The global O-ring market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by increasing demand across industries such as automotive, aerospace, oil & gas, and industrial manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the global O-ring market size was valued at USD 1.78 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by the rising need for reliable sealing solutions in high-pressure and extreme-temperature environments, along with advancements in material science enabling longer lifespan and enhanced performance. As competition intensifies, a new cohort of manufacturers — the “O-ring challengers” — are disrupting the space with innovative manufacturing techniques, cost-effective solutions, and niche material expertise. These emerging players are gaining traction by offering high-quality alternatives to established brands, particularly in regional markets and specialized applications. Below, we examine the top six challenger manufacturers shaping the future of the O-ring industry through agility, technology adoption, and data-driven quality control.
Top 6 O Ring Challenger Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 He Tried to Avert the Challenger Disaster
Domain Est. 1993
Website: uml.edu
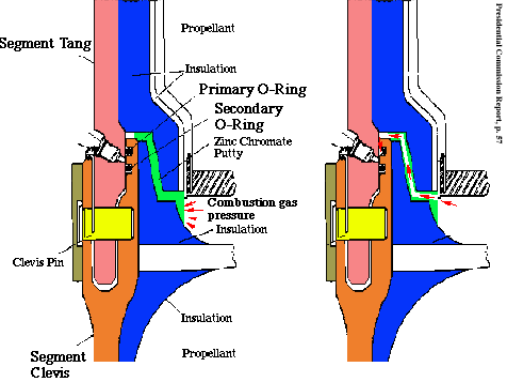
Key Highlights: On the day before the scheduled launch, NASA officials and Morton Thiokol management discussed the O-ring matter and, again, Boisjoly registered his serious ……
#2 v1ch4
Domain Est. 1997
Website: nasa.gov
Key Highlights: The loss of the Space Shuttle Challenger was caused by a failure in the joint between the two lower segments of the right Solid Rocket Motor….
#3 The Space Shuttle Challenger Disaster
Domain Est. 1999
Website: onlineethics.org
Key Highlights: The failure of the O-ring was attributed to several factors, including faulty design of the solid rocket boosters, insufficient low- temperature ……
#4 Truth, Lies, and O
Domain Est. 1999
Website: collectspace.com
Key Highlights: Twenty-three years after the Space Shuttle Challenger disaster, Auburn University Professor and author James Hansen has helped produce a ……
#5 Space Shuttle Challenger Explosion
Domain Est. 2010
Website: challenger-o-ring.com
Key Highlights: The disaster of Challenger mission STS-51-L was the result of human engineering error. The simple “no spin” truth is the O-ring gland was not properly designed….
#6 Roger Boisjoly and the Challenger Disaster
Domain Est. 2021
Website: sdsmtnovum.org
Key Highlights: There had been previous evidence that O-rings might fail to properly work in low temperatures, and Florida was experiencing record-setting lows….
Expert Sourcing Insights for O Ring Challenger

H2: Market Trends Analysis for O-Ring Challenger in 2026
As industrial and manufacturing sectors continue to evolve through technological integration and sustainability demands, the market for O-ring challengers—alternative sealing solutions designed to outperform traditional elastomeric O-rings—is poised for significant transformation by 2026. This analysis explores key market trends shaping the O-ring challenger landscape in the second half (H2) of 2026, based on technological advancements, industry adoption, material innovation, and regulatory influences.
-
Accelerated Adoption in High-Performance Industries
By H2 2026, industries such as aerospace, electric vehicles (EVs), and renewable energy are expected to drive demand for O-ring challengers. These sectors require sealing solutions that withstand extreme temperatures, aggressive chemicals, and prolonged operational cycles. Advanced alternatives such as metal seals, spring-energized seals, and PTFE-based systems are gaining traction due to their superior durability and reliability compared to conventional rubber O-rings. -
Material Innovation and Sustainability Pressures
Environmental regulations and corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals are pushing manufacturers toward recyclable, longer-lasting, and non-outgassing sealing materials. In H2 2026, bio-based polymers and fluorine-free alternatives are emerging as viable challengers, particularly in the pharmaceutical and food processing industries. Companies investing in sustainable sealing technologies are likely to gain competitive advantage and regulatory compliance benefits. -
Digitalization and Predictive Maintenance Integration
The integration of smart sensors and IoT-enabled condition monitoring is reshaping maintenance protocols. O-ring challengers with embedded health-monitoring capabilities—such as pressure-sensitive films or conductive polymers that signal wear—are becoming more common. In H2 2026, predictive maintenance platforms are increasingly factoring in seal performance data, reducing unplanned downtime and favoring advanced sealing systems over traditional O-rings. -
Geopolitical Supply Chain Shifts
Continued diversification of supply chains—driven by trade tensions and regionalization trends—is impacting material sourcing for sealing components. By late 2026, manufacturers in North America and Europe are prioritizing localized production of O-ring challengers to reduce dependency on Asian elastomer suppliers. This shift is accelerating investment in domestic R&D and advanced manufacturing techniques like precision molding and additive manufacturing. -
Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The O-ring challenger market is witnessing increased consolidation, with larger fluid sealing companies acquiring niche innovators specializing in high-performance alternatives. In H2 2026, this trend is expected to intensify, leading to broader commercialization of next-generation sealing solutions and expanded application reach across oil & gas, semiconductor manufacturing, and medical devices.
Conclusion
By H2 2026, the O-ring challenger market is transitioning from a niche alternative to a mainstream solution in critical industries. Driven by performance demands, sustainability imperatives, and digital integration, these advanced sealing technologies are redefining reliability standards. Companies that align with these trends—through innovation, agility, and strategic partnerships—are best positioned to lead in the evolving sealing solutions market.
Common Pitfalls Sourcing O-Rings: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Sourcing O-rings, especially for critical applications, involves more than just finding a low price. Overlooking quality and intellectual property (IP) concerns can lead to costly failures, safety hazards, and legal issues. Here are key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Material Specifications
Using incorrect or substandard elastomer compounds (e.g., wrong durometer, poor chemical resistance, or incorrect temperature range) can lead to premature O-ring failure. Sourcing from suppliers who do not provide full material traceability or certified test reports increases the risk of receiving non-compliant products.
2. Poor Dimensional Tolerances
O-rings must meet precise dimensional standards (e.g., AS568, ISO 3601). Inferior manufacturing processes or lack of quality control can result in inconsistent cross-sections or inner diameters, leading to leaks or improper sealing under pressure.
3. Lack of Certifications and Traceability
Reputable applications—especially in aerospace, automotive, or medical industries—require O-rings with full documentation (e.g., RoHS, REACH, FDA, or AMS certifications). Sourcing from uncertified suppliers risks non-compliance and regulatory penalties.
4. Inconsistent Manufacturing Processes
Suppliers using outdated or poorly controlled molding and curing processes may produce O-rings with flaws such as flash, voids, or incomplete vulcanization, compromising performance and longevity.
5. Insufficient Testing and Validation
O-rings should undergo rigorous testing (e.g., compression set, tensile strength, fluid immersion). Suppliers that skip or falsify test data expose buyers to field failures and liability.
Intellectual Property (IP) and Brand-Related Pitfalls
1. Counterfeit or “Challenger” O-Rings
“Challenger” brands often mimic well-known manufacturers (e.g., Parker, Freudenberg) with similar packaging and part numbers. These counterfeit products may claim compliance with standards but lack genuine testing, materials, or quality control, posing serious reliability and safety risks.
2. Misrepresentation of Material Grades
Some suppliers falsely label O-rings as specific high-performance materials (e.g., Viton®, EPDM, or Kalrez®). Using trademarked names without authorization violates IP rights and may indicate inferior or non-genuine materials.
3. Unauthorized Use of Trademarks and Standards
Sourcing O-rings labeled with registered trademarks (e.g., “FKM per ASTM D2000”) without proper licensing is a legal risk. Buyers may unknowingly support IP infringement, exposing their company to litigation or reputational damage.
4. Lack of Transparency in Supply Chain
Opaque sourcing—especially from third-party distributors or offshore suppliers—increases the risk of receiving unbranded or mislabeled products. Without clear chain-of-custody documentation, verifying authenticity becomes difficult.
5. No Warranty or Technical Support
Reputable O-ring manufacturers offer technical guidance and warranties. Challenger brands often provide neither, leaving buyers without recourse when failures occur.
Mitigation Strategies
- Source from authorized distributors or directly from OEMs.
- Require full material certifications, test reports, and lot traceability.
- Verify supplier credentials and compliance with industry standards.
- Conduct incoming inspections and material verification when possible.
- Avoid suppliers offering “equivalent” parts at suspiciously low prices.
By recognizing these pitfalls and implementing due diligence, organizations can ensure they source O-rings that are both high-quality and legally compliant, reducing operational and legal risks.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for O-Ring Challenger
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for the O-Ring Challenger project to ensure safe, efficient operations and adherence to relevant regulations.
Project Overview and Scope
The O-Ring Challenger refers to a specialized initiative involving the handling, testing, transportation, and potential deployment of O-rings—typically used as mechanical seals in aerospace, automotive, or industrial applications. This guide supports risk mitigation and regulatory alignment throughout the project lifecycle.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
All activities must comply with applicable international, national, and local regulations, including but not limited to:
- ISO Standards: Adherence to ISO 3601 (fluid power systems – O-rings) for dimensions, materials, and quality.
- REACH & RoHS: Compliance with EU regulations on hazardous substances in materials.
- OSHA & ANSI Guidelines: Workplace safety standards for handling and testing procedures.
- DOT & IATA Regulations: Requirements for safe transportation of components, especially if shipped internationally or by air.
- ITAR/EAR (if applicable): Export controls for defense-related components; verify if O-rings are subject to jurisdiction.
Procurement and Supply Chain Management
- Source O-rings only from certified suppliers with documented quality assurance processes.
- Maintain traceability records for all batches, including material certifications (e.g., ASTM D2000).
- Conduct incoming inspection per defined quality control protocols.
- Ensure supplier agreements include compliance clauses and audit rights.
Storage and Handling Procedures
- Store O-rings in a climate-controlled environment (typically 15–25°C, low UV exposure, away from ozone sources).
- Use original packaging until ready for use; avoid stretching or pinching during handling.
- Implement FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory rotation to prevent aging.
- Label all containers with part number, lot code, date received, and expiration date.
Transportation Logistics
- Package O-rings in sealed, static-dissipative bags with desiccants if required.
- Use shock-absorbent packaging for transit; avoid extreme temperatures during shipping.
- For international shipments, prepare accurate shipping documentation, including:
- Commercial invoice
- Packing list
- Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS), if applicable
- Export declarations (if under ITAR/EAR)
- Partner with carriers experienced in handling sensitive technical components.
Testing and Quality Assurance
- Perform dimensional, compression set, and hardness testing per ASTM or ISO standards.
- Document all test results in a centralized QA database.
- Calibrate all test equipment regularly in accordance with ISO 17025.
- Flag and quarantine non-conforming items; initiate corrective actions immediately.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive records for audit and traceability purposes, including:
– Certificates of Conformance (CoC)
– Material test reports
– Inspection logs
– Shipping manifests
– Regulatory compliance declarations
Retention period: Minimum of 7 years unless otherwise specified by customer or regulation.
Risk Management and Contingency Planning
- Identify potential failure modes (e.g., material degradation, misapplication, incorrect installation).
- Develop mitigation strategies including redundant sourcing and environmental monitoring.
- Establish recall procedures in case of non-compliant batch identification.
- Train personnel on emergency response and reporting protocols.
Training and Personnel Compliance
- Ensure all team members complete relevant training in:
- Handling sensitive components
- Regulatory requirements (e.g., hazardous materials, export controls)
- Quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001)
- Conduct annual refreshers and maintain training records.
Audit and Continuous Improvement
- Schedule internal audits quarterly to verify compliance with this guide.
- Address non-conformances through root cause analysis and corrective action plans.
- Review and update this guide annually or when regulations/processes change.
By following this Logistics & Compliance Guide, the O-Ring Challenger project will maintain high standards of quality, safety, and regulatory adherence across all operational phases.
Conclusion for Sourcing O-Ring Challenger:
In conclusion, sourcing the O-Ring Challenger requires a strategic evaluation of suppliers based on quality, reliability, technical specifications, and cost-effectiveness. It is essential to partner with certified manufacturers or distributors who adhere to industry standards such as ASTM, ISO, or MIL-SPEC to ensure performance and safety, especially in critical applications. Conducting thorough due diligence, including material compatibility testing, lead time analysis, and supplier track record reviews, will minimize risks and support long-term operational efficiency. By prioritizing quality assurance and supply chain resilience, organizations can successfully source the O-Ring Challenger to meet technical demands while maintaining compliance and performance expectations.