The global automotive aftermarket is undergoing rapid expansion, driven by rising vehicle production, an increasing focus on vehicle maintenance, and the growing adoption of commercial and passenger vehicles worldwide. According to Mordor Intelligence, the automotive aftermarket size was valued at USD 476.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 635.3 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of approximately 5.0% during the forecast period. As a critical yet often overlooked component of engine maintenance, the oil drain plug market benefits from this upward trend, with continued demand from both OEMs and replacement channels. With durability, leak prevention, and material integrity being paramount, manufacturers are focusing on advanced alloys, magnetic core designs, and precision engineering to meet evolving industry standards. In this context, we spotlight the top seven oil drain plug manufacturers leading innovation, scale, and reliability in a competitive and growing market landscape.
Top 7 Oil Drain Plug Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Standard Drain Plugs
Domain Est. 2004
Website: nospillsystems.com
Key Highlights: Easy to install, the No-Spill™ quick oil drain plug makes your next oil change a breeze. By simply replacing your factory oil drain plug at your next oil change ……
#2 About Us
Domain Est. 1996
Website: femco.com
Key Highlights: Femco has over 40 years of specialist expertise in the development and manufacturing of the high-quality oil drain plug and oil drainage systems….
#3 Oil Drain Plugs
Domain Est. 1996
Website: auveco.com
Key Highlights: Self Tapping Drain Plug with Gasket, 7/8″-14 Single Oversize SKU: 8289 In Stock Log in to see price Add to Cart…
#4 Drain Plugs
Domain Est. 1996
Website: winzer.com
Key Highlights: 90-day returns1/2-20 x 7/16 Inch Bright Zinc Plated Steel Oil Drain Plug With Rubber Molded Gasket Washer · 240.12.16 ; M12 x 1.75 x 15 mm Gray Phosphate Steel Oil Drain Plug ……
#5 Oil Drain Plugs
Domain Est. 1999
Website: agscompany.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsAccufit Oil Drain Plug M14x1.50. Tools. Accufit Oil Drain Plug M14x1.50. $4.36 – $103.95. Accufit Oil Drain Plug M12x1.75. Tools. Accufit Oil Drain Plug…
#6 Buy Fumoto® Valve Online
Domain Est. 2001
Website: fumotousa.com
Key Highlights: By simply replacing your stock oil drain plug, you can drain your engine oil without tools or mess. Trusted by over 10 million satisfied ……
#7 Oil Drain Plugs
Domain Est. 2002
Website: fischer-plath.com
Key Highlights: Oil Drain Plugs. The oil drain plug is a screw plug made of metal or plastic. The oil drain plug with sealing ring seals the drain opening….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Oil Drain Plug
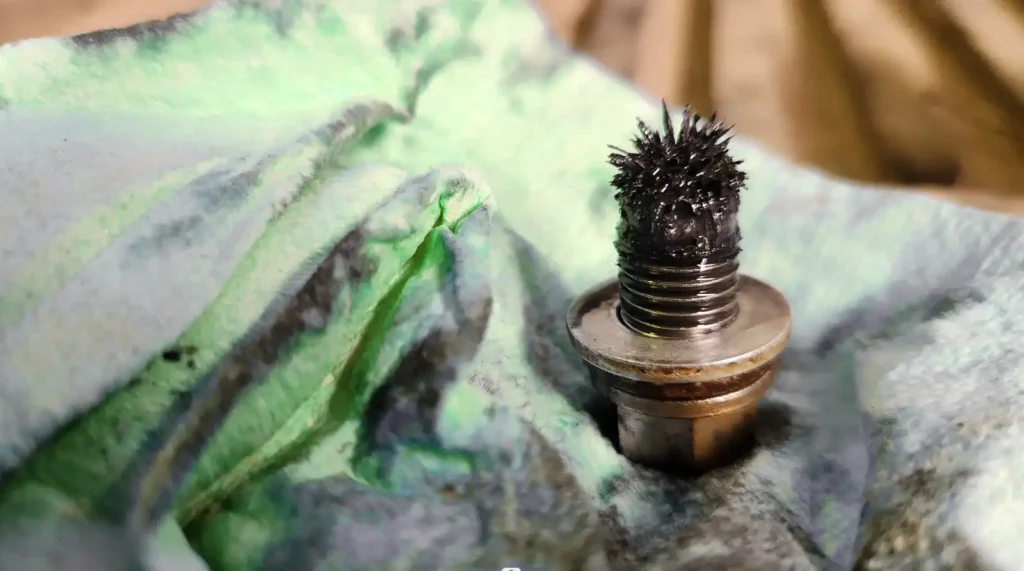

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Oil Drain Plugs
The oil drain plug market in 2026 is poised for moderate but steady growth, driven by underlying automotive demand, technological shifts, and evolving regulatory landscapes. While not a high-growth component market, key trends indicate a focus on durability, efficiency, and adaptation to new vehicle technologies.
1. Continued Dominance of Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Vehicles (for now)
- Stable Core Demand: Despite the rise of EVs, the vast global fleet of gasoline and diesel vehicles (including heavy-duty trucks and industrial equipment) ensures consistent demand for oil changes and, consequently, oil drain plugs. Replacement and maintenance cycles remain a primary market driver.
- Aftermarket Strength: The mature ICE vehicle base fuels a robust aftermarket segment for drain plugs, gaskets, and magnetic plugs. DIY maintenance and independent repair shops will remain significant channels.
2. Gradual Impact of Electrification (BEVs & PHEVs)
- Reduced Plug-Per-Vehicle Count: Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) eliminate the engine oil change, directly reducing the need for standard engine oil drain plugs. This is a long-term structural headwind.
- Shift in Application Focus: Demand will increasingly shift towards drain plugs for:
- Transmission Fluids (in some BEVs/PHEVs): Certain electric and hybrid transmissions still require fluid changes.
- Differential/Oil in Axles: BEVs often have high-torque differentials requiring lubrication.
- Power Electronics Cooling: While not “oil” in the traditional sense, cooling systems in inverters/motors might use fluids requiring drain points, though less frequently than engine oil.
- Hybrid Complexity: Plug-in Hybrids (PHEVs) and hybrids still have ICEs, maintaining demand for standard engine oil drain plugs, but their smaller engines might use different specifications.
3. Material & Design Innovation for Performance & Sustainability
- Enhanced Durability & Corrosion Resistance: Demand for premium materials (e.g., high-grade stainless steel, specialized alloys, advanced plastics) will grow to withstand harsher engine environments, longer oil change intervals, and exposure to contaminants.
- Magnetic Plugs: Increasing popularity due to their ability to capture ferrous metal particles, improving engine longevity. This remains a key value-added segment.
- Integrated Gasket Solutions: Pre-installed, high-performance gaskets (e.g., Viton, silicone) reduce leaks and simplify installation, appealing to both OEMs and consumers.
- Sustainability Focus: Growth in recycled materials (e.g., recycled steel) and designs facilitating easier recycling. OEMs may specify plugs with lower environmental impact.
- Lightweighting: While less critical than for structural parts, weight reduction remains a minor trend, potentially favoring advanced alloys or composites.
4. Supply Chain & Manufacturing Pressures
- Cost Volatility: Fluctuations in raw material prices (steel, copper, plastics) will continue to pressure margins, driving demand for cost-effective manufacturing and sourcing strategies.
- Localization & Resilience: Geopolitical tensions and past disruptions emphasize the need for diversified, regional supply chains. Nearshoring or regional sourcing may increase for key markets (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific).
- Automation & Efficiency: Manufacturers will invest in automation to maintain competitiveness, ensure quality consistency, and offset rising labor costs.
5. Regulatory & Environmental Influences
- Emissions & Efficiency Standards: Stricter global emissions regulations (e.g., Euro 7, CAFE) push for longer lubricant life and reduced fluid leakage, increasing demand for high-integrity drain plugs and gaskets.
- Circular Economy: Potential for regulations promoting repairability and component longevity could indirectly support the drain plug market by encouraging maintenance over replacement. Focus on reducing fluid leaks aligns with environmental goals.
6. Market Consolidation & Competition
- OEM Supplier Consolidation: Tier 1 suppliers may consolidate, leading to fewer but larger customers for plug manufacturers. Relationships and technical capability will be crucial.
- Aftermarket Competition: Intense competition in the aftermarket from established brands and low-cost producers, emphasizing branding, distribution, and value bundling (plug + gasket kits).
- Value-Added Differentiation: Success will depend on offering more than just a basic plug – magnetic features, superior materials, leak-proof designs, and brand trust.
Conclusion for H2 2026:
The oil drain plug market in 2026 will be characterized by a stable core demand from the existing ICE fleet, particularly in the aftermarket, while navigating the inevitable, gradual decline in per-vehicle demand from BEVs. Winners will be those manufacturers who innovate in materials and design (durability, magnetism, leak prevention), adapt to new fluid applications in electrified vehicles, manage supply chains efficiently, and embrace sustainability. While not a high-growth sector, it remains essential, with opportunities lying in premiumization, differentiation, and serving the maintenance needs of the vast, transitioning global vehicle population.
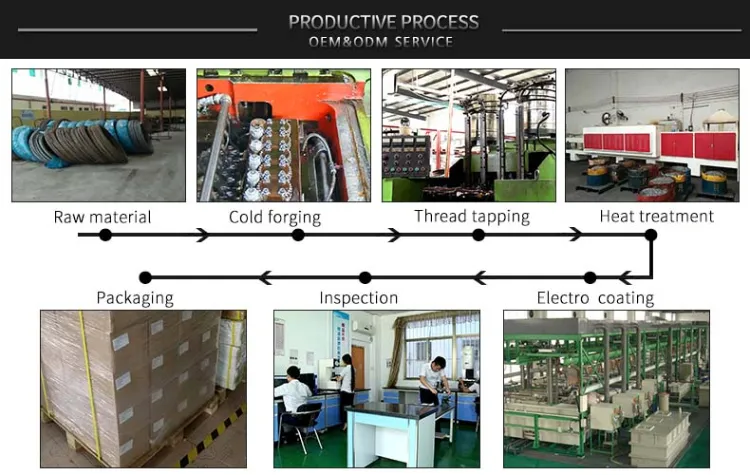
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Oil Drain Plug (Quality, IP)
Sourcing oil drain plugs may seem straightforward, but overlooking key quality and Intellectual Property (IP) aspects can lead to significant operational, safety, and legal risks. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Material Quality and Durability
- Use of Substandard Alloys: Suppliers may use low-grade steel or aluminum that lacks the required tensile strength and corrosion resistance. This increases the risk of stripping, seizing, or shearing during installation or removal.
- Inadequate Surface Treatments: Insufficient or poor-quality plating (e.g., zinc, black oxide) can result in rapid rust formation, especially in harsh environments, leading to premature failure.
- Lack of Heat Treatment: Properly heat-treated plugs ensure durability and resistance to torque stress. Skipping this step compromises structural integrity.
Non-Compliance with Industry Standards
- Missing ISO or DIN Specifications: Many oil drain plugs must comply with international standards (e.g., ISO 6147, DIN 7603). Sourcing non-compliant parts can cause fitment issues, leaks, or warranty voiding.
- Incorrect Thread Tolerances: Poorly machined threads lead to cross-threading or leaks. Verify thread accuracy (pitch, diameter, class) to ensure compatibility with engine blocks.
Magnet and Gasket Integration Issues
- Weak or Missing Magnets: Many drain plugs include magnets to capture ferrous debris. Low-quality magnets lose effectiveness quickly, reducing engine protection.
- Subpar or Missing Sealing Gaskets: Rubber or copper gaskets must be oil-resistant and properly seated. Poor-quality gaskets cause leaks and require frequent re-tightening.
Intellectual Property Risks
- Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Parts: Some suppliers offer “compatible” or “OEM-style” plugs that mimic patented designs. This can infringe on IP rights, exposing buyers to legal action or supply chain disruptions.
- Lack of Licensing or Authorization: Using branded designs (e.g., specific hex shapes, logos, or magnetic configurations) without authorization violates trademark or utility patents.
- Inadequate Supplier Transparency: Suppliers may not disclose design origins. Always request proof of IP clearance or licensing, especially for high-volume or branded applications.
Inconsistent Quality Control
- Inconsistent Torque Specifications: Poor manufacturing leads to variations in torque performance, increasing the risk of over-tightening or loosening.
- Lack of Batch Testing or Certification: Reputable suppliers provide material certifications (e.g., RoHS, REACH) and test reports. Absence of documentation signals potential quality lapses.
Supply Chain and Traceability Gaps
- Unclear Origin of Manufacture: Sourcing from regions with weak IP enforcement increases counterfeit risk. Ensure traceability from raw material to finished product.
- No Serial or Lot Numbering: Without traceability, identifying and recalling defective batches becomes nearly impossible.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence: vet suppliers thoroughly, demand certifications, test samples rigorously, and consult legal experts when sourcing designs close to patented products.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Oil Drain Plug
Product Overview
The oil drain plug is a critical automotive component used to seal the oil pan in internal combustion engines, allowing controlled draining during oil changes. Typically made from steel or aluminum with integrated sealing washers (often copper or crushable), it must meet specific performance, safety, and environmental standards during manufacturing, shipment, and distribution.
Regulatory Compliance
International Standards and Certifications
Oil drain plugs must comply with relevant international standards to ensure quality and safety:
– ISO 898-1: Specifies mechanical and material properties for bolts, screws, and studs—applicable to threaded drain plugs.
– RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): Ensures that materials used (e.g., plating, alloys) do not contain restricted substances like lead, cadmium, or hexavalent chromium, especially in markets like the EU.
– REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals): Requires disclosure of substances of very high concern (SVHCs) in components shipped to the European Union.
– ELV (End-of-Life Vehicles Directive): Mandates recyclability and restricts hazardous materials in automotive parts sold in the EU.
Country-Specific Requirements
- United States: No specific federal certification is required for oil drain plugs, but compliance with EPA guidelines on recyclable materials and hazardous waste handling applies. DOT regulations may affect transportation if shipping in bulk with other regulated items.
- European Union: CE marking is not mandatory for standalone oil drain plugs, but compliance with RoHS, REACH, and ELV is enforceable. Importers must maintain technical documentation and declarations of conformity.
- Canada: Compliance with CEPA (Canadian Environmental Protection Act) and adherence to transportation of dangerous goods (TDG) regulations if packaged with lubricants or contaminants.
Packaging and Labeling
Packaging Standards
- Use durable, moisture-resistant packaging (e.g., polybags, clamshells, or corrugated boxes) to prevent corrosion and physical damage.
- Include desiccant packs in sealed packaging if shipping to humid environments.
- Bulk shipments should use stackable, labeled cartons with weight limits clearly marked (typically ≤ 25 kg per box for manual handling).
Labeling Requirements
- Each package must include:
- Product name and part number
- Manufacturer name and contact information
- Country of origin
- Material composition (e.g., “Steel with Copper Washer”)
- Compliance markings (e.g., RoHS, REACH)
- Batch or lot number for traceability
- Outer shipping cartons must display:
- Gross weight and dimensions
- Handling symbols (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack” if applicable)
- Hazard labels only if packaged with oil or flammable materials
Transportation and Logistics
Domestic and International Shipping
- Air Freight (IATA): Non-hazardous when clean and dry. No special classification required under IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR).
- Ocean Freight (IMDG Code): Classified as non-dangerous goods. Ensure packaging is seaworthy and protected from saltwater exposure.
- Road Transport (ADR/RID in Europe, DOT in US): No hazardous classification for oil drain plugs alone. If shipped with used oil or contaminated parts, full hazardous material regulations apply.
Customs Documentation
- Commercial Invoice: Must detail product description, HS code, value, origin, and buyer/seller information.
- Packing List: Itemize quantities per package, weight, and dimensions.
- Certificate of Origin: Required for preferential tariffs under trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, EU-UK Trade Agreement).
- HS Code Guidance:
- Typical HS Code: 7318.15 (Screws and bolts, with threaded shanks, of iron or steel) or 8708.29 (Parts and accessories of motor vehicles, n.e.s.).
- Confirm code with local customs authority based on exact product specifications.
Storage and Handling
Warehouse Requirements
- Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment to prevent rust and degradation of sealing washers.
- Keep away from chemicals, oils, and solvents that may compromise washer integrity.
- Implement FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory rotation to ensure aging components are shipped first.
Handling Procedures
- Use gloves to prevent skin oils from accelerating corrosion on metal surfaces.
- Avoid dropping or impact to prevent thread damage.
- Segregate non-compliant or recalled batches immediately.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
End-of-Life and Recycling
- Oil drain plugs are recyclable as ferrous or non-ferrous metal. Copper washers should be separated where possible.
- Encourage return programs or recycling partnerships with automotive service centers.
- Comply with local WEEE or ELV take-back requirements in applicable jurisdictions.
Sustainable Practices
- Source materials from suppliers with environmental management systems (e.g., ISO 14001).
- Minimize packaging waste using recyclable or biodegradable materials.
- Optimize shipping routes and consolidate loads to reduce carbon footprint.
Compliance Monitoring and Recordkeeping
Documentation Retention
- Maintain records of:
- Material test reports (MTRs)
- RoHS/REACH compliance declarations
- Batch traceability logs
- Shipping and customs documentation
- Retain records for minimum of 5–10 years, depending on regional legal requirements.
Audits and Supplier Verification
- Conduct regular audits of manufacturing and packaging partners.
- Require suppliers to provide up-to-date compliance certificates.
- Implement a corrective action process for non-conforming shipments.
Summary
Proper logistics and compliance management for oil drain plugs ensures product integrity, regulatory adherence, and smooth global distribution. Key focus areas include material compliance (RoHS, REACH), accurate labeling and documentation, safe transportation practices, and sustainable end-of-life handling. Regular training and audits are recommended to maintain ongoing compliance across supply chains.
Conclusion for Sourcing Oil Drain Plug:
Sourcing the appropriate oil drain plug is a critical yet often overlooked aspect of vehicle and machinery maintenance. After evaluating factors such as material composition, thread size and pitch, sealing mechanism, magnetic properties, and compatibility with specific engine types, it is evident that selecting the right oil drain plug ensures leak-free operation, extends engine life, and enhances safety during oil changes. Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) specifications should be closely followed to maintain warranty compliance and performance standards, though reliable aftermarket alternatives can offer cost-effective solutions when they meet required quality benchmarks. Additionally, sourcing from reputable suppliers guarantees authenticity, durability, and adherence to industry standards. In conclusion, a well-sourced oil drain plug is a small but vital component that contributes significantly to overall system reliability and operational efficiency.