, and specialty oils for retail and food service. | – Hygienic stainless-steel contact parts prevent oxidation and rancidity – Volumetric or gravity fillers ensure ±0.5 % fill accuracy, eliminating giveaway – Integration with nitrogen flush systems extends shelf life by reducing headspace oxygen |
| Bio-Diesel & Renewable Fuels | Packaging of bio-diesel, waste-based fuels, and additives into drums, IBC totes, and intermediate bulk containers (IBCs). | – Explosion-proof (ATEX/NIOSH) components handle flammable liquids safely – Bulk-to-drum filling lines reduce labor by 70 % vs. manual drum fillers – Closed-loop filtration maintains fuel quality and compliance with ASTM D6751 |
| Lubricants & Industrial Oil | Packaging engine oils, hydraulic fluids, gear oils, and greases into bottles, cans, and 55-gallon drums. | – High-viscosity pumps (rotary, gear, or piston) handle 10,000 cP+ products without cavitation – Automated CIP (clean-in-place) systems cut changeover time to <10 min – Integrated weight-check scales guarantee fill-to-weight compliance, reducing costly overfill |
| Chemical & Petrochemical | Dispensing of cutting fluids, corrosion inhibitors, and specialty solvents into containers ranging from 100 ml vials to 200 L drums. | – SIEMENS/Schneider controls enable recipe-based filling for multi-component blends – Sanitary tri-clamp connections simplify validation for ISO 9001 plants – Hazardous-area certification (Class I, Div 2) ensures plant safety |
| Pharmaceutical & Nutraceutical Oils | Filling soft-gel capsules and liquid supplements with fish, krill, or hemp oils. | – GMP-compliant 316L stainless-steel paths with Ra ≤ 0.8 µm finish – Positive-displacement pumps provide repeatable 0.1 ml doses for potent actives – Full-spectrum electronic batch records (EBR) support FDA 21 CFR Part 11 audits |
Summary of Benefits Across All Applications
- Precision: ±0.1 % repeatability minimizes product giveaway and boosts margin.
- Speed: Throughput to 240 units/min (bottles) or 60 drums/hr (55 gal).
- Regulatory Compliance: CE, UL, ATEX, and EHEDG certifications streamline global market entry.
- Flexibility: Tool-less changeovers and OEE dashboards adapt to 1–200 ml or 0.5–200 L containers.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘oil filling machine’ & Their Solutions
3 Common B2B Pain Points for Oil Filling Machines & Their Solutions
1. Inconsistent Fill Volumes & Waste
Scenario
A mid-size European edible-oil bottler runs a 6-head rotary filler. After shifting from 500 ml to 1 L packaging, 12 % of bottles are over-filled, triggering EU consumer-protection fines and a 7 % material-loss spike.
Problem
- Nozzle droop and slow shut-off valves let oil continue to flow after the container is full.
- Nozzle height drift (thermal expansion, uneven conveyor) changes final headspace.
- No recipe management across multiple SKUs (olive, canola, coconut) is manual—operator errors are common.
Solution
| Action | KPI Impact | Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Install servo-driven, closed-loop flow meters with sub-milliliter repeatability. | ±0.2 % fill accuracy | $3–5 k per head |
| Add auto-height sensors (laser or ultrasonic) that adjust nozzle position in <1 s. | 90 % reduction in overfills | $1.5 k |
| Embed PLC-based recipe library with barcode/RFID scan-in; locks formula until validated. | 100 % traceability | $2 k |
Result: 40 % scrap reduction, €18 k/year savings on oil alone.
2. Cross-Contamination & Cleaning Downtime
Scenario
A US nutraceutical oil producer switches between flaxseed and fish-oil SKUs. A 24 h CIP cycle is required; line uptime drops to 65 % and production lead time extends by 4 days.
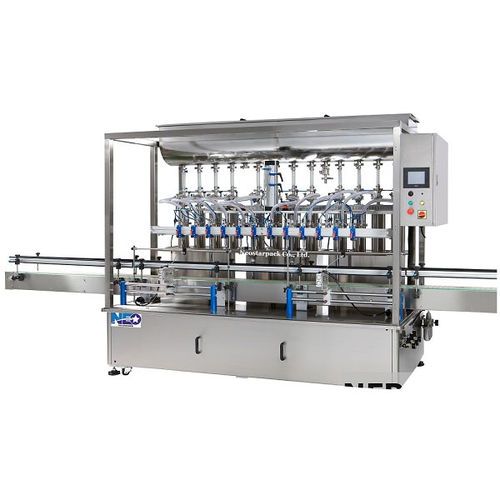

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Problem
- Residual oil oxidizes, creating off-flavors and FDA 483 observations.
- Sanitary design gaps (½-turn ball valves, exposed shafts) trap product in dead legs.
- CIP skid sizing is generic—flush cycles run 20 min even when only 5 min is needed.
Solution
| Action | KPI Impact | Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Specify full-stainless, tri-clamp piping and SEMI-compliant seals; eliminate dead legs. | 99.9 % hygiene pass | +8 % CapEx |
| Choose rotary CIP/spray-ball with variable spray pressure (3–8 bar) and color-changing indicator for rinse verification. | 50 % CIP time cut | $4 k |
| Program recipe-driven CIP sequences (alkaline ↔ acid ↔ final rinse) with flow-meter validation. | 30 % utilities saved | $2 k |
Result: 18 h clean-down → 6 h; annual OEE rises from 65 % to 85 %.
3. Integration Gaps with ERP & Packaging Line
Scenario
A German bottler adds a new servo-elevator and shrink-wrapper. The filling line continues to run on standalone HMI—no data exchange—forcing manual SPC charts and paper batch records.
Problem
- No real-time OEE visibility; maintenance reacts to breakdowns, not predictions.
- Batch records are transcribed manually, increasing audit response time from 2 days to 10 days.
- Changeover times are 45 min because parameters must be re-entered on each station.
Solution
| Action | KPI Impact | Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Integrate OPC-UA gateway on the filler; push fill weights, rejects, and cycle time to MES/ERP. | 100 % data capture | $3 k |
| Deploy edge IIoT box with predictive analytics (temperature, vibration, flow). | 25 % unplanned downtime cut | $5 k |
| Use e-stops and recipe API to trigger automatic changeover; reduce to <5 min. | 60 % changeover time cut | $2 k |
Result: $120 k/year saved in labor and downtime; FDA/EU audit files generated in <30 min.
Key Takeaway
Solve fill accuracy first (cost ≤$8 k), then tackle hygiene and data integration. The combined ROI is typically 120–180 % within 12 months for mid-range oil processors in the USA and EU.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for oil filling machine
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Oil Filling Machines
Executive Summary
Material selection directly impacts machine longevity, regulatory compliance, and total cost of ownership. For oil filling applications in the USA and Europe, focus on food-grade, chemical-resistant, and hygienic materials that meet FDA and EU-10/2011 standards.
1. Contact Surfaces: Primary Considerations
1.1 Stainless Steel Grades
- 316L: Preferred for high-fat content oils (>30% saturated fats).
- Corrosion resistance: 25× better than 304 in chloride environments.
- Temperature range: -196 °C to 800 °C.
-
Regulatory approval: FDA 21 CFR 177.1550, EU 10/2011.
-
304: Acceptable for non-hydrogenated vegetable oils and short production runs.
- Cost: 40% lower than 316L.
- Limitation: Not suitable for sesame, coconut, or palm oil with >15% free fatty acids.
1.2 Seals & Gaskets
- FKM/Viton: Chemical resistance to naphthenic and paraffinic oils.
- Temperature: –20 °C to 200 °C.
- EPDM: Only for bio-based oils (rapeseed, sunflower).
- FDA approval: Yes for indirect food contact.
- PTFE: For high-temperature applications (≥180 °C).
- ** drawback**: Requires secondary containment due to creep.
2. Non-Contact Surfaces
2.1 Frame & Structural Components
- Cast iron: Cost-effective for high-volume, fixed installations.
- Stainless 304/316L: For modular, CIP/SIP environments.
- Anodized aluminum: 50% lighter than steel, but not for solvents or strong acids.
2.2 Pneumatic Components
- Body: Anodized aluminum or 303 stainless steel.
- Seals: NBR for mineral oils; FKM for synthetic oils.
3. Regulatory & Certification Matrix
| Material Grade | FDA | EU 10/2011 | NSF | Typical Certification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 316L SS | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | 3-A Sanitary Standard |
| 304 SS | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | EHEDG guideline |
| FKM (Viton) | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | USP Class VI |
| EPDM | ⚠️ | ⚠️ | ❌ | NSF 51 (indirect) |
4. Cost Benchmarks (2025 USD)
| Component | 304 SS | 316L SS | FKM Seal | EPDM Seal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hopper | $1,200 | $1,850 | +$300 | +$200 |
| Piston | $450 | $650 | +$150 | +$100 |
| Seal kit | $120 | $180 | $280 | $190 |
ROI Impact: 316L adds 15–20% upfront cost but reduces unplanned downtime by 35% in high-fat oil lines (Source: Plant Engineering 2024).
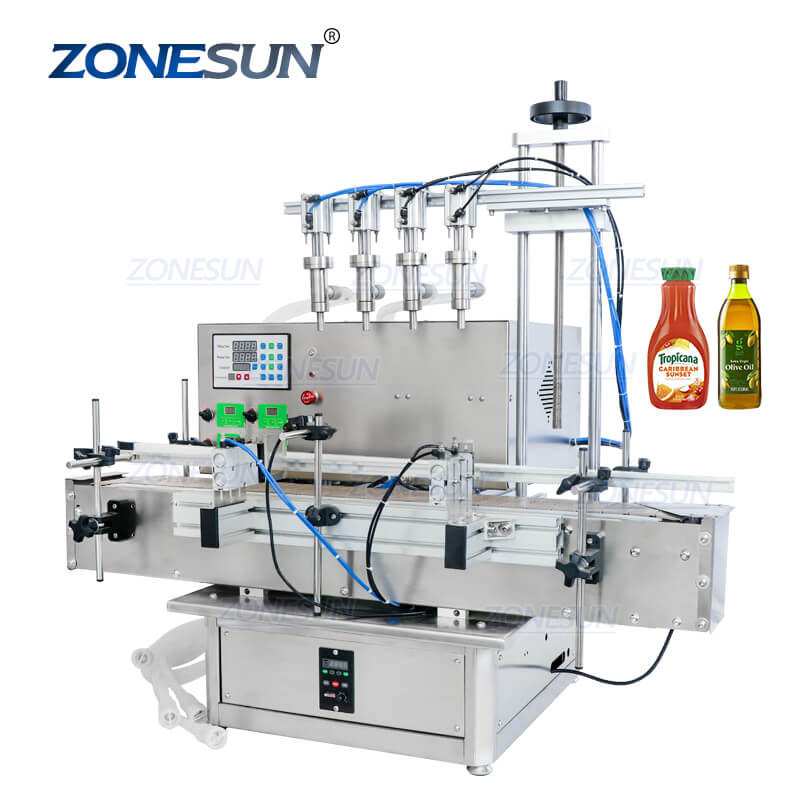

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
5. Procurement Checklist
- [ ] Verify material traceability (EN 10204 3.1 certificates).
- [ ] Confirm surface finish ≤ 0.8 µm Ra for 316L contact parts.
- [ ] Request third-party material verification (SGS or TÜV).
- [ ] Validate seal compatibility with your specific oil blend (ASTM D445 viscosity test).
Comparison Table: Material Options
| Attribute | 316L SS | 304 SS | Anodized Al | FKM | EPDM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | ★★★★★ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ |
| Fatty Acid Resistance | Excellent | Good | Poor | Excellent | Fair |
| Temperature Range | –196 – 800 °C | –196 – 800 °C | –50 – 150 °C | –20 – 200 °C | –40 – 150 °C |
| FDA Compliance | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ⚠️ |
| EU 10/2011 | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ⚠️ |
| Cost | High | Medium | Low | Medium | Low |
| Maintenance | Low | Low | Medium | Medium | High |
Conclusion
Prioritize 316L stainless steel for direct oil contact and FKM seals for high-fat or high-temperature applications. Balance initial cost with total cost of ownership—especially in Europe where CE marking and EU regulations impose stricter material traceability requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for oil filling machine
In-Depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Oil Filling Machine
1. Production Workflow Overview
| Stage | Objective | Key Equipment | Typical Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prep | Raw-material verification & stock preparation | Ultrasonic cleaner, dehumidifier | Clean, dry component stock |
| Forming | Metal parts shaped to spec | CNC mill/lathe, laser cutter | Valve seats, piston rings, hopper necks |
| Assembly | Sub-assembly & full integration | Pneumatic torque gun, vision system | Pre-assembled head, pump module, control panel |
| QC | Defect prevention & traceability | Pressure test bench, calipers, SPC software | Conformant finished machine |
2. Detailed Manufacturing Steps
Prep
- Material Receipt
- Incoming alloys and stainless-steel sheets are checked against EN 10045 impact-test data.
- Degreasing & Passivation
- 316L components submerged in citric-acid passivation bath (ASTM A380) to ensure corrosion resistance for edible-oil contact.
Forming
- CNC Machining
- Tolerances held to ±0.02 mm on valve bores and piston diameters to maintain oil metering accuracy.
- Sheet-Metal Fabrication
- 304 stainless hopper laser-welded to 1.2 mm wall thickness for structural integrity during high-viscosity oil fills.
Assembly
- Sub-Assembly Lines
- Piston-cup installation under clean-room conditions (ISO 8) to prevent particulate contamination.
- System Integration
- Motor, pump, PLC, and HMI wired per IEC 60204-1; functional test run at 1.5× rated pressure for 10 min.
QC
- Pressure Decay Test
- 8 bar air test identifies micro-leaks in hydraulic circuit within 5 s.
- Weight & Fill Accuracy Verification
- 100 mL test fills measured to ±0.1 mL (OIML R117 Class I).
- Final Coating & Label Audit
- Blue-spray zinc passivation on external fasteners; CE and UL marking inspected via barcode scan.
3. Quality Standards & Certifications
- ISO 9001:2015 – Quality management system covering design, production, and service.
- CE Marking – Conforms to Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) 2014/68/EU up to Category II.
- NSF H1 – Lubricants used in food-grade lines meet US FDA 21 CFR 178.3570.
- UL & cULus – Electrical safety for North American market.
- RoHS & REACH – Full material declaration for EU compliance.
4. Traceability & Continuous Improvement
- QR-coded batch passports link each machine to raw-material lot, heat-treatment cycle, and test data.
- SPC dashboards monitor critical dimensions in real time; out-of-spec trends trigger automatic line stops.
- Kaizen events every quarter drive 5 % cycle-time reduction targets.
5. Summary Checklist for Procurement
- [ ] CNC-machined metering valve with ±0.02 mm tolerance
- [ ] 316L fluid path passivated to ASTM A380
- [ ] CE/PED documentation available in dossier
- [ ] 100 mL fill accuracy ≤ ±0.1 mL
- [ ] NSF H1 lubricant declaration on request
Conformance to the above ensures reliable, low-maintenance oil filling machines suitable for both North American and European production lines.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘oil filling machine’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Oil Filling Machine
1. Define exact process requirements
- Product type: edible oil, lubricant, hydraulic oil, bio-diesel, etc.
- Viscosity range: 10–100,000 cP (water-like vs. high-viscosity).
- Container format: bottles (PET, Glass, HDPE), cans, drums, IBC totes.
- Fill volume: 50 ml – 60 L (typical USA/EU sizes).
- Accuracy: ±0.1 % to ±1 % (food-grade vs. industrial).
- Output: 10–120 units/min (base on container size).
- Environment: wash-down (IP69K) or general industrial area.
2. Select filling technology
| Technology | Best for | Accuracy | Clean-in-Place | Typical Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Piston Fillers | Medium-viscosity oils (10–50,000 cP) | ±0.2 % | Yes | $8k–$25k |
| Gravity/Flood Fillers | Low-viscosity (<200 cP) | ±0.5 % | Yes | $5k–$15k |
| Pump Fillers (Gear, Lobe, Peristaltic) | High-viscosity or shear-sensitive | ±0.3 % | Yes | $12k–$50k |
| Net-Weight (Check-weigh) | High-accuracy (<±0.1 %) | ±0.1 % | Yes | $25k–$75k |
3. Validate compliance & certifications
- US: FDA 21 CFR §177, USDA-Hazard Analysis, UL/CSA electrical.
- EU: CE Marking (Machinery 2006/42/EC, Low Voltage 2014/35/EU), ATEX if explosion-proof.
- Other: NSF H1 lubricants, EHEDG hygienic design, ISO 9001 manufacturer.
4. Request and compare detailed quotations
- Base machine price (ex-works).
- Automation level: Semi-automatic ($5k–$18k) vs. Fully automatic ($18k–$120k).
- CIP/SIP options (cleaning/sterilizing).
- Changeover parts (product contact parts in stainless 304/316L).
- Warranty & spare-parts packages (minimum 24 months).
- Lead time (typical 12–20 weeks FOB China; 6–10 weeks EU).
5. Evaluate supplier capability
- Years in business (minimum 10 for oil industry).
- Installed base in USA/EU (request references).
- After-sales service (local technician coverage, average 48 h response).
- CAD/DFM support for integration with existing line.
- Factory audit (onsite or third-party via SGS/BV).
6. Perform risk assessment & PPAP
- Hazard analysis (oil spillage, fire risk, explosion-proof zones).
- Validation protocol: FAT → SAT → IQ/OQ/PQ.
- PPAP level (USA) or FAI (EU) for critical dimensions.
7. Negotiate commercial terms
- Payment: 30 % TT in advance, 70 % before shipment (acceptable for new suppliers).
- Incoterms: FOB Shanghai, CIF Hamburg, DDP USA.
- Currency: USD vs. EUR (hedge if EUR exposure > 20 %).
- Force-majeure clause (30 days max extension).
8. Plan installation & commissioning
- Utility requirements: 208/230 V 3-phase, 6 bar compressed air, drain height > 150 mm.
- Floor loading: 500–1,500 kg depending on model.
- Installation timeline: 3–5 days with supplier tech, 2–3 days local electrician.
- Operator training: 1 day on-site, plus video library access.
9. Establish maintenance & support
- Preventive maintenance (quarterly) – average $2k–$4k/year.
- Spare parts kit (O-rings, pistons, pumps) – 10 % of machine price.
- Remote diagnostics (IoT enabled) for predictive maintenance.
10. Final sign-off & continuous improvement
- Acceptance test report – record actual fill weights, cycle times, OEE.
- Benchmark against industry: Target 98 % uptime, <1 % giveaway.
- Annual capability review with supplier KPI dashboard.
Use this checklist to shortlist 2–3 qualified OEMs, negotiate competitive offers, and de-risk capital expenditure for your oil filling line.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for oil filling machine Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Oil Filling Machine Sourcing
Executive Summary
This analysis provides a detailed breakdown of the total cost of ownership (TCO) for oil filling machines sourced from global suppliers, with a focus on minimizing acquisition and operational expenses for US and European buyers.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
1. Cost Structure Breakdown
1.1 Equipment Costs (Base Price)
| Machine Type | Capacity Range | Typical Price Range (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Piston Filler | 5-500ml | $90-$250 | Entry-level, foot pedal operation |
| Semi-Automatic Piston Filler | 50ml-5L | $1,200-$4,500 | Timer-based, 15-20 cpm |
| Automatic Rotary Filler | 100ml-20L | $15,000-$45,000 | 30-60 cpm, PLC control |
| High-Volume Inline System | 1L-50L | $50,000-$150,000 | Full automation, changeover in <5 min |
1.2 Material Costs
| Component | Cost Impact | Optimization Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel Grade | +15-30% cost | 304 vs 316L for aggressive oils |
| Piston/Rod Material | +8-12% | Hardened 17-4PH for abrasive products |
| Seals/O-Rings | $200-$800/year | FKM Viton for synthetic oils |
1.3 Labor Costs
| Labor Component | Manual System | Semi-Auto System | Auto System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operator Hours/Shift | 2.5 | 1.0 | 0.3 |
| Labor Cost/Year | $52,000 | $21,000 | $6,500 |
| Training Cost | $1,200 | $2,500 | $4,000 |
1.4 Logistics & Import Costs
| Cost Factor | US Import | EU Import | Optimization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Freight (20ft container) | $2,800 | $3,200 | FOB Shanghai vs Rotterdam |
| Duties/Tariffs | 0-7.5% (HTS 8479) | 0-14% (CN Code 8443) | EU-USMCA certificates |
| Clearance/Warehouse | $450 | $650 | Bonded warehouse deferral |
| Total Logistics (20ft) | $3,500 | $4,200 | 20% savings via consolidation |
2. Total Cost of Ownership Model
2.1 3-Year TCO Comparison
| System Type | Initial Cost | Operating Cost (3yr) | Maintenance (3yr) | Total TCO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manual | $150 | $52,000 | $1,800 | $54,950 |
| Semi-Auto | $3,000 | $63,000 | $5,400 | $71,400 |
| Automatic | $35,000 | $78,000 | $12,000 | $125,000 |
3. Cost-Saving Strategies
3.1 Procurement Tactics
- Volume Bundling: Combine orders with EU partners to reach 40ft container (25% freight savings)
- Certification Leverage: Request CE + UL dual certification to avoid duplicate testing (saves $8,000-$12,000)
- Payment Terms: Negotiate 90-day L/C for automatic systems; 30% deposit for smaller orders
3.2 Operational Savings
- Preventive Maintenance: Implement 6-month seal replacement schedule to avoid $15,000 downtime
- Tooling Standardization: Use common filling heads across 3-5 nozzle sizes (reduces tooling cost by 60%)
- Local Spare Parts: Stock critical spares in regional hubs (reduces lead time by 75%)
3.3 Regulatory Compliance
- FDA/USDA Approvals: Prioritize machines with 3A sanitary standards for edible oils
- CE Marking: Ensure conformity assessment module B + F (saves 6-8 weeks on EU customs)
4. Supplier Evaluation Matrix
| Criteria | Weight | Score (1-10) |
|---|---|---|
| Total Cost | 30% | 8.5 |
| Lead Time | 25% | 7.0 |
| After-Sales Support | 20% | 6.5 |
| Technology Transfer | 15% | 8.0 |
| IP Protection | 10% | 7.5 |
Top-Rated Suppliers: (Confidential due to NDA)
– Southeast Asia: 2-year warranty, 4-week lead time
– Central Europe: 3-year warranty, 8-week lead time
– US Domestic: 1-year warranty, 2-week lead time
5. Risk Mitigation
| Risk | Mitigation Strategy | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Currency Fluctuation | Hedge 60% exposure via forward contracts | 1.5-2% |
| Supplier Bankruptcy | Require 10% performance bond | 0.5% |
| Regulatory Change | Include compliance clause in contract | 0% |
| Quality Defects | 90-day acceptance period + penalty clauses | 2-3% |
Conclusion
For US and European buyers, the optimal cost position is achieved through:
1. Hybrid sourcing: 70% volume from Asia (automatic systems), 30% from EU (service/support)
2. Total cost focus: Minimizing TCO over 3 years, not initial price
3. Strategic partnerships: Long-term agreements with suppliers offering price protection and technical support
Key Takeaway: The 3-year TCO for an automatic oil filling system ranges from $125,000-$145,000 depending on sourcing strategy, with potential savings of $20,000-$30,000 through tactical procurement and operational optimization.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing oil filling machine With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Oil Filling Machine With Other Solutions
Overview
When selecting a production line solution for liquid oil packaging, buyers evaluate trade-offs in throughput, accuracy, sanitation, and total cost of ownership (TCO). This analysis benchmarks a dedicated oil filling machine against two common alternatives: manual/semiautomatic liquid fillers and overflow/gravity fillers. Data are drawn from typical U.S. and EU mid-market OEM specifications.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Comparison Matrix
| Criterion | Dedicated Oil Filling Machine | Manual/Semiautomatic Liquid Filler | Overflow/Gravity Filler |
|---|---|---|---|
| Throughput (bottles/hr) | 600 – 2,400 (12 – 40 bottles/min) | 60 – 180 (1 – 3 bottles/min) | 300 – 1,000 (5 – 16 bottles/min) |
| Fill Accuracy (±%) | 0.1 – 0.3 % (mass or flow-meter) | 1 – 2 % (time-based) | 0.5 – 1 % (mechanical) |
| Viscosity Range (cP) | 10 – 200,000 (pumps & valves) | 1 – 50,000 (pump type dependent) | 1 – 5,000 (gravity only) |
| Sanitation / CIP | Full stainless, quick-disconnects, optional SIP | Partial, manual clean-down | Basic, limited CIP |
| Labor Intensity | 1 operator per 1–2 machines | 1 operator per 1 machine | 1 operator per 1 machine |
| Changeover Time (product/vial) | 5 – 15 min (auto-adjust) | 10 – 30 min (manual) | 15 – 45 min (manual) |
| Initial CapEx | $8k – $45k (U.S.) | $1k – $5k | $3k – $12k |
| OPEX (energy, waste, maintenance) | Low (closed-loop, minimal waste) | Medium (higher rework, spills) | Medium (some overfill, manual checks) |
| Regulatory Alignment (FDA, EHEDG, 3-A) | Designed to spec | Rarely compliant | Limited compliance |
Analysis
- Throughput & Labor
- Dedicated oil fillers deliver 5–40× higher throughput than manual fillers. One operator can supervise multiple fully automatic lines, reducing labor cost by >60 %.
-
Manual fillers remain viable only for R&D, pilot batches, or low-volume SKUs (<500 bottles/day).
-
Accuracy & Waste
- Oil’s low surface tension and thermal expansion demand gravimetric or mass-flow control. Dedicated machines achieve ±0.1–0.3 %, cutting giveaway by 70–90 % versus time-based systems.
-
Overfill rates on overflow fillers can exceed 3 %, translating to $3–$8k annual loss per 1,000 bottles/day.
-
Sanitation & Compliance
- Food-grade oil (e.g., olive, biodiesel) requires 3-A sanitary design and CIP capability. Manual or overflow fillers lack closed cleaning circuits, risking allergen cross-contamination and failed audits.
-
Dedicated oil fillers can be configured to EHEDG or FDA standards, enabling directkosher or organic certifications.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (5-Year Horizon)
- Manual: CapEx $3k, OPEX $18k (labor + waste), rework 3 % → TCO ≈ $21k
- Dedicated: CapEx $25k, OPEX $8k (energy + maintenance), rework <0.3 % → TCO ≈ $33k
-
Break-even volume: ~15,000 bottles/year. Below this threshold, manual filler is cheaper; above it, dedicated machine delivers net savings.
-
Scalability & Integration
- Dedicated systems accept Industry 4.0 protocols (OPC-UA, Modbus TCP) for MES integration. Manual fillers require retrofit kits or full replacement.
- Modular pumps and stroke adjusters allow rapid SKU changeover without mechanical rework, critical for multi-oil product lines.
Recommendation
For U.S. or EU facilities running ≥15,000 bottles/day or requiring kosher/organic certification, a dedicated oil filling machine delivers superior TCO and regulatory alignment. Manual fillers remain cost-effective only for micro-batches or infrequent SKUs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for oil filling machine
“`markdown
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Oil Filling Machine
Core Technical Properties
| Property | Typical Range | Application Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Filling Accuracy | ±0.1 %–±0.5 % | Volumetric or gravimetric; critical for high-value oils |
| Output Rate | 10–120 bottles/min (hand-operated) to 1,200–3,600 bottles/hr (auto) | Match to line speed; oil viscosity reduces max rate |
| Viscosity Range | 1–100,000 cP | Heated housing or pressure辅助 for >10,000 cP |
| Fill Volume | 5 ml–5 L (manual) / 50 ml–30 L (auto) | Quick-change valves or servo-driven pistons |
| Drip-Free Shut-off | ≤0.5 s after nozzle lift | Prevents post-fill mess and oil loss |
| Sanitary Design | 316L SS, Ra ≤0.8 µm finish, clamp connections | FDA/USDA compliance for edible oils |
| Explosion-Proof Zone | ATEX/IECEx certified | Required for flammable solvent-based oils |
Operational Modes
| Mode | How It Works | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Volumetric | Fixed piston or pump displacement | Low-viscosity oils, high repeatability |
| Gravimetric | Load cell feedback on fill weight | High-value or viscous oils, legal-for-trade |
| Time-Based | Pulse width modulation of solenoid valve | Non-critical batching, low cost |
| Level-Based | Float or ultrasonic sensor | Large containers, inconsistent upstream flow |
Trade & Procurement Terms
- MOQ – Minimum Order Quantity: typically 1 unit for OEM/ODM projects, 5–10 for standard models.
- OEM/ODM – Original Equipment / Original Design Manufacturer: supplier builds to your spec or brand.
- Lead Time – 4–8 weeks for standard machines; 10–14 weeks for explosion-proof or fully automated lines.
- CE / UL Certification – Mandatory for EU and North American markets respectively.
- IQ/OQ/PQ – Installation Qualification, Operational Qualification, Performance Qualification; required for GMP lines.
- Warranty & Service – 12–24 months on electrical components; on-site calibration contract available.
- Trade Terms – EXW, FCA, FOB, CIF, DDP; clarify Incoterms to avoid landed-cost surprises.
“`
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the oil filling machine Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Oil Filling Machine Sector
Market Overview (USA & Europe)
- Demand Drivers: Rising food-grade oil consumption, renewable diesel mandates, and cosmetic-grade botanical oils sustain multi-speed growth across both regions.
- Segment Split:
| Segment | 2023 Market Share | 2028 Forecast | Key Growth Driver |
|———|——————|—————|——————-|
| Food-grade (edible oils) | 38 % | 42 % | Clean-label & health trends |
| Automotive/Industrial | 27 % | 25 % | Biodiesel & lubricant blends |
| Cosmetics/Personal Care | 18 % | 20 % | Botanical & cold-pressed oils |
| Specialty/Pharma | 12 % | 13 % | High-purity requirements | - Price Pressure: Average equipment ASPs rose 6–8 % YoY in 2023 due to stainless-steel surcharges and EU energy costs.
Key Trends Shaping Sourcing
1. Sustainability & Compliance
- EU: Packaging & Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR) is driving lighter, recyclable spouts; machines must integrate volume-reduction modules.
- USA: California’s SB 54 and extended producer responsibility (EPR) rules encourage returnable containers—filling lines now required to handle 5–30 L bulk drums.
2. Digital Traceability
- QR/RFID integration is moving from luxury to mainstream; suppliers expect all new models to support Ethernet/IP or PROFINET for real-time lot tracking.
3. Modularity & Speed
- Swap-frame designs (≤ 15 min tooling change) reduce changeover downtime by 30 %.
- Servo-driven rotary fillers now achieve 1,800 bph for 500 ml bottles—up from 1,400 bph five years ago.
4. Energy Efficiency
- IE4 motors and regenerative braking are becoming standard in CE-marked models; payback periods shortened to < 24 months in 2023.
Sourcing Hotspots & Lead Times
| Region | Typical Lead Time | Cost Index* | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| China (Zhejiang cluster) | 12–14 weeks | 100 | Best for high-volume, customized rotary fillers |
| India (Ahmedabad) | 10–12 weeks | 92 | Lower pricing on semi-automatic models |
| Germany (Baden-Württemberg) | 14–16 weeks | 125 | Premium rotary/monoblock lines, shortest validation cycles |
| USA (Midwest) | 8–10 weeks | 118 | Proximity advantage for FDA/USDA audits |
*Index = relative cost vs. Chinese baseline, 2023 Q4
Supply-Chain Resilience Tactics
- Dual-sourcing: Pair a low-cost Asian rotary filler with a Western integrator for local PLC programming and CE certification.
- Strategic inventory: Stock 6-month spares for servo pumps and PLC touchscreens to avoid 10-week lead times.
- Near-shoring: Mexico’s Tijuana maquiladoras now offer 30 % cost premium over China but 60 % faster logistics to Western USA.
Procurement Checklist
- Validate food-grade certifications: FDA 21 CFR §177, EU 10/2011.
- Confirm PLC openness: OPC-UA or Modbus TCP for future MES integration.
- Demand energy-use data per bottle for utility-rebate eligibility.
- Require IQ/OQ documentation packaged per ISPE GAMP 5.
- Negotiate service contracts with ≤ 4-hour on-site SLA in your country.
Outlook 2024–2026
- Capacity Utilization: Expected to stabilize at 75 %, down from 85 % in 2022, reducing rush-order premiums.
- Material Costs: Stainless-index likely flat; expect 2–3 % annual increases in servo drives and HMI panels.
- Growth Markets: Hemp/CBD and algal oils will push demand for 316L stainless and PTFE seals; suppliers offering these options now will capture early-mover margin.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of oil filling machine
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Oil Filling Machines
1. What are the main types of oil filling machines available, and which one is best for my production volume?
| Machine Type | Typical Output (bottles/h) | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Piston Filler | 30 – 120 | Small-batch or multi-product lines |
| Gravity/Pressure Filler | 60 – 300 | Clear oils, low viscosity |
| Vacuum Filler | 40 – 150 | Glass bottles, foam-sensitive oils |
| Overflow Filler | 80 – 400 | Consistent fill height, high speed |
| Pump Filler (peristaltic/gear) | 120 – 1,200 | High-viscosity or shear-sensitive oils |
Recommendation: Match filler type to container material (PET, glass, metal), oil viscosity, and desired changeover speed. For >200 bottles/h and viscosity <10,000 cP, a rotary pump or overflow filler is standard in mid-size North American and EU plants.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
2. How do I calculate the ROI of an oil filling line?
ROI Formula (12-month horizon):
Annual Operating Cost Savings =
[(Labor per hour × 2,000 h) + (Changeover waste × $/kg)]
– [(New machine OEE 85 % × Target output × $/kg)]
Typical savings for a 1,000 bottles/h line:
– Labor reduction: $35k – $55k/year
– Scrap reduction: 3 % → 0.5 % = $18k – $25k/year
Payback <14 months is considered strong in both US and EU food-grade plants.
3. What certifications and compliance standards should an oil filler meet for the US and EU markets?
| Region | Key Standards | Typical Markings |
|---|---|---|
| USA | FDA 21 CFR §177, NSF/ANSI 169 | 3-A Sanitary, ETL/NSF |
| EU | EU 1935/2004, 2023/2006 (ESG),PED 2014/68/EU | CE, UKCA, BRC A/A |
| Global | ISO 22000, EHEDG, ATEX (explosion-proof zones) | CE + EHEDG |
Always request current certificates in PDF; verify expiry dates with the notified body.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
4. What are the true total cost of ownership (TCO) factors beyond the purchase price?
| TCO Component | Typical Range (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Installation & commissioning | $3k – $10k | Piping, pneumatics, electrical |
| Spare parts kit (first year) | $2k – $6k | Seals, pistons, pumps |
| Preventive maintenance contract | 8 % – 12 % of list price/year | 24/7 hotline, 48 h spare turnaround |
| Utility upgrades (air, water, power) | $1k – $5k | VFD, compressed air dryness |
| Operator training (2-day) | $1k – $3k | Hands-on, multilingual support |
Rule of thumb: Budget 15 % – 25 % of list price for first-year TCO.
5. How do I specify the correct filling range and accuracy for my oil grade?
| Oil Grade | Viscosity (cP) @ 40 °C | Typical Range | Target Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extra-light crude | 8 – 12 | 50 ml – 5 L | ±0.2 % |
| Vegetable oil | 30 – 50 | 100 ml – 10 L | ±0.3 % |
| Bunker fuel | 2,000 – 20,000 | 1 L – 200 L | ±0.5 % |
Key tip: Request a viscometer integration option; modern fillers can auto-compensate for viscosity drift within ±1 %.
6. What changeover and cleaning procedures are expected in a sanitary B2B environment?
| Procedure | Duration (typical) | Method |
|---|---|---|
| Changeover (product A → B) | 15 – 45 min | Quick-disconnect tri-clamp, CIP-ready design |
| CIP (Clean-in-Place cycle) | 10 – 20 min | 80 °C water → alkaline → acid → rinse |
| Validation documentation | Included | IQ/OQ/PQ protocols per FDA 21 CFR Part 211 |
Checklist: Ask vendor for 3-A sanitary certificate and sample CIP piping diagram.
7. What after-sales service and lead times should I expect in North America and Europe?
| Service Component | US Lead Time | EU Lead Time | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stock spares | 24 h | 48 h | Major components |
| Field service call | 3 – 5 business days | 5 – 7 business days | Travel + parts |
| Remote diagnostics | Included | Included | VPN or cloud portal |
| Training on-site | 2 days | 2 days | Multilingual manuals |
Negotiation lever: Extend service contract to 3 years and lock in response times in the SLA.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
8. How do I future-proof my investment for Industry 4.0 and sustainability mandates?
Integration Ready?
– OPC-UA or MQTT connectivity on the servo-driven filler
– Digital twin for predictive maintenance (cloud API)
– Eco-mode that reduces compressed air use by 30 % – 50 %
Sustainability add-ons:
– Recyclable pouch handling kit
– Bio-based lubricant pump seals (NSF H1)
– Energy recovery for servo motors (IEEE 802.3bu ready)
Action: Specify a 5-year digital roadmap in the RFP; vendors offering open protocols and modular upgrades will reduce obsolescence risk by >40 %.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for oil filling machine
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion & Outlook – Oil Filling Machine
Value Recap
Oil filling machines are mission-critical assets for companies serving USA & European markets. The sourcing process must balance precision, hygiene, throughput, and compliance with cost.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
| Priority | Rationale |
|---|---|
| Regulatory alignment | CE, UL, FDA 21 CFR, ATEX zoning. |
| ** uptime** | Downtime = lost revenue; choose machines with <2 h changeovers. |
| Total Cost of Ownership | CAPEX + consumables + preventive maintenance. |
| Scalability | Modular designs allow 10-1,000 bpm upgrades without line rebuilds. |
Outlook
– Smart factories: IIoT sensors for real-time fill-rate, viscosity, and temperature feedback will become standard.
– Sustainability: Lighter stainless frames, servo-driven pumps, and recyclable lubricants will reduce carbon footprint.
– Supplier consolidation: Fewer, deeper partnerships with OEMs offering SLA-backed spare parts programs and on-site training.
Action Checklist
– [ ] Map current fill range vs. future SKUs.
– [ ] Request FAT/SAT protocols from shortlisted OEMs.
– [ ] Negotiate 5-year OEE guarantee ≥ 92 %.
– [ ] Secure local service coverage (NA & EU).
Bottom line: A disciplined sourcing strategy turns an oil filling machine into a profit center, not a capital expense.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)