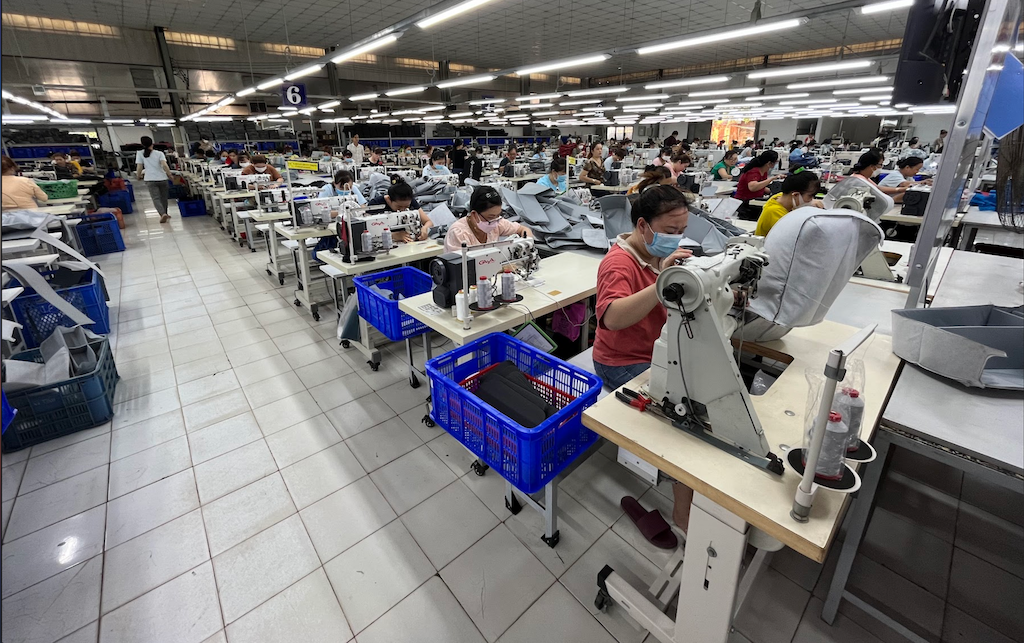
The global apparel manufacturing market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising consumer demand for fashion-forward and cost-effective clothing, as well as the increasing adoption of agile supply chain models. According to Grand View Research, the global apparel market size was valued at USD 1.5 trillion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by expanding e-commerce platforms, fast fashion trends, and the rising outsourcing of production to specialized OEM clothing manufacturers, particularly in Asia and Eastern Europe. Mordor Intelligence further highlights that increasing brand focus on core competencies—such as design and marketing—has led to a surge in partnerships with OEMs capable of end-to-end production, quality control, and compliance. As brands seek scalability, speed-to-market, and sustainable manufacturing solutions, identifying the top-performing OEM clothing manufacturers has become critical for staying competitive in today’s dynamic fashion landscape.
Top 10 Oem Clothing Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Apparel Production Inc.
Domain Est. 2006
Website: apparelproductionny.com
Key Highlights: Apparel Production is New York City’s leading fashion design house, clothing factory, and garment manufacturer for Men’s, Women’s, and Children’s clothing….
#2 Appareify: Clothing Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2023
Website: appareify.com
Key Highlights: Quality Clothing Manufacturer With Comprehensive Services · Private Label. Appareify provides custom labeling services. · OEM · Personalized Support · Lowest MOQ….
#3 Japanese OEM clothing / garment manufacturer
Domain Est. 2001
Website: ogura-m.com
Key Highlights: Discover Ogura Meriyasu’s Return to Japan Project — a cost-effective OEM apparel solution backed by 100 years of Japanese quality and scalable production….
#4 OEM Clothing Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2008
Website: fush.rs
Key Highlights: Fully customized clothes according to your designs, tech packs and quality guidelines, you will choose to work with an OEM clothing manufacturer….
#5 Functional Activewear OEM Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2015
Website: yotex-apparel.com
Key Highlights: No matter start-up owner, private labels, chain store enter into functional apparel market, Yotex would be your quick hand to support you….
#6 Clothing Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2016
Website: createfashionbrand.com
Key Highlights: CFB Textile is a B2B clothing manufacturer in Portugal, producing luxury blanks, private label apparel, and fully custom garments for international brands. Our ……
#7 MMS Clothing
Domain Est. 2018
Website: mmsclothing.com
Key Highlights: MMS Clothing is a leading Chinese clothes manufacturer specializing in custom clothing, garment manufacturing, and wholesale from trusted Clothing Makers….
#8 Women Clothing Manufacturer and Supplier in China
Domain Est. 2017
Website: hfourwing.com
Key Highlights: High End Women Dress Manufacturer in China. Over 10 years women clothing manufacturing experience. A modern women clothing manufacture can offer from design to ……
#9 Hongyu Apparel
Domain Est. 2019
Website: hongyuapparel.com
Key Highlights: Hongyu Clothes Maker is the perfect solution for all your garment and clothing manufacturing needs. From sample development and bulk production to label ……
#10 Zega Apparel
Domain Est. 2013
Website: zegaapparel.com
Key Highlights: Zega Apparel offers leading services including custom clothing manufacturers USA along with cut & sew clothing services to private labels across the globe….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Oem Clothing

2026 Market Trends for OEM Clothing
The OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) clothing market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving consumer demands, technological advancements, and shifting global supply chain dynamics. As fashion brands increasingly outsource production to specialized manufacturers, OEM clothing providers are adapting to meet higher expectations for speed, sustainability, and customization. Below is an analysis of the key trends expected to shape the OEM clothing industry in 2026.
Rise of Sustainable and Ethical Manufacturing
Sustainability will be a dominant force in the OEM clothing sector by 2026. Consumers and brands alike are demanding greater transparency in sourcing and production processes. OEM manufacturers are responding by adopting eco-friendly materials such as organic cotton, recycled polyester, and innovative bio-fabrics. Certifications like GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard) and B Corp are becoming essential for OEMs aiming to attract environmentally conscious clients. Additionally, water-saving dyeing techniques and carbon footprint reduction initiatives will be standard across leading OEM facilities.
Growth of On-Demand and Micro-Production Models
The shift toward on-demand manufacturing is accelerating, particularly among fast-fashion and direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands. By 2026, many OEM clothing manufacturers will offer small-batch and made-to-order services to reduce overproduction and inventory waste. Advanced digital printing and automated cutting systems will enable cost-effective short runs, allowing brands to test designs and respond quickly to market trends without large financial risks.
Technological Integration and Smart Factories
The adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies will redefine OEM clothing production. In 2026, smart factories equipped with AI-driven production planning, IoT-enabled machines, and real-time monitoring systems will be widespread. These technologies will enhance efficiency, reduce lead times, and improve quality control. Digital twins—virtual models of production lines—will allow OEMs to simulate and optimize workflows before physical production begins.
Regionalization of Supply Chains
Geopolitical instability and rising logistics costs are pushing brands to regionalize their supply chains. By 2026, there will be increased investment in nearshoring and friendsourcing models, particularly in regions like Eastern Europe, North Africa, Mexico, and Central America. OEM manufacturers in these areas will benefit from shorter delivery times, reduced carbon emissions, and greater agility in responding to regional market needs.
Emphasis on Customization and Private Label Innovation
Brands are seeking OEM partners that offer high levels of customization, from fabric development to unique trims and branding elements. In 2026, OEM clothing manufacturers will act as innovation partners, offering design support, trend forecasting, and co-development services. This shift transforms OEMs from mere producers to strategic collaborators in brand development.
Digitalization of Client Collaboration
Digital platforms will streamline communication between brands and OEM manufacturers. By 2026, cloud-based product lifecycle management (PLM) systems, 3D sampling, and virtual showrooms will be standard. These tools will enable faster approvals, reduce sample waste, and allow real-time collaboration across global teams.
Labor and Automation Balance
While automation will grow, skilled labor remains crucial—especially for high-quality garment construction. OEM manufacturers in 2026 will invest in upskilling workers and integrating human expertise with automated processes. Ethical labor practices will also be a key differentiator, with fair wages and safe working conditions becoming non-negotiable for brand partnerships.
Conclusion
By 2026, the OEM clothing market will be defined by agility, sustainability, and technological sophistication. Manufacturers that embrace innovation, ethical practices, and closer collaboration with brands will lead the industry. As the line between producer and partner blurs, OEMs will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of global fashion.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing OEM Clothing: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) clothing can offer cost savings and scalability, but it comes with significant risks—particularly in the areas of quality control and intellectual property (IP). Understanding these pitfalls is critical to protecting your brand and ensuring product success.
Quality Inconsistencies
One of the most frequent challenges in OEM clothing production is inconsistent quality. Manufacturers may use substandard materials, deviate from specifications, or lack rigorous quality assurance processes. These issues often arise due to miscommunication, cost-cutting measures, or inadequate oversight. Without regular factory audits, detailed quality control checklists, and clear technical specifications, brands risk receiving garments with poor stitching, incorrect sizing, color variations, or fabric defects—damaging brand reputation and increasing returns.
Intellectual Property Infringement
OEM arrangements can expose brands to serious IP risks. Some manufacturers may replicate your designs and sell them to competitors or produce counterfeit versions under different labels. Additionally, if design files or prototypes are shared without proper legal safeguards, there’s a risk of unauthorized use or theft. It’s essential to secure non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), register trademarks and designs, and ensure contracts explicitly prohibit unauthorized replication or third-party sales.
Lack of Transparency in the Supply Chain
Many OEM suppliers subcontract work to unvetted factories, reducing visibility and control over production. This lack of transparency can lead to ethical concerns (such as poor labor practices) and further quality or IP vulnerabilities. Brands must conduct due diligence, require full supply chain disclosure, and consider third-party audits to ensure compliance with both quality standards and legal requirements.
Inadequate Contractual Protections
Weak or vague contracts increase exposure to both quality disputes and IP theft. Contracts should clearly define quality benchmarks, ownership of designs, usage rights, inspection protocols, and penalties for non-compliance. Without these safeguards, resolving disputes becomes difficult and costly, especially across international jurisdictions.
Overreliance on Supplier Claims
Relying solely on a supplier’s portfolio or promises without independent verification is a common mistake. Requesting physical samples, conducting production trials, and performing third-party lab testing can help validate claims about fabric quality, durability, and compliance before scaling up.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—through strong contracts, vigilant quality control, and robust IP protection—brands can build reliable, ethical, and profitable OEM partnerships.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for OEM Clothing
Understanding OEM Clothing Logistics
Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) clothing production involves manufacturing garments based on a brand’s design, specifications, and branding. Efficient logistics are crucial to ensure timely delivery, cost control, and product quality. Key logistics components include sourcing raw materials, production planning, inventory management, shipping, and distribution.
Supply Chain Management
Effective supply chain management starts with selecting reliable suppliers for fabrics, trims, and accessories. Establish long-term partnerships with vetted vendors to ensure consistency and quality. Implement vendor management systems (VMS) to monitor performance, lead times, and compliance. Maintain a diversified supplier base to mitigate risks related to geopolitical issues, natural disasters, or supply disruptions.
Production Planning and Scheduling
Work closely with manufacturers to create realistic production timelines. Use tools like Gantt charts or ERP software to track milestones, from sample approval to bulk production. Account for lead times in material procurement, cutting, sewing, quality checks, and packaging. Align production schedules with key retail seasons, holidays, and market demand forecasts.
Quality Control and Assurance
Implement stringent quality control (QC) protocols at multiple stages: pre-production, during manufacturing, and pre-shipment. Conduct regular factory audits and use third-party inspection services if necessary. Define clear quality standards in your OEM agreement, including fabric weight, stitching strength, color fastness, and size consistency, to minimize defects and returns.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Ensure packaging meets both brand standards and regulatory requirements. Include proper labeling with fiber content, country of origin, care instructions, and safety certifications (e.g., CPSIA in the U.S.). Use sustainable packaging materials where possible to align with environmental regulations and consumer expectations. Barcodes and RFID tags should be correctly applied for inventory tracking.
International Shipping and Customs Compliance
When shipping across borders, understand and comply with customs regulations in both exporting and importing countries. Prepare accurate documentation, including commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and bill of lading/airway bill. Classify garments correctly under the Harmonized System (HS) codes to avoid delays or penalties. Consider using a licensed customs broker for complex shipments.
Import Regulations and Duties
Research import tariffs, quotas, and trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, RCEP) that may affect landed costs. Be aware of rules of origin requirements to qualify for duty-free or reduced-rate entry. Stay compliant with regulations such as U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP), EU General Product Safety Directive, or Australia’s mandatory labeling laws.
Ethical and Environmental Compliance
Ensure your OEM partners adhere to ethical labor practices and environmental standards. Verify compliance with certifications like WRAP, BSCI, or SA8000. Monitor for forced labor risks, especially in high-risk regions, and comply with legislation such as the Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA). Implement sustainability practices, such as water conservation and waste reduction, in production.
Product Safety and Regulatory Standards
OEM clothing must meet safety standards based on destination markets. For example:
– United States: CPSIA, Flammable Fabrics Act (FFA)
– European Union: REACH, EN 14682 (children’s clothing drawstrings), CE marking if applicable
– Canada: Textile Labeling Act, Canada Consumer Product Safety Act (CCPSA)
Test for restricted substances (e.g., azo dyes, formaldehyde, phthalates) and maintain documentation for audits.
Inventory and Warehouse Management
Use inventory management systems to track stock levels, turnover rates, and reorder points. Employ just-in-time (JIT) or safety stock strategies depending on demand volatility. Optimize warehouse layouts for efficient picking, packing, and shipping. Integrate logistics software with e-commerce platforms or retail partners for real-time visibility.
Risk Management and Contingency Planning
Identify potential risks—production delays, port congestion, currency fluctuations, or political instability—and develop mitigation strategies. Maintain alternative shipping routes, backup suppliers, and insurance coverage for cargo and liability. Regularly review and update your risk management plan.
Final Recommendations
Success in OEM clothing relies on seamless coordination between design, production, logistics, and compliance. Invest in transparent communication with manufacturers, adopt technology for tracking and forecasting, and stay updated on global trade developments. By prioritizing compliance and operational efficiency, brands can deliver high-quality apparel on time and within budget.
In conclusion, sourcing OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) clothing offers numerous advantages for brands and retailers looking to streamline production, maintain quality, and reduce development time. By partnering with experienced OEM manufacturers, businesses can leverage existing designs, advanced production capabilities, and cost efficiencies without the need for extensive R&D. However, success in OEM sourcing depends on careful supplier selection, clear communication, quality control measures, and adherence to ethical and sustainable practices. When managed effectively, OEM clothing sourcing can significantly enhance scalability, market responsiveness, and profitability, making it a strategic choice in today’s competitive apparel industry.